Questions and Answers > University of Minnesota - GCD 4171 ExamII-Key.
Document Content and Description Below
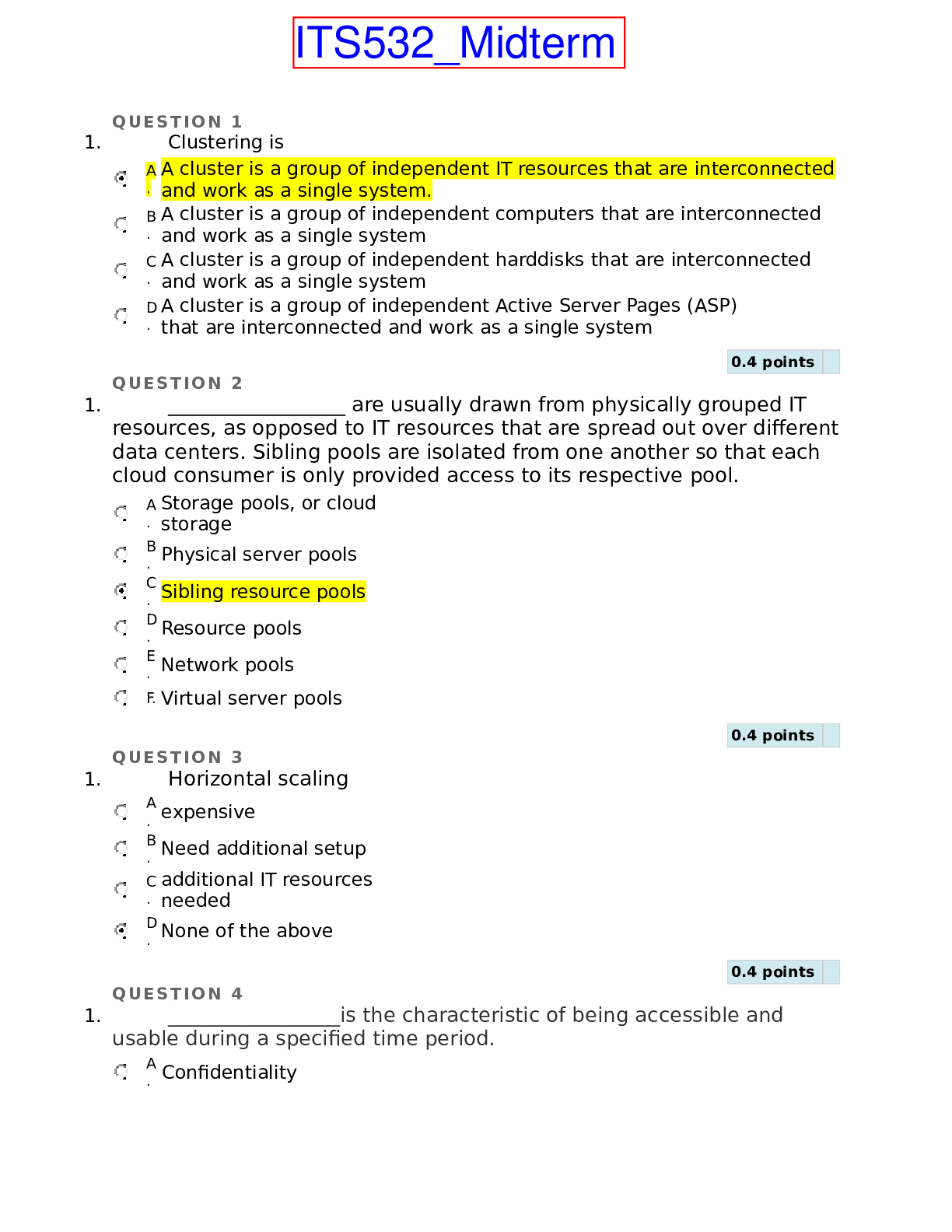
University of Minnesota - GCD 4171 ExamII-Key. 1 GCD 4171 Spring 2020 Exam II – Due by online submission on or before Monday Apr. 6 75 points total NAME: _____Key_________________________... ____________________ ID # __________________________________________________ (The exam has 8 pages [facepage plus 7] and contains 15 questions.) 2 1. (7 points). In CRISPR-Cas-mediated genome editing, two endogenous cellular DNA repair pathways can be used to repair the double-stranded break produced by the Cas9 nuclease. 1A. (2 points). Name these two repair pathways, and identify which is more likely to produce indels (insertions or deletions) and which is more amenable to creating desired single nucleotide substitutions. 1B. (3 points). List the three molecular tools that must be introduced into cells in order to achieve this CRISPR-Cas-mediated single nucleotide change (i.e. correction of a missense mutation). 1) 1C. (2 points). List two alterations that you would need to engineer within a modified version of Cas9 protein in order to deploy CRISPR-Cas tools to achieve targeted gene activation in cells rather than targeted DNA sequence editing. 2. (2 points). Based on your knowledge of the Notch signaling pathway, propose a way of altering pathway component(s) to engineer a cell population where Notch signaling is always active (that is, constitutively ON) and briefly explain the basis for how this would work. 3. (3 points). In the Ohlstein and Spradling 2006 paper on the Drosophila intestinal lineage, a portion of Figure 2 is used to deduce that the number of stem cell divisions per day is approximately one and that differentiated intestinal cells turn over in about 1 week. With reference to this portion of Figure 2, 3 briefly explain how the analysis of marked clones allowed the investigators to deduce that the fully differentiated cells in the fly intestinal epithelium live for about a week in vivo. 4. (5 points). Cancer stem cells have been identified for several types of cancer including leukemias, breast cancer, and intestinal (colon) cancer. 4A. (2 points). List the main steps in a key experiment commonly used to address if a particular tumor type contains cancer stem cells. 4B. (3 points). Find and cite a paper from the primary literature that uses this type of assay to identify a cancer stem cell population from a cancer type aside from the types mentioned above (i.e. cite an example that does not involve cancer of the blood, breast, or intestine). Cite the paper below, using any standard reference format, and state the type of cancer the work addresses. 5. (4 points). On slide 31 of lecture 27 on Planaria, the work of Zeng et al. 2018 (Cell 173:1593) is cited. This paper uses single-cell mRNA profiling and identifies a cell membrane protein called tetraspanin-1 (TSPAN-1) as a robust marker of the truly pluripotent neoblast (cNeoblast) population. 4 As part of the regenerative response, cNeoblasts need to migrate into a wounded region. If TSPAN-1 is required for this neoblast migration, then it might be essential for regenerative capacity. Describe the steps in an experiment you could perform to determine if TSPAN-1 is necessary for Planarian regenerative capacity. 6. (4 points). Stem cell niches. 6A. (2 points). Identify a cell type (aside from stem cells) that resides in any stem cell niche and briefly describe how it helps control stem cell maintenance in that niche. 6B. (2 points). Identify a non-cellular component of any stem cell niche and state the role it plays within that niche. 5 7. (11 points). Pioneer transcription factors. 7A. (2 points). Define “pioneer transcription factor” and describe the molecular property that distinguishes a pioneer factor from most other transcription factors. 7B. (2 points). Explain why a pioneer transcription could play an especially important role in helping to drive cell reprogramming that aims to convert a fully differentiated cell type. 7C. (4 points). One might expect at least one of the four "Yamanaka factors" used in iPS reprogramming to have pioneer transcription factor properties. Search the literature for evidence that any of the four Yamanaka factors (Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, c-Myc) might have pioneer activity. Report what you find below: i) Identify one of these four factors with pioneer activity: ii) Cite a single paper you found which demonstrated this activity:. iii) State a key molecular property of this factor which was experimentally tested in your paper: 6 iv) Name the assay or type of assay used in the paper to test for this property: 7D. (3 points). Search the literature to identify another pioneer transcription factor implicated in any biological or biomedical process, but not discussed in course lectures so far. Cite the name of the pioneer transcription factor you found, the paper that describes it, and state in a single sentence what biological or biomedical process your pioneer transcription is implicated in. i) name of pioneer TF you found: ii) paper that describes it: iii) process the factor is implicated in: 8. Cell lineage tracing. (7 points). Below are diagrams of the two main constructs used to lineage-trace crypt base columnar (CBC) cells in the mouse, revealing them to be intestinal stem cells. A) (2 points). Identify which element in these constructs is responsible for controlling activation of the lineage-tracing mark in space. In other words, which element ensures that the system is activated specifically in crypt base columnar cells? B) (3 points). Identify which element in these constructs allows cell labeling to be induced at a chosen time? In your answer, describe how activity of a key component is switched from off to on, including the molecular basis of this switch. C) (2 points). When this system is used to perform lineage-tracing, briefly explain why all progeny of labeled CBC cells also express the lineage mark? 9. (4 points). Three cell types that are envisioned as potentially providing clinical benefit in patients with spinal cord injury are: a) mesenchymal stem cells, b) ES cell-derived oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs), and c) iPS cell-derived neural stem cells. Choose one of these cell types and describe: 1) a commonly envisioned mechanism by which that cell type could provide clinical improvement and 2) an obstacle or concern associated with applying your chosen cell type in a therapeutic strategy for spinal cord injury. Chosen cell type 1) Envisioned main mechanism of action in providing improvement: 2) Obstacle/concern with use of that cell type: Chosen cell type: 8 1) Envisioned main mechanism of action in providing improvement: 2) Obstacle/concern with use of that cell type: Chosen cell type: 1) Envisioned main mechanism of action in providing improvement: 2) Obstacle/concern with use of that cell type: 10. (6 points). Potential strategies for treating neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s disease envision differentiating pluripotent cells into neurons in vitro and then achieving their functional integration into the brain. Stepwise progress towards this goal can be assessed pre-clinically in the mouse system by demonstrating achievement of particular benchmarks. For each of the following steps or benchmarks, briefly describe an experimental approach that could be used to assess its achievement. i) Differentiation of pluripotent cells into the desired neuronal subtype that produces dopamine Experimental approach: ii) Engraftment of ES cell-derived dopaminergic neurons into brain tissue in a mouse model 9 Experimental approach: iii) Functional improvement after engraftment of ES cell-derived dopaminergic neurons Experimental approach: 11. Fill in the blanks (2 points each): A. Engineering a three-dimensional organ in a dish requires two major components: a source of the cell type(s) that contribute to the organ in question, and __ B. When a primary tumor cell of an epithelial tissue initiates the process of metastasis, its altered properties often include an increase in __ and a decrease in __cell C. The formation of a after spinal cord injury has the benefit of sealing the wound site and limiting the extent of immune cell infiltration and inflammation. However, this structure poses challenges to functional recovery since it also 11. Fill in the blanks, continued. (2 points each): D. Progress on constructing artificial human tissues for use in transplants differs widely depending on the 10 particular type of tissue or organ. A human tissue or organ for which artificial replacement products have been commercially available for many years is _______. E. Extravasation is the process used by metastatic cancer cells to ________. 12-15. Multiple choice questions, 3 points each. (Place an “X” to identify one best answer). 12. A key goal in regenerative medicine has been to develop therapies to replace β-cells that are lost in patients with Type 1 diabetes. In efforts towards this goal, Pagliuca et al. (2014) described methods to produce fully functional β-cells from pluripotent cells in vitro. An alternative approach to produce ß-cells that has been investigated in preclinical experiments, but not yet tried in a clinical context, is: ____ a. encapsulation of pancreatic progenitor cells, followed by reprogramming back to pluripotency. ____ b. islet transplantation, as in the Edmonton protocol. ___ c. transdifferentiation of pancreatic digestive enzyme-secreting exocrine cells directly into ß-cells. ____ d. transdifferentiation of endocrine cells from the thyroid directly into insulin-secreting ß-cells. ____ e. to mobilize them from bone marrow via cytokine treatment. ____ f. none of the above. 13. When a Drosophila germline stem cell in the testis divides, a frequent outcome is that one daughter remains a stem cell and the other starts to differentiate. A cellular factor or property thought to play a role in this decision to self-renew versus differentiate is: ____ a. signaling from nearby clonogenic neoblasts. ____ b. signaling from nearby mesenchymal stem cells. ____ c. activation of cell cycle control factors by FLP-mediated recombination. ____ d. maturation of nearby oocytes that have escaped the influence of the distal tip cell. ___ e. orientation of the mitotic spindle during cell division. ____ f. none of the above. 11 Multiple choice questions, continued. (Place an “X” to identify one best answer). 14. Which of the following is FALSE about cancer stem cells (CSCs)? ____ a. Preferred sites of secondary tumor formation during metastasis may be influenced by adhesion between migrating CSCs and target tissues. ____ b. Secondary tumor formation during metastasis may be influenced by cell signaling that promotes a supportive niche for newly arrived CSCs. _ c. The cancer stem cell hypothesis envisions that all cells in a tumor are equally potent at driving further tumorigenesis. ____ d. An intestinal CSC can be derived from a resident crypt base columnar cell by a mutation that activates the Wnt signaling pathway. ____ e. CSCs from primary mammary tumors in mice can be enriched by cell sorting based upon defined cell surface proteins. ____ f. None of the above are false. 15. Which of the following is FALSE concerning macular degeneration and strategies currently being tested for use in potential treatments for this disease? ____ a. Embryonic stem cell-derived RPEs (retinal pigment epithelial cells) are being tested for impact after delivery to the retina as either cell suspensions or as grafted cell monolayers. ___ b. The vision loss in macular degeneration is mainly due to inability to propagate electrical impulses generated in the RPEs to the optic nerve. ____ c. Macular degeneration is the disease with the largest number of clinical trials so far that test derivatives of pluripotent stem cells. ____ d. Improved visual acuity has been reported for some patients treated with RPEs derived from embryonic stem cells. ____ e. The wet form of macular degeneration occurs when blood vessels penetrate the RPE layer and leak blood or fluid into the diseased region of the retina. ____ f. None of the above are false. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 11 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 27, 2021
Number of pages
11
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 27, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
109
















.png)


.png)