*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NR 508(GRADED A) MIDTERM EXAM 2 – QUESTION AND ANSWERS (All)
NR 508(GRADED A) MIDTERM EXAM 2 – QUESTION AND ANSWERS
Document Content and Description Below
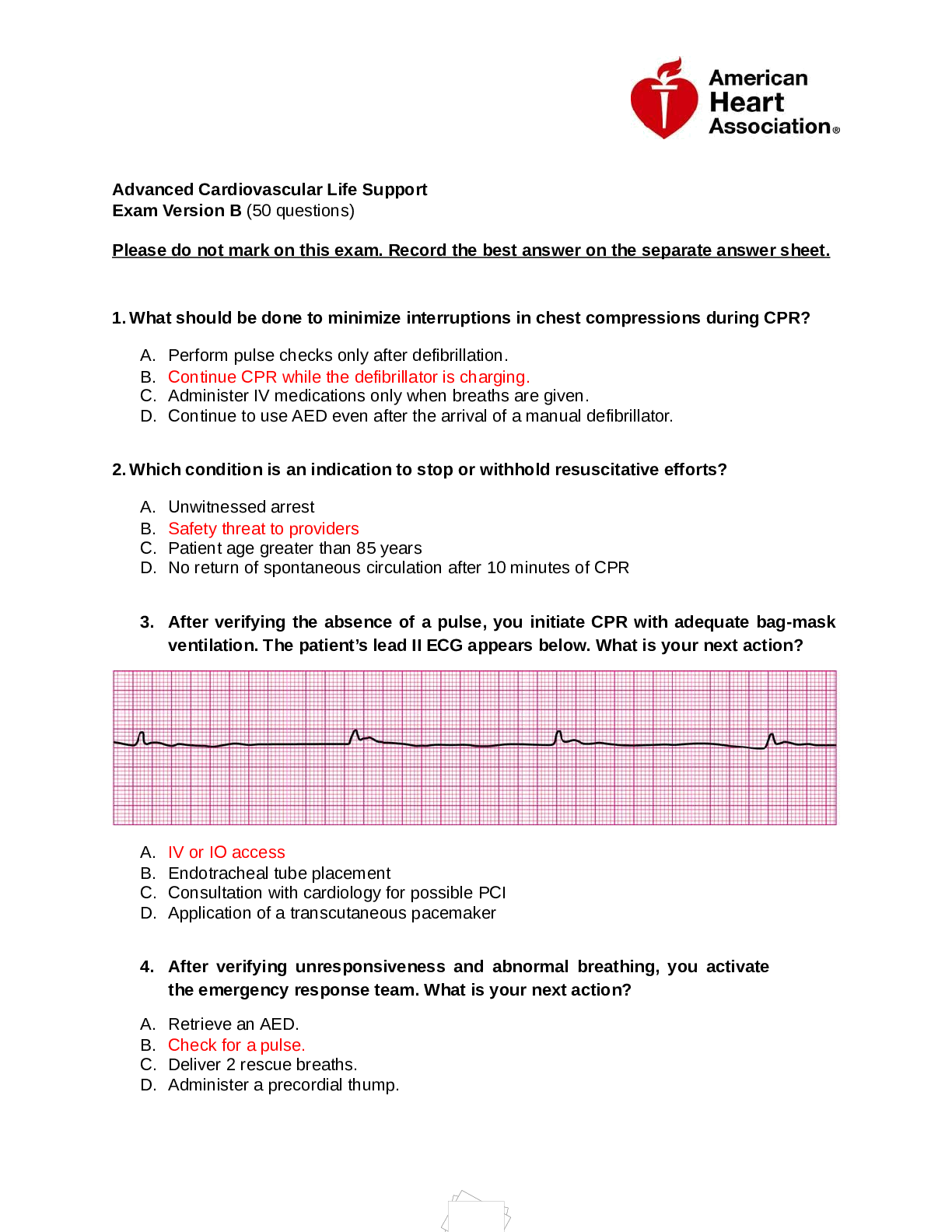
A primary care NP prescribes levothyroxine for a patient to treat thyroid deficiency. When teaching this patient about the medication, the NP should: tell the patient that changing brands of the med... ication should be avoided. Patients should be told not to change brands of the medication; there is potential variability in the bioequivalence between manufacturers. The medication should be taken at approximately the same time each day before breakfast or on an empty stomach. Patients should be instructed to contact the provider if signs of thyrotoxicosis are present. Thyroid replacement medications are usually given for life. An African-American patient is taking captopril (Capoten) 25 mg twice daily. When performing a physical examination, the primary care nurse practitioner (NP) learns that the patient continues to have blood pressure readings of 135/90 mm Hg. The NP should: add a thiazide diuretic to this patient's regimen Some African-American patients do not appear to respond as well as whites in terms of blood pressure reduction. The addition of a low-dose thiazide diuretic often allows for efficacy in blood pressure lowering that is comparable with that seen in white patients. Increasing the captopril dose is not indicated. Losartan is an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) and is not indicated in this case. A primary care NP sees a patient who is about to take a cruise and reports having had motion sickness with nausea on a previous cruise. The NP prescribes the scopolamine transdermal patch and should instruct the patient to apply the patch: every 3 days. The transdermal system allows steady-state plasma levels of scopolamine to be reached rapidly and maintained for 3 days. The onset of action is approximately 4 hours. The patch should be changed every 3 days and left on at all times, not as needed A 12-year-old patient who is obese develops type 2 diabetes mellitus. The primary care NP should order metformin (Glucophage). Metformin is the only drug listed that is recommended for children A patient who has had four to five liquid stools per day for 4 days is seen by the primary care NP. The patient asks about medications to stop the diarrhea. The NP tells the patient that antidiarrheal medications are: not curative and may prolong the illness Treatment of patients with acute diarrhea with antidiarrheals can prolong infection and should be avoided if possible. Antidiarrheals are best used in patients with mild to moderate diarrhea and are used for comfort and not cure. They should not be used for patients with bloody diarrhea or high fever because they can worsen the disease. Prolonged diarrhea can indicate a more serious cause, and antidiarrheals should not be used in those cases. In every state, prescriptive authority for NPs includes the ability to write prescriptions for specified classifications of medications. All states now have some degree of prescriptive authority granted to NPs, but not all states allow authority to prescribe controlled substances. Many states still require some degree of physician involvement with certain types of drugs. A 55-year-old woman has a history of myocardial infarction (MI). A lipid profile reveals LDL of 130 mg/dL, HDL of 35 mg/dL, and triglycerides 150 mg/dL. The woman is sedentary with a body mass index of 26. The woman asks the primary care NP about using a statin medication. The NP should: begin therapy with atorvastatin 10 mg per day This woman would be using a statin medication for secondary prevention because she already has a history of MI, so a statin should be prescribed. Dietary and lifestyle changes should be a part of therapy, but not the only therapy. She is relatively young, and quality-of-life issues are not a concern. There is no clinical evidence to support use of statins as primary prevention in women. A patient develops hypertension. The primary care nurse practitioner (NP) plans to begin diuretic therapy for this patient. The NP notes clear breath sounds, no organomegaly, and no peripheral edema. The patient's serum electrolytes are normal. The NP should prescribe: hydrochlorothiazide (HydroDIURIL) Thiazide diuretics are first-line drugs for treating hypertension. The other three drugs are not thiazide diuretics The primary care nurse practitioner (NP) is using critical thinking skills when analyzing current research and synthesizing new approaches to patient care. Practitioners use critical thinking skills by reviewing and analyzing current knowledge and synthesizing approaches to apply to unique patient situations. Using standardized protocols, adhering to scientific principles, and following practices of seasoned mentors may be useful, but these do not encompass the concept of critical thinking, which requires the practitioner to use what is known in new situations. A patient comes to the clinic and asks the primary care NP about using a newly developed formulation of the drug the patient has been taking for a year. When deciding whether or not to prescribe this formulation, the NP should: tell the patient that when postmarketing data is available, it will be considered. About 6 to 12 months of postmarketing experience can yield information about drug efficacy and side effects, so patients should be cautioned to wait for these data. Drug company promotional materials have biased information. Most new drugs are more expensive, and costs alone should not determine drug choice. Extended-release forms are often more expensive. A patient takes a cardiac medication that has a very narrow therapeutic range. The primary care NP learns that the particular brand the patient is taking is no longer covered by the patient's medical plan. The NP knows that the bioavailability of the drug varies from brand to brand. The NP should: contact the insurance provider to explain why this particular formulation is necessary. In this case, the NP should advocate for the desired drug because changing the drug can have lifethreatening consequences. If this fails, other options may have to be explored. In this case, the NP should advocate for the desired drug because changing the drug can have lifethreatening consequences. If this fails, other options may have to be explored. bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol) Bismuth reduces symptoms through ant [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 15 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 26, 2022
Number of pages
15
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 26, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
90
.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
















.png)





.png)

