Economics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Bentley University EC Intermed Macroeconomics: Problem Set 1 – Econ 225, Sections 002 and 003. Q&A (All)
Bentley University EC Intermed Macroeconomics: Problem Set 1 – Econ 225, Sections 002 and 003. Q&A
Document Content and Description Below
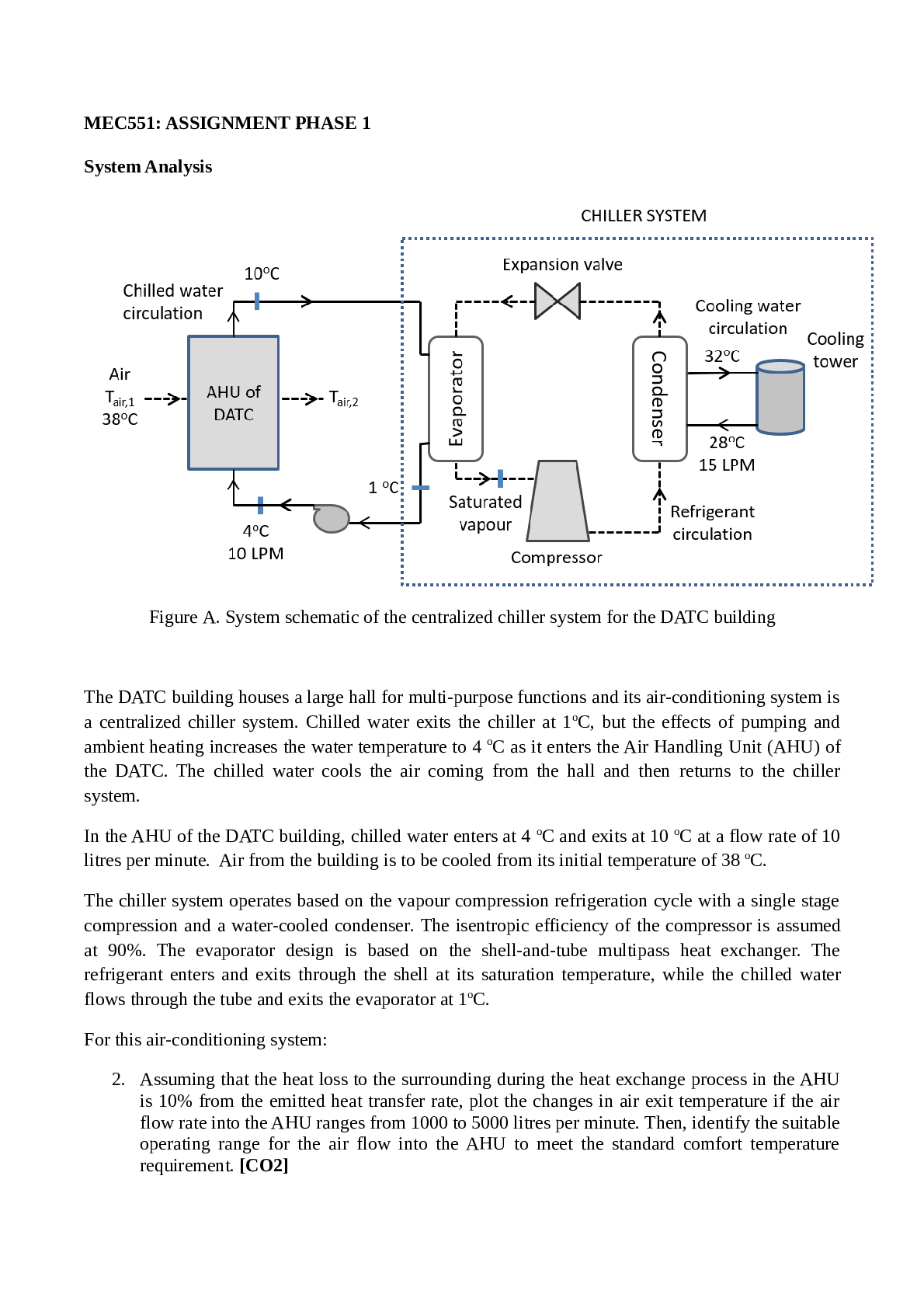
Problem Set 1 – Econ 225, Sections 002 and 003 Chapter 5 – Questions 6, 7, 9 6) The Bush-Greenspan Policy Mix: in 2001, the Fed pursued a very expansionary monetary policy. At the same time, Pr... esident George W. Bush pushed through legislation that lowered income taxes. a) Illustrate the effect of such a policy mix on output. By lowering income taxes, consumptions increases therefore the output increases as well. Decrease in T shifts the IS curve to the right. An expansionary monetary policy means that M will be increased, an increase in M would shift LM curve down, therefore brining the interest rate down. Overall output increases. b) Describe how this policy mix differs from the Clinton-Greenspan mix (described earlier in chapter 5) – illustrate the effects of this in a separate IS/LM diagram. Clinton-Greenspan policy included a contractionary fiscal policy that would shift IS left and an expansionary monetary policy which would shift LM curve down. c) What happened to output in 2001? How do you reconcile the fact that both fiscal and monetary policies were expansionary with the fact that growth was so low in 2002? Illustrate the effect of this in an IS/LM diagram. In 2001 there was a recession which was caused by a decrease in investment spending and then later on there was a decline in the stock market. The expansionary monetary and fiscal policies were supposed to decrease the effect of the recession by unfortunately they were applied too late and the recession was unavoidable. 7) Policy Mixes – suggest a policy mix to achieve each of the following objectives: a) Increase Y while keeping i constant. Increase in G or decrease in T would shift IS curve to the right and then increase in M would shift the LM curve down and therefore the output is increased while the interest rate stayed the same. b) Decrease the fiscal deficit while keeping Y constant. What happens to i? To investment? In order to achieve this state we should reduce government spending or increase taxes which would shift the IS curve to the left. Then we should increase M which would shift the LM curve down. The interest rate would fall and since the interest rate fell the investment would increase. And the output stayed the same. 9) The Clinton-Greenspan policy mix: As described in this chapter, during the Clinton administration the policy mix changed toward more contractionary fiscal policy and more expansionary monetary policy. This question explores the implications of this change in the policy mix, both in theory and fact. a) Suppose G falls, T rises, and M increases, and that this combination of policies has no effect on output. Show the effects of these policies in an IS/LM diagram. What happens to the interest rate? What happens to investment? Well the decrease in G and an increase in T would shift LS curve to the left. The increase in M would shift the LM curve down. Therefore the interest rate would fall and therefore investment would increase. b) Go to the website Economic Report of the President (www.gpoaccess.gov/eop). Look at Table B-79 in the statistical appendix. What happened to federal receipts (tax revenues), federal outlays, and the budget deficit as a percentage of GDP over the period 1992 to 2000? (Note that federal outlays include transfer payments, which would be excluded from variable G, as we define it in our IS/LM model. Ignore the difference.) Receipts rose, outlays fell and the budget deficit fell as well. c) The Federal Reserve Board of Governors posts the recent history of the federal funds rate at http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15.data.htm. You will have to choose to look at the rate on a daily, weekly, monthly, or annual interval. Look at the years between 1992 and 2000. When did monetary policy become more expansionary? In September 4,1992 the FFR was 3 % then it started increasing until February 1, 1995 when it hit 6% and then until the year of 2000 it was playing between 5 and 6 going up and down by basic 25 points. Between those years the lost it got was 4.75 in November 17, 1998. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 4 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 23, 2023
Number of pages
4
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 23, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
79











.png)






.png)












