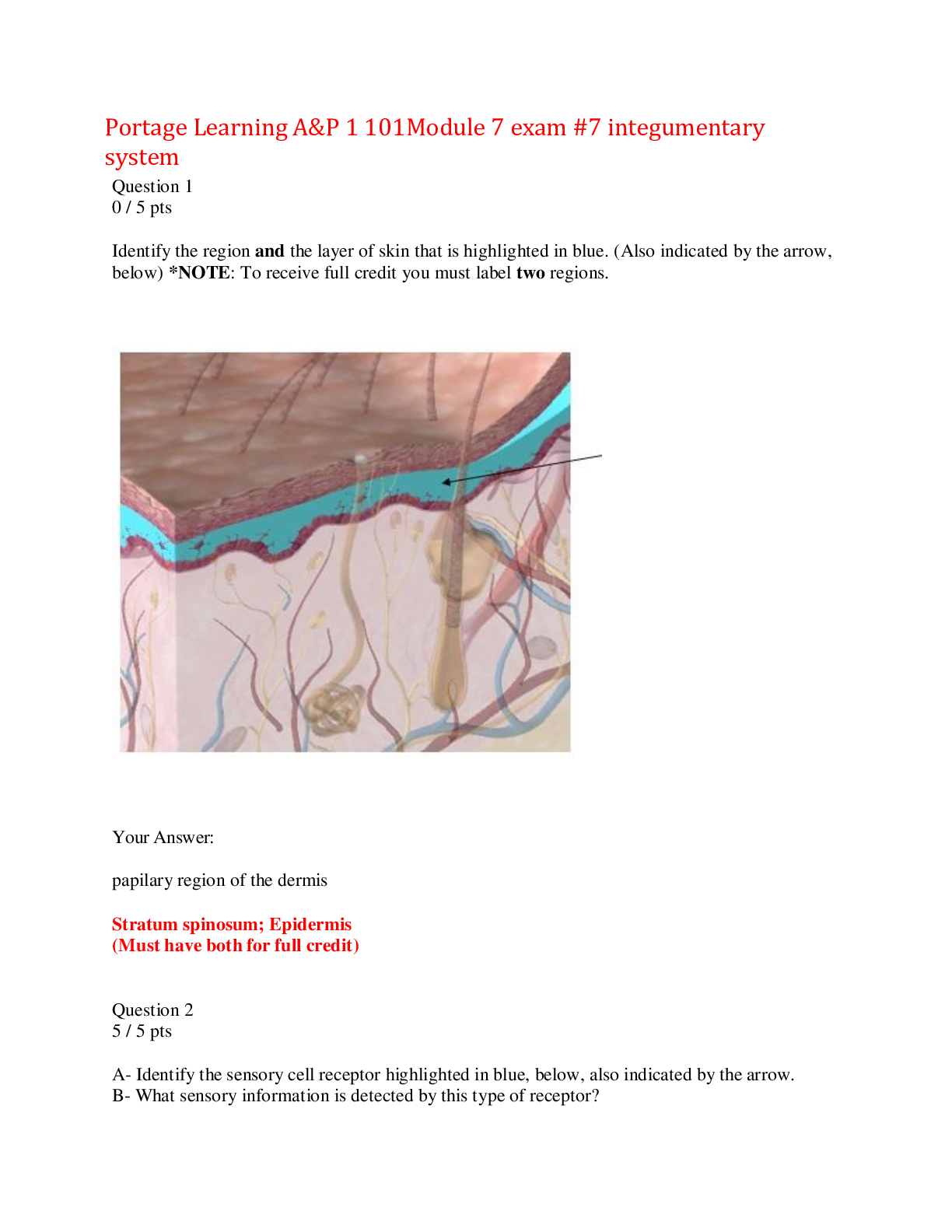
NUR 2513 Maternal Child Health – Exam 1 Blueprint,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
NUR 2513 Maternal Child Health – Exam 1 Blueprint GENERAL Know trends influencing maternal and child healthcare? ● A changing discipline ● Variations in social, structure, family, lifestyle... , and responsibilities change in addition to patterns of illness ● Birth rates, fertility rate, fetal death rate, neonatal death rate, infant mortality rate, maternal mortality rate, and child mortality rate ● Trend of where and how babies are delivered ● Increasing use of technology ● Meeting the needs of the working mother and breastfeeding Smoking and pregnancy: ● Associated with infertility in women ● If used when pregnant, can cause fetal growth restriction ● Greater risk for stillborn and after birth greater risk for sudden infant death syndrome ● Low birth weight results from vasoconstriction of uterine vessels, an effect of nicotine. This limits blood supply to fetus ● Secondary smoke or inhaling smoke of another can be as harmful as actually smoking ● Preterm birth Nutrition counseling/health counseling: ● Calorie needs ○ 2,500 (300 extra/day) ○ At least 1500 for obese ● Protein needs ○ 71 g/day (normal 34-46 g/day) ● Fat needs ○ 200-300 mg/day omega 3 ● Vitamin needs ○ Folic acid ● Fluid and fiber needs ● Foods to avoid or limit ○ Alcohol, caffeine, artificial sweeteners, weight-loss diets, raw foods, cold cuts, saccharin (long ½ life=toxic to fetus) What vitamins/minerals are encouraged? What dosage? What indication? Vitamins- D, A, C & Folic acid (400 micrograms / .4-.8mg daily). Folic acid is the only vitamin recommended for daily supplementation to prevent neural tube defects. Minerals- Calcium, Iodine, Iron (30-60 mg elemental iron daily), Fluoride, Zinc. Iron is the only mineral usually found with a deficiency. Calcium is indicated for women with low dietary intake, Iodine for populations without iodized salt, Iron supplementation reduces maternal anemia, puerperal sepsis, low birth weight, and preterm birth, Fluoride for areas without fluoridated water, Zinc in context of research CONTRACEPTION/BIRTH CONTROL IUD: ● Types ○ Copper T380 (ParaGard): T-shaped plastic device wound with copper. Effective 10 years ○ Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system 52 mg (Mirena or Liletta): progesterone in drug reservoir gradually diffuses into the uterus through plastic; prevents enfometrium proliferation and thickens cervical mucus. Effective 5 years (or 7). ○ Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system 13.5 mg (Skyla) IUD. Lower dose of progesterone in stem. Effective 3 years. ○ Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system 19.5 mg (Kyleena): lower dose of progesterone in stem then Mirena but higher than Skyla. 5 years ● Contraindications ● Considerations ● Populations ○ Used by women who have never had children as well as those who have ● Patient education DIAPHRAGM: • A diaphragm is a circular rubber disk that is placed over the cervix before intercourse. It mechanically stops the passage of sperm. With the use of spermicide, the failure rate is as low as 6% (ideal) to 18% (typical). ● A second fitting should occur when: pregnancy occurs, miscarriage, cervical surgery, or loss of more than 15 lb. ● Diaphragms should remain in place for at least 6 hours after intercourse, and as long as 25 hours. Longer than 24 hrs can = inflammation or urethral irritation ● After use, a diaphragm should be washed in mild soap and water, dried gently, and stored in a protective case. Replace after 2 years. ● Contraindications: prolapsed uterine, acute cervicitis, herpes virus infection, or papillomavirus infection, hx of TSS, allergy to rubber or spermicides, or hx of recurrent UTIs. (may cause UTIs) Do not use during period VAGINAL ESTROGEN/PROGESTIN RINGS: • (Nuvaring) releases a combination of estrogen and progesterone in the vagina continuously. Inserted by the patient and left in place for 3 weeks then removed for 1 week with menstrual bleeding. Rings do not need to be removed for intercourse. ● Hormones are absorbed by mucous membrane, avoiding a “first pass” through the liver - advantage for women with liver disease. ● Some women may experience vaginal discomfort or infection. ● If the ring is out for 4+ hours, pt needs to replace it with a new ring and use a form of barrier protection for 7 days. ORAL: o Combination Oral Contraceptive (COCs) o -Progestin-Only Pills (Mini-pills) ● Contraindications: breastfeeding and <6 weeks postpartum, 35+ y.o. And smoking 15 or more cigarettes per day, hx of thromboembolic disease, major surgery that requires bedrest, current/hx of ischemic heart disease or CVA, complicated valvular heart disease, migraine with aura, current breast cancer or diabetes with nephropathy, retinopathy, neuropathy, vascular disease or 20+ years duration, severe cirrhosis or liver tumors, broad-spectrum antibiotics *Bold= increased tendency toward clotting b/c of increased estrogen! ● Considerations: ● Populations: women without history of thromboembolism or other contraindications/risk factors, women who do not want to have menstrual flows, ability to take consistently and conscientiously and can afford them ● Pt. Education: Medically induced abortion: Usually either Mifepristone (progesterone antagonist that prevents implantation taken any time before 63 gestational age) & misoprostol (a prostaglandin that causes contractions) OR methotrexate (interferes with DNA synthesis of dividing cells) & misoprostol. ● Contraindications: a confirmed/suspected ectopic pregnancy (only methotrexate), an IUD in place, serious medical condition, hx of current long-term systemic corticosteroid therapy, allergy to medications or other prostaglandins, a hemorrhagic disorder or taking anticoagulant therapy ● Advantages of medically induced vs surgical: less risk of damage to uterus through instrument insertion and decreased use of anesthesia. ● Complications: N/V/D, severe uterine cramping, incomplete abortion, prolonged bleeding ● Education: expect mild vaginal spotting and cramps for 2 weeks post procedure. Use pads, not tampons. Do not douche. Take Tylenol, not aspirin for discomfort. Avoid heavy lifting or strenuous exercise for 3 days. Usual period will return 2-4 weeks. ● Pt. to call provider when: heavy vaginal bleeding (2+ pads in 1 hr), passing of clots, abd pain/tenderness, temp over 102.4, depression Emotional tasks/adaptation of family - Developmental tasks of pregnancy and psychological adjustment: ● Psychological changes: social, cultural, family, individual differences ● Psychological tasks: ○ Emotional response to pregnancy: grief, narcissism, introversion vs extroversion, body image and boundary, stress, depression, couvade syndrome, emotional lability, changes in sexual desire, changes in expectant family PREGNANCY Hyperemesis gravidarum: ● Persistent vomiting. Nausea and vomiting prolonged past week 16 of pregnancy or that’s so severe that dehydration, ketonuria, and significant weight loss occur within the first 12 weeks of pregnancy ● Occurs in 2%. Unknown cause but women with it have increased thyroid function ● Weight loss can be severe. Urine positive for ketones, elevated hematocrit. Concentrations of sodium, potassium, and chloride reduced. Hypokalemic alkalosis. Vitamin B1 deficient. ● Management: IV fluids. Antiemetic. If no vomiting in 24 hours, small amounts of clear fluids. Gestational Diabetes: ● Diabetes during pregnancy ○ Decreased control of glucose regulation ○ Effect on fetal size, infant hypoglycemia, and increased incidence of congenital anomalies Chronic hypertension/Preeclampsia/Pregnancy Induced Hypertension: ● Chronic hypertension: is high blood pressure that is diagnosed prior to pregnancy or occurs in the first 20 weeks of gestation ● Preeclampsia: a severe disorder where high blood pressure occurs after the 20th week of gestation. Hypertension is accompanied by proteinuria and can include critical features that indicate multiple organ damage that is involved. S/S- severe headache, upper abdominal pain, usually under ribs on right side, changes in vision, N/V. 140/90 w/ severe features 160/110, 3+ protein, and edema ● Gestational hypertension: high blood pressure that is diagnosed after the 20th week of gestation Physical changes in pregnancy: ● Cardiovascular- heart is pushed upward, laterally to the lefts, cardiac hypertrophy ● Integumentary- hyperpigmentation, chloasma (melasma), linea nigra, stretch marks (striae gravidarum), varicose veins, angiomas, palmar erythema ● Female organs: -Uterus: hypertrophy, Braxton-Hicks contractions, increased blood flow -Cervix: Chadwick’s sign, Goodell sign, softens, forms mucus plug -Vagina and Vulva: thickening of vaginal mucosa, rugae, edematous, pH decreases from 6.0 to 3.5 -Ovaries and breasts: increased pigmentation of areola, breasts enlarge, montgomery tubercles ● Neuro: decreased attention span, poor concentration, or memory lapses can occur Know how to measure fundal height: ● Measured in cm from pubic bone to top of uterus. The cm should match the week of gestation +/- 2. Measuring the distance from the pubic symphysis to the highest part of the uterus. A 33-week baby should measure 33 (+/-2) cm Quickening: Why is the urine checked routinely for glucose? What do the results mean? FHR Strips: Variability definitions: o Absent variability: o Mild variability: o Moderate variability: o Marked variability: Presumptive/Probable/Positive Signs of pregnancy: Stress test/nonstress test: ● Stress test ○ Adding stress to the baby. Give mother pitocin to have contractions and see how the baby responds to those contractions. ● Non-stress test ○ Measures the response of the fetal heart rate to fetal movement ○ Reactive (healthy) if 2 accelerations of FHR (by 15 beats or more) lasting for 15 seconds occur after movement within the time period ○ Nonreactive (fetal health may be affected): if no accelerations occur with fetal movements. No fetal movement occurs or if there’s low short-term FHR variability (less than 6 beats/min) throughout the testing time ○ If 20 minutes pass without any movement this could mean fetus is sleeping, etc Nonreactive reasons: ● Fetus is sleeping, maternal smoking, drug use, hypoglycemia (give apple juice) Goodell’s/Chadwick’s/Hegar’s Sign: ● Goodell’s sign: softening of the cervix. Increased fluid between cells causes it to soften in consistency, and increased vascularity causes it to darken rom pale pink to violet hue (cervix) ● Chadwick’s sign: Color change of vagina from pink to violet Increase in vascularity of vagina parallels the vascular changes in the uterus. The resulting increase in circulation changes color of vaginal walls from their normal light pink to deep violet ● Hegar’s sign: extreme softening of lower uterine segment. GTPAL system: ● G: # pregnancies including current ● T: # full-term infants born (37 weeks or after) ● P: # preterm infants born (before 37 weeks) ● A: # spontaneous miscarriages or therapeutic abortions ● L: # living children Dating of pregnancy: first day of last menstrual cycle - 3 months + 7 days Know normal Lab levels in pregnancy: o Serum creatinine: o BUN: o Glomerular filtration rate: o Creatinine clearance: Placenta Previa – What is it? What should the nurse do/not do? ● Definition: improperly implanted placenta in lower uterine segment near or over internal cervical os. ● Nursing assessment includes sudden onset of painless, bright red vaginal bleeding occurring in last half of pregnancy, the uterus is soft and relaxed, and fundal height may be more than expected for gestation age ● Nursing interventions include monitoring VS, HR, and fetal activity, US, avoid vaginal exams, bed rest with side-lying position, monitoring amount of bleeding (treat signs of shock if present), IV fluids, blood products if need or tocolytic meds. Plan for cesarean if heavy bleeding Placental Abruption: ● Definition: premature separation of placenta from uterine wall after 20th week of gestation and before fetus is delivered ● Nursing assessment: dark red vaginal bleeding with PAIN, uterine rigidity, severe abdominal pain, signs of fetal distress, symptoms of maternal shock if bleeding is excessive. ● Nursing interventions: monitor VS, HR, contractions, assess bleeding, US, abdominal pain, and increased in fundal height. Bed rest, oxygen, IV fluids, and blood products as needed. Place mother in Trendelenburg position if needed to decrease pressure of fetus on placenta or in lateral position with HOB flat if hypovolemic shock occurs. Delivery of newborn-vaginal or cesarean. A concern for postpartum client with this would be to monitor for DIC Preterm/Term/Post-term: ● Preterm ○ Infants born before term (before beginning of 37th week) ● Term ○ Born after beginning of week 37 and before week 42 ● Post-term ○ Born after the end of week 41 Baby positions in utero: ● Vertex: head is down ● Breech: bottom is down ● Transverse: sideways ● Face: face coming first; flexed ● Brow: brow first ● Normal is the crown of the head coming out first Meconium: ● Collection of cellular wastes, bile, fats, mucoproteins, mucopolysaccharides, and portions of vernix caseosa (the lubricating substance that forms on fetal skin), accumulates in intestines as early as 16 weeks ● It’s sticky in consistency and appears black or dark green (containing color from bile pigment) Amniocentesis: ● 15-18 weeks. Collection of amniotic fluid containing fetal skin cells through maternal abdomen. Invasive, risk of miscarriage ● Diagnostic tests that assess karyotype (chromosomes) ● Diagnose chromosomal genetic disorders Maternal positions for labor ● Early Labor: walking, sitting, kneeling, squatting, on all fours. Lie on left side, supine. ● Second stage: semi-Fowler’s with legs raised against abdomen, squatting, or on all fours rather than lying flat to allow gravity to aid the effort. Management of decelerations RH factor. p. 558 When to give Rogam? In what situation? ● Mother is RH negative and baby is RH positive ● RH positive blood has D-factor, which is an antigen ● RH negative doesn’t have D-factor so if RH negative gets RH positive blood, then body will create antibodies to that RH positive and kill it off ● If first baby is RH positive, it can get into mother’s system in which her body will create antibodies and destroy the baby ● Give Rhogam at 28 weeks and again 72 hours postpartum. This prevents the production of antibodies in the mother. It is given postpartum for any subsequent pregnancies HELLP- hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelet count ● Variation of gestational hypertensive process named for the common symptoms that occur ● Hemolysis leads to anemia ● Elevated Liver enzymes lead to epigastric pain ● Low Platelets lead to abnormal bleeding/clotting ● Symptoms: proteinuria, edema, increased BP, nausea, epigastric pain, general malaise, right upper quadrant tenderness from liver inflammation ● Interventions: transfusion of fresh frozen plasma or platelets. If hypoglycemia, give IV glucose infusion. Try not to do interventions that cause bleeding besides an IV ● CAN NOT HAVE EPIDURAL!!!!!! Gestational hypertension aka pregnancy induced hypertension (PIH): ● Triad of hypertension, proteinuria, and edema with vasospasm as a cause. Symptoms: mild preeclampsia, severe preeclampsia, eclampsia, HELLP syndrome ● A potentially severe and even fatal elevation of BP that occurs after 20 weeks. ○ S/S: rapid weight gain (over 2lb/week in 2nd trimester, over 1 lb/week in third), swelling of face and fingers, flashes of light or dots before eyes, dimness/blurring vision, severe continuous headache, decreased urine output, RUQ pain unrelated to fetal position, BP increased above 140-90 ● Condition where vasospasm occurs in both small and large arteries during pregnancy, causing increased BP Pre-eclampsia (aka toxemia)/Eclampsia: ● Preeclampsia: severe disorder where high BP occurs after 20th week of gestation. With this, the high BP is accompanied with proteinuria and can include critical features that indicate multiple organ damage that’s involved ● Eclampsia: when eclampsia has gotten worse to the point of the client experiencing seizures due to worsening of this hypertensive disorder Preterm labor: Pitocin: ● Used to induce labor when at term by stimulating uterine smooth muscle to produce contractions Tocolytics: used to stop contractions Betamethasone: ● Used to encourage fetus to speed up the development of lungs Magnesium Sulfate: ● Used to prevent seizure related to preeclampsia or to slow or stop preterm labor. The nurse needs to continually monitor knee reflex after the client receives this. NEWBORN: Omphalocele: (om-fal-o-seal) ● Intestine remains outside abdomen in based of cord. Congenital anomaly. ● Protrusion (herniation) of abdominal contents through abdominal wall at point of the junction of umbilical cord and abdomen. ○ Herniated organs include intestines, and possibly stomach and liver. ○ Organs usually are covered and contained by thin transparent layer of amnion and chorion with umbilical cord protruding from exposed sac ○ Occurs at week 6-8 when fetal abdominal contents, which grow faster than fetal abdomen, are pushed out from abdomen into base of umbilical cord Surfactant: ● Phospholipid substance that is formed and excreted by alveolar cells of lungs beginning at about 24th week. This decreases alveolar surface tension on expiration preventing alveolar collapse and improving infant’s ability to maintain respirations in the outside environment at birth Sickle Cell Anemia o Passed on from genetics o Managed with blood transfusion o Most common in black people [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 17 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 31, 2021
Number of pages
17
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 31, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
48