Chemistry > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Gas Solubility in Aqueous Solution.pdf (All)
Gas Solubility in Aqueous Solution.pdf
Document Content and Description Below
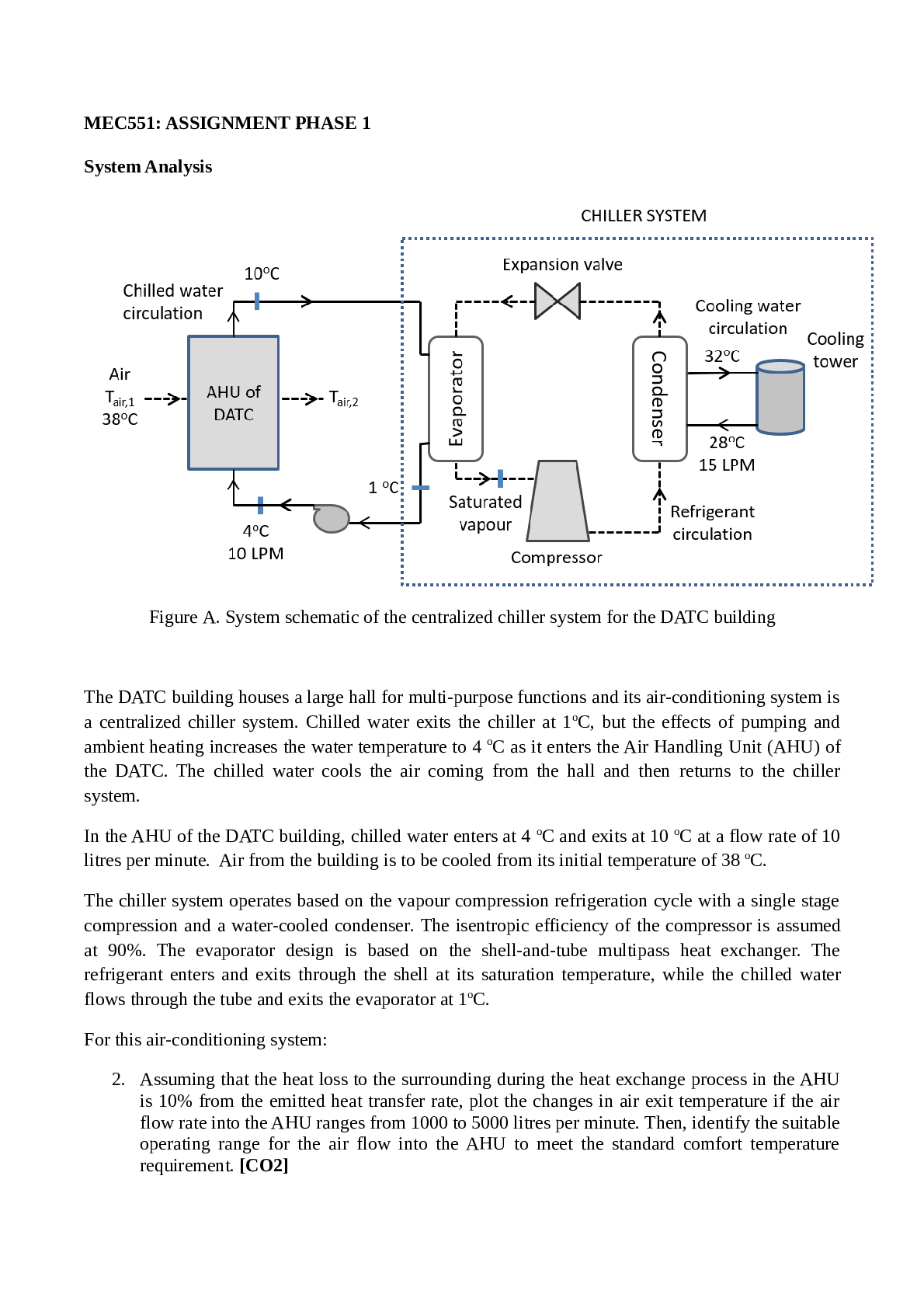
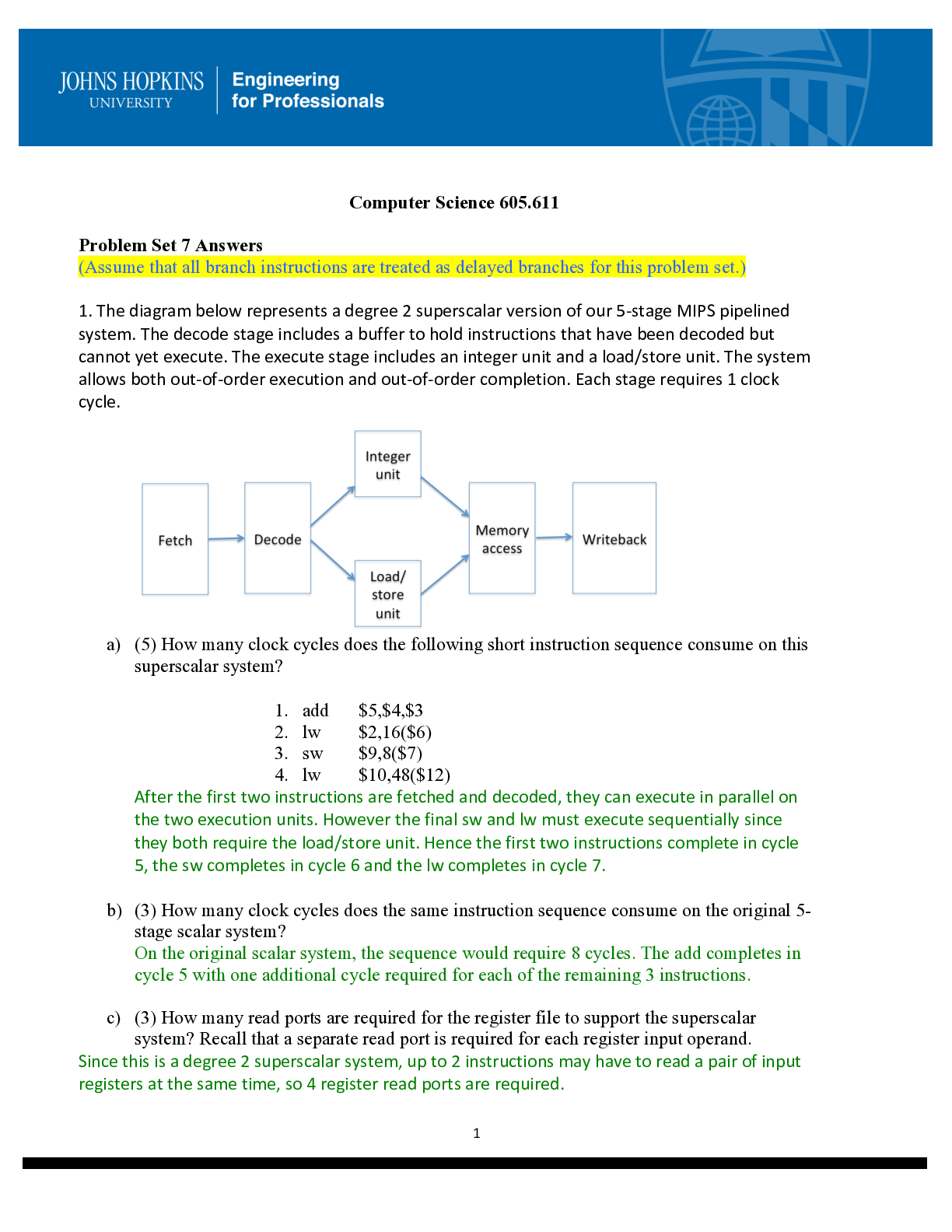
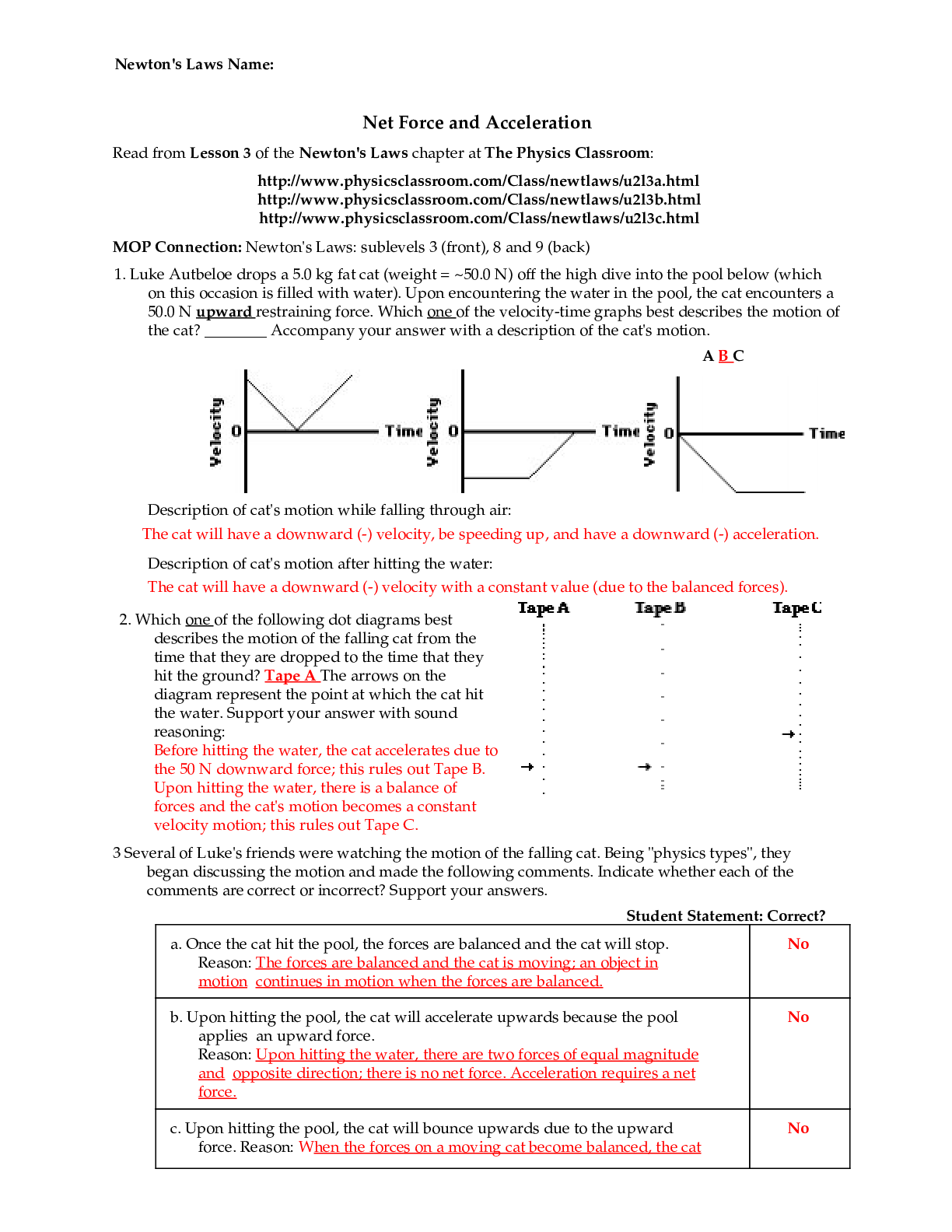
Gas Solubility in Aqueous Solution. At 303 K the concentration of CO2 in water is 0.90 x 10-4 kg CO2/kg water. Using the Henry’s law constant from Appendix A.3, what partial pressure of CO2 must be... kept in the ags to keep the CO2 from vaporizing from the aqueous solution? Given: T = 303 K xA= 0.9 x 10-4 kg CO2 /kg H2O Required: PA of CO2 Solution: From A.3-18 for Henry’s law constant (Geankoplis p. 884) H = 0.186 x 104 atm/mol frac. PA= HxA 4 -4 2 2 A 2 2 kgCO 18 kgmolH O P = 0.186 x 10 atm x 0.9 x 10 0.06848 atm kgH O 44 kgmol CO x 5 A 1.01325 x 10 P = 0.06848 atm x = 1 atm 6.939 x 10 Pa 3 10.3.1 Phase Rule for a Gas-Liquid System. For the systen SO2-air-water, then total pressure is set at 1 atm abs and the partial pressure of SO2 in the vapor is set at 0.20 atm. Calculate the number of degrees of freedom, F. What variables are unspecified that can be arbitrarily set? GIVEN: SO2 – air – H2O system PAT = 1 atm PA of SO2 = 0.2 atm REQUIRED: Degrees of freedom, F Variables that can be set SOLUTION: F = C – P + 2 F = 3 – 2 + 2 F = 3 Variables that can be set: 1. total pressure 2. temperature 3. mole fraction composition xAof SO2 10.3.2 Equilibrium Swtage Contact for Gas-Liquid System. A gas mixture at 2.026 x 105 Pa total pressure containing air and SO2 is contacted in a single-stage equilibrium mixer with pure water at 293 K. The partial pressure of SO2 in the original gas is 1.52x 104 Pa. The inlet gas contains 5.70 total kg mol and the inlet water 2.20 total kg mol. The exit gas and liquid leaving are in equilibrium. Calculate the amounts and compositions of the outlet phases. Use equilibrium data from Fig.10.2-1. GIVEN: Use equilibrium data in Fig. 10.2-1 PT = 2.026 x 105 Pa = T = 293 K PA of SO2 = 1.52 x 104 Pa = .15 atm Inlet gas = 5.70 kg mol Inlet H2O = 2.20 total kgmol REQUIRED XA1, yA1, L1 V1 SOLUTION: xAo = 0 amount of entering acetone = yAN+1vAN+1 = 0.01(30) = 0.30 = 29.7 kgmol/air h acetone leaving in Vi = 0.10(0.30) = 0.30 kgmol/h acetone leaving in Ln = 0.9 (0.30) = 0.27 kgmol/h V1 = 29.7 + 0.03 = 29.73 kgmolH2O + acetone/hr A1 0.030 y = =0.00101 29.73 Ln = 108 + 0.27 = 108.27 kgmol H2O + acetone/hr AN 0.27 X = 0.002493 108.27 [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 130 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 06, 2022
Number of pages
130
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 06, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
93











.png)



.png)

.png)




.png)
.png)

.png)




.png)
.png)

