*NURSING > CASE STUDY > NR222 Exam 1 health care case study 2021/2022 (All)
NR222 Exam 1 health care case study 2021/2022
Document Content and Description Below
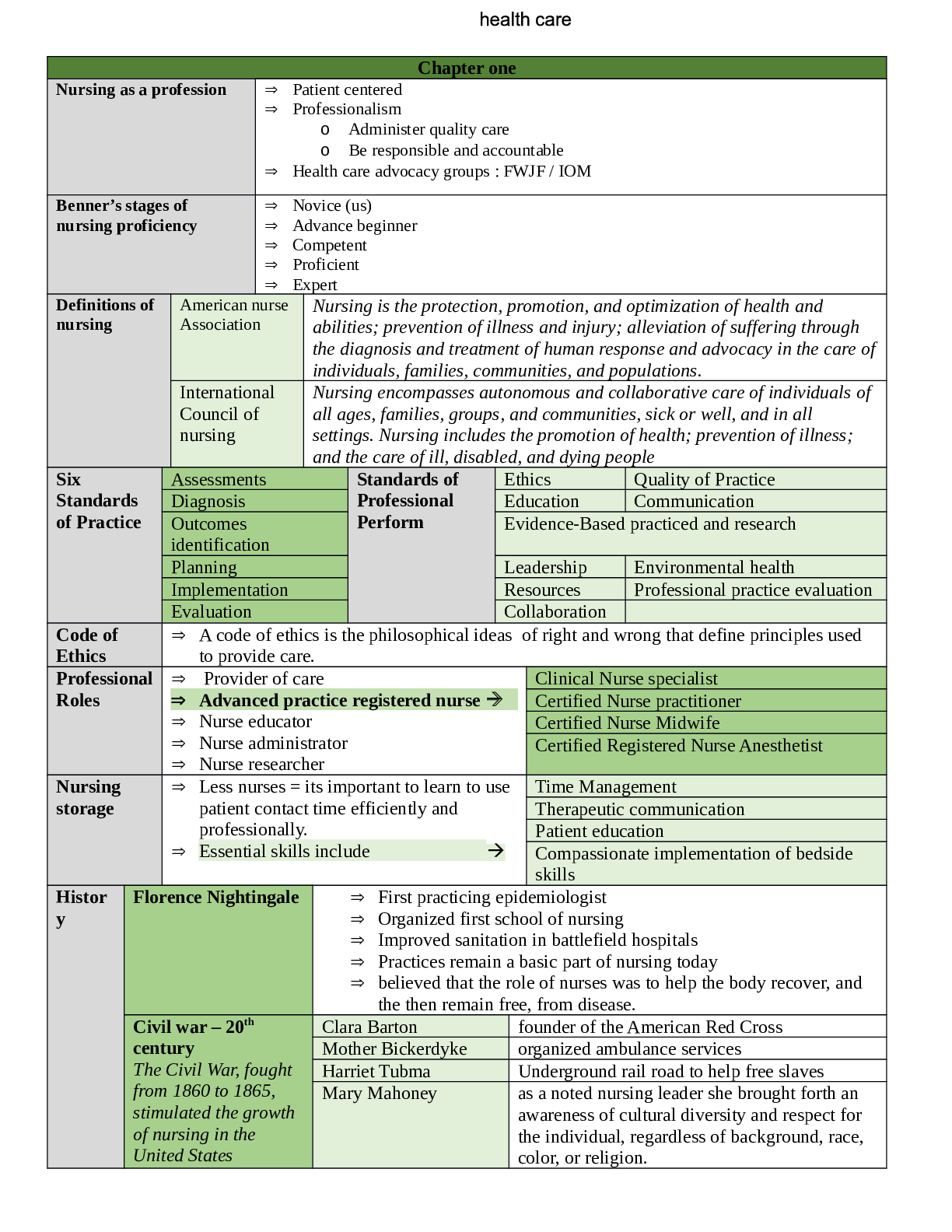
Nursing as a profession Patient centered Professionalism o Administer quality care o Be responsible and accountable Health care advocacy groups : FWJF / IOM Benner’s stages of nurs... ing proficiency Novice (us) Advance beginner Competent Proficient Expert Definitions of nursing American nurse Association Nursing is the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and abilities; prevention of illness and injury; alleviation of suffering through the diagnosis and treatment of human response and advocacy in the care of individuals, families, communities, and populations. International Council of nursing Nursing encompasses autonomous and collaborative care of individuals of all ages, families, groups, and communities, sick or well, and in all settings. Nursing includes the promotion of health; prevention of illness; and the care of ill, disabled, and dying people Six Standards of Practice Assessments Standards of Professional Perform Ethics Quality of Practice Diagnosis Education Communication Outcomes identification Evidence-Based practiced and research Planning Leadership Environmental health Implementation Resources Professional practice evaluation Evaluation Collaboration Code of Ethics A code of ethics is the philosophical ideas of right and wrong that define principles used to provide care. Professional Roles Provider of care Advanced practice registered nurse Nurse educator Nurse administrator Nurse researcher Clinical Nurse specialist Certified Nurse practitioner Certified Nurse Midwife Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist Nursing storage Less nurses = its important to learn to use patient contact time efficiently and professionally. Essential skills include Time Management Therapeutic communication Patient education Compassionate implementation of bedside skills Histor y Florence Nightingale First practicing epidemiologist Organized first school of nursing Improved sanitation in battlefield hospitals Practices remain a basic part of nursing today believed that the role of nurses was to help the body recover, and the then remain free, from disease. Civil war – 20th century The Civil War, fought from 1860 to 1865, stimulated the growth of nursing in the United States Clara Barton founder of the American Red Cross Mother Bickerdyke organized ambulance services Harriet Tubma Underground rail road to help free slaves Mary Mahoney as a noted nursing leader she brought forth an awareness of cultural diversity and respect for the individual, regardless of background, race, color, or religion. Lilian wald opened the Henry Street Settlement, which focused on the health needs of poor people who lived in tenements in New York City. Twenty Century Movement toward scientific, research-based practice and defined body of knowledge Nurses assumed expanded and advanced practice roles Changes in curriculum Advances in tech and informatics New programs and leardership roles. Contemporary influences Importance of nurses’ self-care Changes in society lead to changes in nursing: Affordable Care Act (ACA) Rising health care costs Demographic changes Medically underserved Chapter 2 Health Care Uninsured patients Reducing health care costs while maintaining high quality-care for patients. Challenges Improving access and coverage for more people Encouraging healthy behaviors Earlier healthy behaviors Earlier hospital discharges result in more patients needing nursing homes or home care National priorities partnerships Promote best practices Promote prevention, treatment, and intervention. Ensure person- and family -centered care Make care safer Promote communication and care coordination Make quality care affordable. Institute of medicine (IOM) Nursing need to be transformed by: Practicing to the full extent of their training Achieving higher levels of education through an education system that provides seamless progress Becoming full partners with physical and other health care providers in redesigning the health care system. Improving data collection and the information infrastructure for effective workforce planning and policy making. Health care regulation and Reform Regulators and competitive approaches Professional standards review organizations (PSROs) o Create to review the quality, quantity and cost of hospital care provide through Medicare and Medicaid. Utilization Review (UR) committees o Review admissions, diagnostic testing, and treatments ordered by physicians who cared for patients receiving Medicare. Health care Regulation and Reform Patient protection and Affordable care act Access to health care for all Reducing costs Improving quality Provisions include o Insurance industry reforms o Increased funding for public programs o Improved coverage for children. Emphasis on population wellness Health services pyramid Managing health instead of illness Emphasis on wellness Injury-prevention programs. Preventive Reduces and controls risk factors Primary Focuses on improved health outcomes Requires collaboration Secondary Focus: diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Disease management is the most common expensive service of the health care delivery system Postponement of care by uninsured contributes to high costs. Hospital ED, urgent care, etc. o Work redesign, discharge planning. Intensive care, psychiatric faculties, rural hospitals. Tertiary Restorative Services patients recovering from an acute or chronic illness/ disability. Helps individuals regain maximal function and enhance quality of life. Home Health Care Provision of medically related services and equipment to patients and families in their home for health maintenance. Involves coordination of services and focuses on patient/family independence. Usually reimbursed by gov. Rehabilit ation Aims to restore a person to the fullest physical, mental social, vocation, economic potential possible. All types of therapy: physical, occupational speech and social services. Beginning on admission- focuses on preventing complications Maximizes patient function/ independence. Extended care Provides intermediate medical, nursing, or custodial care for patients recovering from acute illness or disabilities. Intermediate care/skilled nursing facility o Provides care for patients until they can return to their community or residential care location. Continuing Care For people who are disabled, functionally independent, or suffering a terminal disease. Available within institutional settings or in the home o Nursing centers or facilities, assisted living, Respite care, adult day care centers, hospice. Nursing centers or facilities Provide 24 intermediate and custodial care o Nursing rehabilitation, diet, social, recreational and religious services. o Residents of any age with chronic or debilitating illness. Assisted living Long term care setting Home environment Greater resident autonomy No fee caps. Respite care Can provide short-term relief or “time off” for people providing home care to an individual who is ill, disabled, or frail. Setting include home, day care, or health care institution with overnight care. Trained volunteers enable family caregivers to leave the home for errands or social time. Adult day care Provide a variety of health and social services to specific patient populations who live alone or with family in the community. May be associated with a hospital or nursing home or may operate independently. Hospice Family centered care that allow patients to live with comfort independence and dignity while easing the pains of terminal illness. Focuses on palliative (not curative) care Many hospice programs provide respite care, which is important in maintain the health of the primary caregiver and family. Care coordination Care Coordination Health care reform has stimulated the development of two models focused on Accountable care organizations (ACOs) Developed to coordinate medical care Nurses act as leaders and care coordinators coordinating medical care for patients and families Patient-centered medical home (PCMH) Coordinates care, gathers clinical data, monitors patient outcomes. Primary care providers function as the hib of the PCMH. Issues in Health care Delivery Nursing shortage Competency Quality and safety in health care Nursing recognition program Nursing informatics and technological advancements Globalization of health care o Pay for performance o Patient satisfaction o Nursing sensitive outcomes Technological advancements influence where and how nurses provide care to patients and can help nurses improve direct care processes, patient outcomes, and work environments. Technology makes your work easier, but it does not replace nursing judgment. Vulnerable populations ( children, women, older adults) most threatened by urbaniszation. Quality and Performance Improvement Quality data Quality data are the outcome of both QI and PI initiatives. Quality improvement (QI) QI is an approach to the continuous study and improvement of the processes of providing health care services to meet the needs of patients and others and inform health care policy. QI data inform you about how processes work within an organization and thus offer information about how to make evidence-based practice (EBP) changes. Performance improvement (PI) Analyzes what an institution does and how well it does it. an organization analyzes and evaluates current performance and uses the results to develop focused improvement actions. Models and Quality improvement Programs Patient Self-Determination Act (PSDA) Six Sigma or Lean Rapid-cycle improvement or rapid-improvement event (RIE) Future of health care Change opens up opportunities for improvement. Health care delivery systems need to address the needs of the uninsured and the underserved. Health care organizations are striving to become better prepared to deal with these and other challenges in health care. The solutions necessary to improve the quality of health care depend largely on the active participation of nurses. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 16 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 06, 2022
Number of pages
16
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 06, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
77