*NURSING > EXAM > NR 509 APEA Final Exam Answers - Random : Chamberlain College of Nursing - 2018/19 > Already Graded (All)
NR 509 APEA Final Exam Answers - Random : Chamberlain College of Nursing - 2018/19 > Already Graded A+
Document Content and Description Below
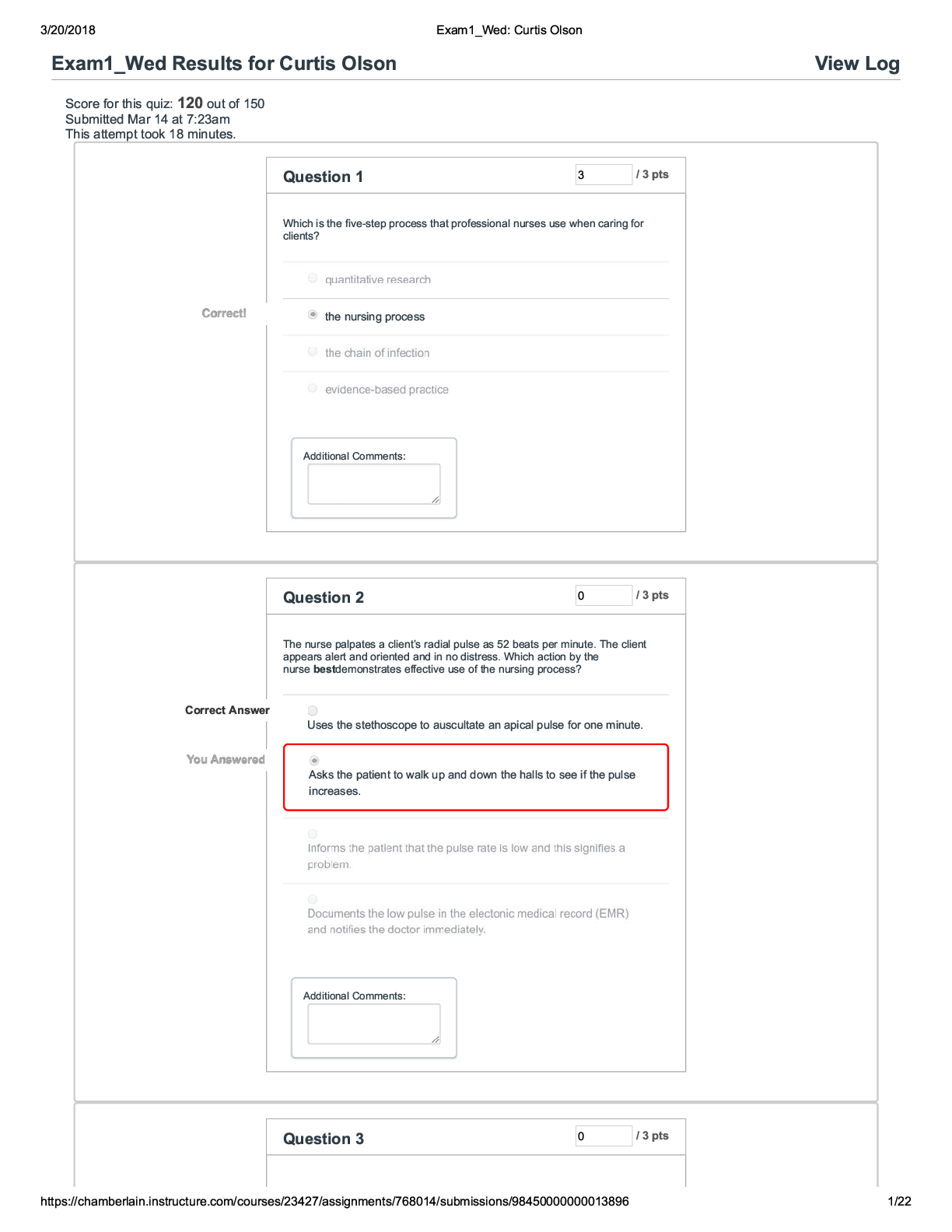
NR 509 APEA Final Exam Answers - Random 1. A transient ischemic attack is: 2. A patient is asked to visually follow a finger through the cardinal fields of gaze. Which cranial nerves are being asses... sed? 3. Uncontrolled electrical activity in the brain, which may produce minor physical signs, thought disturbances, or disturbed motor activity is: 4. When evaluating the sensory system, testing the posterior columns tract would include assessing sensations of: 5. Physical exam of a well two-week-old infant reveals a little dimple with a small amount of hair just above the sacral area. This could be: 6. A female patient complains of weakness in her arm when combing her hair. This finding could be suggestive of which type of weakness pattern? 7. What geriatric condition is characterized by normal alertness but progressive global deterioration of cognition in multiple domains? 8. When assessing coordination of muscle movement, four areas of the nervous system function in an integrated way. These areas include the motor, cerebellar, the vestibular, and the sensory systems. Which system coordinates position sense? 9. A band of skin innervated by the sensory root of a single spinal nerve is termed a: 10. An 8-month-old with a significant head lag would suggest the need for: 11. Hyperalgesia refers to: 12. Brief, repetitive, stereotyped, coordinated movements occurring at irregular intervals are consistent with: 13. When a patient complains of severe headaches that have worsened over the last few weeks but she has no other symptoms, a most likely diagnosis would be: 14. While assessing the cranial nerves, the nurse practitioner touches the cornea lightly with a wisp of cotton. This maneuver assesses which cranial nerve? 15. The patient has his eyes closed and an area on his right leg is briefly touched by the nurse practitioner. The patient is instructed to open his eyes and point to the area that was touched. This is an example of the discriminative sensation known as: 16. When assessing the cranial nerves, the nurse practitioner observes that the soft palate does not rise when the patient is instructed to say "ah". This finding could be suggestive of a bilateral lesion in which cranial nerve? 17. The level of consciousness that refers to the patient that remains unarousable with eyes closed without evidence of response to inner need or external stimuli is said to be in: 18. Having the patient shrug his shoulders and elicit neck movements would be testing Cranial Nerve: 19. The Glasgow coma scale assesses: 20. Discriminative sensations include all of the following except: 21. Symmetric weakness of the distal muscles of the legs suggests a: 22. The thalamus and the basal ganglion are located in the: 23. The most common cause of viral encephalitis in children is: 24. By placing the patient in the supine position, the nurse practitioner raises the patient's relaxed and straightened leg while flexing the leg at the hip, then dorsiflexes the foot. This maneuver is known as: 25. With the adult patient lying supine, the nurse practitioner flexes the patient's neck while observing the hips and knees. Flexion of both hips and knees was noted. This is a positive: 26. When a two-week-old infant presents with irritability, poor appetite, and rapid head growth with distended scalp veins, one should consider: 27. A term used to describe muscle wasting or loss of muscle bulk is: 28. Which one of the following senses is most often affected in patients on long-term antibiotic therapy? 29. Common physical findings in a young child with cerebral palsy include which one of the following? 30. The principal muscles involved when closing the mouth are innervated by which Cranial nerve? 31. The term used to describe involuntary muscle spasms and twisting of the limbs is: 32. Postural tremors appear when the affected part is: 33. A patient presents with sweating, tremors, palpitations, hunger, and confusion. This patient is most likely experiencing: 34. Most peripheral nerves contain afferent and efferent fibers. The term afferent refers to: 35. During this type of seizure activity, the patient loses consciousness suddenly, sometimes with a cry, and the body stiffens into tonic extensor rigidity. Breathing stops, and the person becomes cyanotic. A clonic phase of rhythmic muscular contraction follows. This type of seizure activity is referred to as a: 36. When assessing plantar reflexes, the nurse practitioner strokes the lateral aspect of the sole from the heel to the ball of the right foot. Absence of movement of the big toe is noted. This finding could be suggestive of a pathologic lesion in which segmented level of the spine? 37. A patient is instructed to stand, close both eyes, and extend both arms forward with the palms facing upward for 20-30 seconds. If the forearm drifts downward, this would indicate: 38. When evaluating a patient for weakness of the upper extremities, bilateral distal weakness is noted. This finding could be suggestive of: 39. Ptosis of the left eye would be suggestive of damage to which cranial nerve? 40. While palpating the temporal and masseter muscles, the patient is asked to clench his teeth and move his jaw from side to side. This maneuver would be assessing which cranial nerve? 41. With the adult patient lying supine, the nurse practitioner strokes the lateral aspect of the sole from the heel to the ball of the foot with the end of an applicator stick. Dorsiflexion of the big toe was noted. This is a positive: 42. An ambulatory child with spastic cerebral palsy needs a diet: 43. The part of the brain that relays sensory information between brain regions and controls many autonomic functions of the peripheral nervous system is known as the: 44. Dysarthria refers to: 45. The inability to hop in place on each foot, could be suggestive of a: 46. Hyperesthesia refers to: 47. The part of the brain that maintains homeostasis is the: 48. The patient experiences a sudden loss of consciousness with falling without movements and injury may occur. This type of a seizure is consistent with: 49. Involuntary movements of the body that are slower and more twisting and writhing than choreiform movements, and have a larger amplitude are suggestive of: 50. Which of the following procedures should NOT be performed in a comatose patient? 51. A form of aphasia in which the person has word-finding difficulties for speaking and writing is known as: 52. A neurological assessment to evaluate neurologic input to the cerebellum is: 53. The three important questions that govern the neurological examination include: Is the mental status intact?, Are right-sided and left-sided findings symmetric?, and: 54. Which developmental area is predominantly affected by lead poisoning? 55. A term used to describe an increase in muscular bulk with diminished strength is: 56. On examination of the adult patient, symptoms of flexed posture, tremor, rigidity, and shuffling gait are observed. These findings are consistent with: 57. A form of aphasia where articulation is good but sentences lack meaning is referred to as: 58. When comparing two sides of the body for symmetric sensation a symmetrical distal sensory loss would be suggestive of : 59. When eliciting deep tendon reflexes in the knee, the nurse practitioner notes an abnormal reflex in the right knee. This abnormality is probably consistent with a pathological lesion in which segmented level of the spine? 60. Persistent blinking after glabellar tap and difficulty walking heel-to- toe are common in: 61. To evaluate a patient's response to light touch sensation, the nurse practitioner would ask the patient to identify: 62. A discriminative sensation that describes the ability to identify a number drawn in the hand when the patient's eyes are closed is: 63. When assessing the patient's sense of position, instruct the patient to first stand with his feet together and eyes open, then instruct him to close both eyes for 30-60 seconds. If he loses his balance with his eyes closed, this is: 64. A female patient complaints of weakness in both arms when transferring the wet clothes from the washer and placing them in the dryer. This finding could be suggestive of which type of weakness pattern? 65. With the patient lying supine, the nurse practitioner places her hands behind the patient's head while flexing his neck forward until his chin touches his chest. Neck stiffness with resistance to flexion is noted. This is a positive: 66. When trying to determine the level of consciousness in a patient whose level of consciousness is altered, a lethargic patient: 67. Aphasia refers to: 68. A patient is unable to identify the smell of an orange. This inability could reflect an abnormality in cranial nerves: 69. When assessing the cranial nerves, the nurse practitioner instructs the patient to stick out his tongue and move it from side to side. This maneuver would be used to assess which cranial nerve? 70. The level of consciousness that refers to the ability of the patient to respond fully and appropriately to stimuli is known as: 71. A sudden brief lapse of consciousness with momentary blinking, staring, or movements of the lips and hands but no falling is consistent with: 72. Symptoms of a subdural hematoma include: 73. Analgesia refers to: 74. While assessing the trigeminal nerve V (CN V) for sensory function, the patient reports a pain sensation on the right cheek. This finding could be consistent with a: 75. When trying to determine the level of consciousness in a patient whose level of consciousness is altered, a comatose patient: 76. Disorders of speech fall into three groups that affect all of the following except the: 77. What is an example of a disease or condition that appears in a dermatomal pattern? 78. A 80 year old male visits the nurse practitioner for an annual well exam. History reveals two falls in the prior 12 months and difficulty with balance. The next step the nurse practitioner should take is: 79. When conducting a neurologic exam, which one of the following assessments is not considered part of the mental status assessment? 80. Ataxia, diplopia, and dysarthria can be symptoms associated with all of the following conditions except: 81. An ischemic stroke is: 82. During this type of seizure activity, the patient experiences partial seizures that resemble tonic-clonic seizures. The patient may recall the aura and a unilateral neurologic deficit is present during the postictal period. This type of seizure activity is referred to as a: 83. When assessing abdominal cutaneous reflexes, the nurse practitioner strokes the lower abdomen, the localized twitch is absent. This finding could be suggestive of a pathologic lesion in which segmented level of the spine? 84. An example of symmetric weakness is: 85. Assessment of a 70-year-old's ability to maintain personal safety would be most adversely affected by declining function in the: 86. When assessing an elderly patient for delirium, the recommended instrument with the best supportive data is the: [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 05, 2019
Number of pages
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 05, 2019
Downloads
0
Views
1