Physics > Lab Report > 2.1.8 Lab 11: The Effects of Temperature and Particle Size Lab Assignment AP Chemistry Sem 2 (All)
2.1.8 Lab 11: The Effects of Temperature and Particle Size Lab Assignment AP Chemistry Sem 2
Document Content and Description Below
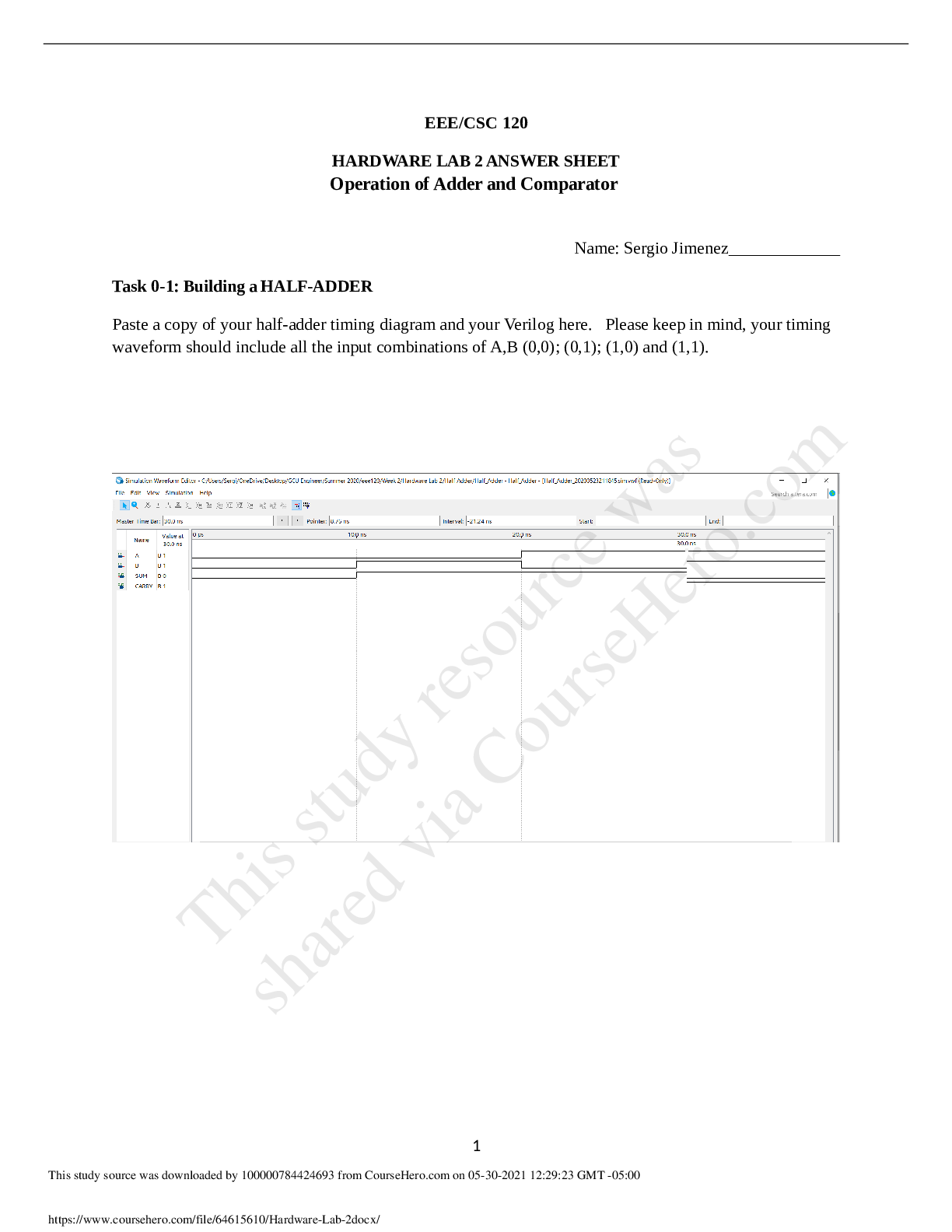
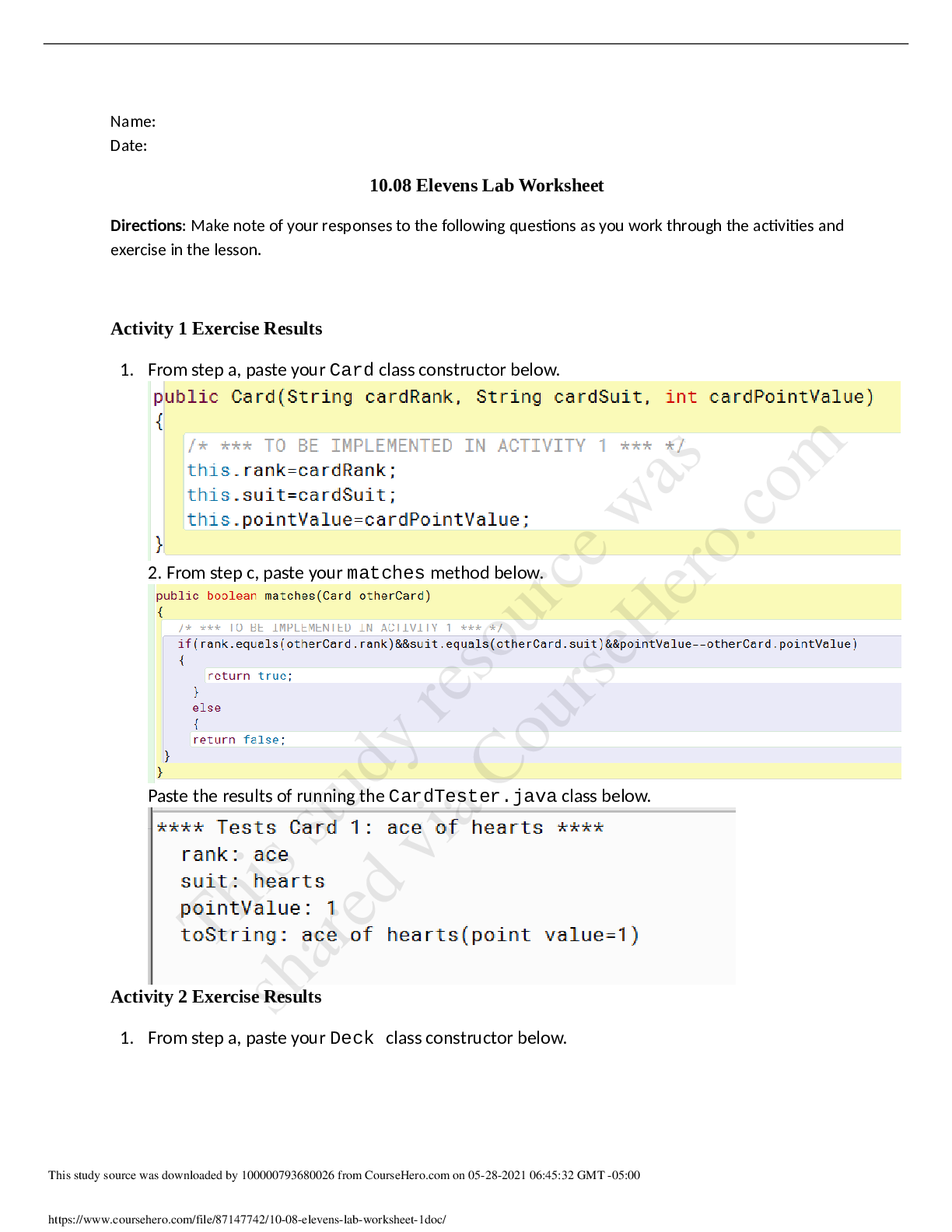
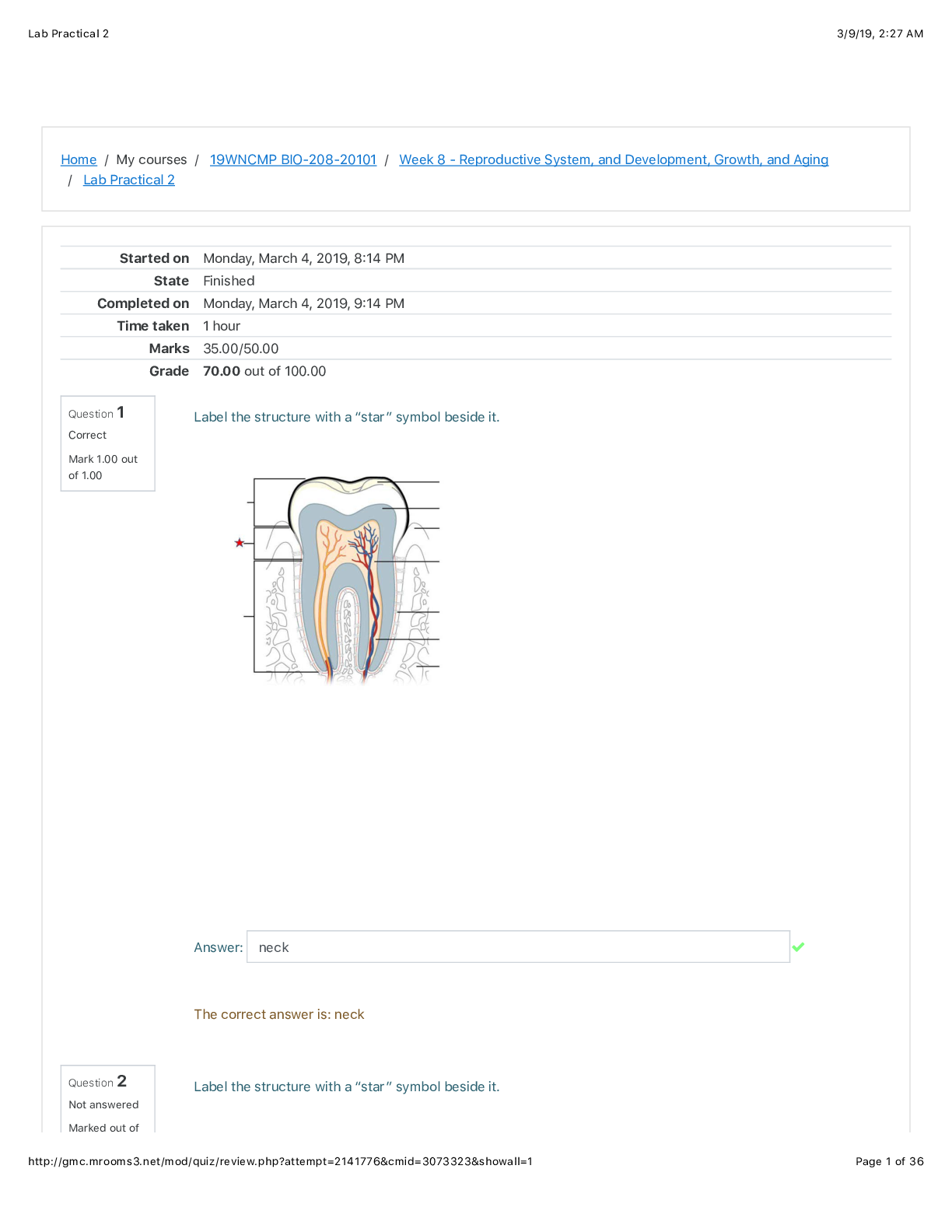
2.1.8 Lab 11: The Effects of Temperature and Particle Size Lab Assignment AP Chemistry Sem 2 Name: ________________________ Points Possible: 50 Date: _____________ Adapted from: Kinetics Guided Inq... uiry, Chris Dewberry. https://phet.colorado.edu/en/contributions/view/4049 DIRECTIONS: Background Four major things affect the rate of a reaction: Concentration: More molecules = more collisions Collisions are necessary for reactions Physical State: Ability to mix reactants Solids can be grinded to increase surface area Liquids can be stirred Temperature: Increases the kinetic energy of molecules Need sufficient energy to react (Activation Energy) Catalysts: Typically lower the activation energy of reactions Procedure ***For the majority of this guided inquiry we are going to use a simulation program written by Linda Koch, Ron LeMaster, Trish Loeblein, and Kathy Perkins. The program can be found by following this link: https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/reactions-and-rates Single Collision 1. Pull back the knob. Describe what happened in 2-3 sentences. (3 points) 2. Click the “Reload Launcher” button and expand the two windows on the right side of the program by clicking the “+” button for the Separation View and the Energy View. Now release the knob from various distances. Indicate on the potential energy diagram when the reaction proceeds forward. (2 points) When the total energy is equal or greater than the peak at which there is the greatest amount of potential energy is when the reaction proceeds forward. ↓ 3. Now click the Angled Shot option in the top right corner. Try launching from a different angle or two. Did the reaction proceed as before? (2 points) The reaction did not proceed as before. Instead, the two reactants proceeded to bounce off of eachother but not react. 4. Why do you think this was the outcome despite having enough energy for the reaction to proceed? (3 points) There was no direct collision of the two reactions. Because the two molecules did not collide directly into each other, there was a low effectiveness of the collision. 5. Set the Choose a reaction option to the last preset chemical reaction that isn’t Design your own. Now Change the Launcher Options back to Straight Shot and release the knob. What happens to the translational speed of the molecules as the reaction goes forwards and backwards? (Hint: the effect will be easiest to observe at a low energy). Please explain why this occurs. (5 points) The translational speed increases as the products are formed and slow down when the reactants are formed. This is because there is more potential in the reactants than the products as observed in the potential energy chart. Rate Experiments [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 7 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 30, 2021
Number of pages
7
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 30, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
86

.png)


















 (1).png)






.png)

.png)

