Psychology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > GCSE Psychology - Development (AQA) Latest 2023 Graded A+ (All)
GCSE Psychology - Development (AQA) Latest 2023 Graded A+
Document Content and Description Below
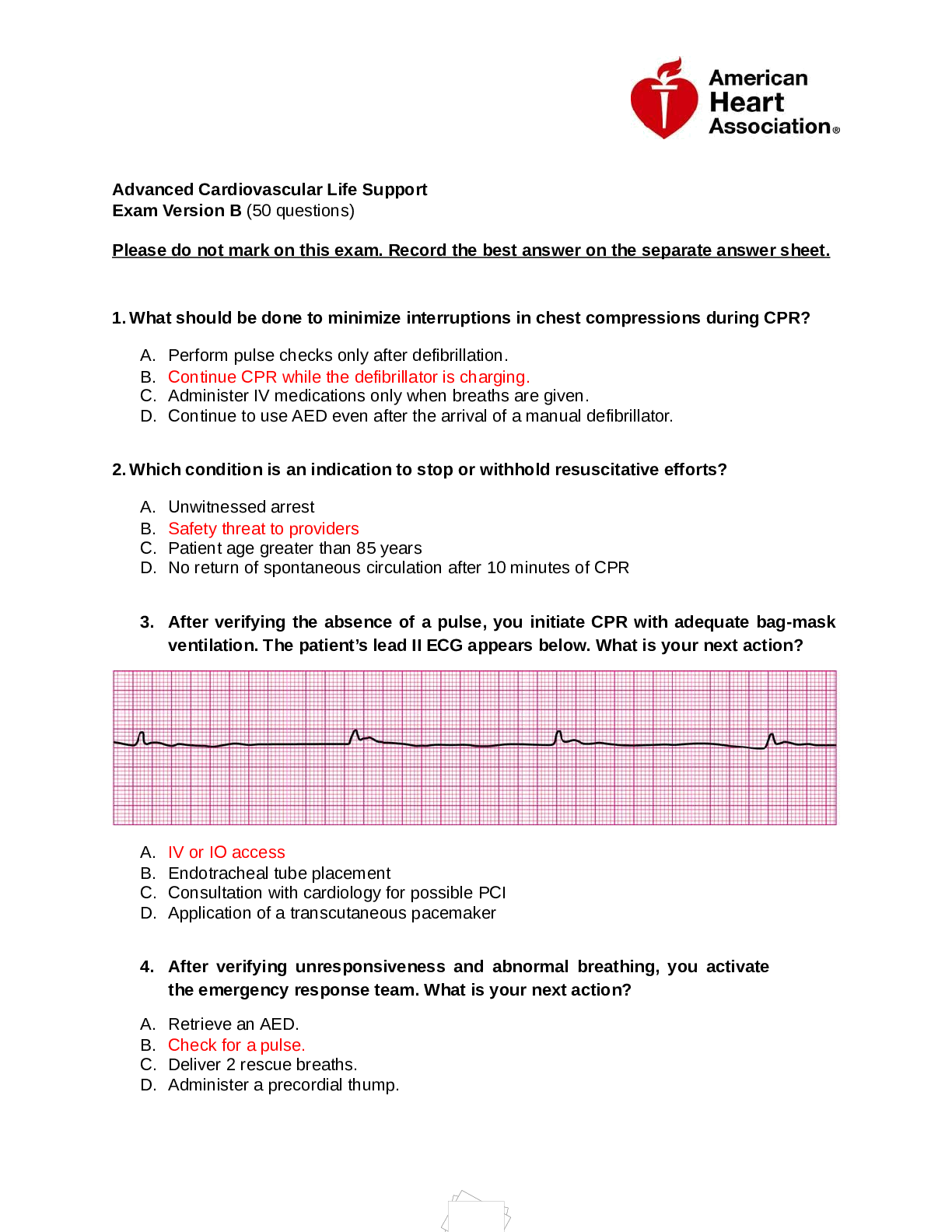
GCSE Psychology - Development (AQA) Latest 2023 Graded A+ Autonomic function ✔✔involuntary bodily functions such as breathing and heart rate. Brain stem ✔✔the part of the brain that control... s basic functions such as breathing and heart rate. Cerebellum ✔✔a small, wrinkled structure at the back of the brain which coordinates motor movement, dexterity, and balance, among other things. Cognition ✔✔the mental processes involved in gaining knowledge; these include thinking, planning and problem solving. Cortex ✔✔the outer layer of the brain where higher cognitive functions takes place, e.g. speech. Thalamus ✔✔the part of the brain that passes information from the sense organs to the cortex. Nature ✔✔The idea that our characteristics and behaviour are inherited. Nurture ✔✔The idea that our characteristics and behaviour are influenced by the environment. Twin studies ✔✔Identical twins share 100% of their genes. Non-identical twins share around 50% of their genes. Where there are more common traits between identical twins than nonidentical twins, it is likely that this is due to nature. But where their are common traits between all twins that have been raised in the same environment then this is likely to be due to nurture. Newborn baby studies ✔✔Newborn baby studies are important as there will be very little nurture impacting the baby before birth. Psychologists have found that besides being able to cry, newborn babies can also recognise faces. This means that nature is responsible for these abilities. As babies are not able to talk much later on, it is believed that nurture is responsible for language development. Animal studies ✔✔Baby rats were kept in cages on their own with no toys. Another group of baby rats were kept in cages together with a lot of stimulating toys. The rats then lived in the group in the stimulating environment development bigger brains and demonstrated better problem solving skills than the rats that lived on their own. This supports the idea that nurture is very important for early brain development. Cognitive development ✔✔All of the things that go on inside your brain, including perception, thinking, memory, attention, language, problem-solving, and learning. Schemas ✔✔Blocks of knowledge that develop in response to our experiences of the world. Assimilation ✔✔When new information is added to an existing schema. Accommodation ✔✔Changing a schema, or developing new schema to cope with new situations Concrete operational ✔✔The ability to apply logic to physical (concrete) objects to solve problems Conservation ✔✔Knowing that the amount of something stays the same, even though its appearance might change Egocentric ✔✔Not being able to see things from another's point of view Pre-operational ✔✔Before logic being unable from another person's point of view Sensorimotor ✔✔Learning through the senses and by physical (motor) activities. Formal operational ✔✔The ability to apply logic in an abstract (non-physical) way to solve problems, for example mental calculations. Sensorimotor stage ✔✔(0-2) Stage of development where children develop object permanence, in accordance to Piaget's study where a toy was hidden under a blanket while the children was watching, to see if the child would look for it under the blanket and therefore demonstrate object permenance. Pre-operational stage ✔✔(2-7) The stage where children are still egocentric. Piaget investigated this using the Mountain Study. Children were presented with three mountains and a doll seeing a different view of the mountains to the child. The child was asked to select the photo that showed the doll's view. Children over the age of 7 could select the right photo. Concrete operational stage ✔✔(7-11) Stage of development where children have developed the ability to conserve, in accordance to Piaget's study in which children were shown two rows of counters and asked if there were the same number of counters in each row. The experimenter spread out the counters in one row and asked the same question. Children over the age of 7 showed conservation and said that there were still the same number of counters in each row. Formal operational stage ✔✔(11+ years) A main feature of this stage is that children can solve problems in a systematic way. Children were given different lengths of string and a number of weights that could be attached to the string. The child's task was to investigate what factor affected how fast the pendulum would swing. The child had to vary the length of the string, and the number of weights attached. Piaget found that children under the age of 11 would attempt to change both of the weight and length of the string at the same time. However, children over the age of 11 would solve the problem systematically. Apply Piaget's theory to education ✔✔Readiness: teachers should present opportunities for the child to learn new concepts only when they are at the right stage of development and ready to learn. Teaching should be child-centered: The teacher should allow the child to discover the answers for themselves. Suitable material should be provided: Lessons should consist of objects that the child can get to know and manipulate, for example; strings and weights for the pendulum task. Evaluation of Piaget's theory ✔✔Other psychologists have since shown that the ages Piaget said could do certain tasks are incorrect. E.g. Hughes study and McGarrigle and Donaldson's study. Other psychologists criticise the way he conducted his experiments. For E.g., in the conservative tasks, he asked the children the same questions more than once. This may have led the children to think that their first answer was wrong, so they changed it. His theory has been criticised because of the way he collected the data. He used small samples that were unrepresentative of most children and he did a lot of research on his own children. The questions he put to children were not always standardised as each child was treated differently. However, Piaget's work has led other psychologists to study children's cognitive development. His methods of testing children's intellectual development were new and fun, and they used simple resources which others could replicate. His research has had a major impact on early years education, where his ideas are still being used today. Hughes' Policeman doll study - Aim: ✔✔To see if children see things from another person's point of view, at an earlier age than Piaget's theory suggests. Hughes' Policeman doll study - Method: ✔✔The children were shown a model with 2 intersecting walls that formed a cross. A policeman doll was placed on the model. The child was asked to hide the boy doll so the policeman doll could not see him. The policeman was then placed in different positions on the model, and the child was asked to hide the boy each time. This was to practice and show that they understood. Then the actual experiment began. Another policeman doll was placed on the model and the child was asked to hide the boy doll so that neither policeman doll could see him. This was repeated three times so that a different section of the grids was left as the only hiding place each time. Hughes' Policeman doll study - Results: ✔✔90 percent of the children aged between 3-5 were able to hide the boy doll from the two policeman Hughes' Policeman doll study - Conclusion: ✔✔Children aged between three and a half years and five years can see things from someone else's point of view if the situation is familiar to them, and the tasks make sense. Hughes' Policeman doll study - Evaluation: ✔✔Strength: Hughes' study is supported by other research - three mountains study but using children's TV characters. The task in the study has ecological validity because it resembles a game of hide and seek, which the children might have played at home. Limitations: There may be inaccuracies to Hughes' results due to the study taking place in a laboratory environment which was unfamiliar to the students. The task lacked ecological validity as children of this age would not be used to hiding from the police. The study is unethical as hiding from a policeman which could give children a negative impression of policemen, thinking they should hide from them instead of going to them when they need help. McGarrigle and Donaldson's Naughty teddy study - Aim: ✔✔To see if children developed conservation skills at an earlier age that Piaget found, if the change to the materials was accidental. McGarrigle and Donaldson's Naughty teddy study - Method: ✔✔The children were shown 2 rows of counters and asked if there was the same amount in each row. Then a glove puppet called 'Naughty Teddy' made an appearance. Naughty Teddy accidentally messed up one row of counters in front of the child. The messed-up row was spread out to look longer than the other row. The experimenter pretended to be really cross with Naughty Teddy and told it off. The child was then asked if there were the same amount of counters in each row. McGarrigle and Donaldson's Naughty teddy study - Results: ✔✔62% of the children aged 4-6 stated that there was still the same amount of counters in each row, even though the appearance of one of the rows had changed. Only 16% of children aged 4-6 said there were still the same amount of counters in Piaget's conservation of number study, when the adult made the changes to the counters. McGarrigle and Donaldson's Naughty teddy study - Conclusion: ✔✔Children from age 7 can conserve if the change to the materials is accidental. McGarrigle and Donaldson's Naughty teddy study - Evaluation: ✔✔Strength:It showed the contrary to Piaget's conclusion, children younger than 7 can conserve. Limitations: Over 30% of children still failed to conserve when 'Naughty Teddy' made the change. The study was replicated by another psychologist who found that although more children could conserve when 'Naughty Teddy' was used the results were not as high as McGarrigle and Donaldson had found. Dweck's mindset theory ✔✔A theory that describes how students can achieve success in their learning. and identified students as either having a fixed mindset or growth mindset. Fixed mindset ✔✔The belief that ability is genetic and unchanging Growth mindset ✔✔The belief that ability comes from hard work and can be increased Praise ✔✔An expression of approval Person praise ✔✔The student is praised for their intelligence. For example, they are told they are clever or they are told they are a great scientist. Process praise ✔✔The student is praised for their effort and the processes they use in completing a task. For example, they are praised for the strategies they use or the progress they have made. Evaluate Dweck's Mindset Theory ✔✔The theory helps us understand how students can increase their exam grades. It informs teachers that mindsets can be changed and how. There are studies to support Dweck's theory, which suggests her findings are correct. Self-efficacy ✔✔The belief in your own ability to succeed at a task How can students increase their self-efficacy? ✔✔Students can increase their self-efficacy by: Being successful at something. Observing other people succeed at something due to their effort. Being persuaded they can achieve by a role model such as a teacher. Being guided through a task. Learning styles ✔✔The different ways that a person can process information. Kinaesthetic learner ✔✔Learners learn best by doing something. They like to move or make what they are learning. They remember best when some type of physical activity is involved. Verbalisers ✔✔Someone who processes information by speaking and listening. Visualisers ✔✔Someone who processes information by looking at it. [Show More]
Last updated: 11 months ago
Preview 1 out of 8 pages

Also available in bundle (1)

GCSE Psychology Bundled Exams Questions and Answers with Verified Solutions
GCSE Psychology Bundled Exams Questions and Answers with Verified Solutions
By Nutmegs 10 months ago
$22
15
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 10, 2023
Number of pages
8
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 10, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
102

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)










.png)












.png)
.png)



