*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Primary Care: Art and Science of Advanced Practice Nursing - An Interprofessional Approach 5th editi (All)
Primary Care: Art and Science of Advanced Practice Nursing - An Interprofessional Approach 5th edition Dunphy Test Bank | Every single chapter complete solutions|A+ Guide.
Document Content and Description Below
Primary Care: Art and Science of Advanced Practice Nursing - An Interprofessional Approach 5th edition Dunphy Test Bank Chapter 1. Primary Care in the Twenty-First Century: A Circle of Caring ... 1. A nurse has conducted a literature review in an effort to identify the effect of handwashing onthe incidence of nosocomial (hospital-acquired) infections in acute care settings. An article presented findings at a level of significance of <0.01. This indicatesthat A) the control group and the experimental group were more than 99%similar. B) the findings of the study have less than 1% chance of being attributable tochance. C) the effects of the intervention were nearlyzero. D) the clinical significance of the findings was less than1:100. 2. A nurse has read a qualitative research study in order to understand the lived experience ofparents who have a neonatal loss. Which of the following questions should the nurse prioritize when appraising the results of thisstudy? A) How well did the authors capture the personal experiences of theseparents? B) How well did the authors control for confounding variables that may have affected thefindings? C) Did the authors use statistical measures that were appropriate to the phenomenon inquestion? D) Were the instruments that the researchers used statistically valid andreliable? 3. A nurse has expressed skepticism to a colleague about the value of nursing research, claimingthat nursing research has little relevance to practice. How can the nurses colleague best defend the importance of nursingresearch? A) The existence of nursing research means that nurses are now able to access federal grant money, something that didnt use to be thecase. B) Nursing research has allowed the development of masters and doctoral programs and hasgreatly increased the credibility of theprofession. C) The growth of nursing research has caused nursing to be viewed as a true profession, rather than simply as a trade or askill. D) The application of nursing research has the potential to improve nursing practice andpatient outcomes. 4. Tracy is a nurse with a baccalaureate degree who works in the labor and delivery unit of abusy urban hospital. She has noticed that many new mothers abandon breast-feeding their babies when they experience early challenges and wonders what could be done to encourage more women to continue breast-feeding. What role is Tracy most likely to play in a research project that tests an intervention aimed at promotingbreast-feeding? A) Applying for grant funding for the researchproject B) Posing the clinical problem to one or more nursingresearchers C) Planning the methodology of the researchproject D) Carrying out the intervention and submitting the results for publication . 5. A patient signed the informed consent form for a drug trial that was explained to patient by a research assistant. Later, the patient admitted to his nurse that he did not understand the research assistants explanation or his own role in the study. How should this patients nurse respond to this revelation? A) Explain the research process to the patient in greaterdetail. B) Describe the details of a randomized controlled trial for thepatient. C) Inform the research assistant that the patients consent is likelyinvalid. D) Explain to the patient that his written consent is now legallybinding. 6. A nurse leader is attempting to increase the awareness of evidence-based practice (EBP) among the nurses on a unit. A nurse who is implementing EBP integrates which of the following? (Select all thatapply.) A) Interdisciplinaryconsensus B) Nursingtradition C) Researchstudies D) Patient preferences andvalues E) Clinical expertise 7. Mrs. Mayes is a 73-year-old woman who has a diabetic foot ulcer that has been extremely slow to heal and which now poses a threat of osteomyelitis. The wound care nurse who has been working with Mrs. Mayes applies evidence-based practice (EBP) whenever possible and has proposed the use of maggot therapy to debride necrotic tissue. Mrs. Mayes, however, finds the suggestion repugnant and adamantly opposes this treatment despite the sizable body of evidence supporting it. How should the nurse reconcile Mrs. Mayes views with the principles ofEBP? A) The nurse should explain that reliable and valid research evidence overrides the patientsopinion. B) The nurse should explain the evidence to the patient in greaterdetail. C) The nurse should integrate the patients preferences into the plan ofcare. D) The nurse should involve the patients family members in the decision-makingprocess. 8. The administrators of a long-term care facility are considered the use of specialized, pressure- reducing mattresses in order to reduce the incidence of pressure ulcers among residents. They have sought input from the nurses on the unit, all of whom are aware of the need to implement the principles of evidence-based practice (EBP) in this decision. Which of the following evidence sources should the nursesprioritize? A) A qualitative study that explores the experience of living with a pressureulcer B) A case study that describes the measures that nurses on a geriatric unit took to reduce pressure ulcers amongpatients C) Testimonials from experienced clinicians about the effectiveness of the mattress inquestion D) A randomized controlled trial that compared the pressure-reducing mattress with standard mattresses 9. Hospital administrators are applying the principles of evidence-based practice (EBP) in their attempt to ascertain the most efficient and effective way to communicate between nurses who are on different units, a project that will consider many types of evidence. Which of the following information sources should the administratorsprioritize? A) A systematic review about communication in nursingcontexts B) Nurses ideas about communicationmethods C) The results of a chartreview D) The hospitals accreditation status . 10. A nurse has resolved to apply the evidence-based practice (EBP) process to the way that admission assessments are conducted and documented on a unit. How should the nurse begin the process of establishingEBP? A) Gather evidence showing the shortcomings of currentpractices B) Formulate a clear and concise question to beaddressed C) Elicit support from the nurses who are most often responsible foradmissions D) Search the literature for evidence that is potentially relevant to the practice need 11. Which of the following questions best exemplifies the PICOT format for asking evidence-based questions? A) What affect does parents alcohol use have on the alcohol use of their teenagechildren? B) Among postsurgical patients, what role does meditation rather than benzodiazepines haveon anxiety levels during the 48 hours followingsurgery? C) Among high school students, what is the effectiveness of a sexual health campaign undertaken during the first 4 weeks of the fall semester as measured by incidence of new sexually transmitted infections? D) In children aged 68, is the effectiveness of a descriptive pain scale superior to a numeric rating scale in the emergency roomcontext? 12. A nurse has made plans to implement the University of North Carolina (UNC) model of 5 As during the process of applying evidence-based practice (EBP) to a practice problem. What is the final step that the nurse will take in applying thismodel? A) Analyze the results of the EBPprocess B) Advocate for others to embrace the identifiedchange C) Adopt the changes identified in the reviewprocess D) Assess the outcomes of the new practice 13. A nurse has been asked to make a presentation to a group of high school students on the subject of sexual health. However, the nurse does not have a background in this practice area and requires rapid access to evidence-based guidelines. Which of the following strategies is most likely to provide the nurse with valid and reliable evidence in a time-efficientmanner? A) Search the Cochrane Library of SystematicReviews B) Google search terms such as sexual health teens and sexualeducation C) Search Medline using PubMed and order relevantarticles D) Scan the most recent issues of nursing journals that address this area ofpractice 14. The nurses at a university hospital have been informed that a computerized record system will be implemented over the next 12 months. The nurses should be aware that such as system presents particular challenges in the areaof A) vulnerability to errors in charting and the inability to makechanges. B) patient privacy and confidentiality ofrecords. C) enforcing compliance with the system on the part ofnurses. D) ensuring compatibility with different computer operatingsystems. 15. A nurse is nervous about the impeding introduction of computerized nursing care records atthe hospital because he does not consider himself to be technologically adept. How should this nurse best respond to thissituation? A) Take courses in advanced practice nursing to build hisknowledge. B) Explore employment opportunities in settings that use written documentationsystems. C) Advocate for a delay in the introduction of the proposedsystem. D) Seek out opportunities to learn the relevant knowledge and practice the necessaryskills. Chapter 2. Caring and the Advanced Practice Nurse Multiple Choice 1. A goal of community nursing is to provide primary prevention from disease. Which ofthe following nursing actions reflect thisgoal? A) A nurse creates a pamphlet discussing heart-healthy foods and distributes it in the neighborhood communitycenter. B) A nurse starts an intravenous line on a dehydrated baby who has been brought to theemergency department. C) A nurse performs range-of-motion exercises for a patient intraction. D) A nurse repositions an elderly patient confined to a wheelchair to avoid the formation of pressure ulcers. 2. A nurse decides to pursue a career in community-based nursing. Which of the following statements represents the environment in which the nurse will beworking? A) Community-based nursing is limited to work in public clinics, schools, andindustry. B) The key to community-based settings is that the nurse is incharge. C) The nurse serves as an educator, guide, and resource person and determines the action takenby the client. D) Care in the community iscost-effective. 3. The movement of a client from acute care to a long-term nursing care facility involves planningto provide continuity of care. What is the term for this type ofplanning? A) Dischargeplanning B) Comprehensiveplanning C) Ongoing planning D) Transition planning 4. A nurse is called into work to perform triage in the aftermath of an earthquake. Which of the following are the expected responsibilities of thisnurse? A) Set up and monitor IVlines. B) Prepare the emergency room for multiplevictims. C) Screen victims to prioritizetreatment. D) Check available blood products and assist withtransfusions. 5. A client asks a nurse for help in obtaining an alternative healthcare provider. Which of the following is an accurate fact regarding alternative care that the nurse should share with thisclient? A) Most alternative healthcare practitioners do not have education-based credentials to practice their medicine. B) Alternative providers are not usually included in the federal HIPAA legislation that mandates confidentiality in conventional healthcaresettings. C) The cost of alternative therapy is never covered by insurance carriers or healthcareplans. D) It is easy to find accurate safety and efficacy data for alternative medicine on theInternet. 6. There is an increasing trend for nursing care to move from the hospital setting into the community. Nurses who are to provide excellent care in a community setting should prioritize which of thefollowing? A) Integrating culture and family into the planning and delivery ofcare B) Becoming more assertive in client education and the planning of clientcare C) Encouraging clients to limit their interactions withphysicians D) Teaching clients to replace biomedical interventions with complementary therapies 7. In spite of the important role that hospitals play in American healthcare, there is growing importance of community-based healthcare and community-based nursing. Which of the following statements best conveys a central aspect of the philosophy of communitycare? A) The client is in charge of his or her health and healthcare in thecommunity. B) Nurses maximize their scope of practice in noninstitutionalsettings. C) Community settings allow for the greatest number and variety of treatmentoptions. D) The nurse becomes the key member of the healthcare team in a communitysetting. 8. Mr. Hammond is a 70-year-old man with a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes who developed a diabetic foot ulcer earlier this year. He has recently been discharged from the hospital and now requires regular wound care. Karen is a community health nurse who provides wound care for Mr.Hammond twice weekly. Which of Karens actions is most likely to empower Mr.Hammond? A) Encourage Mr. Hammond to acknowledge his contribution to the development of hiswound. B) Provide information to Mr. Hammond that matches his expressedneeds. C) Encourage Mr. Hammond to involve members of his family in hiscare. D) Delegate wound care to Mr. Hammond and reduce the frequency of hervisits. 9. An elderly female client who resides in the community tends to defer decisions regarding her care to her eldest son. How should the community health nurse respond to the clients reluctance to make independentdecisions? A) Discuss this observation with the client and her son in an open manner and explorealternatives. B) Organize care so that it takes place at times when the son is not present in thehome. C) Accommodate this aspect of the clients family dynamics when planning and carrying outcare. D) Teach the client assertiveness skills that she can apply in her interactions with herson. 10. A client with a long-standing diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) has been enrolled in a disease management program. Which of the following activities will beprioritized in thisprogram? A) Providing comprehensive and evidence-based care of the clientsCOPD B) Creating collaborative relationships between the client and the careteam C) Ensuring that the client qualifies for Medicare andMedicaid D) Liaising between the client and his health maintenance organization (HMO) 11. One of the expressed goals of Healthy People 2020 is to achieve health equity and eliminate disparities. What health indicator can most accurately gauge whether this goal is beingachieved? A) Environmentalquality B) Injury andviolence C) Mentalhealth D) Access to healthcareservices 12. Nurses have the potential to positively impact the health of communities. Which of thefollowing actions is most likely to improve the health of acommunity? A) Publicizing the consequences of unhealthylifestyles B) Advocating politically for laws and policies that foster communityhealth C) Ensuring that nurses are practicing to the full extent of their scope ofpractice D) Providing nursing care to individuals who are not patients or clients 13. A nurse who provides care in an acute medical unit is aware of the importance of thorough discharge planning. The discharge planning process shouldbegin A) once the patient has stabilized and is assured of positiveoutcomes. B) as soon as possible after the patient isadmitted. C) once the patient has received a discharge order from his or her primary careprovider. D) 48 to 72 hours before the projected date ofdischarge. 14. A hospital patient has discussed with the nurse her use of visualization, biofeedback, and relaxation exercises in managing the chronic pain that results from her fibromyalgia. The nurse should recognize this patients use of what category of complementary/alternative medicine(CAM)? A) Biologically-basedpractices B) Manipulativepractices C) Traditional indigenousmedicine D) Mind-body 15. A hospital patient who suffered a spinal cord injury has expressed an interest in exploring complementary/alternative therapies. The nurse should encourage the patient to begin this processby doing which of the followingactivities? A) Asking practitioners of different therapies to provide lists of satisfiedclients B) Asking the patients primary care provider for permission to explore nonbiomedicaltreatments C) Finding reliable evidence regarding the safety and effectiveness oftherapies D) Determining whether the patients health insurance would cover the cost of alternative/complementarytherapies Chapter 3. Health Promotion Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is a primary prevention measure for a 76-year-old man newly diagnosed with a testosteronedeficiency? a. Calciumsupplementation b. Testicularself-examination c. Bone densitytest d. Digital rectalexamination 2. Which of the following is an example of secondary prevention in a 50-year-oldwoman? a. Yearlymammogram b. Low animal fatdiet c. Use of seatbelt d. Daily application ofsunscreen 3. Which of the following is an example of tertiary prevention in a patient with chronic renalfailure? a. Fluidrestriction b. Hemodialysis 4 days aweek c. High-proteindiet d. Maintenance of blood pressure at120/80 4. Immunizations are an example of which type ofprevention? a. Primary b. Secondary c. Tertiary True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Prevalence is the number of new cases of a particulardisease. 2. The number of cases of a particular disease for the past 5 years is an example of the incidencerate. 3. “There are 1,185,000 cases of HIV/AIDS in the United States” is an example of the morbidityrate. 4. Endemic is the term used when the presence of an event isconstant. 5. The “bird” flu of 2005 to 2006 is considered a sporadicoutbreak. 6. A pandemic affects many communities in a short period oftime. Chapter 4. The Art of Diagnosis and Treatment MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. An 85-year-old man has come in for a physical examination, and the nurse notices that he uses a cane. When documenting general appearance, the nurse should document this information under the section thatcovers: a. Posture. b. Mobility. c. Mood andaffect. d. Physicaldeformity. Use of assistive devices would be documented under the mobility section. The other responses are all other categories of the general appearance section of the health history. 2. The nurse is performing a vision examination. Which of these charts is most widely usedfor visionexaminations? a. Snellen b. Shetllen c. Smoollen d. Schwellon The Snellen eye chart is most widely used for vision examinations. The other options are not tests for vision examinations. 3. After the health history has been obtained and before beginning the physical examination,the nurse should first ask the patientto: a. Empty thebladder. b. Completelydisrobe. c. Lie on the examinationtable. d. Walk around theroom. Before beginning the examination, the nurse should ask the person to empty the bladder (save the specimen if needed), disrobe except for underpants, put on a gown, and sit with the legs dangling off side of the bed or table. 4. During a complete health assessment, how would the nurse test the patientshearing? a. Observing how the patient participates in normalconversation b. Using the whispered voicetest c. Using the Weber and Rinnetests d. Testing with anaudiometer During the complete health assessment, the nurse should test hearing with the whispered voice test. The other options are not correct. 5. A patient states, Whenever I open my mouth real wide, I feel this popping sensation in front ofmy ears. To further examine this, the nursewould: a. Place the stethoscope over the temporomandibular joint, and listen forbruits. b. Place the hands over his ears, and ask him to open his mouth reallywide. c. Place one hand on his forehead and the other on his jaw, and ask him to try to open hismouth. d. Place a finger on his temporomandibular joint, and ask him to open and close his mouth. The nurse should palpate the temporomandibular joint by placing his or her fingers over the joint as the person opens and closes the mouth. 6. The nurse has just completed an examination of a patients extraocular muscles. When documenting the findings, the nurse should document the assessment of which cranialnerves? a. II, III, andVI b. II, IV, andV c. III, IV, andV d. III, IV, andVI Extraocular muscles are innervated by cranial nerves III, IV, and VI. 7. A patients uvula raises midline when she says ahh, and she has a positive gag reflex. The nurse has just tested which cranialnerves? a. IX andX b. IX andXII c. X andXII d. XI andXII Cranial nerves IX and X are being tested by having the patient say ahh, noting the mobility of the uvula, and when assessing the patients gag reflex. 8. During an examination, the nurse notices that a patient is unable to stick out his tongue.Which cranial nerve is involved with the successful performance of thisaction? a. I b. V c. XI d. XII Cranial nerve XII enables the person to stick out his or her tongue. 9. A patient is unable to shrug her shoulders against the nurses resistant hands. What cranial nerve is involved with successful shouldershrugging? a. VII b. IX c. XI d. XII Cranial nerve XI enables the patient to shrug her shoulders against resistance. 10. During an examination, a patient has just successfully completed the finger-to-nose and the rapid-alternating-movements tests and is able to run each heel down the opposite shin. The nurse will conclude thatthepatients function is intact. a. Occipital b. Cerebral c. Temporal d. Cerebellar The nurse should test cerebellar function of the upper extremities by using the finger-to-nose test or rapid-alternating-movements test. The nurse should test cerebellar function of the lower extremities by asking the person to run each heel down the opposite shin. 11. When the nurse performs the confrontation test, the nurse hasassessed: a. Extraocular eye muscles(EOMs). b. Pupils (pupils equal, round, reactive to light, and accommodation[PERRLA]). c. Near vision. d. Visualfields. The confrontation test assesses visual fields. The other options are not tested with the confrontation test. 12. Which statement is true regarding the complete physicalassessment? a. The male genitalia should be examined in the supineposition. b. The patient should be in the sitting position for examination of the head andneck. c. The vital signs, height, and weight should be obtained at the end of the examination. d. To promote consistency between patients, the examiner should not vary the order of theassessment. The head and neck should be examined in the sitting position to best palpate the thyroid and lymph nodes. The male patient should stand during an examination of the genitalia. Vital signs are measured early in the assessment. The sequence of the assessment may need to vary according to different patient situations. 13. Which of these is included in an assessment of generalappearance? a. Height b. Weight c. Skin color d. Vital signs General appearance includes items such as level of consciousness, skin color, nutritional status, posture, mobility, facial expression, mood and affect, speech, hearing, and personal hygiene. Height, weight, and vital signs are considered measurements. 14. The nurse should wear gloves for which of theseexaminations? a. Measuring vitalsigns b. Palpation of thesinuses c. Palpation of the mouth andtongue d. Inspection of the eye with anophthalmoscope Gloves should be worn when the examiner is exposed to the patients body fluids. 15. The nurse should use which location for eliciting deep tendonreflexes? a. Achilles b. Femoral c. Scapular d. Abdominal Deep tendon reflexes are elicited in the biceps, triceps, brachioradialis, patella, and Achilles heel. 16. During an inspection of a patients face, the nurse notices that the facial features aresymmetric. This finding indicates which cranial nerve isintact? a. VII b. IX c. XI d. XII 17. During inspection of the posterior chest, the nurse should assessfor: a. Symmetricexpansion. b. Symmetry of shoulders andmuscles. c. Tactilefremitus. d. Diaphragmaticexcursion. 18. During an examination, the patient tells the nurse that she sometimes feels as if objects are spinning around her. The nurse would document that she occasionallyexperiences: a. Vertigo. b. Tinnitus. c. Syncope. d. Dizziness. 19. A patient tells the nurse, Sometimes I wake up at night and I have real trouble breathing. Ihave to sit up in bed to get a good breath. When documenting this information, the nurse wouldnote: a. Orthopnea. b. Acuteemphysema. c. Paroxysmal nocturnaldyspnea. d. Acute shortness of breathepisode. 20. During the examination of a patient, the nurse notices that the patient has several small, flat macules on the posterior portion of her thorax. These macules are less than 1 cm wide.Another name for these macules is: a. Warts. b. Bullae. c. Freckles. d. Papules. 21. During an examination, the nurse notices that a patients legs turn white when they are raised above the patients head. The nurse shouldsuspect: a. Lymphedema. b. Raynauddisease. c. Chronic arterialinsufficiency. d. Chronic venousinsufficiency. 22. The nurse documents that a patient has coarse, thickened skin and brown discoloration overthe lower legs. Pulses are present. This finding is probably the resultof: a. Lymphedema. b. Raynauddisease. c. Chronic arterialinsufficiency. d. Chronic venousinsufficiency. 23. The nurse notices that a patient has ulcerations on the tips of the toes and on the lateral aspectof the ankles. This findingindicates: a. Lymphedema. b. Raynauddisease. c. Arterialinsufficiency. d. Venousinsufficiency. 24. The nurse has just recorded a positive iliopsoas test on a patient who has abdominal pain. This test is used to confirma(n): a. Inflamedliver. b. Perforatedspleen. c. Perforatedappendix. d. Enlargedgallbladder. . 25. The nurse will measure a patients near vision with whichtool? a. Snellen eye chart withletters b. Snellen Echart c. Jaegercard d. Ophthalmoscope The Jaeger card is used to measure near vision 26. If the nurse records the results to the Hirschberg test, the nursehas: a. Tested the patellarreflex. b. Assessed forappendicitis. c. Tested the corneal lightreflex. d. Assessed forthrombophlebitis. 27. During the examination of a patients mouth, the nurse observes a nodular bony ridge down the middle of the hard palate. The nurse would chart this findingas: a. Cheilosis. b. Leukoplakia. c. Ankyloglossia. d. Toruspalatinus. 28. During examination, the nurse finds that a patient is unable to distinguish objects placed in his hand. The nurse woulddocument: a. Stereognosis. b. Astereognosis. c. Graphesthesia. d. Agraphesthesia. 29. After the examination of an infant, the nurse documents opisthotonos. The nurse recognizesthat this finding often occurswith: a. Cerebralpalsy. b. Meningealirritation. c. Lower motor neuronlesion. d. Upper motor neuronlesion. 30. After assessing a female patient, the nurse notices flesh-colored, soft, pointed, moist, papules in a cauliflower-like patch around her introitus. This finding is mostlikely: a. Urethralcaruncle. b. Syphiliticchancre. c. Herpes simplexvirus. d. Humanpapillomavirus. 31. While recording in a patients medical record, the nurse notices that a patients Hematest results are positive. This finding means that thereis(are): a. Crystals in hisurine. b. Parasites in hisstool. c. Occult blood in hisstool. d. Bacteria in hissputum. 32. While examining a 48-year-old patients eyes, the nurse notices that he had to move thehandheld vision screener farther away from his face. The nurse wouldsuspect: a. Myopia. b. Omniopia. c. Hyperopia. d. Presbyopia. Chapter 5. Evidence-Based Care Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following are parts of evidence-basedpractice? a. Clinician b. Patient c. Evidence d. All of theabove 2. Which is the most important question to ask in nursingresearch? a. What findings constituteevidence? b. How will the findings beused? c. Is this a randomized controlledtrial? d. What theory is beingutilized? 3. Nursing research should be utilizedby: a. Nurses at thebedside b. Advanced practicenurses c. Nurseresearchers d. Nurses at all levels ofpractice 4. Applying evidence at the point of carerequires: a. Readily available evidence-basedresources b. Ability to review researchliterature c. Single articles injournals d. Currenttextbooks 5. Practice guidelines are designedto: a. Beinflexible b. Be utilized in everycircumstance c. Provide a reference point for decision making d. Be created by a professional organization to guide the practice of aprofession 6. Which of the following is a crucial element of developing aguideline? a. Creating a physician expertpanel b. Reviewing the literature with ratings of availableevidence c. Conducting an external review of aguideline d. Developing evidence-basedtables 7. Which of the following would be considered the research design for Level Ievidence? a. Single, well-designed randomized clinicaltrial b. Systematic review of randomized clinical trialstudies c. Well-designed controlled trials withoutrandomization d. Systematic reviews of descriptive or qualitativestudies 8. Which of the following would be considered the research design for Level IIevidence? a. Single descriptive or qualitativestudy b. Well-designed case control or cohortstudies c. Single, well-designed, randomized clinicaltrial d. Systematic review of randomized clinical trialstudies 9. Which of the following would be considered the research design for Level IIIevidence? a. Well-designed controlled trials withoutrandomization b. Systematic reviews of descriptive or qualitativestudies c. Systematic review of randomized clinical trialstudies d. Opinion of authorities and expertcommittees 10. Which of the following would be considered the research design for Level IVevidence? a. Single descriptive or qualitativestudy b. Opinion of authorities and expertcommittees c. Systematic review of randomized clinical trialstudies d. Well-designed controlled trials withoutrandomization 11. Which of the following would be considered the research design for Level Vevidence? a. Systematic review of randomized clinical trialstudies b. Well-designed controlled trials withoutrandomization c. Systematic reviews of descriptive or qualitativestudies d. Single descriptive or qualitativestudy 12. Which of the following would be considered the research design for Level VIevidence? a. Systematic reviews of descriptive or qualitativestudies b. Opinion of authorities and expertcommittees c. Well-designed case control or cohortstudies d. Single descriptive or qualitativestudy 13. Which of the following would be considered the research design for Level VIIevidence? a. Well-designed controlled trials withoutrandomization b. Opinion of authorities and expertcommittees c. Well-designed case control or cohortstudies d. Single descriptive or qualitativestudy Chapter 6. Common Neurological Complaints Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which statement about confusion istrue? a. Confusion is a diseaseprocess. b. Confusion is alwaystemporary. c. Age is a reliable predictor ofconfusion. d. Polypharmacy is a major contributor to confusion in olderadults. 2. Sondra’s peripheral vestibular disease causes dizziness and vertigo. Which of the following medications will help to decrease edema in the labyrinth of theear? a. Meclizine b. Diphenhydramine c. Diamox d. Promethazine 3. The hallmark of an absence seizureis: a. No activity atall b. A blankstare c. Urine is usually voidedinvoluntarily d. The attack usually lasts severalminutes 4. How often should drug levels be monitored when a seizure medication has controlled the seizures, and the drug level isadequate? a. Every 3months b. Every 6months c. Annually d. Whenever there is aproblem 5. Which of the following persons fits the classic description of a patient with multiple sclerosis(MS)? a. A teenagemale b. A 65-year-oldmale c. A 25-year-oldfemale d. A 60-year-oldfemale 6. Which of the following is a specific test toMS? a. Magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) b. Computed tomography (CT)scan c. A lumbarpuncture d. There is no specifictest. 7. Which drug for Alzheimer’s disease should be administered beginning at the time ofdiagnosis? a. Cholinesteraseinhibitors b. Anxiolytics c. Antidepressants d. Atypicalantipsychotics 8. Which hematoma occurs along the temporal cranial wall and results from tears in the middle meningealartery? a. Epiduralhematoma b. Subduralhematoma c. Subarachnoidhematoma d. Intraparenchymalhemorrhage 9. Which cranial nerve is affected in a patient with a cerebrovascular accident who has difficulty chewing? a. CNV b. CNVII c. CNIX d. CNX 10. Which statement best describes a carotidbruit? a. It is felt with the middle three fingers over the carotidartery. b. A bruit becomes audible when the lumen is narrowed to 1 mm orless. c. A low-pitched bruit is a medicalemergency. d. The higher the pitch of the bruit, the higher the degree ofstenosis. 11. Which patient is more likely to have a clusterheadache? a. A female in her reproductiveyears b. A 40-year-old African Americanmale c. A 55-year-old female who drinks 10 cups of coffeedaily d. A 45-year-old male awakened atnight 12. Inattention and a sleep-wake cycle disturbance are the hallmark symptomsof? a. Dementia b. Alzheimer’sdisease c. Parkinson’sdisease d. Delirium 13. Which type of meningitis is more benign, self-limiting, and caused primarily by avirus? a. Purulentmeningitis b. Chronicmeningitis c. Asepticmeningitis d. Herpesmeningitis 14. Which is the most sensitive neuroimaging test to evaluate patients withencephalitis? a. MRI b. CT c. Electroencephalogram(EEG) d. An initial lumbarpuncture 15. What is usually the first sign or symptom that a patient would present with that would make you suspect herpeszoster? a. A stabbing pain on one small area of thebody b. A vesicular skin lesion on one side of thebody c. A pain that is worse uponawakening d. A lesion on the exterior earcanal 16. Gabby, aged 22, has Bell’s palsy on the right side of her face. Her mouth is distorted, and she is concerned about permanent paralysis and pain. What do you tellher? a. “Most patients have complete recovery in 3 to 6months.” b. “Unfortunately, you’ll probably have a small amount of residualdamage.” c. “Don’t worry, I’ll take care ofeverything.” d. “You may have a few more episodes over the course of your lifetime but no permanentdamage.” 17. Sam, aged 65, is started on L-dopa for his Parkinson’s disease (PD). He asks why this isnecessary. You tell him: a. “L-dopa isneuroprotective.” b. “The primary goal of therapy is to replace depleted stores ofdopamine.” c. “This is the only drug that can provide symptomaticbenefit.” d. “This is the initial monotherapydrug.” 18. Which of the following signs is seen in a patient with more advancedPD? a. Restingtremor b. Bradykinesia c. Rigidity d. Posturalinstability 19. Which of the following is the most commonly experienced symptom ofmigraine? a. Lightsensitivity b. Pulsatilepain c. Soundsensitivity d. Experiencing anaura 20. Which of the following characteristics differentiates peripheral vertigo from centralvertigo? a. The duration of central vertigo is shorter than that of peripheralvertigo. b. There is an auditory-associated symptom with peripheral vertigo and a visual- associated symptom with centralvertigo. c. Central vertigo is positional, and peripheral vertigo isnot. d. The onset of central vertigo is more sudden than that of peripheralvertigo. 21. Carotid endarterectomy should be considered only for symptomatic patients with greater than what percentage ofstenosis? a. Greater than25% b. Greater than50% c. Greater than75% d. Only for 100%occlusion 22. What antiplatelet agent is most widely used for secondary prevention ofstroke? a. Aspirin b. Ticlopidine c. Clopidogrel d. Aspirin andclopidogrel 23. Which adjunctive diagnostic test should be used in the work-up of a patient with suspected Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease or transient epilepticamnesia? a. MRI b. CT c. Cerebrospinal fluidanalysis d. EEG 24. Which herbal preparation may cause delirium and should be avoided in an elderlypatient? a. Sam-e b. Saint John’sWort c. Melatonin d. SawPalmetto 25. Which of the following activities is part of the functional activitiesquestionnaire? a. Asking the patient to unravel a Rubik’scube b. Determining if the patient can drive on thehighway c. Asking the patient about a news event from the currentweek d. Seeing if the patient can keep his or her homeclean 26. About 90% of all headachesare? a. Tension b. Migraine c. Cluster d. Without pathologicalcause 27. Which statement is true regarding driving and patients with a seizuredisorder? a. Once diagnosed with a seizure disorder, patients must never driveagain. b. After being seizure free for 6 months, patients maydrive. c. Each state has different laws governing driving for individuals with a seizure disorder. d. These persons may drive but neveralone. 28. Julie has relapsing-remitting muscular sclerosis. She has not had a good response tointerferon. Which medication might help given intravenously once a month? a. Glatirameracetate b. Natalizumab c. Fingolimod d. Glucocorticoids 29. The ‘freezing phenomenon’ is a cardinal featureof? a. Parkinson’sdisease b. Alzheimer’sdisease c. ACVA d. Bell’spalsy 30. A ratchet-like rhythmic contraction, especially in the hand, during passive stretching is knownas? a. Spinothalamicdysfunction b. Ratcheting c. Cogwheeling d. Handtremors 31. Clinical features of insidious onset, slow progression, and a lack of other findings to explain the symptoms are fairly diagnostic of whichcondition? a. Guillain-Barrésyndrome b. Parkinson’sdisease c. Alzheimer’sdisease d. Huntington’sdisease 32. Which condition is characterized by the impaired ability to learn new information along with either a cognitive disturbance in language, function, orperception? a. Guillain-Barrésyndrome b. Parkinson’sdisease c. Alzheimer’sdisease d. Delirium 33. A score of 20 to 25 on this test indicates early-stage Alzheimer’sdisease: a. SLUMS b. MoCA c. FAST d. MMSE 34. Intravenous thrombolytic therapy following an ischemic CVA should be given within how many hours of symptomonset? a. 1 hour b. 3 hours c. 6 hours d. 12 hours 35. When administered at the beginning of an attack, oxygen therapy may help this kind ofheadache? a. Tension b. Migraine c. Cluster Chapter 7. Seizure Disorders 1. A client asks the nurse to explain symptoms that would indicate the presence of a brain tumor. Which ofthe following should the nurse respond to this client? (Select all thatapply.) 1. There are no symptoms specific to a braintumor. 2. Dizziness is a commonsymptom. 3. Ringing or buzzing in the ears canoccur. 4. Seizures mayoccur. 5. A headache that gets worse in the afternoon is specific to a braintumor.. 6. A headache is usually experienced by 50% of all people diagnosed with a braintumor. 2. The nurse is instructing a client diagnosed with a brain tumor on symptoms to immediately report toher physician. Which of the following should be included in these instructions? (Select all thatapply.) 1. New onset ofseizures 2. One-sidedweakness 3. Loss ofbalance 4. Problems withvision 5. Inability totalk 6. Loss ofappetite Brain tumor symptoms that require immediate attention include new onset of seizures, slow progressing hemiparesis, gait or balance disturbances, visual problems, hearing loss, and aphasia. Loss of appetite is not a brain tumor symptom. 3.A client is diagnosed with seizures occurring because of hepatic encephalopathy. The nurse realizes that the cause for this clients seizures wouldbe: 1. physiological. 2. iatrogenic. 3. idiopathic. 4. psychokinetic. 4.A client tells the nurse that he sees flashing lights that occur prior to the onset of a seizure. Which of the following phases of a seizure is this client describing to thenurse? 1. Prodromalphase 2. Aural phase 3. Ictalphase 4. Postictalphase 5.A client is experiencing a grand mal seizure. Which of the following should the nurse do during this seizure? 2. Leave the clientalone. 3. Give water to the client to avoiddehydration. 4. Place a finger in the clients mouth to avoid swallowing thetongue. 6.A client is prescribed phenytoin (Dilantin) for a seizure disorder. Which of the following would indicate that the client is adhering to the medicationschedule? 1. The client issleepy. 2. The client is not experiencingseizures. 3. The client no longer hasheadaches. 4. The client is eating morefood. 7. The nurse is unable to insert an intravenous access line into a client who is currentlyexperiencing a seizure. Which of the following routes can the nurse use to provide medication to the client at this time? 1. Oral 2. Intranasal 4. Intramuscular 8. One of the most important things a nurse can teach a client about seizure control isto: 1. take the medication every day as prescribed by thedoctor. 2. eat a balanceddiet. 3. get lots ofexercise. 4. take naps during theday. 9.A client is diagnosed with tonic-clonic seizures. Which are the characteristics of these types of seizures? (Select all thatapply.) 1. Progressing through all of the seizurephases 2. Beginning before age5 3. Lasting 2 to 3minutes 4. Causing injury to theclient 5. Occurring at any time, day ornight Chapter 8. Degenerative Disorders MULTIPLE CHOICE 1.A client is diagnosed with a headache from a secondary cause. The nurse realizes this type of headache can be caused by: 1.a tumor. 2.tension. 3.a migraine. 4.cluster 2.The nurse should instruct a client diagnosed with migraine headaches to be careful not to overdose on acetaminophen (Tylenol). Which drug should the nurse tell the patient to avoid? 1.Aleve 2.Aspirin 3.Ibuprofen 4.Vicodin 3.A client is diagnosed with seizures occurring because of hepatic encephalopathy. The nurse realizes that the cause for this clients seizures would be: 1.physiological. 2.iatrogenic. 3.idiopathic. 4.psychokinetic. 4.A client tells the nurse that he sees flashing lights that occur prior to the onset of a seizure. Which of the following phases of a seizure is this client describing to the nurse? 1.Prodromal phase 2.Aural phase 3.Ictal phase 4.Postictal phase 5.A client is experiencing a grand mal seizure. Which of the following should the nurse do during this seizure? 1.Protect the clients head. 2.Leave the client alone. 3. Give water to the client to avoiddehydration. 4. Place a finger in the clients mouth to avoid swallowing thetongue. 6.A client is prescribed phenytoin (Dilantin) for a seizure disorder. Which of the following would indicate that the client is adhering to the medication schedule? 1. The client issleepy. 2. The client is not experiencing seizures. 3.The client no longer hasheadaches. 4.The client is eating more food. 7.The nurse is unable to insert an intravenous access line into a client who is currently experiencing a seizure. Which of the following routes can the nurse use to provide medication to the client at this time? 1.Oral 2.Intranasal 3.Rectal 4.Intramuscular 8.One of the most important things a nurse can teach a client about seizure control is to: 1.take the medication every day as prescribed by the doctor. 2.eat a balanced diet. 3.get lots of exercise. 4.take naps during the day. 9.The nurse is instructing a client newly diagnosed with multiple sclerosis (MS). To determine the effectiveness of his teaching, the nurse would expect the client to state: 1.It is best for me to be in a cold environment. 2.I should avoid taking a hot bath. 3.I should eat foods low in salt. 4.I should be better in a week. . 10.An adult female in her 30s complains of numbness and tingling in the hands, fatigue, loss of coordination, incontinence, nystagmus, and ataxia. Which of the following health problems do these symptoms suggest to the nurse? 1.Brain tumor 2.Myasthenia gravis 3.Multiple sclerosis 4.Diabetes 11.For a client diagnosed with Parkinsons disease, which of the following might be contraindicated? 1.Performing range-of-motion exercises 2.Drinking bottled water 3.Instituting fall precautions 4.Taking naps 12.A client diagnosed with Parkinsons disease is beginning medication therapy. The nurse realizes that the goal of treatment for Parkinsons disease is to: 1. improvesleep. 2. reduceappetite. 3. control tremor andrigidity. 4. reduce the need for joint replacement surgery. 13.A client presents complaining of abnormal muscle weakness and fatigability. The physician suspects myasthenia gravis. Which drug can be used to test for this disease? 1.pyridostigmine (Mestinon) 2.Neostigmine (Prostigmin) 3.Ambenonium (Mytelase) 4.Edrophonium (Tensilon) . MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1.A client is diagnosed with tonic-clonic seizures. Which are the characteristics of these types of seizures? (Select all that apply.) 1.Progressing through all of the seizure phases 2.Beginning before age 5 3.Lasting 2 to 3 minutes 4.Causing injury to the client 5.Occurring at any time, day or night 6.Being highly variable 2.Which of the following nursing interventions would be appropriate for a client diagnosed with Alzheimers disease? (Select all that apply.) 1.Make changes to the room often to stimulate memory function. 2.Assign simple tasks to be completed by the client. 3.Assist the client with any needs associated with activities of daily living (ADLs). 4.Have personal/familiar items around the client. 5.Do complex games and puzzles to improve memory. 3.A client has been diagnosed with Parkinsons disease. Which of the following will the nurse most likely assess in this client? (Select all that apply.) 1.Tremor 2.Muscle rigidity 3.Akinesia 4.Mask-like face 5.Dysphagia 6.Reduced appetite 4.The nurse is planning care for a client diagnosed with myasthenia gravis. Which of the following should be included in this clients plan of care? (Select all that apply.) 1.Monitor activities frequently and assist as needed. 2.Encourage progressive increase in activities. 3. Determine the best communicationmethod. 4.Monitorweight. 5. Restrictfluids. 6. Instruct in energy conservation measures. 5.The nurse is instructing a client and family regarding the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Which of the following should be included in this teaching? (Select all that apply.) 1. The length of the curativetreatment 2. That exercise and physical therapy can help the patient maximizefunction 3.The physical, emotional, and social aspects of thedisease 4. End-of-lifeissues 5. The use of devices to prevent aspiration pneumonia 6.The use of a speech therapist to aid with communication 6.The nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with Huntingtons disease. Which of the following are considered hallmark clinical manifestations of this disorder? (Select all that apply.) 1.Intellectual decline 2.Weight loss 3.Decreased appetite 4.Reduced blood pressure 5.Nausea 6. Abnormal movements Chapter 9. Cerebrovascular Accident (Stroke) MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. For the client who is at risk for stroke, the most important guideline the nurse should teach isto: 1. increase drinks withcaffeine. 2. monitor bloodpressure. 3. increase amounts of sodium in thediet. 4. monitor weight andactivity. 2. The family of a client diagnosed with a stroke asks the nurse if this health problem is very common. The nurse should respond that in the United States a person has a strokeevery: 1. 40 seconds. 2. 1minutes. 3. 2minutes. 4. 5minutes. 3.A client is being evaluated for a stroke. The nurse knows that one of the easiest and mostcommon diagnostic tests used to differentiate between strokesis: 1. computed tomography(CT). 3. electrocardiography(EEG). 4. positron emission tomography(PET). 4. While instructing a client on stroke prevention, the nurse mentions medications that are usefulin stroke prevention. The following medications are effective in preventing a stroke,EXCEPT: 1. anticoagulants. 2. antiplatelets. 3. anticholinergics. 4. neuroprotectiveagents. 5.A client is being seen in the emergency department experiencing symptoms of a stroke. Thenurse realizes that the administration of a medication to break clots, such as tPA, should be administered within how many minutes of the client presenting to the emergencydepartment? 1. 30minutes 2. 60minutes 4. 120 minutes 6.A client diagnosed with an embolic stroke is not a candidate for tPA. The nurse realizes that the client might be eligible for which of the following forms oftreatment? 1. Carotidstenting 2. Antiarrhythmic medication 3. Intravenous fluidtherapy 4. Carotidendarterectomy 7.A client, being tested for a stroke, is not a candidate for tPA. Which of the following would be contraindicated for the use of tPA? (Select all thatapply.) 1. Minor ischemic stroke within 30days 2. Glucose level 120mg/dL 3. Blood pressure 190/120mmHg 4. Lumbar puncture 2 daysago 6. INR1.0 1. A patient with a temporary loss of motor function is diagnosed with a transient ischemic attack (TIA). What should the nurse include when assisting in the teaching about this healthproblem? a. You had a small hemorrhage in yourbrain. b. Your brain was temporarily deprived ofoxygen. c. The neurons in your brain are tangled, so messages get mixedup. d. You have a vessel that is occluded, blocking the blood supply to your brain. . 2. The nurse is assisting with teaching a patient who has had a transient ischemic attack (TIA). On which understanding should the nurse baseteaching? a. TIAs are not serious, and the patient should have no furtherproblems. b. A TIA is predictive that the patient will have a heart attack within 1year. c. A TIA is a medical emergency that requires immediate surgicalintervention. d. A TIA is a forewarning that the patient is at risk for a cerebrovascular accident(stroke). 3. The nurse is planning care for a client with right-sided weakness and aphasia from a transient ischemic attack (TIA). Which area of the brain should the nurse realize was affected in this client? a. Medulla b. Occipitallobe c. Lefthemisphere d. Righthemisphere 4. A patient with a cerebrovascular accident (stroke) has left-sided flaccidity and is unable to speak but seems to understand everything the nurse says. Which term should the nurse use to document the patients communicationimpairment? a. Sensoryaphasia b. Motordysphagia c. Expressiveaphasia d. Receptive dysphagia 5. The nurse is documenting care provided to a patient with left-sided flaccidity caused by a stroke. Which term should the nurse use to document this patients motorstatus? a. Ipsilateralparaplegia b. Ipsilateralhemiparesis c. Contralateralhemiplegia d. Contralateralquadriparesis 6. A patient comes into the emergency department with symptoms of a stroke. Which medication should the nurse expect may be given to the patient if diagnostic testing confirmsan ischemicstroke? a. Heparin b. Clopidogrel(Plavix) c. Warfarin(Coumadin) d. Tissue-type plasminogen activator(tPA) 7. A patient is prescribed an antiplatelet agent to prevent strokes. Which agent was this patient most likelyprescribed? a. Aspirin b. Warfarin(Coumadin) c. Acetaminophen(Tylenol) d. Tissue-type plasminogen activator(tPA) 8. A patient with symptoms of impending stroke is scheduled to have a cerebral angiogram. Which statement should the nurse include when assisting with patientteaching? a. This test is designed to detect vascular lesions in thebrain. b. The angiogram is done to help identify swelling in thebrain. c. We need to do this to evaluate electrical function of thebrain. d. This test is done to examine cerebrospinal fluid for signs ofbleeding. 9. The nurse is caring for a hospitalized patient who has had a stroke and is waiting to betransferred to a rehabilitation facility. What nursing action can best maximize the patients rehabilitation potential while awaiting thetransfer? a. Teach the patient what to expect at the rehabilitationfacility. b. Keep the patient on bedrest to conserve energy forrehabilitation. c. Call the physical therapist for bedside rehabilitation until thetransfer. d. Turn the patient every 2 hours to prevent pressure ulcers andcontractures. 10. The nurse is assisting in preparing a patient for transfer to a rehabilitation facility after a stroke. What should the nurse explain as the goal forrehabilitation? a. To monitor neurologicalstatus b. To cure any effects of thestroke c. To maximize remainingabilities d. To determine the extent of neurological deficits 11. A patient is admitted to the hospital with a severe headache and photophobia. A lumbarpuncture confirms a bleeding aneurysm. What nursing interventions should the nurse anticipate assisting with to prevent increased intracranial pressure (ICP) during the acute phase ofillness? a. Morphine, dark glasses, andexpectorants b. Quiet room, head of bed up, and stoolsofteners c. Coughing and deep breathing exercises andtranquilizers d. Range of motion exercises, bedside commode, and suctioning as needed 12. A client with a subarachnoid bleed refuses to use a bedpan and becomes angry when denied permission to walk to the bathroom. While waiting to hear from the health care provider (HCP), which action should the nursetake? a. Help the patient to get up on a bedsidecommode b. Wait for the neurosurgeon to call back withorders c. Page security to restrain the patient from harming thenurse d. Administer an as-needed dose of a sedative that is ordered 13. A patient is experiencing bilateral hemiparesis, dysphasia, visual changes, and altered level of consciousness, ataxia, and dysphagia. Which artery was most likely affected in this patientsstroke? a. Carotid b. Middlecerebral c. Posteriorcerebral d. Vertebrobasilar/cerebellar 14. The patient is diagnosed with a cerebral vascular accident that has the slowest rate of recovery and the highest probability of causing extensive neurological deficits. For which type of stroke should the nurse plan care for thispatient? a. Thromboticstroke b. Cerebralaneurysm c. Subarachnoid hemorrhage(SAH) d. Reversible ischemic neurological deficit (RIND) 15.A patient enters the emergency department with right-sided weakness and vision changes. What assessment finding should be communicated to the registered nurse (RN) or HCPimmediately? a. Blood glucose 150mg/dL b. Blood pressure 148/92 mmHg c. Onset of symptoms occurred 90 minutesago d. History of transient ischemic attack (TIA) 3 months ago 16. The nurse is reviewing teaching provided to a patient with transient ischemic attack (TIA). Which statement indicates that further teaching isrequired? a. The risk factors and symptoms of a TIA are just like those of astroke. b. I need to stop smoking to help lower my chances of this happeningagain. c. My risk for Alzheimers disease is increased now, so Ill have to stopdriving. d. I recognize how important it is to take my anti-hypertension medications regularly. 17. A patient began experiencing manifestations of a stroke at 0800 hours. By which time should thrombolytic medications be provided to reverse strokesymptoms? a. 0900 hours b. 1250 hours c. 1400 hours d. 1660 hours 18. A patient is diagnosed with a stroke that occurred at 12 noon the previous day. When shouldthe nurse plan to begin bedside physical therapy with thispatient? a. After 5days b. Within 2 to 3days c. By 12 noon on the currentday d. At least one week after theoccurrence . . 19. The nurse is planning care for a patient with an intracerebral hemorrhage. What should be identified as a goal for thispatient? a. Maintain blood pressure below 120/80 mmHg b. Resume activities of daily living as soon aspossible c. Expect to experience transient numbness andtingling d. Receive thrombolytic medication therapy within an hour Chapter 10. Infectious and Inflammatory Neurological Disorders 1. What should the nurse do when the child arrives on the floor with the diagnosis ofbacterial meningitis? a. Arrange for humidified oxygen permask b. Place the child in respiratoryisolation c. Inquire about drugallergy d. Hold NPO until orders arrive 2. What should the nurse do when the child arrives on the floor with the diagnosis ofbacterial meningitis? a. Arrange for humidified oxygen permask b. Place the child in respiratoryisolation c. Inquire about drugallergy d. Hold NPO until orders arrive Chapter 11.Common Skin Complaints Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Simon presents with alopecia areata with well-circumscribed patches of hair loss on the crown of his head. How do you respond when he asks you thecause? a. “You must be under a lot of stresslately.” b. “It is hereditary. Did your father experience thisalso?” c. “The cause is unknown, but we suspect it is due to an immunologicmechanism.” d. “We’ll have to do sometests.” 2. Which of the following is “a linear crack extending from the epidermis to thedermis?” a. Anulcer b. Afissure c. Lichenification d. Anexcoriation 3. A bullais: a. A vesicle larger than 1 cm indiameter b. An elevated solid mass with a hard texture; the shape and borders can be regular or irregular c. A superficial elevated lesion filled with purulentfluid d. Thinning of the skin (epidermis and dermis) that appears white ortranslucent 4. An example of ecchymosisis: a. Ahematoma b. Akeloid c. Abruise d. Apatch 5. When looking under the microscope to diagnose an intravaginal infection, you see a cluster of small and oval to round shapes. What do you suspect theyare? a. Spores b. Leukocytes c. Pseudohyphae d. Epithelialcells 6. Your patient is in her second trimester of pregnancy and has a yeast infection. Which of the following is a treatment that you usually recommend/order in nonpregnant patients, but is listed asa Pregnancy categoryD? a. Vagistat vaginalcream b. Monistat combinationpack c. Terazol vaginalcream d. Diflucan, 150 mg 7. Tinea unguium is also knownas: a. Onychomycosis b. Tineaversicolor c. Tinea manuum d. Tineacorporis 8. Sally, age 25, presents with impetigo that has been diagnosed as infected with Staphylococcus. The clinical presentation is pruritic tender, red vesicles surrounded by erythema with a rash that is ulcerating. Her recent treatment has not been adequate. Which type of impetigo isthis? a. Bullousimpetigo b. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome(SSSS) c. Nonbullousimpetigo d. Ecthyma 9. Mark has necrotizing fasciitis of his left lower extremity. Pressure on the skin reveals crepitus due to gas production by which anaerobicbacteria? a. Staphylococcalaureus b. Clostridiumperfringens c. S. pyrogenes d. Streptococcus 10. When using the microscope for an intravaginal infection, you see something translucent and colorless. What do yoususpect? a. A piece of hair or athread b. Hyphae c. Leukocytes d. Spores 11. Marci has a wart on her hand. She says she heard something about “silver duct tape therapy.” What do you tell her abouthis? a. It is an old wives’tale. b. It is used as a lastresort. c. Salicylic acid is moreeffective. d. It is a simple treatment that should be triedfirst. 12. Which is the most potent and irritating dose oftretinoin? a. 0.05% liquidformulation b. 0.1% cream c. 1% foam d. 0.02%cream 13. Of the following types of cellulitis, which is a streptococcal infection of the superficial layers of the skin that does not involve the subcutaneouslayers? a. Necrotizingfasciitis b. Periorbitalcellulitis c. Erysipelas d. “Flesh-eating”cellulitis 14. Mandy presents with a cauliflower-like wart in her anogenital region. You suspect it was sexually transmitted and document this asa: a. Filiform/digitatewart b. Dysplastic cervicallesion c. Condyloma acuminata d. Koilocytosis 15. Jeffrey has atopic dermatitis. You are prescribing a low-dose topical corticosteroid for him. Which would be a goodchoice? a. Betamethasone dipropionate0.05% b. Hydrocortisone base2.5% c. Halcinonide0.1% d. Desonide0.05% 16. Harvey has a rubbery, smooth, round mass on his chest that is compressible and has a soft-to-very- firm texture. What do you diagnose thisas? a. Alipoma b. Anevi c. A skintag d. A possibleadenoma 17. Which of the following statements is accurate when you are removing a seborrheic keratosis lesion using liquidnitrogen? a. Do not use lidocaine as it may potentiatebleeding. b. Pinch the skin tauttogether. c. Use gel foam to controlbleeding. d. This should be performed by a dermatologistonly. 18. The “B” in the ABCDEs of assessing skin cancerrepresents: a. Biopsy b. Bestpractice c. Boundary d. Borderirregularity 19. The majority of HSV-1 and HSV-2 infections are asymptomatic so that only which elevated antibody titer shows evidence of previousinfection? a. IgA b. IgE c. IgG d. IgM 20. Eighty percent of men have noticeable hair loss by whatage? a. 35 b. 50 c. 70 d. 85 21. Prevalence of psoriasis is highest in whichgroup? a. Scandinavians b. AfricanAmericans c. Asians d. NativeAmericans 22. The most common precancerous skin lesion found in Caucasiansis: a. A skintag b. Actinickeratosis c. Amelanoma d. A basal celllesion 23. Ian, age 62, presents with a wide, diffuse area of erythematous skin on his lower left leg that is warm and tender to palpation. There is some edema involved. Yoususpect: a. Necrotizingfasciitis b. Kaposi’ssarcoma c. Cellulitis d. A diabeticulcer 24. Josh, aged 22, has tinea versicolor. Which description is the most likely for thiscondition? a. There are round, hypopigmented macules on hisback. b. Josh has red papules on hisface. c. There are crusted plaques in Josh’s groinarea. d. There are white streaks on hisneck. 25. Tori is on systemic antifungals for a bad tinea infection. You are aware that the antifungals may cause: a. Renalfailure b. Skindiscoloration c. Breathingdifficulties d. Hepatotoxicity 26. Which scalp problem can be caused by a fever and certaindrugs? a. Telogen effluvium(TE) b. Trichotillomania c. Psoriasis d. Alopeciaareata 27. Why do people of African descent have a lower incidence of non-melanoma skincancer? a. They have an increased number ofmelanocytes. b. Their darker skin protects from ultravioletradiation. c. Their skin isthicker. d. Their immune system isstronger. 28. Which statement is true regarding chloasma, the ‘mask ofpregnancy’? a. It is caused by a decrease in the melanocyte-stimulating hormone during pregnancy. b. This condition only occurs on theface. c. Exposure to sunlight will even out thediscoloration. d. It is caused by increased levels of estrogen andprogesterone. 29. When instructing your elderly client about treating her xerosis, what do you tellher? a. A daily hot bath may help the associatedpruritus. b. Rub the skin briskly to make sure it is completely dry afterbathing. c. Only take short tepidshowers. d. Use a gel that is alcohol-based after bathing to soften theskin. 30. Which medication used for scabies is safe for children 2 months andolder? a. Permethrincream b. Lindane c. Crotamiton lotion andcream d. Ivermectin 31. Which of the following is an infraorbital fold skin manifestation in a patient with atopicdermatitis? a. Keratosispilaris b. Dennie’ssign c. Keratoconus d. Pityriasisalba 32. Which of the following statements about performing cryosurgery for actinic keratosis istrue? a. It is better to slightly overfreeze the area, so you only have to do itonce. b. Using liquid nitrogen, freeze each lesion for at least 30seconds. c. Every lesion should be biopsied after using liquidnitrogen. d. The ‘freeze balls’ should be approximately one-and-a-half times as wide as they are deep. 33. An example of a primary skin lesion isa/an: a. Bulla b. Scale c. Excoriation d. Fissure 34. Which statement regarding necrotizing fasciitis istrue? a. The hallmark of this infection is its slow and steadyprogression. b. Once the border of the infection is “established,” it does notspread. c. Loss of life or limb is a potentialcomplication. d. The lesion is most dangerous, because it ispainless. 35. When staging a malignant melanoma using Clark’s levels, which level extends into the papillary dermis? a. Level I b. LevelII c. LevelIII d. LevelIV Chapter 12. Parasitic Skin Infestations 1. The school nurse recognizes the signs of scabies when a child presentswith: a. small fluid filled blisters that sting whenscratched. b. dry scaly patches in body creases thatitch. c. wavy threadlike lines on the body andpruritus. d. cluster of papular lesions withpruritus. 2. Which of the following are nursing interventions and patient teaching for the treatment of headlice and scabies? (Select all thatapply.) a. Clothing, linens, and bath articles thoroughly cleaned in hotwater b. Stress nature and transmission of thedisease c. Special carbohydrate diet to promotehealing d. Complete isolation from the public . 3. The nurse is caring for a patient with lesions on the skin. Which assessment finding should cause the nurse to suspectscabies? a. Large, fluid-filledblisters b. Short, wavy, brownish blacklines c. Reddish brown dots at the base ofhairs d. Gray blue macules on the thighs and axillae Chapter 13. Fungal Skin Infections 1. A client is experiencing a circular lesion with an advancing, red, scaly border on theabdomen. The nurse recognizes this lesion asbeing: 1 tineacapitis. 2 tineacorporis. 3 tineacruris. 4 tineapedis. 2.A client is diagnosed with tinea versicolor. Which of the following should the nurse instruct this client regarding the care for this skincondition? 1 Do nothing since there is notreatment. 2 Utilize shampoo withselenium. 3 Utilize an oral antifungal preparation asprescribed. 4 Apply warm compresses to the affectedareas. . 3.A school nurse assesses a child who has an erythematous circular patch of vesicles on her scalp with alopecia and complains of pain and pruritus. Why would the nurse use a Woodslamp? a. To dry out thelesions b. To reduce thepruritus c. To kill thefungus d. To cause fluorescence of the infected hairs Chapter 14. Bacterial Skin Infections 1.A client has what appears to be a bacterial infection or warts on her fingertips. This can be a sign of: 1 herpesgladiatorum. 2 herpessimplex. 3 herpeszoster. 4 herpeticwhitlow. . 2.A school-age child is experiencing pruritic vesicles around the mouth. The lesions have a honey- colored crust. The nurse realizes that the child is most likelyexperiencing: 1 candidiasis. 2 herpessimplex. 3 impetigo. 4 tineacorporis. . 3.A client is diagnosed with severe nodulocystic acne. The nurse should instruct the client on which of the following types of treatments? (Select all thatapply.) 1 Oralantibiotics 2 Benzoylperoxide 3 Sulfur 4 Intralesionalinjections 5 Soap andwater 6 Topicaltherapy 4. Which patient statement indicates that more teaching is needed regarding antibiotic therapy forthe treatment ofcellulitis? a. My skin is cleared up. I dont think I need the medicationanymore. b. Cellulitis can come back at any time. c. If I had washed that scratch with soap and water, I probably would not have gottencellulitis. d. Cellulitis is contagious. 5. The nurse is participating in planning care for a patient with pemphigus. What nursing diagnosis should the nurse recommend be used to guide this patientscare? a. Risk forInfection b. Fluid VolumeExcess c. Self-Care Deficit: SkinCare d. Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than BodyRequirements 6A patient is prescribed vitamin A acid (Retin-A) as treatment of acne vulgaris. What shouldthe nurse instruct the patient about the purpose of this medication? (Select all thatapply.) a. It decreasesscarring. b. It loosens poreplugs. c. It kills bacteria infollicles. d. It stabilizes hormone levels. e. It stimulates the immunesystem. f. It prevents occurrence of comedomes. Chapter 15. Viral Skin Infections 1.A client is diagnosed with a viral skin infection. The nurse realizes that which of the following medications may be prescribed for this client? (Select all thatapply.) 1 Nystatin(Mycostatin) 2 Docosanol(Abreva) 3 Boricacid 4 Penciclovir(Denavir) 5 Hydrogen peroxide 6 Acyclovir(Zovirax) 2.A client is diagnosed with genital herpes simplex virus. The nurse know that symptoms of the primary infectionoccur: 1 1 to 4 days afterexposure. 2 3 to 7 days afterexposure. 3 5 to 9 days afterexposure. 4 7 to 11 days afterexposure. 3. What should a patient be assessed for upon the diagnosis of genitalherpes? a. HepatitisB b. Syphilis c. Human immunodeficiency virus(HIV). d. Cirrhosis 4. The nurse is care for a patient with shingles. Which statement should the nurse include inpatient teaching? a. Herpes simplex 2 causesshingles. b. Shingles is caused by herpes simplex 1virus. c. Varicella zoster is the virus responsible forshingles. d. Herpes zoster is a virus that is common in olderpatients. Chapter 16. Dermatitis 1. Which of the following should the nurse instruct a client who is prescribed a topical medicationfor a skincondition? 1 Apply directly to broken or irritatedskin. 2 Apply beforebathing. 3 Apply afterbathing. 4 Cover the area with an occlusivedressing. . 2.A client is diagnosed with a dermatologic condition causing pruritis and inflammation. Which of the following should the nurse instruct thisclient? 1 Use regular perfumed lotion to moisturize theskin. 2 Use scented soap to bathe the skindaily. 3 Apply skin oildaily. 4 Apply a body moisturizer to the skin within 3 to 5 minutes afterbathing. 3. What is the initial intervention for relief of the pruritus of dermatitisvenenata? a. Apply baking soda tolesions b. Wash area with copious amounts ofwater c. Apply cool compressescontinuously d. Expose area to air . 4.A patient developed a severe contact dermatitis of the hands, arms, and lower legs after spending an afternoon picking strawberries. The patient states that the itching is severe and cannot keep from scratching. Which instruction would be most helpful in managing thepruritus? a. Use cool, wet dressings and baths to promotevasoconstriction. b. Trim the fingernails short to prevent skin damage fromscratching. c. Expose the areas to the sun to promote drying and healing of thelesions. Wear cotton gloves and cover all other affected areas with clothing to prevent environmental d. irritation. Chapter 17. Skin Lesions 1.A client is experiencing a circular lesion with an advancing, red, scaly border on the abdomen. The nurse recognizes this lesion asbeing: 1 tineacapitis. 2 tineacorporis. 3 tineacruris. 4 tineapedis. 2.A middle-aged construction worker has a raised lesion with a pearly border on his arm thatbleeds easily. The nurse realizes that this client most likely is experiencinga(n): 1 actinickeratosis. 2 basal cellcarcinoma. 3 malignantmelanoma. 4 melanoma insitu. . 3.A client is experiencing elevated fluid-filled lesions on the skin. The nurse would document these lesions as being: 2. nodules. 3. vesicles. 4. wheals. 4.A client has a nonpalpable skin lesion that is causing a change in skin color greater than 1 cm in diameter. The nurse would document this finding as beinga(n): 1. patch. 2. macule. 3. wheal. 4. vesicle. 5. The nurse is assessing a client for primary skin lesions. Which of the following wouldbe considered primary lesions of the skin? (Select all thatapply.) 1. Crust 2. Scales 4. Nodules 5. Macules 6. Plaques 6. The nurse is describing the distribution and configuration of lesions. Which of the following can be used for this description? (Select all thatapply.) 1. Iris 2. Annular 3. Linear 4. Keratosis 5. Wheal 6. Bullae 7. The nurse assesses a linear lesion along the length of a clients leg. Which diagnosis does thenurse realize is associated with linear lesions? (Select all thatapply.) 1. Drugreaction 3. Herpessimplex 4. Hookworm 5. Dermatitis 6. Poisonivy 8. The home health nurse assessing skin lesions uses the PQRST mnemonic as a guide. Whatdoes the S in this guideindicate? a. Severity of thesymptoms b. Site of thelesions c. Symptomatology of thelesions d. Surface area of the lesions Chapter 18. Common Eye Complaints MULTIPLE CHOICE 1.A client is diagnosed with strabismus. Which of the following will the client most likely experience with this disorder? 1.Nystagmus 2.Diplopia 3.Aphakic vision 4.Ptosis 2.A client is experiencing a gradual blurring of vision in both eyes not associated with any pain. The nurse suspects the client is experiencing: 1.glaucoma. 2.cataracts. 3. maculardegeneration. 4. retinaldetachment. 3.The nurse should instruct a client, diagnosed with glaucoma, that the purpose of medication isto: 1.help dry up excesssecretions. 2.lower the intraocular pressure. 3.strengthen the muscles of the eye. 4.improve the vision in theeye. . 4.After surgery to remove a cataract, which of the following should the nurse instruct the client? 1.Be sure to follow the schedule for the prescribed eyedrop medication. 2. Sleep on the right side to promotedrainage. 3. It is okay to rub the eye because the surgery was on theinside. 4. This is an outpatient procedure, and there are no instructions for thepatient. 5.A tonometry test has been performed with a client and the results are 25 mmHg. The nurse know that: 1. the reading is low and there is noproblem. 2. the reading is normal and nothing needs to be done at this time. 3.the results are high and follow-up readings and tests are needed. 4.the results are high and there is no cure to bring the pressuredown. 6.A client has been diagnosed with cataracts. The nurse realizes that the only treatment for this disorder is? 1.Medical management with eyedrops 2.Surgical removal of the lens 4.Phototherapy 7.Which of the following should the nurse assess in a client diagnosed with open-angle glaucoma? 1.Degree of lost vision 2.Severity of headaches 3.Amount of blurred vision 4.Date of onset 8.A client is experiencing little flashes of lights and things floating in the visual field. The nurse suspects: 1. cataracts. 2. glaucoma. 3. conjunctivitis. 4. retinaldetachment. 9.A client tells the nurse that she sees a shadow that is slowing getting worse in her left eye. Which of the following should the nurse do? 1. Instruct the client to return home to rest inbed. 2. Encourage the client to continue with normal daily activities. 3.Notify anophthalmologist. 10.A client is experiencing a loss of central vision but not a loss of peripheral vision. The nurse realizes the client should be evaluated for: 1.detached retina syndrome. 2.nystagmus. 3. maculardegeneration. 4. conjunctivitis. 11.A client is experiencing redness, burning, itching, and pain of the eyes. The nurse suspects the client is experiencing: 1.blepharitis. 2.conjunctivitis. 3.keratitis. 4.iritis. . 12.A client has been diagnosed as being legally blind. The nurse realizes this clients vision is: 2.20/200 or less in the worse eye without correction. 3.20/100 or less in the better eye without correction. 4.20/100 or less in the worse eye with correction. 13.The nurse realizes that the best medication treatment for open-angle glaucoma would be: 1.timolol (Timoptic) eyedrops. 2. latanoprost (Xalatan)eyedrops. 3. timolol (Timoptic) and Latanoprost (Xalatan) eyedrops. 4.metoprolol oralmedication. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1.A client tells the nurse that he does not want to develop macular degeneration like his mother. Which of the following should the nurse instruct the client as being risk factors for the development of this disorder? (Select all that apply.) 1.There is greater risk as people age. 2.Women are at greater risk than men. 3.African Americans are at greater risk than Caucasians. 4.Family history of macular degeneration increases risk. 5.Smoking does not increase risk. 6.Alcohol prevents the onset of this disorder. 2.A client is receiving tests to diagnose glaucoma. Which of the following diagnostic tests will be used to identify this disorder in the client? (Select all that apply.) 1.Visual acuity 2.Visual field test 3.Tonometry 4.Weber test 5.Rinne test 6.Electroencephalogram 3.A client is diagnosed with ocular cancer. The nurse realizes this client could be treated with: (Select all that apply.) 1.Enucleation 2.Laser surgery 3.Plaque brachytherapy 4.Block incision 5.Trabeculoplasty 6.Trabeculectomy 4.A client, diagnosed with keratoconus, asks the nurse what caused the disorder to develop. The nurse should instruct the client on which of the following as risk factors for the development of this disorder? (Select all that apply.) 1.Sun exposure 2.Ocular allergies 3.Wearing rigid contact lenses 4.Vigorous eye rubbing 5.Herpes simplex virus 6.Dry eyes 5.The nurse is planning instruction for a client experiencing dry eyes. Which of the following should be included in these instructions? (Select all that apply.) 1.Drink 8 to 10 glasses of water each day. 2.Apply petroleum jelly to the eyelids. 3. Blink morefrequently. 4. Avoid sunexposure. 5. Avoid rubbing the eyes. 6.Avoid dryair. 6. Which of the following should the nurse instruct a client diagnosed with type 2 diabetesmellitus regarding vision care? (Select all thatapply.) 1.Maintain good glucose control. 2.Stop smoking. 3. Limitexercise. 4. Reducereading. 5. Frequently rest theeyes. 6. Rub eyesdaily. Chapter 19. Lid and Conjunctival Pathology 1. When examining the eye, the nurse notices that the patients eyelid marginsapproximate completely. The nurse recognizes that this assessmentfinding: a. Is expected. b. May indicate a problem with extraocularmuscles. c. May result in problems withtearing. d. Indicates increased intraocular pressure. . 2. During ocular examinations, the nurse keeps in mind that movement of the extraocular musclesis: a. Decreased in the olderadult. b. Impaired in a patient withcataracts. c. Stimulated by cranial nerves (CNs) I andII. d. Stimulated by CNs III, IV, and VI. . 3. The nurse is performing an external eye examination. Which statement regarding the outerlayer of the eye istrue? a. The outer layer of the eye is very sensitive totouch. b. The outer layer of the eye is darkly pigmented to prevent light from reflectinginternally. The trigeminal nerve (CN V) and the trochlear nerve (CN IV) are stimulated whenthe c. d. outer surface of the eye is stimulated. The visual receptive layer of the eye in which light waves are changed into nerve impulses is located in the outer layer of the eye. 4. When examining a patients eyes, the nurse recalls that stimulation of the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervoussystem: a. Causes pupillaryconstriction. b. Adjusts the eye for nearvision. c. Elevates the eyelid and dilates thepupil. d. Causes contraction of the ciliary body. 5. The nurse is reviewing causes of increased intraocular pressure. Which of these factors determines intraocularpressure? a. Thickness or bulging of thelens b. Posterior chamber as it accommodates increasedfluid c. Contraction of the ciliary body in response to the aqueous within theeye Amount of aqueous produced and resistance to its outflow at the angle of the anterior d. chamber 6. The nurse is conducting a visual examination. Which of these statements regarding visual pathways and visual fields istrue? a. The right side of the brain interprets the vision for the righteye. The image formed on the retina is upside down and reversed from its actual appearance in b. the outsideworld. c. Light rays are refracted through the transparent media of the eye before striking thepupil. d. Light impulses are conducted through the optic nerve to the temporal lobes of the brain. 7. The nurse is testing a patients visual accommodation, which refers to whichaction? a. Pupillary constriction when looking at a nearobject b. Pupillary dilation when looking at a farobject c. Changes in peripheral vision in response tolight d. Involuntary blinking in the presence of bright light . 8. A patient has a normal pupillary light reflex. The nurse recognizes that this reflex indicatesthat: a. The eyes converge to focus on thelight. b. Light is reflected at the same spot in botheyes. c. The eye focuses the image in the center of thepupil. d. Constriction of both pupils occurs in response to bright light. 9. A mother asks when her newborn infants eyesight will be developed. The nurse shouldreply: a. Vision is not totally developed until 2 years ofage. b. Infants develop the ability to focus on an object at approximately 8 months ofage. By approximately 3 months of age, infants develop more coordinated eye movements and c. can fixate on anobject. d. Most infants have uncoordinated eye movements for the first year of life. . 10. The nurse is reviewing in age-related changes in the eye for a class. Which of these physiologic changes is responsible forpresbyopia? a. Degeneration of thecornea b. Loss of lenselasticity c. Decreased adaptation todarkness d. Decreased distance vision abilities . 11. Which of these assessment findings would the nurse expect to see when examining the eyes ofa blackpatient? a. Increased nightvision b. Dark retinalbackground c. Increasedphotosensitivity d. Narrowed palpebral fissures 12. A 52-year-old patient describes the presence of occasional floaters or spots moving in frontof his eyes. The nurseshould: a. Examine the retina to determine the number offloaters. b. Presume the patient has glaucoma and refer him for furthertesting. c. Consider these to be abnormal findings, and refer him to anophthalmologist. d. Know that floaters are usually insignificant and are caused by condensed vitreousfibers. 13. The nurse is preparing to assess the visual acuity of a 16-year-old patient. How should thenurse proceed? a. Perform the confrontationtest. b. Ask the patient to read the print on a handheld Jaegercard. c. Use the Snellen chart positioned 20 feet away from thepatient. d. Determine the patients ability to read newsprint at a distance of 12 to 14 inches. 14. A patients vision is recorded as 20/30 when the Snellen eye chart is used. The nurse interprets these results to indicatethat: a. At 30 feet the patient can read the entirechart. b. The patient can read at 20 feet what a person with normal vision can read at 30feet. c. The patient can read the chart from 20 feet in the left eye and 30 feet in the righteye. d. The patient can read from 30 feet what a person with normal vision can read from 20 feet. 15. A patient is unable to read even the largest letters on the Snellen chart. The nurse should take which actionnext? a. Refer the patient to an ophthalmologist or optometrist for furtherevaluation. Assess whether the patient can count the nurses fingers when they are placed in front of his b. or hereyes. c. d. Ask the patient to put on his or her reading glasses and attempt to read the Snellen chart again. Shorten the distance between the patient and the chart until the letters are seen, and record that distance. 16. A patients vision is recorded as 20/80 in each eye. The nurse interprets this finding to meanthat thepatient: a. Has poorvision. b. Has acutevision. c. Has normal vision. d. Is presbyopic. 17. When performing the corneal light reflex assessment, the nurse notes that the light is reflectedat 2 oclock in each eye. The nurseshould: a. Consider this a normalfinding. b. Refer the individual for furtherevaluation. c. Document this finding as an asymmetric lightreflex. d. Perform the confrontation test to validate the findings. 18. The nurse is performing the diagnostic positions test. Normal findings would be which of these results? a. Convergence of theeyes b. Parallel movement of botheyes c. Nystagmus in extreme superiorgaze d. Slight amount of lid lag when moving the eyes from a superior to an inferior position 19. During an assessment of the sclera of a black patient, the nurse would consider which of these an expectedfinding? a. Yellow fatty deposits over thecornea b. Pallor near the outer canthus of the lowerlid c. Yellow color of the sclera that extends up to theiris d. Presence of small brown macules on the sclera 20. A 60-year-old man is at the clinic for an eye examination. The nurse suspects that he has ptosis of one eye. How should the nurse check forthis? a. Perform the confrontationtest. b. Assess the individuals nearvision. c. Observe the distance between the palpebralfissures. d. Perform the corneal light test, and look for symmetry of the light reflex. 21. During an examination of the eye, the nurse would expect what normal finding whenassessing the lacrimalapparatus? a. Presence of tears along the innercanthus b. Blocked nasolacrimal duct in a newborninfant c. Slight swelling over the upper lid and along the bony orbit if the individual has acold d. Absence of drainage from the puncta when pressing against the inner orbital rim 22. When assessing the pupillary light reflex, the nurse should use whichtechnique? a. Shine a penlight from directly in front of the patient, and inspect for pupillaryconstriction. Ask the patient to follow the penlight in eight directions, and observe for bilateral pupil b. constriction. c. d. Shine a light across the pupil from the side, and observe for direct and consensual pupillary constriction. Ask the patient to focus on a distant object. Then ask the patient to follow the penlight to approximately 7 cm from the nose. 23. The nurse is assessing a patients eyes for the accommodation response and would expect tosee which normalfinding? a. Dilation of thepupils b. Consensual lightreflex c. Conjugate movement of theeyes d. Convergence of the axes of the eyes 24. In using the ophthalmoscope to assess a patients eyes, the nurse notices a red glow in thepatients pupils. On the basis of this finding, the nursewould: a. Suspect that an opacity is present in the lens orcornea. b. Check the light source of the ophthalmoscope to verify that it isfunctioning. c. Consider the red glow a normal reflection of the ophthalmoscope light off the inner retina. Continue with the ophthalmoscopic examination, and refer the patient forfurther d. evaluation. 25. The nurse is examining a patients retina with an ophthalmoscope. Which finding is considered normal? a. Optic disc that is a yellow-orangecolor b. Optic disc margins that are blurred around theedges c. Presence of pigmented crescents in the maculararea d. Presence of the macula located on the nasal side of the retina 26. A 2-week-old infant can fixate on an object but cannot follow a light or bright toy. The nurse would: a. Consider this a normalfinding. b. Assess the pupillary light reflex for possibleblindness. c. Continue with the examination, and assess visualfields. d. Expect that a 2-week-old infant should be able to fixate and follow an object. 27. The nurse is assessing color vision of a male child. Which statement is correct? The nurse should: a. Check color vision annually until the age of 18years. b. Ask the child to identify the color of his or herclothing. c. Test for color vision once between the ages of 4 and 8years. d. Begin color vision screening at the childs 2-year checkup. 28. The nurse is performing an eye-screening clinic at a daycare center. When examining a2-year- old child, the nurse suspects that the child has a lazy eye andshould: a. Examine the external structures of theeye. b. Assess visual acuity with the Snellen eyechart. c. Assess the childs visual fields with the confrontationtest. d. Test for strabismus by performing the corneal light reflex test. 29. The nurse is performing an eye assessment on an 80-year-old patient. Which of these findings is consideredabnormal? a. Decrease in tearproduction b. Unequal pupillary constriction in response tolight c. Presence of arcus senilis observed around thecornea d. Loss of the outer hair on the eyebrows attributable to a decrease in hair follicles 30. The nurse notices the presence of periorbital edema when performing an eye assessment on a70- year-old patient. The nurseshould: a. Check for the presence ofexophthalmos. b. Suspect that the patient hashyperthyroidism. c. Ask the patient if he or she has a history of heartfailure. d. Assess for blepharitis, which is often associated with periorbital edema. . 31. When a light is directed across the iris of a patients eye from the temporal side, the nurseis assessingfor: a. Drainage fromdacryocystitis. b. Presence of conjunctivitis over theiris. c. Presence of shadows, which may indicateglaucoma. d. Scattered light reflex, which may be indicative of cataracts. 32. In a patient who has anisocoria, the nurse would expect toobserve: a. Dilatedpupils. b. Excessivetearing. c. Pupils of unequalsize. d. Uneven curvature of the lens. 33. A patient comes to the emergency department after a boxing match, and his left eye is swollen almost shut. He has bruises on his face and neck. He says he is worried because he cant see well from his left eye. The physician suspects retinal damage. The nurse recognizes that signs of retinal detachmentinclude: a. Loss of centralvision. b. Shadow or diminished vision in one quadrant or one half of the visualfield. c. Loss of peripheralvision. d. Sudden loss of pupillary constriction andaccommodation. 34. A patient comes into the clinic complaining of pain in her right eye. On examination, the nurse sees a pustule at the lid margin that is painful to touch, red, and swollen. The nurse recognizes that this isa: a. Chalazion. b. Hordeolum(stye). c. Dacryocystitis. d. Blepharitis. Chapter 20. Visual Disturbances and Impaired Vision MULTIPLE CHOICE 1.A client is diagnosed with an inability to recognize visual information. The nurse realizes that which of the following cranial nerves is involved in the transmitting of visual stimuli to the brain for interpretation? 1. CNII 2. CNIII 3. CNIV 4. CN VI . 2.A client is diagnosed with a vision disorder. The nurse realizes that the client will experience an alteration in sensory information because the eyes transmit what percentage of all sensory information to the brain? 1.30% 2.50% 3.70% 4.90% 3.The nurse is performing an assessment on a client. To test the optic nerves function, what should the nurse do? 1.Check for extraocular movement. 2.Check the pupils for reaction to light. 3.Check to see if the patient can blink. 4.Use a Snellen chart. 4.The nurse realizes that a client, diagnosed with chronic dry eyes, may have a disorder of the lacrimal gland because it: 1.covers the eye for protection. 2.produces tears to lubricate the eye. 3.helps the eye keep its shape. 4. provides blood to the eye. 5. When assessing the corneal reflex, the nurse realizes this reflex is a function of which cranialnerve (CN)? 1. CNII 2. CNIII 3. CNIV 4. CN V 6.A client is having difficulty perceiving different colors. The nurse realizes the client may havea disorder that affects the photosensitive receptor cells of the retina, which makes the perception of color possible, or a disorder that affectsthe: 1.rods. 2.cones. 3.optic discs. 4.irises. 7.A client was assessed as having normal intraocular pressure. The nurse would document this clients pressure as being: 1.5 mmHg 3 mmHg. 2.15 mmHg 3mmHg. 3.30 mmHg 3mmHg. 4.50 mmHg 3mmHg. Chapter 21. Common Ear, Nose, and Throat Complaints Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An acutely presenting, erythematous, tender lump within the eyelid iscalled: a. Blepharitis b. Hordeolum c. Chalazion d. Iritis 2. The clinician is seeing a patient complaining of red eye. The clinician suspects conjunctivitis. The presence of mucopurulent discharge suggests which type ofconjunctivitis? a. Viralconjunctivitis b. Keratoconjunctivitis c. Bacterialconjunctivitis d. Allergicconjunctivitis 3. Which subtype of cataracts is characterized by significant nearsightedness and a slow indolent course? a. Nuclearcataracts b. Corticalcataracts c. Posteriorcataracts d. Immaturecataracts 4. Which of the following statements is true concerning the use of bilberry as a complementary therapy forcataracts? a. The body converts bilberry to vitamin A, which helps to maintain a healthylens. b. Bilberry blocks an enzyme that leads to sorbitol accumulation that contributes to cataract formation indiabetes. c. Bilberry boosts oxygen and blood delivery to theeye. d. Bilberry is a good choice for patients with diabetes as it does not interact with antidiabeticdrugs. 5. A 65-year-old man presents to the clinician with complaints of increasing bilateral peripheral vision loss, poor night vision, and frequent prescription changes that started 6 months previously.Recently, he has also been seeing halos around lights. The clinician suspects chronic open-angleglaucoma. Which of the following statements is true concerning the diagnosis of chronic open-angle glaucoma? a. The presence of increased intraocular pressure measured by tonometry is definitive for the diagnosis of open-angleglaucoma. b. The clinician can definitively diagnosis open-angle glaucoma based on the subjective complaints of thepatient. c. Physical diagnosis relies on gonioscopic evaluation of the angle by an ophthalmologist. d. Early diagnosis is essential in order to reverse any damage that has occurred to the optic nerve. 6. Acute angle-closure glaucoma involves a sudden severe rise in intraocular pressure. Which of the following ranges represents normal intraocularpressure? a. 0 to 7 mmHg b. 8 to 21 mmHg c. 22 to 40 mmHg d. 40 to 80 mmHg 7. As diabetic retinopathy progresses, the presence of ‘cotton wool’ spots can be detected. Cotton wool spots referto: a. Nerve fiber layerinfarctions b. Blood vesselproliferation c. Venous beading d. Retinalhemorrhage 8. Which of the following is an example of sensorineural hearingloss? a. Perforation of the tympanicmembrane b. Otosclerosis c. Cholesteatoma d. Presbycusis 9. The clinician is assessing a patient complaining of hearing loss. The clinician places a tuning fork over the patient’s mastoid process, and when the sound fades away, the fork is placed without restriking it over the external auditory meatus. The patient is asked to let the clinician know when the sound fades away. This is an example of which type oftest? a. Weber test b. Schwabachtest c. Rinnetest d. Auditory brainstem response (ABR)test 10. A patient presents to the clinician complaining of ear pain. On examination, the clinician finds that the patient has tenderness on traction of the pinna as well as when applying pressure over the tragus. These findings are classic signs of whichcondition? a. Otitismedia b. Meniere’sdisease c. Tinnitus d. Otitisexterna 11. Otitis media is considered chronicwhen: a. Inflammation persists more than 3 months with intermittent or persistent otic discharge. b. There are more than six occurrences of otitis media in a 1-yearperiod. c. Otitis media does not resolve after two courses ofantibiotics. d. All of theabove 12. The most significant precipitating event leading to otitis media with effusionis: a. Pharyngitis b. Allergies c. Viral upper respiratory infection(URI) d. Perforation of theeardrum 13. Patients with acute otitis media should be referred to a specialist in which of the following situations? a. Concurrent vertigo orataxia b. Failed closure of a ruptured tympanicmembrane c. If symptoms worsen after 3 or 4 days oftreatment d. All of theabove 14. Which immunoglobulin mediates the type 1 hypersensitivity reaction involved in allergicrhinitis? a. IgA b. IgE c. IgG d. IgM 15. Fluctuations and reductions in estrogen may be a contributing factor in which type ofrhinitis? a. Vasomotorrhinitis b. Rhinitismedicamentosum c. Atrophicrhinitis d. Viralrhinitis 16. Sinusitis is considered chronic when there are episodes of prolonged inflammation with repeated or inadequately treated acute infection lasting greaterthan: a. 4weeks b. 8weeks c. 12weeks d. 16weeks 17. Which of the following antibiotics provides the best coverage in acute or chronic sinusitis when gram-negative organisms aresuspected? a. PenicillinV b. Amoxicillin c. Levofloxacin d. Clindamycin 18. In which of the following situations would referral to a specialist be needed forsinusitis? a. Recurrentsinusitis b. Allergicsinusitis c. Sinusitis that is refractory to antibiotictherapy d. All of theabove 19. Which type of stomatitis results in necrotic ulceration of the oral mucousmembranes? a. Vincent’sstomatitis b. Allergicstomatitis c. Apthousstomatitis d. Herpeticstomatitis 20. The presence of hairy leukoplakia in a person with no other symptoms of immune suppression is strongly suggestive of which type ofinfection? a. HSV type2 b. HIV c. Pneumonia d. Syphilis 21. Heart valve damage resulting from acute rheumatic fever is a long-term sequelae resulting from infection with which of the followingpathogens? a. Coxsackievirus b. Cytomegalovirus c. Francisellatularensis d. Group Astreptococcus 22. A patient presents with the following signs and symptoms: gradual onset of low-grade fever, marked fatigue, severe sore throat, and posterior cervical lymphadenopathy. Based on the signs and symptoms alone, which of the following conditions is most likely thecause? a. Gonorrhea b. Mononucleosis c. Influenza d. Herpeszoster 23. A patient presents to the clinician with a sore throat, fever of 100.7F, and tender anterior cervical lymphadenopathy. The clinician suspects strep throat and performs a rapid strep test that is negative. What would the next stepbe? a. The patient should be instructed to rest and increase fluid intake as the infection is most likely viral and will resolve without antibiotictreatment. b. Because the patient does not have strep throat, the clinician should start broad spectrum antibiotics in order to cover the offendingpathogen. c. A throat culture should be performed to confirm the results of the rapid streptest. d. The patient should be treated with antibiotics for strep throat as the rapid strep test is not verysensitive. 24. Which of the following medications used in the treatment of glaucoma works by constricting the pupils to open the angle and allow aqueous fluid toescape? a. Pilocarpine b. Timolol c. Brinzolamide d. Acetazolamide 25. You have a patient who is a positive for Strep on rapid antigen testing (rapid strep test). You order amoxacillin after checking for drug allergies (patient is negative) but he returns 3 days later, reporting that his temperature has gone up, not down (101.5 F in office). You also note significant adenopathy, most notably in the posterior and anterior cervical chains, some hepatomegaly, and a diffuse rash. Youdecide: a. to refer thepatient. b. that he is having an allergic response and needs to be changed to a macrolide antibiotic. c. that his antibiotic dosage is not sufficient and should bechanged. d. that he possibly has mononucleosis concurrent with his strepinfection. 26. You are in the park playing with your children when you see that your friend is screaming for help. Her toddler has fallen and there is a stick lodged in his eye. The child is kicking and screaming and grabbing for the stick. You: a. instruct his mother to hold him securely and not allow him to touch the stick, then carefully remove the stick from theeye. b. stabilize the foreign object and accompany the mother and child to the localER. c. find a water fountain, hold the child to the water, and flush theeye. d. call 911. True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Severe pain associated with acute otitis media signifies perforation of the tympanicmembrane. Chapter 22. Hearing and Balance Disorders MULTIPLECHOICE 1.A client is not able to successfully pass the whisper test. Which of the following would be indicated for thisclient? 1. Head CT scan 2.Audiometry 3.MRI of thebrain 4.Electroencephalogram 2.A client is prescribed a medication that is ototoxic. The nurse realizes that this medication may cause: 1.permanent or temporary vision loss. 2.permanent or temporary hearing loss. 3.nausea and vomiting. 4.central nervous system (CNS) depression. 3.The nurse is trying to communicate with a hearing-impaired client. The best way to do this is to: 1.write down all of the message. 2. shout in the impairedear. 3. speak slowly and clearly while facing theclient. 4.talk in a regular voice in the goodear. . 4.A client is diagnosed with a conductive hearing loss. The nurse realizes type of hearing loss is not associated with: 1.cerumen. 2.brain damage. 3.otitis media. 4.otosclerosis. 5.A client is complaining of dizziness, unilateral ringing in the ear, feeling of pressure or fullness in the ear, and unilateral hearing loss. The nurse would suspect the client is experiencing: 1.Mnires disease. 3.otitis media. 4.mastoiditis. 6.A client complains of a slight itching, slight pain, and a scratching sound in the ear. The nurse suspects that an insect may have entered the ear. Which of the following should not be done? 1.Add water to flush out the insect. 2.Add mineral oil to kill the insect. 3.Add lidocaine to kill the insect. 4.Call an otologist for a referral. 7.The hearing of an unresponsive client needs to be assessed. Which of the following will be usedto assess the hearing of thisclient? 1. Audiometer 2. Brainstem auditory evoked responses (BAER)test 3.Rinnetest 4.Weber test . 8.The nurse is planning to assess a client diagnosed with conductive hearing loss. When performing the Weber test, the nurse would expect which of the following findings? 2. The sound will be louder in the goodear. 3. Air conduction is shorter than bone conduction. 4.No sounds will beheard. 9.The nurse is performing postoperative teaching with a client recovering from a stapedectomy. Which of the following instructions would the nurse want to include in the teaching? 1.It is okay to resume exercise the next day. 2.It is okay to resume work the same day. 3. It is okay to shower and shampoo the nextday. 4. It is okay to blow the nose gently one side at atime. 10.After a mastoidectomy, the most important complication for the nurse to assess for is: 1.vomiting. 2. headache. 3. fever. 4. stiff neck. 11.When instructing a client on cleaning the ear, the nurse should instruct the client to clean: 1. only the outerear. 2. all the way to the middleear. 3. all parts of the ear outer, middle, and inner ear. 4.just the tympanicmembrane. . 12.Which of the following would prohibit an elderly client from wanting to obtain and use a hearing aid? 1. Fears sounds will be tooloud 2. Thinks not necessary for a temporary problem 3.Fears thecost 4.Prefers silence 13.Which of the following should the nurse instruct a client who is being fitted for a hearing aid? 1.Keep the appliance turned on at all times. 2.Store the hearing aid in a warm, moist place. 3.Batteries last for at least 1 month. 4.Clean ear molds at least once a week. . MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1.The nurse is instructing a client diagnosed with otitis media on management during the acute phase. Which of the following should the nurse include in the teaching? (Select all that apply.) 1. Take the antibiotics asordered. 2. Take over-the-counter analgesics for mild pain asrecommended. 3.It is okay to goswimming. 4.It is okay to go on vacation and trips that require flying. 5.If excruciating pain develops, seek medical care. 6.Limit fluids. . 2.When caring for a client with total hearing loss, the nurse is instructing the client about the many options that are available to function in a hearing world. Which of the following should the nurse include? (Select all that apply.) 1.Flashing lights for alarms 2.TV with closed captions 3.Talking computer 4.Lip reading and sign language 5.Cell phones with headsets 6.Loud ringers on telephones 3.A client is diagnosed with a congenital hearing loss. Which causes does the nurse realize are reasons for this type of hearing loss? (Select all that apply.) 1.Genetics 2.Natal infections 3.Physical deformities 4.Noise levels 5.Maternal ototoxic drugs 6.Maternal TORCH infections 4.A client with a family history of hearing loss asks the nurse what he can do to prevent this disorder as he ages. Which of the following should the nurse instruct this client? (Select all that apply.) 1.Turn down radio and television volume. 2.Avoid noisy areas such as rock concerts. 3.Wear protective devices. 4.Use plain cotton balls in the ears. 5.Avoid sun exposure. 6.Flush the ears daily with mineral oil. 5.Which of the following are indications that a client has been exposed to excessive noise? (Select all that apply.) 1.Raising the voice to talk in normal conversation 2.Clear drainage from the ears 3.Inability to hear a conversation 2 feet away 4.Sounds are muffled 5. Ringing of theears 6. Short periods of pain in the ears Chapter 23. Inflammatory and Infectious Disorders of the Ear MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The nurse needs to pull the portion of the ear that consists of movable cartilage and skin down and back when administering eardrops. This portion of the ear is calledthe: a. Auricle. b. Concha. c. Outermeatus. d. Mastoid process. ANS:A The external ear is called the auricle or pinna and consists of movable cartilage and skin. 2. The nurse is examining a patients ears and notices cerumen in the external canal. Which of these statements about cerumen iscorrect? a. Sticky honey-colored cerumen is a sign ofinfection. b. The presence of cerumen is indicative of poorhygiene. c. The purpose of cerumen is to protect and lubricate theear. d. Cerumen is necessary for transmitting sound through the auditory canal. . 3. When examining the ear with an otoscope, the nurse notes that the tympanic membrane should appear: a. Light pink with a slightbulge. b. Pearly gray and slightlyconcave. c. Pulled in at the base of the cone oflight. d. Whitish with a small fleck of light in the superior portion. 4. The nurse is reviewing the structures of the ear. Which of these statements concerning the eustachian tube istrue? a. The eustachian tube is responsible for the production ofcerumen. b. It remains open except when swallowing oryawning. c. The eustachian tube allows passage of air between the middle and outerear. d. It helps equalize air pressure on both sides of the tympanic membrane. . 5. A patient with a middle ear infection asks the nurse, What does the middle ear do? The nurse responds by telling the patient that the middle ear functionsto: a. Maintainbalance. b. Interpret sounds as they enter theear. c. Conduct vibrations of sounds to the innerear. d. Increase amplitude of sound for the inner ear to function. 6. The nurse is reviewing the function of the cranial nerves (CNs). Which CN is responsible for conducting nerve impulses to the brain from the organ ofCorti? a. I b. III c. VIII d. XI . 7. The nurse is assessing a patient who may have hearing loss. Which of these statements is trueconcerning airconduction? a. Air conduction is the normal pathway forhearing. b. Vibrations of the bones in the skull cause airconduction. c. Amplitude of sound determines the pitch that isheard. d. Loss of air conduction is called a conductive hearing loss. . 8. A patient has been shown to have a sensorineural hearing loss. During the assessment, it would be important for the nurseto: a. Speak loudly so the patient can hear thequestions. b. Assess for middle ear infection as a possiblecause. c. Ask the patient what medications he is currentlytaking. d. Look for the source of the obstruction in the external ear. 9. During an interview, the patient states he has the sensation that everything around him is spinning. The nurse recognizes that the portion of the ear responsible for this sensation isthe: a. Cochlea. b. CNVIII. c. Organ ofCorti. d. Labyrinth. 10. A patient in her first trimester of pregnancy is diagnosed with rubella. Which of these statements is correct regarding the significance of this in relation to the infantshearing? a. Rubella may affect the mothers hearing but not theinfants. b. Rubella can damage the infants organ of Corti, which will impairhearing. c. Rubella is only dangerous to the infant in the second trimester ofpregnancy. d. Rubella can impair the development of CN VIII and thus affect hearing. 11. The mother of a 2-year-old is concerned because her son has had three ear infections in thepast year. What would be an appropriate response by thenurse? It is unusual for a small child to have frequent ear infections unless something else is a. b. c. d. wrong. We need to check the immune system of your son to determine why he is having so many ear infections. Ear infections are not uncommon in infants and toddlers because they tend to have more cerumen in the external ear. Your sons eustachian tube is shorter and wider than yours because of his age, which allows for infections to develop more easily. 12. A 31-year-old patient tells the nurse that he has noticed a progressive loss in his hearing. He says that it does seem to help when people speak louder or if he turns up the volume of a television or radio. The most likely cause of his hearing lossis: a. Otosclerosis. b. Presbycusis. c. Trauma to thebones. d. Frequent ear infections. . 13. A 70-year-old patient tells the nurse that he has noticed that he is having trouble hearing, especially in large groups. He says that he cant always tell where the sound is coming from andthe words often sound mixed up. What might the nurse suspect as the cause for thischange? a. Atrophy of the apocrineglands b. Cilia becoming coarse andstiff c. Nerve degeneration in the innerear d. Scarring of the tympanic membrane 14. During an assessment of a 20-year-old Asian patient, the nurse notices that he has dry,flaky cerumen in his canal. What is the significance of this finding? Thisfinding: a. Is probably the result of lesions from eczema in hisear. b. Represents poorhygiene. c. Is a normal finding, and no further follow-up isnecessary. d. Could be indicative of change in cilia; the nurse should assess for hearing loss. e. 15. The nurse is taking the history of a patient who may have a perforated eardrum. What wouldbe an important question in thissituation? a. Do you ever notice ringing or crackling in yourears? b. When was the last time you had your hearingchecked? c. Have you ever been told that you have any type of hearingloss? d. Is there any relationship between the ear pain and the discharge you mentioned? 16. A 31-year-old patient tells the nurse that he has noticed pain in his left ear when people speak loudly to him. The nurse knows that thisfinding: a. Is normal for people of hisage. b. Is a characteristic ofrecruitment. c. May indicate a middle earinfection. d. Indicates that the patient has a cerumen impaction. 17. While discussing the history of a 6-month-old infant, the mother tells the nurse that she took a significant amount of aspirin while she was pregnant. What question would the nurse want to include in thehistory? a. Does your baby seem to startle with loudnoises? b. Has your baby had any surgeries on herears? c. Have you noticed any drainage from herears? d. How many ear infections has your baby had since birth? 18. The nurse is performing an otoscopic examination on an adult. Which of these actions iscorrect? a. Tilting the persons head forward during theexamination b. Once the speculum is in the ear, releasing thetraction c. Pulling the pinna up and back before inserting thespeculum d. Using the smallest speculum to decrease the amount of discomfort 19. The nurse is assessing a 16-year-old patient who has suffered head injuries from a recent motor vehicle accident. Which of these statements indicates the most important reason for assessing for any drainage from the earcanal? a. If the drum has ruptured, then purulent drainage willresult. b. Bloody or clear watery drainage can indicate a basal skullfracture. c. The auditory canal many be occluded from increasedcerumen. d. Foreign bodies from the accident may cause occlusion of the canal. 20. In performing a voice test to assess hearing, which of these actions would the nurseperform? a. Shield the lips so that the sound ismuffled. b. Whisper a set of random numbers and letters, and then ask the patient to repeatthem. c. Ask the patient to place his finger in his ear to occlude outsidenoise. d. Stand approximately 4 feet away to ensure that the patient can really hear at this distance. 21. In performing an examination of a 3-year-old child with a suspected ear infection, the nurse would: a. Omit the otoscopic examination if the child has afever. b. Pull the ear up and back before inserting thespeculum. c. Ask the mother to leave the room while examining thechild. d. Perform the otoscopic examination at the end of the assessment. . 22. The nurse is preparing to perform an otoscopic examination of a newborn infant.Which statement is true regarding thisexamination? a. Immobility of the drum is a normalfinding. b. An injected membrane would indicate aninfection. c. The normal membrane may appear thick andopaque. d. The appearance of the membrane is identical to that of an adult. . 23. The nurse assesses the hearing of a 7-month-old by clapping hands. What is the expected response? The infant: a. Turns his or her head to localize thesound. b. Shows no obvious response to thenoise. c. Shows a startle and acoustic blinkreflex. d. Stops any movement, and appears to listen for the sound. 24. The nurse is performing an ear examination of an 80-year-old patient. Which of these findings would be considerednormal? a. High-tone frequencyloss b. Increased elasticity of thepinna c. Thin, translucentmembrane d. Shiny, pink tympanic membrane 25. An assessment of a 23-year-old patient reveals the following: an auricle that is tender and reddish-blue in color with small vesicles. The nurse would need to know additional information that includes which ofthese? a. Any change in the ability tohear b. Any recent drainage from theear c. Recent history of trauma to theear d. Any prolonged exposure to extreme cold 26. While performing the otoscopic examination of a 3-year-old boy who has been pulling on hisleft ear, the nurse finds that his left tympanic membrane is bright red and that the light reflex is not visible. The nurse interprets these findings to indicatea(n): a. Fungalinfection. b. Acute otitismedia. c. Perforation of theeardrum. d. Cholesteatoma. 27. The mother of a 2-year-old toddler is concerned about the upcoming placement of tympanostomy tubes in her sons ears. The nurse would include which of these statements in the teachingplan? a. The tubes are placed in the innerear. b. The tubes are used in children with sensorineuralloss. c. The tubes are permanently inserted during a surgicalprocedure. d. The purpose of the tubes is to decrease the pressure and allow for drainage. . 28. In an individual with otitis externa, which of these signs would the nurse expect to findon assessment? a. Rhinorrhea b. Periorbitaledema c. Pain over the maxillarysinuses d. Enlarged superficial cervical nodes 29. When performing an otoscopic examination of a 5-year-old child with a history of chronic ear infections, the nurse sees that his right tympanic membrane is amber-yellow in color and that air bubbles are visible behind the tympanic membrane. The child reports occasional hearing loss and a popping sound with swallowing. The preliminary analysis based on this information is that thechild: a. Most likely has serous otitismedia. b. Has an acute purulent otitismedia. c. Has evidence of a resolvingcholesteatoma. d. Is experiencing the early stages of perforation. 30. The nurse is performing an assessment on a 65-year-old man. He reports a crusty nodule behind the pinna. It intermittently bleeds and has not healed over the past 6 months. On physical assessment, the nurse finds an ulcerated crusted nodule with an indurated base. The preliminary analysis in this situation is thatthis: a. Is most likely a benign sebaceouscyst. b. Is most likely akeloid. c. Could be a potential carcinoma, and the patient should be referred for abiopsy. d. Is a tophus, which is common in the older adult and is a sign of gout. . 31. The nurse suspects that a patient has otitis media. Early signs of otitis media include which of these findings of the tympanicmembrane? a. Red andbulging b. Hypomobility c. Retraction with landmarks clearlyvisible d. Flat, slightly pulled in at the center, and moves with insufflation . 32. The nurse is performing a middle ear assessment on a 15-year-old patient who has had a history of chronic ear infections. When examining the right tympanic membrane, the nurse sees the presence of dense white patches. The tympanic membrane is otherwise unremarkable. It is pearly, with the light reflex at 5 oclock and landmarks visible. The nurseshould: a. Refer the patient for the possibility of a fungalinfection. b. Know that these are scars caused from frequent earinfections. c. Consider that these findings may represent the presence of blood in the middle ear. Be concerned about the ability to hear because of this abnormality on thetympanic d. membrane. . 33. The nurse is preparing to do an otoscopic examination on a 2-year-old child. Which one ofthese reflects the correctprocedure? a. Pulling the pinnadown b. Pulling the pinna up andback c. Slightly tilting the childs head toward theexaminer d. Instructing the child to touch his chin to his chest . 34. The nurse is conducting a child safety class for new mothers. Which factor places young children at risk for earinfections? a. Familyhistory b. Airconditioning c. Excessivecerumen d. Passive cigarette smoke 35. During an otoscopic examination, the nurse notices an area of black and white dots on the tympanic membrane and the ear canal wall. What does this findingsuggest? a. Malignancy b. Viralinfection c. Blood in the middleear d. Yeast or fungal infection 36. A 17-year-old student is a swimmer on her high schools swim team. She has had three bouts of otitis externa this season and wants to know what to do to prevent it. The nurse instructs herto: a. Use a cotton-tipped swab to dry the ear canals thoroughly after eachswim. b. Use rubbing alcohol or 2% acetic acid eardrops after everyswim. c. Irrigate the ears with warm water and a bulb syringe after eachswim. d. Rinse the ears with a warmed solution of mineral oil and hydrogenperoxide. 37. During an examination, the patient states he is hearing a buzzing sound and says that it is driving me crazy! The nurse recognizes that this symptomindicates: a. Vertigo. b. Pruritus. c. Tinnitus. d. Cholesteatoma. 38. During an examination, the nurse notices that the patient stumbles a little while walking, and, when she sits down, she holds on to the sides of the chair. The patient states, It feels like the room is spinning! The nurse notices that the patient isexperiencing: a. Objectivevertigo. b. Subjectivevertigo. c. Tinnitus. d. Dizziness. . 39. A patient has been admitted after an accident at work. During the assessment, the patient is having trouble hearing and states, I dont know what the matter is. All of a sudden, I cant hear you out of my left ear! What should the nurse donext? a. Make note of this finding for the report to the nextshift. b. Prepare to remove cerumen from the patientsear. c. Notify the patients health careprovider. d. Irrigate the ear with rubbing alcohol. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. The nurse is testing the hearing of a 78-year-old man and is reminded of the changes inhearing that occur with aging that include which of the following? Select all thatapply. a. Hearing loss related to aging begins in the mid40s. b. Progression of hearing loss isslow. c. The aging person has low-frequency toneloss. d. The aging person may find it harder to hear consonants thanvowels. e. Sounds may be garbled and difficult tolocalize. f. Hearing loss reflects nerve degeneration of the middle ear. Chapter 24. Inflammatory and Infectious Disorders of the Nose, Sinuses, Mouth, and Throat 1.A child is diagnosed with severe allergic rhinitis. Which of the following manifestations would the nurse most likely assess in this client? 1.Edematous neck glands 2.Reduced hearing 3.Pruritis 4.Frequent wiping of the nose with the palm of the hand . 2.A client tells the nurse that she experiences a stuffy nose, nasal pain, and postnasal drip every time she works in her companys office. Which of the following types of allergic rhinitis is this client most likely experiencing? 1.Infectious 2.Perennial 3.Occupational 4.Seasonal 3.A client asks the nurse if there is an antihistamine that does not cause drowsiness. Which of the following medications would this client most likely prefer to treat allergic rhinitis? 1.Diphenhydramine 2.Chlorpheniramine maleate 3.Clemastine 4.Fexofenadine 4.A client diagnosed with hypertension is experiencing allergic rhinitis. The nurse realizes that the medication that would not be indicated for this client would be: 1.loratadine. 2.montelukast. 4.zafirlukast. 5.A 16-year-old client is being prescribed a medication to treat acute sinusitis. The nurse realizes that this client should not be prescribed: 1.amoxicillin. 2.cefuroxime. 3.ciprofloxacin. 4.erythromycin. 6.The nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with acute sinusitis. Which of the following symptoms is the client most likely experiencing? 1.Anosmia 2.Fever 3.Halitosis 4.Metallic taste . 7.The nurse is planning care for the client diagnosed with viral rhinitis. Which of the following would be the best goal of care for this client? 1.Prevent secondary bacterial infection. 2.Prevent rhinitis medicamentosa. 4.Encourage complete participation in activities. 8.The nurse is instructing the mother of a client recovering from a tonsillectomy. Which of the following should the nurse instruct the mother to report? 1.Difficulty swallowing 2.Difficulty talking 3.Excessive swallowing 4.Pain 9.Which of the following should the nurse instruct a client recovering from a tonsillectomy? 1.Drink milk to promote healing. 2. Gargle with saltwater. 3. Maintain good hydration. 4.Use a straw todrink. . 11.A client has been diagnosed with stage IV cancer of the larynx. The nurse realizes that which of the following surgeries is recommended for this type of cancer? 1. Hemilaryngectomy 2. Partial laryngectomy 3.Supraglottic laryngectomy 4.Totallaryngectomy . 12.A client is recovering from a total laryngectomy with the placement of a tracheostomy. The nurse should include which of the following instructions to this client? 1.Clean the tracheostomy tube with soap and water daily. 2.Limit protein in the diet. 3. Restrictfluids. 4. The nasogastric tube will be in for 2weeks. 13.A client diagnosed with viral rhinitis tells the nurse that she has been using a decongestant nasal spray for several weeks and the symptoms are getting worse. Which of the following does the nurse suspect is occurring with this client? 1.Developing pneumonia 2.Subacute rhinitis 3.Rhinitis medicamentosa 4.Chronic otitis media MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1.The nurse is teaching a client how to use a nasal spray. Which of the following should be included in these instructions? (Select all that apply.) 1. Blow the nose before instilling thespray. 2. Tilt the head back and angle the tip of the bottle to the side of the nostril. 3.Use a finger to occlude the nostril that is not receiving thespray. 4.Inhale gently and evenly while discharging the spray into the nostril. 5.If a second spray is recommended, immediately repeat the procedure. 6.Blow the nose after administration of the spray. . 2.A client has been diagnosed with allergic rhinitis. Which of the following should the nurse instruct the client regarding strategies to avoid this disorder? (Select all that apply.) 1. Remove homecarpeting 2. Reduce the use of an air conditioner 3.Remove pets from thehome 4.Open windows in the spring and summer 5.Use feather pillows 6.Wash bed linens in cold water 3.A client is demonstrating signs of chronic sinusitis. Which of the following will the nurse most likely assess in this client? (Select all that apply.) 1. Facialpain 2. Fever 3.Headache 4.Toothache 5.Fatigue 6.Swollen neck glands 4.With which of the following can the nurse instruct a client who is experiencing pain from a sore throat? (Select all that apply.) 1.Gargle with warm salt water. 2.Eat salty foods. 3. Suck on hard candy. 4. Drinkfluids. 5. Avoid citrus fruits. 6.Suck onpopsicles. 5.A client is demonstrating signs of peritonsillar abscess. Which of the following will the nurse most likely assess in this client? (Select all that apply.) 1. Bradypnea 2. Drop in blood pressure 3.Hot potato voice 4.Trismus 5.Dysphagia 6.Sore throat Chapter 25. Epistaxis 1.A client is experiencing epistaxis. Which of the following interventions would the nursecomplete? 1. Call thedoctor. 2. Check laboratory testresults. 3. Obtain an emesisbasin. 4. Show the patient how to pinch thenose. 2. A woman who is in the second trimester of pregnancy mentions that she has had more nosebleeds than ever since she became pregnant. The nurse recognizes that this is a resultof: a. A problem with the patients coagulationsystem. b. Increased vascularity in the upper respiratory tract as a result of thepregnancy. c. Increased susceptibility to colds and nasalirritation. d. Inappropriate use of nasal sprays. Chapter 26. Temporomandibular Disorders 1. The articulation of the mandible and the temporal bone is known asthe: a. Intervertebralforamen. b. Condyle of themandible. c. Temporomandibularjoint. d. Zygomatic arch of the temporal bone. . 2. To palpate the temporomandibular joint, the nurses fingers should be placed in the depression of theear. a. Distal to thehelix b. Proximal to thehelix c. Anterior to thetragus d. Posterior to the tragus 3. Bones classified as irregular wouldinclude: a. skull bones. b. themandible. c. wrist bones. d. thefemur. 4. The articulation of the mandible and the temporal bone is known asthe: a. Intervertebralforamen. b. Condyle of themandible. c. Temporomandibularjoint. d. Zygomatic arch of the temporal bone. . 5. To palpate the temporomandibular joint, the nurses fingers should be placed in the depression of theear. a. Distal to thehelix b. Proximal to thehelix c. Anterior to thetragus d. Posterior to the tragus 56 A patient states, Whenever I open my mouth real wide, I feel this popping sensation in front of my ears. To further examine this, the nurse would: a. Place the stethoscope over the temporomandibular joint, and listen forbruits. b. Place the hands over his ears, and ask him to open his mouth reallywide. c. Place one hand on his forehead and the other on his jaw, and ask him to try to open hismouth. d. Place a finger on his temporomandibular joint, and ask him to open and close his mouth. . Chapter 27. Dysphonia 1. During an assessment, the nurse knows that expected assessment findings in the normal adultlung include the presenceof: a. Adventitious sounds and limited chestexpansion. b. Increased tactile fremitus and dull percussiontones. c. Muffled voice sounds and symmetric tactilefremitus. d. Absent voice sounds and hyperresonant percussion tones. 2. The nurse is assessing voice sounds during a respiratory assessment. Which of these findings indicates a normal assessment? Select all thatapply. Voice sounds are faint, muffled, and almost inaudible when the patient whispers one, two, a. three in a very softvoice. As the patient repeatedly says ninety-nine, the examiner clearly hears the words ninety- b. nine. When the patient speaks in a normal voice, the examiner can hear a sound but cannot c. exactly distinguish what is beingsaid. d. As the patient says a long ee-ee-ee sound, the examiner also hears a long ee-ee-eesound. e. As the patient says a long ee-ee-ee sound, the examiner hears a long aaaaaa sound. Chapter 28. Common Respiratory Complaints Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A chronic cough lasts longerthan: a. 3weeks b. 1month c. 6 months d. 1 year 2. You are doing a cerumen extraction and touch the external meatus of your patient’s ear. He winces and starts coughing. What is the name of thisreflex? a. Bakerphenomenon b. Arnoldreflex c. Coughreflex d. Tragusreflex 3. Julie has a postnasal drip along with her cough. You assess herfor: a. Asthma b. Sinusitis c. Allergic or vasomotorrhinitis d. Influenza 4. A patient with hypertension comes in and insists that one of his new medications is causing him to cough. When looking at his list of medications, you think the cough must befrom: a. Metoprolol b. Clopidogrel c. Tadalafil d. Captopril 5. African American patients seem to have a negative reaction to which of the following asthma medications? a. Inhaledcorticosteroids b. Long-term beta-agonistbronchodilators c. Leukotriene receptoragonists d. Oralcorticosteroids 6. Sam, age 78, presents to the clinic with respiratory symptoms. His pulmonary function tests are as follows: a normal total lung capacity, a decreased PaO2, and an increased PaCO2. On assessment, you auscultate coarse crackles and forced expiratory wheezes. What is yourdiagnosis? a. Asthma b. Emphysema c. Chronicbronchitis d. Influenza 7. You are using the CURB-65 clinical prediction tool to decide whether Mabel, whom you have diagnosed with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), should be hospitalized or treated athome. Her score is 3. What should youdo? a. Consider hometreatment. b. Plan for a short inpatienthospitalization. c. Closely supervise her outpatienttreatment. d. Hospitalize and consider admitting her to the intensive careunit. 8. Why do you suspect that your patient may have a decreased response to the tuberculin skin test (TBT)? a. She is on a high-proteindiet. b. She is anadolescent. c. She has been on long-term corticosteroidtherapy. d. She just got over acold. 9. Marci has been started on a tuberculosis (TB) regimen. Because isoniazid (INH) may cause peripheral neuropathy, you consider ordering which of the following drugsprophylactically? a. Pyridoxine b. Thiamine c. Probiotic d. Phytonadione 10. Jolene has breast cancer that has been staged as T1, N0, M0. What might thismean? a. The tumor size cannot be evaluated; the cancer has not spread to the lymphnodes; and the distant spread cannot beevaluated. b. The cancer is in situ; it is spreading into the lymph nodes, but the spread cannotbe evaluatedotherwise. c. The cancer is less than 2 cm in size and has not spread to the lymph nodes or other parts of thebody. d. The cancer is about 5 cm in size; nearby lymph nodes cannot be evaluated; and there is no evidence of distantspreading. 11. Nathan, a 32-year-old policeman, has a 15-pack-a-year history of smoking and continues to smoke heavily. During every visit, he gets irate when you try to talk to him about quitting. What should you do? a. Hand him literature about smoking cessation at everyvisit. b. Wait until he is ready to talk to you aboutquitting. c. Document in the record that he is not ready toquit. d. Continue to ask him at every visit if he is ready toquit. 12. Your patient has decided to try to quit smoking with Chantix. You are discussing his quit date, and he will begin taking the medicine tomorrow. When should he plan to quitsmoking? a. He should stop smoking today. b. He should stop smoking tomorrow. c. His quit date should be in 1week. d. He will be ready to quit after the first 30days. 13. Which information should be included when you are teaching your patient about the use of nicotine gum? a. The gum must be correctly chewed to a softened state and then placed in the buccalmucosa. b. Patients should not eat for 30 minutes prior to or during the use of thegum. c. Initially, one piece is chewed every 30 minutes whileawake. d. Acidic foods and beverages should be encouraged during nicotinetherapy. 14. Your patient states he has a strep throat infection. Which of the following symptoms makes you consider a viral etiologyinstead? a. Fever b. Headache c. Exudativepharyngitis d. Rhinorrhea 15. What is the first-line recommended treatment against Group A -hemolytic streptococci (GABHS), the most common cause of bacterialpharyngitis? a. Penicillin b. Quinolone c. Cephalosporin d. Macrolide 16. Cydney presents with a history of asthma. She has not been treated for a while. She complains of daily but not continual symptoms, greater than 1 week and at nighttime. She has been using her rescue inhaler. Her FEV1 is 60% to 80% predicted. How would you classify her asthmaseverity? a. Mildintermittent b. Mildpersistent c. Moderatepersistent d. Severepersistent 17. Joyce is taking a long-acting beta agonist for her asthma. What additional medication should she be taking? a. Inhaledcorticosteroid b. Leukotriene receptorantagonist c. Systemiccorticosteroid d. Methylxanthenes 18. Your patient is on Therabid for his asthma. You want to maintain his serum levelsbetween: a. 0 to 5mcg/mL b. 5 to 10mcg/mL c. 5 to 15mcg/mL d. 10 to 20mcg/mL 19. George has chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and an 80% forced expiratory volume in 1 second. How would you classify the severity of hisCOPD? a. Stage 1 mildCOPD b. Stage 2 moderateCOPD c. Stage 3 severeCOPD d. Stage 5 very severeCOPD 20. Most nosocomial pneumonias are causedby: a. Fungi b. Viruses c. Gram-negativebacteria d. Pneumococcalpneumonia 21. Which of the following statements regarding TST istrue? a. Tests should be read 48 hours after theinjection. b. The size of the TST reaction has nothing to do with erythema but is based solely oninduration. c. It is a type V T cell-mediated immuneresponse. d. The diameter of the induration is measured incentimeters. 22. Which obstructive lung disease is classified asreversible? a. Asthma b. Chronicbronchitis c. Emphysema d. COPD 23. You have taught Jennifer, age 15, about using a flow meter to assess how to manage her asthma exacerbations. She calls you today because her peak expiratory flow rate is 65%. What would you tellher? a. “Take your short-acting beta-2 agonist, remain quiet, and call backtomorrow.” b. “Use your rescue inhaler, begin the prescription of oral glucocorticoids you have, and call backtomorrow.” c. “Drive to the emergency roomnow.” d. “Call 911.” 24. Which statement about adenocarcinoma of the lung isaccurate? a. It is the least common type of lung cancer, representing approximately 5% to10% ofcases. b. It is the most prevalent carcinoma of the lungs in both sexes and in nonsmokers, representing 35% to 40% of alltumors. c. It is more common in men than in women and occurs almost entirely in cigarette smokers. d. It is aggressive, with rapid growth and early local and distant metastases via the lymphatic and bloodvessels. 25. Jason, age 62, has obstructive sleep apnea. What do you think is one of his contributingfactors? a. He is a recovering alcoholic of 6years. b. His collar size is 17inches. c. He is the only person in his family who hasthis. d. He is extremelythin. 26. The forced vital capacity is decreasedin: a. Asthma b. Chronicbronchitis c. Emphysema d. Restrictivedisease 27. The most common cause of CAPis? a. Streptococcuspneumoniae b. Klebsiellapneumoniae c. Legionellapneumoniae d. Pseudomonasaeruginosa 28. Which of the following patients would you expect to have a decreased response toTST? a. Julie, a 50-year-old postalworker b. Sandy, a 40-year-old patient who recently survived a fire that left 40% of her total body surface covered inburns c. Jill, a 16-year-oldcheerleader d. Mark, a 29-year-old tennisplayer 29. Which of the following is a possible consequence of sleepapnea? a. Asthma b. Increased white bloodcells c. Insulinresistance d. Hyperactivity 30. Which of the following conditions is associated with cigarettesmoking? a. Glaucoma b. Increased spermquality c. Bladdercancer d. Eczema 31. Marta is taking TB drugs prophylactically. How do you instruct her to takethem? a. Take them on an empty stomach to facilitateabsorption. b. Take them with aspirin (ASA) to preventflushing. c. Take them with ibuprofen to prevent aheadache. d. Take them with food to preventnausea. 32. Which of the following statements regarding pulmonary function istrue? a. Cigarette smoking accelerates the decline in pulmonary functiontenfold. b. Smoking cessation can reverse most pathologicalchanges. c. Cigarette smoking decreases mucusproduction. d. There is a normal age-related decline in pulmonaryfunction. 33. The barrel chest characteristic of emphysema is a resultof: a. Chroniccoughing b. Hyperinflation c. Polycythemia d. Pulmonary hypertension 34. Supplemental oxygen for how many hours per day has been shown to improve the mortality associated withCOPD? a. 3 to 5 hours b. 6 to 10hours c. 11 to 14 hours d. 15 to 18 hours 35. Which ethnic group has the highest lung cancer incidence and mortalityrates? a. African Americanmen b. Scandinavian men and women c. Caucasianwomen d. Asianme Chapter 29. Sleep Apnea 1. The use of a continuous positive airway pump in the treatment of sleep apneawill: a. reducebronchospasm. b. force expansion of pleuralmembranes. c. maintain an openairway. d. awaken the person and increaserespirations. 2.A client diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is experiencing pneumonia. The nurse applies oxygen at 2 L/min via nasal cannula. When the nurse leaves the room, a family member increases the oxygen to 5 L. Which complication may occur? a.Angina b.Apnea c.Metabolic acidosis d.Respiratory alkalosis 3. Jason, age 62, has obstructive sleep apnea. What do you think is one of his contributingfactors? a. He is a recovering alcoholic of 6years. b. His collar size is 17inches. c. He is the only person in his family who hasthis. d. He is extremely thin. 4. Which of the following is a possible consequence of sleepapnea? a. Asthma b. Increased white bloodcells c. Insulinresistance d. Hyperactivity Chapter 30. Infectious Respiratory Disorders MULTIPLE CHOICE 1.The nurse is reviewing clients for risk factors in the development of pneumonia. Which of the following clients would be at the highest risk for developing this disorder? 1.A 48-year-old client experiencing menopause 2.An 18-year-old client with abdominal pain 3.A 23-year-old client diagnosed with sickle-cell anemia and a cough 4.A 3-year-old client with fever . 2.A client diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is experiencing pneumonia. The nurse applies oxygen at 2 L/min via nasal cannula. When the nurse leaves the room, a family member increases the oxygen to 5 L. Which complication may occur? 1.Angina 2.Apnea 3.Metabolic acidosis 4.Respiratory alkalosis 3.The nurse has a positive PPD during the last testing cycle for tuberculosis. Which of the following is indicated for this nurse? 1. Nothing 2. Chest x-rays every 2 months 3.Pharmacological treatment 4.Admission for inpatienttreatment 4.A client undergoes a purified protein derivative (PPD) test. The test should be read: 1.immediately after the test. 2.24 to 48 hours after the test. 3.48 to 72 hours after the test. 4.anytime after 72 hours. 5.The nurse is instructing a client on ways to reduce the transmission of tuberculosis. Which of the following should be included in these instructions? 1. The disease is transmitted by inhaling droplets exhaled by an infectedperson. 2. The disease is transmitted by not fully cookingfoods. 3.The disease is transmitted by not washinghands. 4.The disease is transmitted by sexual contact. 6.A client receiving oral medications for the treatment of tuberculosis develops hepatitis. Which of the following medications would be indicated for the client at this time? 1.Ethambutol 2.Isoniazid 3.Rifampin 4.Streptomycin 7.The spouse of a client diagnosed with tuberculosis is to begin isoniazid prophylactic therapy. Which of the following should the nurse instruct the spouse regarding length of time to take this medication? The medication should be taken for: 1.10 to 24days. 2.1 to 3months. 3.4 to 7months. 4.6 to 12 months. 8.A client diagnosed with a lung abscess is being prescribed antibiotic therapy. Which of the following medications would be indicated if this client has a history of penicillin allergy? 1.Metronidazole 2.Clindamycin 3.Ampicillin 4.Steroid 9.A client diagnosed with a hemothorax has had a chest tube inserted and attached to a portable water-seal drainage system. Which of the following interventions would be inappropriate for this client? 1. Clamp the tubing whenambulating. 2. Date and mark the amount of drainage in the collection chamber every shift. 3.Monitor the suction chamber for continuousbubbling. 4.Watch the water-seal chamber for fluctuation. 10.A clients chest tube has been accidentally dislodged while the client was being transferred from the bed to a stretcher. Which of the following should the nurse do to help this client? 1.Cover the site with occlusive petroleum jelly gauze and tape to four sides. 2.Cover the site with occlusive petroleum jelly gauze and tape to three sides. 3.Cover the site with occlusive petroleum jelly gauze and tape to two sides. 4.Cover the site with occlusive petroleum jelly gauze and tape to one side. 11.A client is diagnosed with fractured ribs. Which of the following should the nurse instruct this client? 1.Engage in routine activities of daily living after taking pain medication. 2.Splint the rib cage when deep breathing and coughing. 3. Restrictfluids. 4. Stay on bed rest until the ribs heal. 12.A client is prescribed a diuretic for treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Which of the following should the nurse instruct the client regarding this medication? 1. This medication expands the bloodvessels. 2. This medication causes smooth muscle relaxation to reduce pulmonaryengorgement. 3.This medication reduces the amount of water in thebody. 4.This medication keeps the blood from clotting. 13.The nurse is assessing a client experiencing manifestations of cor pulmonale. Which of the following will the nurse most likely assess in this client? 1.Low blood pressure 2.Low heart rate 3.Hoarseness 4.Lumbar pain MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1.The nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with pneumonia. Which of the following signs and symptoms would the nurse most likely assess in this client? (Select all that apply.) 1.Abdominal pain 2.Anorexia 3.Cough 4.Dyspnea 5.Fever 6.Frequent wiping of the nose 2.The nurse is planning to administer the pneumococcus vaccination to a client. Which of the following would indicate that a client is a candidate for this vaccination? (Select all that apply.) 1. Age70 2. Age55 3. Diagnosis of heartfailure 4. Recovering from knee replacement surgery 5.Diagnosis ofasthma 6.Recovering from an appendectomy 3.The nurse is planning care for a client diagnosed with bronchiolectasis. Which of the following would be goals for this clients care? (Select all that apply.) 1.Treat the infection. 2.Reduce the heart rate. 3.Minimize further damage. 4.Improve urine output. 5. Promotebreathing. 6. Removesecretions. 4.The nurse, planning care for a client diagnosed with a pneumothorax, identifies which types of pneumothorax? (Select all that apply.) 1.Spontaneous 2.Radical 3.Traumatic 4.Incomplete 5.Iatrogenic 6.Tension 5.Which of these instructions are for a client diagnosed with a pneumothorax? (Select all that apply.) 1.Remove air from the pleural space. 2.Correct acid-base imbalances. 3.Treat infection. 4. Minimizedamage. 5. Reexpand the lung. 6. Improve fluid balance. . Chapter 31. Inflammatory Respiratory Disorders 1. How does pursed lip breathing assist patients with asthma during anattack? a. It distracts the patient with breathing technique to reduceanxiety. b. It gets rid of CO2faster. c. It opens bronchioles by backflow airpressure. d. It increasesPACO2.. 2. How do leukotriene modifiers reduce the symptoms ofasthma? a. By drying up mucus b. By causing bronchodilation and anti-inflammationeffects c. By suppressingcough d. By liquefying mucus 3. How should a patient be positioned after a thoracentesis is completed and the dressingapplied? a. HighFowler b. Semi-Fowler c. Side lying on unaffectedside d. Prone 4.What should the nurse do to keep the chest tubes from becoming occluded? a. Irrigate tubes asneeded b. Prevent dependentloops c. Loop the tube over the bedrail d. Milk the tube frequently Which patient assessment indicates the most severe respiratorydistress? a. Nasal flaring, symmetrical chest wall expansion, SaO288% b. Abdominal breathing, SaO297% c. Substernal retraction, SaO284% d. Substernal retraction, SaO2 90% MULTIPLE RESPONSE 6. Which preoperative teaching should a nurse include for a person scheduled for apartial laryngectomy? (Select all thatapply.) a. Tracheal suction will befrequent b. The presence of a temporarytracheotomy c. That isolation will be required for 24hours d. The surgery involves removal of a diseased vocalcord e. Some speech will beretained f. The sense of smell and taste will be lost 7. Which independent nursing measures are effective in aiding a patient to expectorate? (Select all thatapply.) a. Positioning in orthopneicposition b. Suctioning c. Assisting tocough d. Providinghydration e. Starting IVfluids f. Starting mucolytic agents 8. Identify the purposes of chest drainage. (Select all thatapply.) a. Drains air, blood, and fluid from pleuralspace b. Restores positive pressure in chestcavity c. Restores negative intrapleuralpressure d. Allows lung to collapse andrest e. Allows route for medication administration 9. What are age-related changes in the older adult that make them at risk for respiratorydiseases? (Select all thatapply.) a. Moist mucousmembranes b. Kyphosis c. Decrease in pulmonary bloodflow d. Stasis pooling ofsecretions e. Reduced number of cilia , which make infection of the upper and lower airway more likely. 10. The nurse explains to the person with pneumonia in the left lung that being positioned in the good lung down offers the advantage of (select all thatapply): a. PaO2 rising in the goodlung. b. blood flow to bad lung beingincreased. c. the dependent lung being betterperfused. d. dyspneadisappearing. e. decreased hypoxia. 11. How would the nurse examining a patient with pleurisy document a low-pitched gratinglung sound? a. Sonorouswheeze b. Frictionrub c. Coarsecrackles d. Crackles 12. The nurse describes the pathophysiologic process of an asthma attack. Place the events intheir proper sequence. (Separate letters by a comma and space as follows: A, B, C,D) a. Inflammatory process in the mast cells of thelungs b. Increase in edema and mucus production in thebronchioles c. Release ofhistamine d. Narrowing of theairways e. Exposure to allergen . Chapter 32. Lung Cancer MULTIPLE CHOICE 1.A client states, I dont know why I should quit smoking. It cant improve anything. The nurse responds by informing the client about the decrease in lung cancer rates over time after a person quits smoking. Which of the following iscorrect? 1. The lung cancer rate corresponds to that of nonsmokers 1 year after quittingsmoking. 2. The lung cancer rate corresponds to that of nonsmokers 2 years after quittingsmoking. 3. The lung cancer rate corresponds to that of nonsmokers 5 years after quittingsmoking. 4. The lung cancer rate corresponds to that of nonsmokers 10 years after quittingsmoking. 2. A patient with lung cancer is receiving chemotherapy. Why should the nurse closely monitor the patients white blood cell (WBC)count? a. Chemotherapy drugs cause polycythemia and can precipitatethrombosis. b. Chemotherapy drugs attack WBCs and shorten their life span, which increases risk forinfection. c. Chemotherapy drugs cause proliferation of blood cells, which can lead to sluggishcirculation. d. Chemotherapy drugs depress the bone marrow, which can lead to infection and an increase in WBCcount. 3. The nurse is caring for a patient with lung cancer who is receiving chemotherapy. Which assessment finding suggests that the patient is experiencing pericardialeffusion? a. Bruising and tarrystools b. Edema and shortness ofbreath c. Nausea and decreased bowelsounds d. Peripheral numbness and tingling Chapter 33. Smoking Addiction 1.A client has been smoking for the last 40 years and has a history of emphysema. Which of the following findings would the nurse not expect tofind? 1. Decreased forced vital capacity(FVC) 2. Increased anterior-posterior chestdiameter 3. Increased forced expiratory volume (FEV1) 4. Pursed lipbreathing Chapter 34. Common Cardiovascular Complaints Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which group would most benefit fromstatins? a. Those with a low density lipoprotein-cholesterol greater than 100mg/dL b. Individuals with clinical arteriosclerotic cardiovasculardisease c. Individuals with a 10-year risk greater than10% d. Individuals of all ages with diabetes mellitus(DM) 2. If chest pain can be alleviated with time, analgesics, and heat applications, what might the differential diagnosisbe? a. Pepticulcer b. Hiatalhernia c. Costochondritis d. Pericarditis 3. Sandra has palpitations that occur with muscle twitching, paresthesia, and fatigue. What specific diagnostic test might help determine thecause? a. Serumcalcium b. Electrocardiogram(ECG) c. Thyroid-stimulating hormonetest d. Complete blood cellcount 4. A blood pressure (BP) of 150/90 isconsidered: a. Stage 2hypertension b. Hypertensive c. Normal in healthy olderadults d. Acceptable if the patient hasDM 5. Lifestyle modifications to manage hypertension (HTN)include: a. Maintaining a body mass index of17 b. Restricting dietary sodium to 2 grams perday c. Engaging in exercise or physical activity for 90 minutes aday d. Limiting beer intake to 24 ounces perday 6. Mary has hypertension and previously had a stroke. Which hypertensive drug would you order for her? a. Angiotensin converting enzymeinhibitor b. Calcium channelblocker c. Angiotensin II receptorblocker d. Betablocker 7. Which high-density lipoprotein (HDL) level is consideredcardioprotective? a. Greater than30 b. Greater than40 c. Greater than50 d. Greater than60 8. You are assessing Sigred for metabolic syndrome. Which of her parameters is indicative of this syndrome? a. Her waist is 36inches. b. Her triglyceride level is 140mg/dL. c. Her BP is128/84. d. Her fasting blood sugar (BS) is 108mg/dL. 9. Which type of angina do you suspect in Harvey, who complains of chest pain that occurs during sleep and most often in the early morninghours? a. Stableangina b. Unstableangina c. Variant (Prinzmetal’sangina) d. Probably not angina but hiatalhernia 10. Which ECG change is typical of cardiacischemia? a. T-waveinversion b. ST-segmentelevation c. Significant Qwave d. U-wave 11. In which type of arterioventricular (AV) block does the pulse rate (PR) interval lengthen until a beat isdropped? a. First-degree AVblock b. Second-degree Mobitz I AVblock c. Second-degree Mobitz II AVblock d. Third-degree AVblock 12. A Delta wave on the ECG may be present in whichcondition? a. Prinzmetal’sangina b. Bundle branchblock c. Wolff-Parkinson-Whitesyndrome d. Aorticstenosis 13. Which heart sound may be heard with poorly controlled hypertension, angina, and ischemic heart disease? a. A physiologic splitS2 b. A fixed splitS2 c. S3 d. S4 14. Samuel is going to the dentist for some work and must take endocarditis prophylaxis because of his history of: a. Severeasthma b. A common valvularlesion c. Severehypertension d. A prosthetic heartvalve 15. George, age 64, has cardiovascular disease (CVD), a total cholesterol of 280 mg/dL, and a systolic BP of 158. He is being treated for hypertension. You are doing a Framingham Risk Assessment on him. Which assessment factor would give him the highest number of points on the scale? a. His age b. His cholesterollevel c. His systolicBP d. The fact that he is on antihypertensivemedication 16. Which pain characteristic is usually indicative of cardiacpathology? a. Fleeting b. Moving c. Diffuse d. Localized 17. What percentage of patients with angina pectoris will have simultaneous dyspnea, caused by transient increase in pulmonary venous pressures that accompany ventricular stiffening during an episode of myocardialischemia? a. About20% b. About30% c. About50% d. Almostall 18. Nitroglycerine (NTG) is given for a patient having ischemic chest pain. One tablet or one spray should be used under the tongue every 5 minutes for three doses. What should be done if the pain has not been relieved after threedoses? a. 911 should be called, and the patient should be transported immediately to the emergencydepartment. b. One more dose of NTG may betried. c. The person should be given two aspirin tochew. d. A portable defibrillator should be located to ascertain the cardiacrhythm. 19. For the best therapeutic effect after a myocardial infarction (MI), thrombolytics should be administered within the first 3 hours (ideally 30 minutes) of symptom onset. Studies haveshown, however, that thrombolytic therapy can be of benefit up to how many hours after the initial presentation of MIsymptoms? a. 6 hours b. 8 hours c. 10 hours d. 12 hours 20. When teaching post MI patients about their NTG tablets, the clinician should stress that the tablets should remain in the light-resistant bottle in which they are packaged and should not be put in another pill box or remain in areas that are or could become warm and humid. Once opened, the bottle must be dated and discarded after how manymonths? a. 1 month b. 3months c. 6months d. As long as the tablets are kept in this special bottle, they will lastforever. 21. There are four stages of heart failure, classified as A to D, that describe the evolution and progression of disease. In which stage are patients hospitalized or treated with specialized interventions or hospice care for refractory symptoms of heart failure despite medicaltherapy? a. StageA b. StageB c. StageC d. StageD 22. Which of the following is abundant in the heart and rapidly rises in the bloodstream in the presence of heart failure, making it a good diagnostictest? a. B-type natriureticpeptide b. C-reactiveprotein c. Serumalbumin d. Erythrocyte sedimentationrate 23. Which test has long been considered the gold standard for a diagnosis of venousthromboembolism? a. Ultrasound b. Magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) c. Ascendingvenogram d. D-dimer 24. Statins are approved for which agegroup? a. Children over the age of2 b. Children over the age of6 c. Children over the age of10 d. Only adolescents andadults 25. The American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association states which of the following regarding the use of non-statin lipid-loweringagents? a. Nicotinic acid derivatives are effective for lowering LDL and triglycerides(TGs). b. Bile acid sequestrates increaseHDL. c. Cholesterol absorption inhibitors decreaseLDL. d. There is no sufficient evidence to use non-statinlipid-drugs. 26. Which of the following medications can causehyperlipidemia? a. Diuretics b. NSAIDs c. Opioids d. Insulin 27. Jamie, age 55, has just started on a statin after having his liver function tests (LFTs) come back normal. He now asks you how often he has to have the LFTs repeated. What do you tellhim? a. Initially in 6weeks b. Every 3months c. Every 6months d. It’s no longer necessary for his statinregimen. 28. In the CHADS2 Index for the stroke risk score for AF, the ‘A’ standsfor: a. Anticoagulation b. Autoimmunedisease c. Age d. Antihypertension 29. Which murmurs are usually ‘watch andwait’? a. Systolicmurmurs b. Diastolicmurmurs c. They both are dangerous and need immediateattention. d. You can ‘watch and wait’ for both ofthem. 30. Which of the following statements about dabigatran istrue? a. It is difficult to keep the patient in therapeuticrange. b. Anticoagulation cannot be immediatelyreversed. c. It allows for the use of tPA if the patient has a stroke despiteanticoagulation. d. None of the statements aretrue. 31. What value on the ankle-brachial index diagnoses peripheral arterydisease? a. Less than0.25 b. Less than0.50 c. Less than0.90 d. Greater than1 32. Your patient with permanent afib asks when he can discontinue his warfarin. You tellhim: a. When your internalized normalized ratio reaches 3.0, you can stop taking your warfarinpermanently. b. When you no longer feelill c. One month after your symptoms dissipate d. You’ll probably be on itindefinitely. 33. You just started Martha on HTN therapy. The Eighth Joint National Committee recommends that if her goal BP is not reached in what length of time, you should increase the initial drug or add a second drug toit? a. 1 month b. 3months c. 6months d. 1 year Chapter 34. Common Cardiovascular Problems Chapter 35. Cardiac and Associated Risk Disorders MULTIPLE CHOICE 1.The nurse suspects a clients heart is failing when which of the following heart sounds is assessed? 1. S1 2. S2 3. S3 4. S4 2.A client is diagnosed with heart failure. Which of the following diagnostic tests is useful to determine the degree of the failure? 1.Brain natriuretic peptide level 2.Blood cultures 3.Sedimentation rate 4.Arterial blood gas 3.A nurse is instructing a client regarding medications and substances contraindicated for the client with heart failure. Which of the following would not be contraindicated? 1.Alcohol 2.Furosemide 3.Metformin 4.Pioglitazone 4.The nurse is determining nursing diagnoses appropriate for a client demonstrating productive cough with pink frothy sputum, shortness of breath, and crackles. Which of the following nursing diagnoses is of the most importance? 1.Activity intolerance 2.Anxiety 3. Impaired gasexchange 4. Risk for ineffective respiratoryfunction 5. In planning the care for a client diagnosed with heart failure, which of the following would bean appropriategoal? 1.Reduce myocardial contractility. 2.Increase cardiac workload. 3.Decrease ejection fraction. 4.Increase activity levels. 6.The nurse is instructing a client diagnosed with mild heart failure on dietary modifications. Which of the following client statements indicates that the instruction has been effective? 1.I will avoid greenbeans. 2.I will avoid orangejuice. 3.I will avoid soy sauce. 4.I will avoid apple sauce. 7.A client is undergoing diagnostic testing for infective endocarditis. Which of the following laboratory tests would be most useful in diagnosis? 1.Basic metabolic panel 2.Blood cultures 3.Reticulocyte count 4.Prothrombin time 8.Which of the following would the nurse most likely assess in a client diagnosed with right-sided heart failure? 1.Distended neck veins 2.Oliguria 3.Cough with frothy blood-tinged sputum 4.Syncope 9.Which of the following diagnostic tests is useful to diagnose mitral valve prolapse? 1.Electrocardiogram 2.Echocardiogram 3.Cardiac angiography 4.Transesophageal echocardiography 10.A client diagnosed with mitral valve prolapse is experiencing palpitations. Which of the following should the nurse instruct this client? 1. Avoidtobacco 2. Ingest alcohol in moderation 3.Avoid weightloss 4.Limit caffeine intake 11.A client tells the nurse that she had rheumatic heart disease as a child. For which of the following valvular disorders should this client be assessed? 1.Mitral valve prolapse 2.Mitral stenosis 3.Aortic regurgitation 4.Aortic stenosis 12.A client, recovering from surgery to replace a calcified aortic valve with a mechanical valve, should be instructed that which of the following medications will be needed long term? 1.ACE inhibitor 2.Beta-blocker 3.Antibiotic 4.Anticoagulant 13.A client is scheduled for annuloplasty surgery to the aortic valve. Which of the following will most likely occur during this clients procedure? 1.A catheter will be inserted through the femoral vein. 2.A heart bypass machine will be used. 3.Local anesthesia will be provided. 4.A balloon will inflate and stretch the valve open. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1.The nurse suspects a client is experiencing left-sided heart failure when which of the following is assessed? (Select all that apply.) 1.Decreased basilar lung sounds 2.Distended neck veins 3.Extra heart sounds 4.Lung crackles 5.Tachycardia 6.Weight gain 2.A client diagnosed with heart failure is prescribed furosemide (Lasix). Which of the following should this client be monitored for because of this medication? (Select all that apply.) 1. Dehydration 2. Rebound fluid volumeoverload 3.Hyponatremia 4.Hypokalemia 5.Hypernatremia 6.Hyperkalemia 3.The nurse is reviewing the medications prescribed for a client diagnosed with dilated cardiomyopathy. Which of the following medications are commonly prescribed for this disease process? (Select all that apply.) 1.ACE Inhibitor 2.Beta-blocker 3.Diuretic 4.Anticoagulant 5.Antiarrhythmic 6.Antibiotic 4.Which of the following should the nurse instruct a client diagnosed with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy? (Select all that apply.) 1.Follow recommended activity level 2.Avoid all alcohol 3.Take hot tub baths routinely 4.Avoid overexertion 5.Avoiddehydration 6.Unexplained breathlessness is a common symptom 5.The nurse determines that a client diagnosed with pericarditis is demonstrating the classic signs of the Beck triad. What are the signs of the Beck triad? (Select all that apply.) 1.Fever 2.Dyspnea 3.Muffled heart sounds 4.Elevated jugular vein pressure 5.Hypotension 6.Abdominal pain Chapter 36. Dysrhythmias and Valvular Disorders MULTIPLE CHOICE 1.A client is experiencing an alteration in heart rate. The nurse realizes this client is experiencing a disorder of which part of the heart? 1. Atrioventricular node 2.Bundle branches 3.Purkinje fibers 4.Sinoatrialnode 2.A client is suspected of having cardiac damage. The nurse realizes that which of the following diagnostic tests is most commonly used to help diagnose this clients possible cardiac damage or disease? 2. Arterial blood gases 3.Cardiac angiogram 4.Cardiacenzymes 3. The nurse is analyzing a clients electrocardiogram tracing. Which of the following complexesis not normally seen on an electrocardiogramtracing? 1.P wave 2.QRScomplex 3.T wave 4.U wave 4. The nurse is analyzing a clients electrocardiogram tracing and realizes that each small squareon the paper is equalto: 1.0.04 second. 2.0.12 second. 3.0.20 second. 4.0.40 second. 5. The nurse is reading an ECG rhythm strip and notes that there are nine QRS complexes in a 6- second strip. The heart rateis: 2.54. 3.81. 4.90. 6. The nurse notes that on a clients electrocardiogram tracing, there is one P wave for every QRS complex and a delay in the impulse transmission at the AV node. This regular rhythm is identified as: 1.first-degree AV block. 2.second-degree AV block type I. 3.second-degree AV block type II. 4.complete heart block. 7.A client is unresponsive and has no pulse. The nurse notes that the electrocardiogram tracing shows continuous large and bizarre QRS complexes measured greater than 0.12 each. This rhythm is identified as: 1.premature ventricular complexes. 2.torsades de pointes. 3.ventricular fibrillation. 4.ventricular tachycardia. 8.An elderly client is demonstrating a change in heart rate that occurs with respirations. When planning care for the client, the nurse knows that treatment may include: 1.Oxygen therapy 2.Analgesics 3.Antibiotics 4.Pacemaker insertion 9.A clients electrocardiogram tracing shows a sawtooth pattern with F waves. The nurse realizes this client is demonstrating: 1. atrialflutter. 2. atrialfibrillation. 3. premature atrial contractions. 4.atrialtachycardia. 10.The electrocardiogram tracing for a client shows premature junctional complexes. Which of the following should the nurse do to assist this client? 1.Administer oxygen 2.Increase intravenous fluids 3.Check on the serum digoxin level 4.Assist the client to a side-lying position 11.Which of the following should the nurse instruct a client who has been diagnosed with an arrhythmia? 1. Exerciselevel 2. Avoidance of calorie-dense foods 3.How to take his own pulse 4.Reasons why fatigue isexpected 12.A client is diagnosed with supraventricular tachycardia. The nurse should prepare to administer which of the following medications? 1.Procainamide 2.Amiodarone 3.Verapamil 4.Adenosine 13.A client is recovering from insertion of a pacemaker to pace the activity of the ventricles. At which point on the electrocardiogram tracing will the nurse assess pacer spikes? 1.Before the QRS complex 2.Before the P wave 3.After the QRS complex 4.After the P wave MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1.A client with a heart rate of 40 who is experiencing shortness of breath and nausea is diagnosed with second-degree AV block type II. Which of the following will be included in this clients treatment? (Select all that apply.) 1.Administer digoxin 2.Administer antiemetic 3.Administer atropine sulfate 4.Insert external pacemaker 5.Decrease intravenous fluids 6.Lower the head of the bed 2.A clients electrocardiogram rhythm strip is a straight line. Which of the following should the nurse do to help this client? (Select all that apply.) 1. Assess for looseleads. 2. Assess for power to themonitor. 3. Assess the strip for possible fine ventricularfibrillation. 4. Begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation once verified the client has nopulse. 5.Raise the head of thebed. 6.Stop intravenous fluid infusion. . 3.The nurse is assessing a client who is diagnosed with pulseless electrical activity. Which of the following will the nurse include in this assessment? (Select all that apply.) 1.Hypovolemia 2.Hypoxia 3.Hypothermia 4.Tamponade 5.Thrombosis 6.Throat pain . 4.Which of the following should be implemented to ensure the safe use of a defibrillator? (Select all that apply.) 1.Do not place over monitoring electrodes. 2.Do not place over an implanted pacemaker. 3.Place the paddles at inch from the implanted pacemaker site. 4.Apply transdermal medication to the chest before using the paddles. 5.Insert an oral airway before using the paddles. 6.Have another person hold the clients airway open while using the paddles. 5.Which of the following interventions would be appropriate for a client recovering from a pacemaker insertion? (Select all that apply.) 1.Monitor vital signs every 15 minutes until stable. 2.Assess for chest pain. 3.Restrict movement of affected extremity. 4.Monitor electrocardiogram every 8 hours. 5.Begin intravenous fluid infusion at 150 mL/hr. 6.Reinforce dressing with excessive bleeding. Chapter 37. Disorders of the Vascular System MULTIPLE CHOICE 1.Which of the following should the nurse instruct a client in order to reduce the risk factors for developing arteriosclerosis? 1.Limit diet to contain less than 40% fat 2.Restrict exercise 3. Stopsmoking 4. Avoid prescriptionmedications 2. The nurse is concerned that an elderly client has evidence of arteriosclerosis since theclients capillary refill is greaterthan: 1.3 seconds. 2.4 seconds. 3.5 seconds. 4.6 seconds. 3. When instructing a client on ways to lower his cholesterol levels, which of the followingshould the nurseinclude? 1.Eat more meat and eggs. 2.Consume less meat and eggs. 4.Limit fruits. 4.A client diagnosed with arteriosclerosis is prescribed an anticoagulant. For which of the following should the nurse assess in this client? 1.Respiratory distress 2.Skin breakdown 3.Decreased urine output 4.Bruising and bleeding . 5.The nurse is assessing a client diagnosed with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Which of the following sounds did the nurse auscultate during the assessment? 1. Pleuralrub 2. Hyperactive bowel sounds 3.Crackles 4.Bruit 6.A client is admitted with abdominal aortic aneurysm. For which of the following complications should the nurse be concerned? 2.Cardiac arrhythmias 3.Aneurysm rupture 4.Loss of bowel sounds 7.A client who has experienced signs of Virchows triad has developed a deep vein thrombosis. Which of the following is not a part of this triad? 1.Venous stasis 2.Vessel wall injury 3.Alteration in blood clotting 4.Pregnancy 8.A client is diagnosed with Buergers disease. Which of the following should the nurse instruct the client regarding this disorder? 1. It is a commondisorder. 2. It appears in women more than inmen. 3.Smoking exacerbates thedisease. 4.It is more common in African Americans. . 9.A client is diagnosed with Raynauds disease. Which of the following will the nurse most likely assess in this client? 2.Pain, cyanosis, and numb, cold extremities 3.Absent peripheral pulses 4.Increase in varicose veins 10.A client is diagnosed with acute peripheral arterial occlusion. The nurse should prepare to provide which of the following interventions for this client? 1. Administeroxygen. 2. Assist withambulation. 3. Administer heparin as prescribed. 4.Restrictfluids. 11.A client receiving a heparin infusion is demonstrating signs of acute bleeding. Which of the following should the nurse prepare to administer to this client? 1.Aspirin 2.Vitamin K 3.Protamine sulfate 4.Narcan 12.A clients blood pressure measurements have a 20 mmHg difference between the upper extremity readings. Which of the following does this assessment finding suggest to the nurse? 1.Arteriosclerosis 2.Aortic aneurysm 3.Deep vein thrombosis 4.Subclavian steal syndrome 13.The nurse is assessing a client for risks in the development of varicose veins. Which of the following findings would increase this clients risk? 1.Normal weight 2.Prolonged standing 3. Engages in golf three times aweek 4. Eats several servings of fruits and vegetables each day MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1.A client is having laboratory tests conducted to confirm a diagnosis of arteriosclerosis. Which of the following laboratory values would support this clients medical diagnosis? (Select all that apply.) 1.Serum cholesterol 300 mg/dL 2.LDL 125 mg/dL 3.Blood glucose 90 mg/dL 4.HDL 45 mg/dL 5.Triglycerides 400 mg/dL 6.Serum potassium 4.0 mEq/L 2.The nurse is assessing a client diagnosed with a peripheral arterial occlusion. Which of the following will the nurse assess in this client? (Select all that apply.) 1.Pulselessness 2.Pain 3.Pallor 4.Paresthesia 5.Paralysis 6.Petechiae 3.The nurse is instructing a client recovering from arterial aneurysm repair. Which of the following should be included in these instructions? (Select all that apply.) 1.Do not lift anything heavier than 15 to 20 lbs. 2.Limit activity for up to 8 weeks after the surgery. 3.Use a pillow to splint when coughing. 4. Driving is permitted 1 week aftersurgery. 5. Notify the physician for pain, redness, or swelling around theincision. 6.Avoid painmedication. following is assessed when using this scale? (Select all that apply.) 1. Treatment forcancer 2. Recent immobility for greater than 3days 3. Recovery from surgery with general anesthesia within 12weeks 4.Entire legedematous 5.Pitting edema of the symptomatic leg 6.Blood pressure 130/86 mmHg 5.A client is diagnosed with a venous stasis ulcer on the foot. Which of the following will be included in this clients plan of care? (Select all that apply.) 1.Administer oral antibiotics if infection is present. 2.Keep the foot open to the air. 3.Cover the foot with a hydrocolloidal dressing. 4.Provide pain medication with debridement. 5. Restrictfluids. 6. Instruct the client to ambulate without shoes. MULTIPLE CHOICE developing arteriosclerosis? 1.Limit diet to contain less than 40% fat 2.Restrict exercise 3. Stopsmoking 4. Avoid prescriptionmedications 2. The nurse is concerned that an elderly client has evidence of arteriosclerosis since theclients capillary refill is greaterthan: 1.3 seconds. 2.4 seconds. 3.5 seconds. 4.6 seconds. 3. When instructing a client on ways to lower his cholesterol levels, which of the followingshould the nurseinclude? 1.Eat more meat and eggs. 2.Consume less meat and eggs. 3.Incorporate more vegetables. 4.Limit fruits. 4.A client diagnosed with arteriosclerosis is prescribed an anticoagulant. For which of the following should the nurse assess in this client? 1.Respiratory distress 2.Skin breakdown 3.Decreased urine output 4.Bruising and bleeding 5.The nurse is assessing a client diagnosed with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Which of the following sounds did the nurse auscultate during the assessment? 1. Pleuralrub 2. Hyperactive bowel sounds 3.Crackles 4.Bruit 6.A client is admitted with abdominal aortic aneurysm. For which of the following complications should the nurse be concerned? 1.Hypotension 2.Cardiac arrhythmias 3.Aneurysm rupture 4.Loss of bowel sounds 7.A client who has experienced signs of Virchows triad has developed a deep vein thrombosis. Which of the following is not a part of this triad? 1.Venous stasis 2.Vessel wall injury 3.Alteration in blood clotting 4.Pregnancy 8.A client is diagnosed with Buergers disease. Which of the following should the nurse instruct the client regarding this disorder? 1. It is a commondisorder. 2. It appears in women more than inmen. 3.Smoking exacerbates thedisease. 4.It is more common in African Americans. 9.A client is diagnosed with Raynauds disease. Which of the following will the nurse most likely assess in this client? 1. Elevated bloodpressure 2. Pain, cyanosis, and numb, cold extremities 3.Absent peripheralpulses 4.Increase in varicose veins 10.A client is diagnosed with acute peripheral arterial occlusion. The nurse should prepare to provide which of the following interventions for this client? 1. Administeroxygen. 2. Assist withambulation. 3. Administer heparin as prescribed. 4.Restrictfluids. 11.A client receiving a heparin infusion is demonstrating signs of acute bleeding. Which of the following should the nurse prepare to administer to this client? 1.Aspirin 2.Vitamin K 3.Protamine sulfate 4.Narcan 12.A clients blood pressure measurements have a 20 mmHg difference between the upper extremity readings. Which of the following does this assessment finding suggest to the nurse? 1.Arteriosclerosis 2.Aortic aneurysm 3.Deep vein thrombosis 4.Subclavian steal syndrome . 13.The nurse is assessing a client for risks in the development of varicose veins. Which of the following findings would increase this clients risk? 1.Normal weight 2.Prolonged standing 3. Engages in golf three times aweek 4. Eats several servings of fruits and vegetables each day Chapter 38. Common Abdominal Complaints Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A 35-year-old female patient is seen in the clinic complaining of abdominal pain. Which of the following should be included in the history and physicalexamination? a. Digital rectalexam b. Pelvicexam c. Sexualhistory d. All of theabove 2. A patient comes to the office complaining of constipation. The patient lists all of the following medications. Which drug could be responsible for theconstipation? a. Multivitamin b. Magnesiumhydroxide c. Pepto-Bismol® d. Ibuprofen 3. A patient is seen with complaints of diarrhea. Which of the following should be included in the patient’s differentialdiagnosis? a. Gastroenteritis b. Inflammatory boweldisease c. Lactasedeficiency d. All of theabove 4. Mr. J. K., 38 years old, is 5 feet 8 inches tall and weighs 189 pounds. He reports that he has had intermittent heartburn for several months and takes Tums® with temporary relief. He has been waking during the night with a burning sensation in his chest. Which additional informationwould lead you to believe that gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is the cause of hispain? a. The pain seems better when he smokes to relieve hisnerves. b. Coffee and fried foods don’t botherhim, c. He wakes at night coughing with a bad taste in hismouth. d. All of theabove 5. A 29-year-old Englishman is seen in the office with complaints of pain in his chest and belly. He has been suffering the pain for 2 weeks and gets temporary relief from Alka-Seltzer®. The burning pain wakes him at night and radiates up to his chest. Which factor favors a diagnosis of gastriculcer? a. His gender b. His age c. His use ofAlka-Seltzer d. His ethnicorigin 6. Which of the following is most effective in diagnosingappendicitis? a. History andphysical b. Sedimentationrate c. Kidney, ureter, and bladderx-ray d. Complete blood count (CBC) withdifferentials 7. Which of the following is associated with celiac disease (celiacsprue)? a. Malabsorption b. Constipation c. Rectalbleeding d. Esophagealulceration 8. A 45-year-old patient presents with a chief complaint of generalized abdominal pain. Her physical examination is remarkable for left lower quadrant tenderness. At this time, which of the following should be considered in the differential diagnosis? a. Endometriosis b. Coloncancer c. Diverticulitis d. All of theabove 9. A 46-year-old patient is seen in the clinic with abdominal pain. Which of the following tests is essential for thispatient? a. CBC withdifferential b. Urine human chorionicgonadotropin c. Bariumenema d. Computed tomography of theabdomen 10. A 25-year-old accountant is seen in the clinic complaining of crampy abdominal pain aftermeals. She is often constipated and takes laxatives, which are followed by a couple of days of diarrhea. She temporarily feels better after a bowel movement. She states she is embarrassed by flatulence and has abdominal distension. She has had no weight loss or blood in her stool. This problem has gone on for about 6 months. What should the next step be? a. Obtain a completehistory. b. Order a bariumenema. c. Schedule a Bernstein’stest. d. Prescribe a trial ofantispasmodics. 11. A 28-year-old patient is seen in the clinic with colicky abdominal pain particular with meals. She has frequent constipation, flatulence, and abdominal distension. Which of the data make a diagnosis of diverticulitisunlikely? a. Her age b. Frequentconstipation c. Flatulence d. Colicky abdominalpain 12. A 28-year-old patient is seen with complaints of diarrhea. Which of the following responses to the history questions would help the primary care physician (PCP) establish the diagnosis of irritable bowelsyndrome? a. Feels relief after a bowelmovement b. Sometimes isconstipated c. Does not defecate in the middle of thenight d. All of theabove 13. A patient is diagnosed with GERD, and his endoscopic report reveals the presence of Barrett’s epithelium. Which of the following should the PCP include in the explanation of the pathology report? a. This is a premalignanttissue. b. This tissue is resistant to gastricacid. c. This tissue supports healing of theesophagus. d. All of theabove 14. Which of the following dietary instructions should be given to a patient withGERD? a. Eliminatecoffee. b. Drink peppermint tea to relieve stomachdistress. c. Recline and rest aftermeals. d. Limit the amount ofantacids. 15. The patient with GERD should be instructed to eliminate which of theseactivities? a. Swimming b. Weightlifting c. Golfing d. Walking 16. A patient is diagnosed with giardia after a backpacking trip in the mountains. Which of the following would be an appropriatetreatment? a. Vancomycin b. Penicillin c. Metronidazole d. Bactrim 17. A 22-year-old is seen complaining of vague belly pain. This type of pain is seen at what point in appendicitis? a. Veryearly b. 3 to 4 hours afterperforation c. Late ininflammation d. Appendicitis never presents with vaguepain. 18. The nurse practitioner (NP) suspects a patient has a peptic ulcer. Which of the following items on the history would lead the NP to thisconclusion? a. Use ofNSAIDs b. Cigarettesmoker c. Ethanolconsumption d. All of theabove 19. A patient is seen with dark-colored urine, and the urine dipstick reveals a high level ofbilirubin. Which of the following could be a cause of this problem? a. Increased breakdown of red bloodcells b. Inadequate hepatocytefunction c. Biliaryobstruction d. All of theabove 20. A 21-year-old student presents with complaints of fatigue, headache, anorexia, and a runny nose, all of which began about 2 weeks ago. She started taking vitamins and over-the-counter cold preparations but feels worse. The smell of food makes her nauseated. Her boyfriend had mononucleosis about a month ago, and she wonders if she might have it also. Examination reveals cervical adenopathy and an enlarged liver and spleen. Which of the following labs would be most helpful in the differential diagnosis at thispoint? a. Stoolculture b. Liverenzymes c. Antihepatitis Dvirus d. Thyroid-stimulating hormonetest 21. On further questioning, the 21-year-old patient with complaints of fatigue, headache, anorexia, and a runny nose explains that she is sexually active only with her boyfriend, does not use injectable drugs, and works as an aide in a day-care center. Which of the following tests would be most helpful in confirming your diagnosis? a. Hepatitis A virus (HAV)IgM b. HAVIgG c. Anti-HAcAg d. Anti-HAsAg 22. A patient is seen in the clinic with right upper quadrant pain that is radiating to the middle of the back. The NP suspects acute cholelithiasis. The NP should expect which of the following laboratory findings? a. Decreased alanine aminotransferase and decreased aspartateaminotransferase b. Elevated alkalinephosphatase c. Elevated indirectbilirubin d. Decreased white bloodcells 23. A patient has acute pancreatitis with seven of the diagnostic criteria from Ranson’s criteria. In order to plan care, the NP must understand that this criteria score has which of the followingmeanings? a. A high mortalityrate b. An increased chance ofrecurrence c. A 7% chance of the disease becomingchronic d. All of theabove 24. A patient is seen in the office with complaints of six to seven liquid bowel movements perday. Which of the following assessment findings would lead the NP to a diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease? a. Intermittent constipation with periods ofdiarrhea b. Wakens at night withdiarrhea c. History of internationaltravel d. All of theabove 25. Which of the following is part of the treatment plan for the patient with irritable bowelsyndrome? a. High fiberdiet b. Tylenol withcodeine c. Dailylaxatives d. All of theabove Chapter 39. Infectious Gastrointestinal Disorders MULTIPLE CHOICE 1.In caring for a client diagnosed with a small bowel obstruction, what would the nurse expect to do first? 1.Prepare to put in a nasogastric (NG) tube. 2.Give pain medication. 3. Draw labwork. 4. Start an intravenous (IV)line. 2.The nurse, instructing a client about malabsorption syndrome, should include that food is absorbed in the: 1. mouth. 2. bloodstream. 3. stomach. 4. smallintestine. 3.A client is diagnosed with appendicitis. One of the laboratory tests the nurse would expect to monitor would be: 1. serumsodium. 2. white blood cell (WBC) count. 3.hemoglobin (Hgb) and hematocrit (Hct). 4.bilirubinlevel. 4.When assessing the pain in a client diagnosed with appendicitis, the nurse would expect to assess: 1.extreme pain with slight palpation anywhere on the abdomen. 2.pain in the upper back when the right lower quadrant is palpated. 3.more pain when the pressure is released in the right lower quadrant. 4.no pain when the abdomen is palpated. 5.A client is being evaluated for symptoms associated with diverticular disease. The nurse realizes that the best diagnostic test to be used to aid in this diagnosis would be: 1.computed tomography (CT) scan. 2.barium enema. 3.ultrasound. 4.x-ray study. 6.An elderly client has noted blood in her stool for the past few months. Which information in the medical history would strongly suggest colorectal cancer? 1.Increased bouts of vomiting 2.Change in bowel habits 3.Recent infection in the blood 4.Decrease in appetite 7.The nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) who is experiencing diarrhea. What medication would the nurse expect to administer? 1.Loperamide (Imodium) 2.Docusate sodium (Colace) 3.Lorazepam (Ativan) 4.Haloperidol (Haldol) 8.A client complains of acute gastrointestinal distress. While obtaining a health history, the nurse asks about the family history. Which disorder has a familial basis? 1.Hepatitis 2.Ulcerative colitis 4.Bowel obstructions 9.A client diagnosed with appendicitis asks the nurse why this illness occurred. The nurse should respond that the most common cause of appendicitis is: 1.ulcerative colitis. 2.obstruction of the appendix. 3.low-fat diet. 4.infection. 10.A young client is experiencing acute abdominal pain. The nurse realizes that the most common cause for this type of pain would be: 1.appendicitis. 2.biliary tract disease. 3.kidney stones. 4.urinary tract infection. 11.A client experiencing abdominal pain and diarrhea tells the nurse that he used to smoke. Which of the following gastrointestinal disturbances is this client most likely experiencing? 1.Irritable bowel syndrome 3.Acute appendicitis 4.Small bowel obstruction 12.A client has a history of being treated for ulcerative colitis. The nurse realizes that a life- threatening complication of this disorder is: 1. Crohnsdisease. 2. small bowel obstruction. 3.peptic ulcerdisease. 4.toxic megacolon. 13.The nurse assesses no bowel sounds with occasional splashing sounds over the large intestines. Which of the following do these assessment findings suggest to the nurse? 1.Ulcerative colitis 2.Irritable bowel syndrome 3.Appendicitis 4.Bowel obstruction 14.The nurse is instructing a client on diagnostic tests used to screen for colorectal cancer. Which of the following should be included in these instructions? 1.A digital rectal exam should be done annually. 2.A test for fecal occult blood should be done annually. 3.A flexible sigmoidoscopy should be done annually. 4.A colonoscopy should be done every 5 years after age 40. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1.Laparoscopic surgery is scheduled for a client diagnosed with appendicitis. Which of the following may be a result of laparoscopic surgery? (Select all that apply.) 1.No risk of infection 2.Less pain 3.Faster recovery times 4.Maybe more complications 5.Shorter hospital stays 6.Better visualization of the abdominal organs 2.The nurse is assessing a client diagnosed with diverticulitis. Which of the following are clinical manifestations associated with this disorder? (Select all that apply.) 1. Constipation ordiarrhea 2. Left lower quadrant abdominal pain 3.Low-gradefever 4. Increasedexcitability 5. Changes in level of consciousness 6.Thirst 3.The nurse is assessing a client diagnosed with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Which of the following characteristics are associated with this disorder? (Select all that apply.) 1. Recurrent abdominalpain 2. Abdominal pain that improves with defecation 3.Pain associated with a change in stool frequency 4.Pain associated with a change in stoolappearance 5.Pain that occurs only duringdefecation 6.Pain associated with passing flatus 4.A client, diagnosed with a vitamin B-12 deficiency, tells the nurse that she does not want to receive injections every month to treat the disorder. Which of the following should the nurse instruct the client regarding the effects of vitamin B-12 deficiency? (Select all that apply.) 1.Paresthesias in the hands 2.Paresthesias in the feet 3.Ataxia 4.Spinal cord degeneration 5.Loss of memory 6.Loss of the sense of smell 5.The nurse is planning care for a client diagnosed with an acute abdomen. Which of the following nursing diagnoses would be appropriate for this client? (Select all that apply.) 1. Fear 2. Deficient fluid volume 3.Ineffective coping 4.Acutepain 5.Risk of infection 6.Altered self-perception Chapter 40. Gastric and Intestinal Disorders MULTIPLE CHOICE 1.Before administering an antacid, the nurse should instruct a client that this medication works in the: 1. blood. 2. stomach. 3. smallintestine. 4. esophagus. 2.The nurse is assessing a client diagnosed with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Which of the following should be included in this assessment? 1.Degree of mouth burning 2.Difficulty swallowing 3.Presence of pyrosis 4.Painful swallowing 3.During an assessment, the nurse determines a client is at risk for ulcerative stomatitis and gum disease because the client has a history of: 1.alcohol intake. 2.smoking. 3. kissing. 4. eating. 4.A client is diagnosed with a swallowing disorder. The nurse realizes that which type of diet would be indicated for this client? ? 1.Regular diet 2.Clear liquid diet 3.Mechanical soft diet 4.Low-fat diet following are mechanisms to provide enteral feeding EXCEPT: 1. nasogastrictube. 2. percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG)tube. 3.jejunostomy tube. 4.hyperalimentation. 6.A client is scheduled for diagnostic tests to determine the ability to swallow. Which of the following diagnostic tests will provide the best information regarding this clients status? 1.Pulse oximetry with water 2.Esophageal transit scintigraphy 3.Videofluoroscopy 4.Esophageal manometry 7.A client, diagnosed with a hiatal hernia, will experience which of the following symptoms most frequently? 1.Nausea 2.Vomiting 3.Diarrhea 4.Heartburn Which of the following should be included in these instructions? 1. Eat large meals to keep the stomachfull. 2. Drink lots of liquids so that the stomach does not have to work so hard. 3.Avoid lying down aftermeals. 4.Lie down after eating. 9.A client is diagnosed with burning mouth syndrome. Which of the following interventions should be included in this clients plan of care? 1.Assess the condition of the clients teeth. 2.Collect a saliva specimen for analysis. 3.Tell the client to avoid vitaminsupplements. 4.Teach the client how to conduct an oral self-assessment daily. 10.During an assessment, the nurse learns that a client is inhaling while swallowing food. Which of the following does this assessment finding suggest to the nurse? 1.The client is recovering from a stroke. 2.The client is at risk for aspiration. 3.The client will experience dyspepsia. 4.The client has esophageal reflux disease. . 11.A client is experiencing brash water. The nurse realizes this symptom is associated with: 1.oral cancer. 2. gastriculcers. 3. dysphagia. 4. Barretts esophagus. 12.A client has been prescribed Zantac for gastroesophageal reflux disease. The nurse realizes this medication is classified as a: 1.histamine H2-receptor antagonist. 2.proton pump inhibitor. 3.prokinetic agent. 4.antihistamine. 13.A client is diagnosed with peptic ulcer disease caused by NSAID use. Which of the following would be indicated for this client? 1. Antibiotictherapy 2. Treatment similar to a client with peptic ulcer disease 3.Preparation forsurgery 4.Insertion of a nasogastric tube for gastric lavage MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1.The nurse is instructing a client about symptoms associated with peptic ulcer disease. Which of the following should be included in these instructions? (Select all that apply.) 1. Abdominalpain 2. Pain in the middle of the night 3.Weightloss 4.Poor appetite 5.Bloating 6.Constipation 2.The nurse is planning care for a client diagnosed with oral ulcers. Which of the following should be included in this clients plan of care? (Select all that apply.) 1.Encourage frequent oral hygiene. 2.Rinse mouth with chlorhexidine. 3.Increase consumption of hot fluids. 4.Instruct in the use of topical corticosteroids. 5.Encourage the client to limit smoking. 6.Avoid the use of dental floss. should be included in the nurses instructions? (Select all that apply.) 1.Check the face for symmetry. 2.Check skin on the face for changes. 3.Check the neck for swellings or lumps. 4.Check inside of cheeks for tenderness. 5.Check the tongue for changes. 6.Check urine for change in color. 4.The nurse is assisting a client with indirect techniques to improve swallowing. Which of the following are techniques included in the nurses assistance? (Select all that apply.) 1.Tongue mobility exercises 2.Application of ice 3.Repetitive head lift exercises 4.Positioning 5.Range-of-motion exercises for the neck 6.Range-of-motion exercises for the shoulders 5.A client is diagnosed with esophageal pain. Which of the following medications would be indicated for this client? (Select all that apply.) 1. Vasodilators 2. Calcium channel blockers 3.Isosorbide dinitrate 4.Antibiotics 5.Antipyretics 6.Antihistamines Chapter 41. Gallbladder and Pancreatic Disorders MULTIPLE CHOICE 1.A child care worker complains of flu-like symptoms. On further assessment, hepatitis is suspected. The nurse realizes that this individual is at risk for which type of hepatitis? 1. Hepatitis A 2.Hepatitis B 3.Hepatitis C 4.HepatitisD 2. An older male is diagnosed with cirrhosis of the liver. The nurse knows that the most likelycause of this problemis: 1.being in the military. 2.traveling to a foreign country. 3.drinking excessive alcohol. 4.eating bad food. 3.When the liver is seriously damaged, ammonia levels can rise in the body. One of the treatments for this is: 1.administering intravenous (IV) neomycin. 2.giving vitamin K. 3. givinglactulose. 4. starting the patient oninsulin. 4.A client is scheduled for a liver biopsy. The nurse realizes that the most important sign to assess for is: 1.infection. 2.bleeding. 3.pain. 4. nausea andvomiting. 5. The nurse realizes that the organ which is a major site for metastases, harboring andgrowing cancerous cells that originated in some other part of the body, isthe: 1.spleen. 2.gallbladder. 3.liver. 4.stomach. . 6.A school age child is placed on a waiting list for a liver transplant. The nurse knows that the most common reason for children to need this type of transplant is because of: 1.cirrhosis due to hepatitis C. 2.biliary atresia. 3. diabetes. 4. Crohnsdisease. 7.Because health care workers are at a greater risk of hepatitis B infection, it is recommended that all health care workers: 1. wash their handsoften. 2. avoid foreigntravel. 3. become vaccinated. 4.drink bottled wateronly. 8.A client who usually smokes a pack of cigarettes a day tells the nurse that he cannot stand the smell of smoke. The nurse realizes that this client is in which phase of hepatitis? 1.Preicteric 2.Icteric 3.Posticteric 4.Recovery 9.A female client is surprised to learn that she has been diagnosed with hemochromatosis. Which of the following should the nurse respond to this client? 1. It doesnt affect people until they are in their50s. 2. I would ask the doctor if hes sure about thediagnosis. 3. Females often do not experience the effects of the disease until menopause. 4.All women have the disorder but not thesymptoms. 10.A client is diagnosed with liver disease. Which of the following is one impact of this disorder on a clients fluid and electrolyte status? 1.Hyperkalemia 2.Hypercalcemia 3.Hypernatremia 4.Hyponatremia hypertension, should assess the client for which of the following complications associated with this surgery? 1.Myocardial infarction 2.Pulmonary emboli 3.Pulmonary edema 4.Decreased peripheral pulses 12.A client is diagnosed with macrovesicular fatty liver. Which of the following should the nurse instruct this client? 1.Expect to develop jaundice. 2.Avoid all alcohol. 3. Increaseexercise. 4. Treatment includes antibiotictherapy. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1.A client diagnosed with cirrhosis is experiencing the complication of ascites. Which of the following would be considered treatment for this complication? (Select all that apply.) 1.Fluid restriction 2.Low-sodium diet 3.Increased exercise 4.Diuretic therapy 5.Pain medication 6.Bed rest 2.A client is recovering from an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatogram (ERCP). Which of the following should the nurse assess as possible complications from this procedure? (Select all that apply.) 1.Perforation of the stomach 2.Perforated duodenum 3.Pancreatitis 4.Aspiration of gastric contents 5.Anaphylactic reaction to the contrast dye 6.Perforated bladder . 3.A client is demonstrating yellow pigmentation of the skin and sclera. Which of the following can be used to describe this clients symptoms? (Select all that apply.) 1.Jaundice 2.Dyspepsia 3.Icterus 4.Sclerosis 5.Kernicterus 6.Cirrhosis following should be included in these instructions? (Select all that apply.) 1.Avoid liver. 2.Avoid shellfish. 3.Eat soy products. 4. Use avocados insalads. 5. Avoidnectarines. 6. Avoid mushrooms. 5.A client is diagnosed with a disorder of the liver. The nurse realizes this client might experience which of the following? (Select all that apply.) 1.Low vitamin A levels 2.Increased bleeding 3.Poor digestion of fats 4.Insulin resistance 5.Elevated levels of vitamin E 6.Nerve damage 6.A client is diagnosed with portal hypertension. The nurse should assess the client for which of the following disorders associated with this diagnosis? (Select all that apply.) 1.Esophageal varices 2.Splenomegaly 3.Hemorrhoids 4.Caput medusae 5.Gastritis 6.Gallstoneformation Chapter 42. Cirrhosis and Liver Failure MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The nurse clarifies that unconjugated bilirubin, which is made up of broken-down red cells,is: a. stored in the gallbladder to makebile. b. water insoluble bilirubin that must be converted by theliver. c. a by-product which is excreted directly into the bowel forexcretion. d. necessary for digestion of fats. . 2. The patient with cirrhosis has an albumin of 2.8 g/dL. The nurse is aware that normal is 3.5 g/dL to 5 g/dL. Based on these findings, what would the nurse expect the patient toexhibit? a. Jaundice b. Edema c. Copious urineoutput d. Pallor 3. Which nursing intervention should be completed immediately after the physician has performeda needle liverbiopsy? a. Assisting to ambulate for thebathroom b. Keeping the patient on the right side for a minimum of 2hours c. Taking vital signs every 4hours d. Keeping the patient on the left side for a minimum of 4hours 4. Immediately following a liver biopsy, the patient becomes dyspneic, the pulse increases to 100, and no breath sounds can be heard on the affected side. What should the nursesuspect? a. Peritonitis b. Pneumothorax c. Hemorrhage of theliver d. Pleuraleffusion 5. The patients cirrhosis of the liver has also caused a dilation of the veins of the loweresophagus secondary to portal hypertension, resulting in the development of the complicationof: a. esophagealvarices. b. diverticulosis. c. Crohndisease. d. esophageal reflux (GERD). 6. The patient with cirrhosis has a rising ammonia level and is becoming disoriented. Thepatient waves to the nurse as she enters the room. How should the nurse interpretthis? a. As an attempt to get the nursesattention b. Asasterixis c. As an indication of respiratory obstruction fromvarices d. As spasticity 7. How does the administration of neomycin (Mycifradin) reduce the production ofammonia? a. By assisting the hepatic cells toregenerate b. By reducingascites c. By decreasing the bacteria in thegut d. By helping to digest fats and proteins . 8. The nurse explains that the use of cyclosporine as an immunosuppressant has been successful in the reduction of rejection of liver transplants because thedrug: a. increases the rate of the regeneration of livercells. b. can overcome complications presented by hepatitisC. c. increases blood supply totransplant. d. does not suppress bone marrow. . 9.A family member of a patient asks the nurse about the protein-restricted diet ordered because of advanced liver disease with hepatic encephalopathy. What statement by the nurse would bestexplain the purpose of thediet? The liver cannot rid the body of ammonia that is made by the breakdown of protein in the a. digestivesystem. b. The liver heals better with a high-carbohydrate diet rather than with a diet high in protein. Most people have too much protein in their diets. The amount in this diet is better forliver c. d. healing. Because of portal hypertension, the blood flows around the liver, and ammonia made from protein collects in the brain, causing hallucinations. 10. The nurse would make provisions in the plan of care for a person who has had a livertransplant toprevent: a. fluidcongestion. b. fatigue. c. infection. d. urinaryretention. 11. The nurse clarifies that deterioration progresses through stages before presenting with liver disease. Place the stages in order. (Separate letters by a comma and space as follows: A, B, C,D) a. Liverdisease b. Inflammation c. Hepaticinsufficiency d. Destruction e. Fibrotic regeneration 12. What are the indications for a liver transplant? (Select all thatapply.) a. Congenital biliaryabnormalities b. Hepaticmalignancy c. Chronichepatitis d. Cirrhosis due toalcoholism e. Gallbladder disease Chapter 43. Common Urinary Complaints 1. An intravenous pyelogram confirms the presence of a 4-mm renal calculus in the proximal left ureter of a newly admitted patient. Physician orders include meperidine (Demerol) 100 mg IM q4h PRN, strain all urine, and encourage fluids to 4000 mL/day. What should be the nurses highest priority when planning care for thispatient? a. Pain related to irritation of astone b. Anxiety related to unclear outcome ofcondition c. Ineffective health maintenance related to lack of knowledge about prevention ofstones d. Risk for injury related to disorientation 2.A patient is receiving chlorothiazide (Diuril), a thiazide diuretic for hypertension. What nursing action is most important for prevention ofcomplications? a. Measureoutput b. Increase fluidintake c. Assess forhypokalemia d. Assess for hypernatremia 3.A patient with cystitis is receiving phenazopyridine (Pyridium) for pain and is voiding a bright red- orange urine. What should the nursedo? a. Report thisimmediately b. Explain to the patient that this isnormal c. Increase fluidintake d. Collect a specimen . 4. The patient, age 43, has cancer of the urinary bladder. He has received a cystectomy with an ileal conduit. Which characteristics would be considered normal for hisurine? a. Hematuria b. Clear amber with mucus shreds c. Darkbile-colored d. Darkamber 5.A patient, age 78, has been admitted to the hospital with dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. She is confused and incontinent of urine on admission. Which nursing intervention does the nurse include in developing a plan ofcare? a. Restrict fluids after the eveningmeal b. Insert an indwellingcatheter c. Assist the patient to the bathroom every 2hours d. Apply absorbent incontinence pads . 6. The home health nurse suggests the use of complementary and alternative therapies to prevent and/or treat urinary tract infections (UTIs). Which of the following is an example of suchtherapies? a. Grapejuice b. Caffeine c. Tea d. Cranberryjuice 7. Which action can reduce the risk of skin impairment secondary to urinaryincontinence? a. Decreasing fluidintake b. Catheterization of the elderlypatient c. Limiting the use of medication (diuretics,etc.) d. Frequent toileting and meticulous skin care . 8. Why are pediatric patients, especially girls, susceptible to urinary tractinfections? a. Genetically females have a weaker immunesystem b. Females have a short and proximal urethra in relation to thevagina c. Girls are more sexually active thanmales d. Girls have a weakened musculature and sphincter tone 9. Which foods should the home health nurse counsel hypokalemic patients to include in theirdiet? a. Bananas, oranges,cantaloupe b. Carrots, summer squash, greenbeans c. Apples, pineapple,watermelon d. Winter squash, cauliflower, lettuce 10. To help a patient control incontinence, what should the nurse recommend the patientavoid? a. Spicyfoods b. Citrusfruits c. Organmeats d. Shellfish 11.What should the nurse counsel the young man with chronic prostatitis to avoid? a. Cessation ofintercourse b. Warmbaths c. Stoolsofteners d. Continuing antibiotics when symptoms abate MULTIPLE RESPONSE 12. The nurse reassures the patient recovering from acute glomerulonephritis that after all othersigns and symptoms of the disease subside, it is normal to have some residual (select all thatapply): a. proteinuria b. oliguria c. hematuria d. anasarca e. oliguria 13.Why are urinary tract infections (UTI) common in older adults? (Select all that apply.) a. Older adults have weakened musculature in the bladder andurethra. b. Older adults have urinarystasis. c. Older adults have increased bladdercapacity. d. Older adults have diminished neurologicsensation. e. The effects of medications such as diuretics that many older adults take. 24 hours) can lead to urinary stasis. 14. Which of the following are signs of fluid overload in the patient with nephrosis? (Select all that apply.) a. Increase in pulserate b. Increase in dailyweight c. Clear lungsounds d. Edema e. Labored respirations 15. The nurse is reviewing the urinalysis report on an assigned patient. The nurse recognizes which findings to be normal? (Select all thatapply.) a. Turbidityclear b. pH6.0 c. Glucosenegative d. Red blood cells, 15 to20 e. White blood cells COMPLETION 16. Exercises to increase muscle tone of the pelvic floor areknownas exercises. 17. In the nephrotic syndrome, the glomeruli are damaged by inflammation andallowsmall to pass through into theurine. Chapter 44. Urinary Tract Disorders MULTIPLE CHOICE 1.A client is being evaluated for a lower urinary tract infection. Which of the following symptoms would the nurse expect to find? 1. Cloudy urine 2.Flank pain 3.Nausea 4.Temperature 102.9F 2. An elderly client is diagnosed with a urinary tract infection. Which of the following will thenurse most likely assess in thisclient? 1.Jaundice 2.Vomiting 3.Poor eating habits 4.Change in mental status 3.A nurse is collecting a post-void residual urine volume for a client. Which of the following volumes would be abnormal? 1.30mL 2.60mL 3.95mL 4.125 mL 4.A client is prescribed trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for a urinary tract infection. Which of the following instructions would not be appropriate for this medication? 1.Complete all the medication even if you feel better. 2.Drink extra water during the day. 3.Take on an empty stomach with water. 4.Take with an antacid. 5.A client with a urinary tract infection is being discharged with a prescription for ciprofloxacin. The nurse should include which of the following discharge instructions? 1.Do not take within 2 hours of antacid use. 2.Limit fluids. 3. Restrictactivity 4. Expect to be nauseated with this medication. 6.A client is recovering from a cystoscopy. The nurse would expect to assess which of the following regarding the clients urine after the procedure? 1.Anuria 2.Blood clots 4.Pink-tinged ANS: 4 The bladder and urethra are usually irritated as a result of the procedure. This causes pink-tinged urine. Large amounts of blood in the urine, anuria, or blood clots are not expected findings after this procedure. 7.A client is being treated for interstitial cystitis. Which of the following medications would not be prescribed for this client? 1.Cortisone acetate (Cortone) 2.Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) 3.Pimecrolimus (Elidel) 4.Polysulfate sodium (Elmiron) 8.After being diagnosed, a client asks the nurse What is pyelonephritis? The nurse should respond: 1.Pyelonephritis is an infection of the bladder. 2. Pyelonephritis is an infection of theurethra. 3. Pyelonephritis is an infection of theprostate. 4. Pyelonephritis is a common infection that needs to be treated to preventcomplications. 9.The nurse is reviewing the health history of a client diagnosed with glomerulonephritis. Which of the medical conditions would be a risk factor for developing glomerulonephritis? 1.Asthma 2.Hypertension 4.Renal failure 10.The nurse is assessing a client diagnosed with glomerulonephritis. Which of the following findings is consistent with this disorder? 1.Brown urine 2.Hip pain 3.Hypotension 4.Bradycardia . 11.A client is diagnosed with nephrotic syndrome. Which of the following is the nurse most likely going to assess in this client? 1.Glucosuria 2.Proteinuria 3.Hematuria 4.Oliguria 12.A client is surprised to learn that his acute pain is caused by a kidney stone. The nurse should instruct the client that the most common type of renal calculi is composed of: 1. calcium. 2. cystine. 3.struvite. 4.uricacid. 13.A client is hospitalized with kidney trauma resulting in lacerations to the parenchyma. Which of the following would be included in the management of this clients care? 1.Bed rest with antibiotic therapy 2.Restrict fluids 3.Encourage early ambulation 4.Nephrectomy 14.The nurse is reviewing a clients risk factors for the development of renal cancer. Which of the following would be considered a risk factor for the development of this disease? 1.Cigarette smoking 2.Being underweight 3.History of hypotension 4.History of type 2 diabetes mellitus 15.A client is scheduled for surgery to remove the bladder and create a urinary diversion. If the client has a history of complications after surgery, the type of urinary diversion that might be indicated would be: 1.continent diversion with a surgical opening to the abdomen. 2.continent diversion with a replacement bladder made out of intestine. 3.noncontinent diversion with anastomose of the ureters to the anterior wall. 4.noncontinent diversion with anastomose of the ureters to the rectum. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1.The nurse is instructing a client on ways to prevent urinary tract infections. Which of the following should be included in these instructions? (Select all that apply.) 1.Drink cranberry juice. 2.Drink eight glasses of water. 3.Take baths instead of showers. 4.Urinate before and after intercourse. 5. In women, wipe back to front aftervoiding. 6. Take the prescribed medication until the symptomssubside 2.A client is diagnosed with an upper urinary tract infection. Which structures are affected by this infection? (Select all that apply.) 1.Bladder 2.Kidney 3.Prostate 4.Ureters 5.Urethra 6.Rectum 3.The nurse is instructing a client on ways to reduce formation of future kidney stones. Which of the following should be included in these instructions? (Select all that apply.) 1.Drink plenty of fluids. 2.Drink soft drinks. 3. Limit the intake ofspinach. 4. Take a vitamin B-12 supplement or eat foods rich in vitaminB-12. 5. Take a magnesium citrate supplement or eating foods rich in magnesium citrate. 6.Adjust calciumintake. 4.A client is diagnosed with renal vein thrombosis. The nurse realizes that which of the following could be indicated in this clients plan of care? (Select all that apply.) 1.Corticosteroids 2.Nephrectomy 3.Anticoagulants 4.Antihypertensives 5.Surgical intervention 6.Antibiotics 5.The nurse is assessing a client for type of urinary incontinence. Which of the following are considered types of this disorder? (Select all that apply.) 1.Stress 2.Radical 3.Urge 4.Temporary 5.Overflow 6.Functional Chapter 45. Kidney and Bladder Disorders Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A patient is seen in the clinic with a chief complaint of hematuria. To make a differential diagnosis, which of the following questions should beasked? a. “Do you have a history of liverdisease?” b. “What medications are you currentlytaking?” c. “Have you noticed swelling in yourankles?” d. All of theabove 2. The result of the patient’s 24-hour urine for protein was 4.2 g/day. The clinician should take which of the followingactions? a. Repeat thetest. b. Refer to anephrologist. c. Measure the serumprotein. d. Obtain a blood urea nitrogen (BUN) andcreatinine. 3. A patient is seen complaining of “leaking urine when I sneeze.” Which of the following actions should the clinician takefirst? a. Order acystometrogram. b. Obtain a computed tomographyscan. c. Instruct the patient on Kegelexercises. d. Prescribeimipramine. 4. A patient is seen in the clinic with hematuria confirmed on microscopic examination. The clinician should inquire about the ingestion of which of these substances that might be the cause of hematuria? a. NSAIDs b. Beets c. VitaminA d. Red meat 5. A 27-year-old female presents with a chief complaint of burning and pain on urination. She has no previous history of urinary tract infection (UTI). What are some additional symptoms consistent with a diagnosis of lowerUTI? a. Back and abdominalpain b. Fever, chills, costovertebral angle (CVA)tenderness c. Blood in urine andfrequency d. Foul-smelling discharge, perinealitch 6. A 30-year-old patient presents with pain on urination. The urine microscopy of unspun urine shows greater than 10 leukocytes/mL, and a dipstick is positive for nitrites. What is the probablediagnosis? a. Lower urinary tractinfection b. Chlamydiainfection c. Candidiasis d. Pyelonephritis 7. A patient presents with CVA tenderness and a several-day history of high fever, chills, anddysuria. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely given the above information? a. Pyelonephritis b. Cystitis c. Renalcalculi d. Bladdertumor 8. Which of the following information is essential before prescribing Bactrim DS to a 24-year-old woman with aUTI? a. Last menstrualperiod b. Method of birthcontrol c. Last unprotected sexualcontact d. All of theabove 9. A patient is seen in the office complaining of severe flank pain. The clinician should assess this patient for which risk factor for kidneystones? a. Hypertension b. Constipation c. Tuballigation d. Diabetes 10. A patient is diagnosed with urge incontinence. Before prescribing Detrol XL, the provider should question the patient about which of these contraindications to thismedication? a. Diarrhea b. Parkinson’sdisease c. Closed-angleglaucoma d. Breastcancer 11. A patient is diagnosed with overactive bladder. Which of the following instructions should be given to thiswoman? a. “Limit the amount of water that youdrink.” b. “Eliminate caffeine from yourdiet.” c. “Wear pantyliners.” d. All of theabove 12. A 34-year-old patient was treated for a UTI and has not responded to antibiotic therapy. Which of the following actions should be takennext? a. Send a urine specimen for microscopy and evaluate for fungalcolonies. b. Increase the dose ofantibiotic. c. Order acytoscopy. d. Order a differentantibiotic. 13. Which of the following are predisposing factors forpyelonephritis? a. Pregnancy b. Dehydration c. Smoking d. Alkalineurine 14. A 42-year-old woman is seen in the clinic with fever, chills, vomiting, and severe dysuria. She is diagnosed with acute pyelonephritis. How should this patient bemanaged? a. 3-day course of oralantibiotics b. Hospitalization c. Encourage cranberry juiceintake. d. 6-week course ofantibiotics 15. A patient is seen with a sudden onset of flank pain accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and diaphoresis. In addition to nephrolithiasis, which of the following should be added to the list of differentialdiagnoses? a. Pancreatitis b. Peptic ulcerdisease c. Diverticulitis d. All of theabove 16. Which of the following instructions should be given to the patient withnephrolithiasis? a. Take ibuprofen, 600 mg every 8hours. b. Take Tums for stomachupset. c. Drink more black tea. d. Increase intake of vegetables, likespinach. 17. Which of the following patients is at risk for developing urinary tractcancer? a. The 45-year-old woman who is 100 lbs overweight b. The 78-year-old man who smokes three packs of cigarettes aday c. The 84-year-old man who worked in the asbestosmines d. All of theabove 18. A patient is seen in the clinic and diagnosed with Stage I renal cancer. The provider should refer the patient to a nephrologist for which of thesetreatments? a. Chemotherapy b. Nephrectomy c. Palliativetreatment d. Radiation 19. An 86-year-old woman is seen in the clinic for recurrent hematuria. The provider suspects bladder cancer. Which of the following data from the history is considered a risk factor for this type of cancer? a. History ofalcoholism b. Sedentarylifestyle c. Obesity d. 65-year smokinghistory 20. Which of the following diagnostic tests should be ordered for a patient suspected of having bladder cancer? a. Kidneys, ureter, bladderx-ray b. Cystoscopy withbiopsy c. Magnetic resonanceimaging d. Urine tumor marker (NMP22) 21. A 78-year-old man is diagnosed with Stage D bladder cancer and asks the provider what thatmeans. Which is the best response? a. “There is no such thing as Stage Dcancer.” b. “You have cancer that has spread to the surroundingtissue.” c. “Your cancer has spread to otherorgans.” d. “Your cancer can be cured by removing yourbladder.” 22. The patient is diagnosed with acute renal failure (ARF). Which of the following data obtained from the history should alert the provider that this is a case of prerenalazotemia? a. Recent heatstroke b. Nephrolithiasis c. Recent infection where gentamicin was used intreatment d. All of theabove 23. The patient is diagnosed with ARF. Which of the following conditions is the most commoncause? a. Renalcalculi b. Acute tubularnecrosis c. Cardiacfailure d. Acuteglomerulonephritis 24. An 82-year-old woman with renal failure is seen in the clinic. The provider should question the patient about the intake of which of these substances that can cause renaltoxicity? a. Ibuprofen b. Captopril c. Losartan d. All of theabove 25. Which of the following clinical manifestations are consistent with a patient inARF? a. Pruritis b. Glycosuria c. Irritability d. Hypotension 26. Which of the following examination findings should be expected in a patient with chronic renal failure(CRF)? a. Weak, threadypulse b. Auscultatorycrackles c. Hypotension d. Pleural frictionrub 27. Which of the following tests is most useful in determining renal function in a patient suspected of CRF? a. BUN andcreatinine b. Electrolytes c. Creatinineclearance d. Urinalysis 28. Which of the following foods should be limited in a patient withCRF? a. Milk b. Bananas c. Soy sauce d. All of theabove True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. The urine osmolality is greater than 500 mOsm/L in patients with postrenalARF. 2. Cigarette smoking is a risk factor forCRF. Chapter 46. Common Reproductive System Complaints MULTIPLE CHOICE 1.A male client asks the nurse about the purpose of the prostate gland. The nurse should respond that it is a structure that: 1. secretes an alkaline substance that neutralizes residual acidic urine in theurethra. 2. provides a milky alkaline substance that neutralizes the acidity of the male urethra and thefemale vagina. 3. secretes a fluid for the health and nutrition ofsperm. 4.propels sperm into the ejaculatoryduct. 2.A 50-year-old male client has had a prostate-specific antigen test. The nurse realizes that the normal range for this test would be: 1.0 to 2ng/mL. 2.0 to 3ng/mL. 3.0 to 4ng/mL. 4.0 to 5 ng/mL. 3.A male client, having difficulty voiding, tells the nurse that he thinks something is wrong with his penis. The nurse reviews the structures of the penis with the client and explains that the structure that surrounds the urethra is the: 1. corpuscavernosa. 2. corpusspongiosum. 3. glanspenis. 4. prepuce. 4.The nurse is preparing to discuss the male reproductive system with a group of adolescent school students. Which of the following would the nurse not include as a primary function of the male reproductive system? 1.Frequent erectile functioning and increased libido 2.Production of sperm 3.Secretion of testosterone 4.Transportation and depositing of sperm 5.A male client is diagnosed as being infertile. The nurse realizes which of the following structures of the clients reproductive system is affected? 1.Epididymis 2.Rete testes 3.Seminal vesicles 4.Seminiferous tubules 6.The nurse, preparing to discuss the female reproductive system with a group of adolescent females, would include that which of the following is not a primary function of the female reproductive system? 1.Breastfeeding 2.Hormone secretion 3.Pregnancy 4.Sensory innervation 7.A young adult female client is concerned that she does not have enough eggs since she has not yet become pregnant. The nurse should assure her that the number of ova available to produce a pregnancy would be around: 1.500. 2.10,000. 3.300,000. 8.During a gynecological exam, it is noted that a clients os is in the shape of a slit. The nurse realizes that this shape means that the client has: 1. bornechildren. 2. not startedmenses. 3. not borne any children. 4.gone throughmenopause. 9.The nurse, reviewing the reproductive hormones needed to produce sperm and ova, realizes that which of the following hormones is not involved in the formation of sperm and ova? 1.Follicle-stimulating hormone 2.Gonadotropin-releasing hormone 3.Luteinizing hormone 4.Prolactin 10.During the examination of the male testes, the nurse should instruct the client on: 2. monthly testicularself-examinations. 3. why a colonoscopy is important every 10 years after the age of 50. 4.how a condom prevents the spread of sexually transmittedinfections. 11.A male client has a prostate specific antigen level of 22 nanograms. The nurse realizes that this client will most likely be scheduled for a(n): 1.bone scan 2.CT scan 3.testicular biopsy 4.duplex ultrasonography 12.A female clients Pap test revealed atypical results. The nurse realizes that this client will most likely be scheduled for a(n): 1. culdoscopy. 2. colposcopy. 3. loop electrosurgical excision. 4.cold-knifeconization. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1.A female client has an infection of the paraurethral glands. When asked by the client what these glands do, the nurse should respond: (Select all that apply.) 1.These glands function like the prostate gland in the male. 2.These glands secrete mucus near the vaginal opening. 3. These glands secretemucus. 4. These glands are similar to the Cowpers glands in themale. 5.These glands are located inside theurethra. 6.These glands serve no real function. 2.The nurse is instructing a postmenopausal client in the importance of having serum lipid levels analyzed because after menopause, which of the following changes can occur? (Select all that apply.) 1. Total cholesterolincreases 2. Low-density lipoprotein increases 3.Triglyceridesincrease 4.High-density lipoprotein decreases 5.Low-density lipoprotein decreases 6.High-density lipoprotein increases 3.The nurse is reviewing the physiological sexual response pattern within males and females and realizes that which of the following occur in both genders? (Select all that apply.) 1.Resolution 2.Orgasm 3.Erection 4.Lubrication 5.Plateau 6.Excitement 4.A female client is concerned that she has not had sexual intercourse with her husband for over 2 months. Which of the following can the nurse respond as causes for an alteration in sexual functioning? (Select all that apply.) 1.Chronic illnesses 2.Physical disabilities 3.Negative body image 4.Medications 5.Surgical procedures 6.Employment status 5.The nurse is concerned that a female client might be experiencing intimate partner violence. Which of the following assessment questions can be used to gain more information from the client? (Select all that apply.) 1.In the last year have you been hit, slapped, or physically hurt by someone? 2.Are you currently sexually active? 3.Within the last year has someone made you do something sexual that you did not want to do? 4.Is sex satisfying to you? 5.Are you afraid of your partner or anyone else? 6.Do you have discomfort with intercourse? Chapter 47. Breast Disorders MULTIPLE CHOICE 1.A client who has just given birth is planning on breastfeeding the baby. The nurse realizes that which of the following hormones influences breast milk secretion? 1.Follicle-stimulating hormone 2.Luteinizing hormone 3.Oxytocin 4.Prolactin 2. The nurse is instructing a female client about breast self-examination. Which of the following instructions would not be correct for the nurse toprovide? 1.A menstruating woman should check her breast monthly 8 days following her menses. 2.An inverted nipple is not a cause for alarm. 3. During menopause, you should check your breasts once a month during the same timeframe. 4.Visually check the breasts in front of amirror. 3.A client who has been breastfeeding a newborn for the last 3 months is experiencing an inflammation of the breast. The nurse realizes this client is experiencing: 1.intraductal papilloma. 2.mastalgia. 3. mastitis. 4.mastodynia. 4. During the examination of a female clients breasts, the nurse determines that which ofthe following assessment findings would benormal? 1.Nipple discharge 2.Masses 3.Scaling 4. Symmetrical nipples 5. The nurse is instructing a female client on the importance of having routine mammogramsbecause mammograms: 1.can detect masses before they become palpable. 2.involves no radiation. 3.has a 25% rate of false positives. 4.combines a blood test with radiology. . 6.The nurse is instructing a female client on what should be done if a lump is discovered while performing breast self-examination (BSE). What should the nurse instruct the client to do? 1.Call her physician and immediately schedule an appointment. 2.Call to schedule an appointment next month. 3. Take the antibiotics she has in her medicinecabinet. 4. Wait until next months BSE to make sure the lump is still there. 7.The nurse determines that a female client has a lower risk for developing breast cancer when which of the following is assessed? 1.Alcohol intake 2.Breastfeeding 3.Obesity 4.Smoking 8.The nurse should instruct the client that when performing a breast self-examination, pay particular attention to which of the following areas since the greatest number of malignancies are found in this breast area? 1. Upper outer quadrant of the breast to theaxilla 2. Portion of the breast closest to the xiphoidprocess 3.Portion of the breast closest to the abdomen 4.Portion of the breast closest to theneck 9.The nurse should instruct a client, diagnosed with mastalgia, to do which of the following? 1.Have an immediate mammogram. 2.Expect to need a biopsy. 3.Decrease the intake of caffeine. 4.Determine if breast augmentation surgery is desired. 10.A female client tells the nurse that she is planning on having plastic surgery to correct a minor facial defect and then have her breasts done. The nurse would identify which of the following nursing diagnoses as being appropriate for this client? 1.Ineffective coping 2.Anxiety 3.Hopelessness 4.Body dysmorphic disorder 11.The nurse is determining if a female client is at risk for benign breast disease. Which of the following is a risk factor for this disorder? 1.Smoking 2.Caffeine use 3.Alcohol intake 4.Age 55 12.A client is scheduled for a prophylactic mastectomy. The nurse should remind the client that skin flaps will be left after the surgery for: 1. reconstruction. 2. suturing to the chestwall. 3. possible use for other skindisorders. 4. donation for someone needing a skin transplant. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1.When instructing a client on breast self-examination, the nurse reviews the importance of visual inspection of the breasts. Which of the following should the nurse instruct the client to focus on when doing this part of the examination? (Select all that apply.) 1.Contour and symmetry of the breasts 2.Skin changes 3.Position of the nipples 4.Presence or absence of masses 5.Pain 6.Size . 2.The nurse is preparing to assess a clients nipples during a breast examination. Which of the following are considered pathological conditions that affect the nipple? (Select all that apply.) 1.Bleeding 2.Lumps 3.Discharge 4.Scars 5.Fissures 6.Large size 3.Which of the following should the nurse do if a female client is experiencing nipple discharge? (Select all that apply.) 1. Note the color of thedischarge. 2. Determine if the discharge is from one or bothbreasts. 3. Obtain a sample of the discharge with a sterile cotton-tipped swab. 4.Assess the nipple drainage for occultblood 5.Apply sterile bandages over the nipple. 6.Pad the clients bra with gauze. 4.A client is experiencing galactorrhea. Which of the following should the nurse assess in this client? (Select all that apply.) 1. Recent vigorous nipplestimulation 2. Prescribed hormones, blood pressure medications, orantidepressants 3.Intake of herbal remedies such as fennel oranise 4.Use of street drugs such as opiates and marijuana 5.Recent chest trauma 6.Age of menarche 5.A client is considering breast augmentation surgery. Which of the following postoperative complications should the nurse discuss with the client regarding this surgery? (Select all that apply.) 1.Change in sensation 2.Development of a hematoma 3.Fibrous tissue around the implant 4.Heart palpitations 5.High blood pressure 6.Arm pain Chapter 48. Vaginal, Uterine, and Ovarian Disorders Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A 23-year-old sexually active woman presents for her first Pap smear. Her history includes nulligravida, age at first intercourse 14, and more than 10 sexual partners. Which of the following conditions should the clinician be particularly alert for during herexamination? a. Human papillomavirus(HPV) b. Endometrialhyperplasia c. Vagismus d. Polycystic ovariansyndrome 2. A 20-year-old woman is seen in the clinic because her boyfriend was found to havegonorrhea. Which of the following is the treatment of choice for gonorrhea? a. Ceftriaxone b. Doxycycline c. Acyclovir d. Metronidazole 3. A 24-year-old woman presents to the clinic with dysuria, dyspareunia, and a mucopurulent vaginal discharge. Her boyfriend was recently treated for nongonococcal urethritis. What sexually transmitted disease has she most probably been exposedto? a. Gonorrhea b. HPV c. Chlamydia d. Trichomonas 4. A 45-year-old woman is seen in the clinic with complaints of a vaginal discharge. The clinician identifies clue cells on the vaginal smear. Which of the following diagnoses is associated with this finding? a. Trichomonas b. Bacterialvaginosis c. HPV d. Herpes simplexvirus 5. Which of the following medications is the treatment of choice fortrichomonas? a. Metronidazole b. Ceftriaxone c. Diflucan d. Doxycycline 6. A 58-year-old woman presents with a breast mass. Which of the following responses by the clinician would be mostappropriate? a. “It is probably just a cyst because that is the most common breastmass.” b. “We will order a mammogram and ultrasound to help establish adiagnosis.” c. “We will go ahead and schedule you for a biopsy because that is the only way to know forsure.” d. “Because your lump is painful, it is most likely notcancer.” 7. A 26-year-old woman is seen with complaints of irregular vaginal bleeding. Which of the following tests should be the firstpriority? a. Pregnancytest b. Pelvicultrasound c. Endometrialbiopsy d. Plateletcount 8. A 42-year-old woman presents to the clinic with complaints of painful intercourse for the lastmonth. Which of the following should be explored as the likely cause of her dyspareunia? a. Menopause b. Dehydration c. Excessprogesterone d. Sexual trauma as achild 9. A 36-year-old woman is seen with complaints of vaginal itching, burning, and discharge. On potassium hydroxide (KOH) wet mount of vaginal discharge, the clinician notices hyphae. Whichof the following treatments would beappropriate? a. Fluconazole b. Estrogen vaginalcream c. Metronidazole d. Doxycycline 10. A 21-year-old woman is seen in the clinic requesting birth control pills. Which of the following tests is essential before prescribing any oralcontraceptive? a. Pregnancytest b. Complete blood cellcount c. Thyroid-stimulatinghormone d. Urine dip forprotein 11. A 40-year-old woman is seen for her yearly examination. She is single and not in a monogamous relationship. Her social history includes smoking cigarettes “occasionally” and drinking about two beers a day. Her body mass index (BMI) is 25. She is requesting birth control. Which of the following methods would be best for thispatient? a. Intrauterinedevice b. Oralcontraceptive c. Condom d. Vaginal contraceptivesponge 12. A 44-year-old patient with breast cancer is prescribed tamoxifen by her surgeon. She is complaining about hot flashes. Which of the following responses by the clinician would be mostappropriate? a. “You must be having menopause.” b. “The hot flashes are a result of the antiestrogenic effects oftamoxifen.” c. “Tamoxifen will impact your temperature regulationcenter.” d. “The drug destroys yourovaries.” 13. A 32-year-old woman is seen in the clinic because she has been unable to get pregnant after 12 months of unprotected sex. In order to determine the cause of the infertility, the clinician should question her about which of these possiblecauses? a. Pelvic inflammatorydisease b. Oral contraceptive use for 15years c. Earlymenarche d. Diet high in soyprotein 14. When assessing a woman for infertility, which of the following tests should be donefirst? a. Analysis of partner’ssperm b. Magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) c. Hysterosalpingogram d. Estrogenlevel 15. A 15-year-old girl is seen in the clinic because she has not yet had her first period. Which of the following questions would help the clinician determine thecause? a. “Are you sexuallyactive?” b. “How long have you beenunderweight?” c. “Did your mother take diethylstilbestrol during herpregnancy?” d. “Have you noticed any changes in your moodslately?” 16. What is the most common cause of secondaryamenorrhea? a. Pregnancy b. Pituitarydysfunction c. Inadequate estrogenlevels d. Geneticdisorders 17. A 22-year-old woman is diagnosed with premenstrual syndrome. Which of the following lifestyle changes should the clinician suggest to help minimize the patient’ssymptoms? a. At least 4 cups of green teadaily b. Regularexercise c. Take vitamin Asupplements d. Eat a diet high iniron 18. A 25-year-old woman is seen in the clinic complaining of painful menstruation. Which of the following pelvic pathologies is the most common cause ofdysmenorrhea? a. Pelvic inflammatorydisease b. Endometriosis c. Sexually transmittedinfections d. Ovariancyst 19. A 26-year-old woman tells the clinician that she has endometriosis, because she has frequent pelvic pain. The clinician also should consider which of these differentialdiagnoses? a. Diverticulitis b. Cholelithiasis c. Kidneystones d. Ovariancysts 20. Which of the following would be appropriate treatment for a woman with mildendometriosis? a. Oralcontraceptives b. Leuprolide acetateinjections c. Nafarelin nasalspray d. Hysterectomy 21. A 45-year-old woman is seen in the clinic with abnormal uterine bleeding and pain during intercourse. The clinician should consider which of the followingdiagnoses? a. Leiomyoma b. Pregnancy c. Ovariancancer d. All of theabove 22. A 48-year-old woman is seen in the clinic with complaints of prolonged heavy menstrualperiods. She is pale and states she can no longer exercise. Pelvic exam reveals a single, very large mass. Which of the following diagnostic tests should the clinician order first? a. Transvaginalultrasound b. Endometrialbiopsy c. MRI d. Abdominal computed tomographyscan 23. A 45-year-old woman is seen because of irregular menstrual periods. Her follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) level is 48 mIU/mL, and her luteinizing hormone (LH) level is elevated. Sheasks the clinician what this means. Which would be the bestresponse? a. “You are approachingmenopause.” b. “You have a hormonalimbalance.” c. “Your FSH is normal, but your pituitary is making too muchLH.” d. “There is an imbalance between your ovaries andpituitary.” 24. Which of the following tests is essential for a 46-year-old woman who the clinician suspects is perimenopausal? a. Pregnancy b. Estrogenlevel c. Progesteronelevel d. LHlevel 25. A 60-year-old woman is seen for an annual checkup. Her obstetric history reveals para 6, gravida 6. She reports that she went through menopause at age 45. Her grandmother died at age 80 of colon cancer, and her father died of lung cancer. What in her history would be a risk factor for ovarian cancer? a. Her numerouspregnancies b. Her age atmenopause c. Her father’s history of lungcancer d. Her grandmother’s history of coloncancer 26. A 58-year-old woman, who had a total abdominal hysterectomy at the age of 45, is diagnosed with atrophic vaginitis. Which of the following is the most appropriatetreatment? a. Conjugated estrogen, 0.625 mg/dayoral b. Estradiol, 7.5 mcg/24 hr vaginalring c. Medroxyprogesterone, 10 mg/day oral d. Conjugated estrogen, 0.3 mg + medroxyprogesterone 1.5 mg/dayoral True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Oral contraceptive pills can cause endometrialcancer. 2. A woman taking estradiol is at risk for developing endometrialcancer. 3. Most breast cancer cases are in women with a family history of breastcancer. Chapter 49. Prostate Disorders Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A 63-year-old man is seen in the clinic with a chief complaint of nocturia. Which of the following should be included in the differentialdiagnosis? a. Psychogenicnocturia b. Urethralpolyp c. Irritative posterior urethrallesion d. Benign prostatichypertrophy 2. A 76-year-old man is seen in the office for complaints of urinary incontinence. The clinician should explore which of these causes of incontinence inmen? a. Urethralpolyps b. Urinary tract infection(UTI) c. Anticholinergicmedication d. All of theabove 3. A 14-year-old male is seen with complaints of severe testicular pain. The clinician suspects testicular torsion. Which of the following is the appropriateaction? a. Refer to a urologistimmediately. b. Obtain a computed tomography (CT)scan. c. Instruct the patient to elevate thescrotum. d. Prescribeibuprofen. 4. An 82-year-old man is seen in the primary care office with complaints of dribbling urine and difficulty starting his stream. Which of the following should be included in the list ofdifferential diagnoses? a. Benign prostatic hyperplasia(BPH) b. Parkinson’sdisease c. Prostatecancer d. All of theabove 5. Which of the following would be an appropriate treatment for a patient with mildBPH? a. Refer to a urologist forsurgery. b. Prescribe a trial oftamsulosin. c. Recommend cranberry supplements. d. Reevaluate symptoms in 1 to 3months. 6. A 30-year-old man is seen with a chief complaint of loss of libido. Which of the following laboratory tests would help establish adiagnosis? a. Testosteronelevel b. Prostate-specificantigen c. Nocturnal penile tumescence andrigidity d. Prolactinlevel 7. Which of the following should be considered in a patient presenting with erectiledysfunction? a. Diabetesmellitus b. Hypertension c. Atherosclerosis d. All of theabove 8. A 35-year-old man presents with complaints of painful erections, and he notices his penis is crooked when erect. What is the most likelydiagnosis? a. Peyronie’sdisease b. Damage to the pudendalartery c. Scarring of thecavernosa d. All of theabove 9. The patient with BPH is seen for follow-up. He has been taking finasteride (Proscar) for 6months. The clinician should assess this patient for which of these side effects? a. Erectiledysfunction b. Glaucoma c. Hypotension d. Headache 10. The clinician should prescribe an antibiotic that covers which of these organisms for a patient with acuteprostatitis? a. Gram-positivecocci b. Gram-negativecocci c. Gram-positivebacillus d. Gram-negativebacillus 11. The 56-year-old man with chronic prostatitis should be treated with trimethoprim 80 mg- sulfamethoxazole 400 mg (TMP-SMX, Bactrim) for howlong? a. 3 to 7 days b. 14 to 21days c. 3 to 6weeks d. 6 to 12weeks 12. A 46-year-old man presents with urinary hesitancy and low back pain. He has no history of UTI. Digital rectal examination (DRE) reveals a normal prostate, and a diagnosis of prostatodynia is made. Which is the appropriatetreatment? a. Terazosin 2 mg PO once aday b. Ice pack to the scrotalarea c. Saw palmetto 320 mg perday d. All of theabove 13. A 23-year-old sexually active man is seen in the clinic with unilateral painful testicular swelling, and he is diagnosed with epididymitis. In order to prescribe the correct drug, the clinician must understand that which of these is the most common causativeorganism? a. Escherichiacoli b. Staphylococcusaureus c. Chlamydiatrachomatis d. Pseudomonasaeruginosa 14. Which test is used to confirm a diagnosis ofepididymitis? a. Urinalysis b. Gram stain of urethraldischarge c. Complete blood cell count withdifferential d. Ultrasound of thescrotum 15. Treatment for epididymitis includes which of thefollowing? a. Warm sitzbaths b. Scrotalelevation c. Masturbation d. All of theabove 16. Which of the following data is indicative of testiculartorsion? a. Absent cremastericreflex b. Pain relieved on testicularelevation c. Testicle very low in thescrotum d. Swollen scrotum with “red dotsign” 17. A 60-year-old man presents with an enlarged scrotum. The clinician uses a penlight to transilluminate the scrotum. In a patient with a hydrocele, what would the clinician expect tofind? a. The scrotum will bedark. b. The scrotum will appear light pink oryellow. c. The scrotum will appear milkywhite. d. The internal structures will be clearlyvisible. 18. During a DRE on a 75-year-old man, the clinician suspects the patient has prostate cancer. What physical finding should make the cliniciansuspicious? a. An enlarged rubberygland b. A hard irregulargland c. A tendergland d. A boggygland 19. A 78-year-old man is diagnosed with C2 prostate cancer, and he asks the clinician what that means. In order to answer the patient, the clinician must have which of these understandings of the Jewett ratingsystem? a. The cancer involves the seminalvesicles. b. There is metastatic disease to regional lymphnodes. c. The cancer is confined to thecapsule. d. There is metastasis to distantorgans. 20. A 58-year-old patient has been receiving leuprolide as treatment for prostate cancer. The clinician should instruct the patient about which of these sideeffects? a. Risk ofosteoporosis b. May have hotflushes c. May haveimpotence d. All of theabove 21. A 22-year-old male is seen in the clinic because he found a hard lump in his testicle when performing testicular self-examination (TSE). Which of the following should be included in the list of differentialdiagnoses? a. Testicularcancer b. Inguinalhernia c. Varicocele d. All of theabove 22. What is the treatment of choice for a patient diagnosed with testicularcancer? a. Radicalorchidectomy b. Lumpectomy c. Radiationimplants d. All of theabove 23. A patient with testicular cancer is being followed after completing treatment 1 year ago. He has been symptom-free with no evidence of disease. How often should he have a CTscan? a. Everymonth b. Every 3 to 4months c. Every 6 to 12 months d. Every year True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Patients treated for Neisseria gonorrhoeae also should be treated for Chlamydiatrachomatis. 2. Hepatitis A is considered a sexually transmitted infection by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Chapter 50. Penile and Testicular Disorders MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The nurse is instructing a client diagnosed with acute prostatitis. Which of the following instructions would be the least beneficial to theclient? 1. Avoid alcohol andcaffeine. 2. Sex should be avoided during the acute phase. 3.Sit for as long as youcan. 4.Sitz baths may provide comfort. 2.The nurse is documenting the health history of a client diagnosed with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). In which of the following areas would the nurse take a careful history? 1.Bowel patterns 2.Eating patterns 3.Sleeping patterns 4.Urinary patterns 3.A client, diagnosed with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), should be instructed to do which of the following? 1.Do nothing since this disorder does not require any follow-up. 2.Decrease water intake to avoid dribbling. 3.Void every 2 to 3 hours. 4.Wear scrotal support. 4.A client, recovering from a transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) with a continuous bladder irrigation system to a three-way indwelling urinary catheter, tells the nurse he has to void. What nursing intervention should the nurse perform? 1. Call thephysician. 2. Increase the flow of the irrigant. 3.Irrigate thecatheter. 4.Tell the client to void. 5.A client who is 12 hours postoperative after a transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is concerned about the blood clots in the catheter and urinary collection bag. How should the nurse respond? 1.I need to call your physician. 2.I will need to stop the bladder irrigation. 3.Blood clots are common during this time frame and will start to decrease in a day. 4.You need to stop moving and irritating the catheter. 6.A client is being screened for prostate cancer. What tests would be completed at this time? 1.Digital rectal examination and transrectal ultrasonography 2.Biopsy of the prostate and magnetic resonance imagery 3.Complete blood cell count and prostate-specific antigen 4.Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and digital rectal examination 7.The nurse is instructing a client about testicular self-examination (TSE). Which of the following would not be included in these instructions? 1.The testis should feel smooth and egg-shaped. 2.Perform TSE after a bath or shower. 3.TSE should be performed monthly by every male older than age 40. 4.Any lumps and changes in the testicles should be reported. 8.A male client is diagnosed with orchitis. The nurse should assess the client for which of the following? 1.Recent infection with mumps 2.Recent diagnosis of prostatitis 3.History of type 2 diabetes mellitus 4.Diagnosis of renal insufficiency 9.A client is diagnosed with a spermatocele. The nurse should instruct the client on which of the following? 1. The use of heat to reduce the size of the inflamed area 2.The potential need for surgery to correct the disorder 3.The use of ice packs to reduce the size of the inflamed area 4.The importance of using antibiotics to treat thedisorder 10.A client is diagnosed with a varicocele. The nurse realizes that this client is likely to develop: 1.hydrocele. 2. prostate cancer. 3.prostatitis. 4.infertility. 11.A newborn male child is diagnosed with cryptorchidism. The nurse should prepare to administer which of the following to this client? 1.Intravenous fluids 2.Antipyretic medication 3.Human chorionic gonadotropin medication 4.Antibiotics 12.A client is experiencing priapism. Which of the following should the nurse do first to help the client? 1.Apply ice packs to the perineum. 2.Prepare for emergency surgery. 3.Prepare for an aspiration of blood from the penis. 4.Apply heat to the perineum. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1.A client is diagnosed with testicular torsion. Which of the following might be indicated for this client? (Select all that apply.) 1.Manually untwist the testicle 2.Orchiopexy 3.Testicle removal 4.Pain management 5. Application of ice and a scrotalsupport 6. Prescribe medication 2.A client is diagnosed with epididymitis. The nurse should instruct the client on which of the following as treatment for the disorder? (Select all that apply.) 1.Broad spectrum antibiotics 2.NSAIDs 3. Bed rest 4. Elevate the scrotum 5.Apply cold packs 6.Applyheat 3.Which of the following should the nurse instruct a client who is recovering from a vasectomy? (Select all that apply.) 1.Use ice packs to control postoperative bleeding. 2.Wear cotton jockey type briefs for scrotal support. 3.Use warm sitz baths to aid in comfort. 4.Recognize the signs and symptoms of postoperative infection. 5.A vasectomy protects the client from sexually transmitted illnesses. 6.Ejaculate will be reduced after the procedure. 4.The nurse is assessing a client diagnosed with balanitis and posthitis. Which of the following will the nurse most likely assess in this client? (Select all that apply.) 1.Penile discharge 2.Hematuria 3.Pain 4.Erythema 5.Flank pain 6.Edema 5.The nurse is assessing a client who is experiencing erectile dysfunction. For which of the following should the nurse assess the client? (Select all that apply.) 1.Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus 2.Thyroid disease 3.Chronic renal failure 4.Multiple sclerosis 5.Parkinsons disease 6.Gastroesophageal reflux disease Chapter 51. Sexually Transmitted Infections Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. During data collection the nurse notes the presence of a chancre on a male patients penis. For which sexually transmitted infection should the nurse focus additional datacollection? a. Herpes b. Syphilis c. Gonorrhea d. Chlamydia 2. A patient is diagnosed with a parasitic infection caused by close contact with another persons genitals. For which infection should the nurse plancare? a. Phthiruspubis b. Treponemapallidum c. Neisseriagonorrhoeae d. Chlamydiatrachomatis 3. It is documented in the medical record that a patient has gummas. For which sexually transmitted infection should the nurse plancare? a. Syphilis b. Gonorrhea c. Chlamydia d. Genitalherpes 4. The nurse is assisting with teaching a 22-year-old female patient who is diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection (STI). She says, I dont understand. My boyfriend always wears a condom. Which understanding by the nurse should guide teaching in thissituation? a. Condoms are a reliable source of protection againstSTIs. b. It is a myth that condoms provide any protection againstSTIs. c. Condoms can decrease the risk of STIs, but they are notfoolproof. d. Condoms must be used with a spermicide to guarantee protection againstSTIs. 5. The nurse is providing care for a patient with genital herpes who has vesicular lesions. What term should the nurse use to describe these lesions to thepatient? a. Warts b. Rashes c. Blisters d. Papules 6. Human papillomavirus (HPV) produces verrucous growths. What term should the nurse use to describe these lesions to thepatient? a. Warts b. Rashes c. Blisters d. Papules 7. The nurse is collecting data on a patient with Chlamydia. Which assessment finding should be reported immediately to the RN orphysician? a. Painfulurination b. Redconjunctivae c. Vaginaldischarge d. Sharp pain at the base of theribs 8. Because Trichomonas is relatively large, unusually shaped, and diagnosed quickly, thenurse is asked to assist the physician obtain which type ofspecimen? a. Culture b. Blood test c. Wetmount d. Litmuspaper 9. A patient diagnosed with Trichomonas asks the nurse how the diagnosis will affect herrisk for cervical cancer. Which response by the nurse isbest? a. Wet-mount slides should be done yearly to help detect cervicalcancer. b. Serological testing will be done to detect tumor proteins and screen for cervicalcancer. c. Papanicolaou smears should be done more frequently because results may be altered by Trichomonas. d. Culture and sensitivity testing is done with Papanicolaou (Pap) smears every other year to determine if you have cervicalcancer. 10. A patient asks why the physician has recommended systemic interferon treatmentfor genital warts. Which explanation should the nurse provide to thepatient? a. Interferon can improve liverfunction. b. Interferons can increase your red blood cellcount. c. Interferon treatment does not have any sideeffects. d. Interferon therapy can attack warts all over the body at the sametime. 11. A patient with hepatitis B virus (HBV) delivers a 6-pound 2-ounce baby boy. Which action should the nurse anticipate will be needed for theinfant? a. Intravenous antibiotics for 12hours b. Antiviral eye medication less than 2 hours afterbirth c. There is no treatment that is safe and effective forinfants. d. HBV-immune globulin less than 12 hours after birth and then HBV vaccineseries 12. The nurse must bathe a patient with herpes. What is the nurses best protection against contracting sexually transmitted infections (STIs) from patients while providing perinealhygiene? a. Wearing gloves at alltimes b. Washing hands followingcare c. Practicing standardprecautions d. Avoiding touching patients who haveSTIs 13. The nurse is caring for a pregnant woman who is fearful that her unborn child will be born blind because of having a sexually transmitted infection (STI). For which STI should the nurse plan care to prevent ophthalmia neonatorum in the newborn? a. Syphilis b. Gonorrhea c. Genitalwarts d. Genitalherpes 14. The nurse is caring for a young woman who is newly diagnosed with genital warts. She states, I heard you can get cancer from STIs. Is that true? Which response by the nurse iscorrect? a. No, you cannot get cancer fromSTIs. b. Yes, most STIs can lead to cancerous changes if not treatedpromptly. c. Yes, some STIs have been linked to cancer, so adequate treatment is veryimportant. d. No, that is not true, but a diagnosis of cancer does increase the risk of contracting anSTI. 15. The nurse is identifying ways for a young adult to reduce the risk of contracting a sexually transmitted infection (STI). What should the nurse teach about the relationship betweenconsumption of alcohol and immediate risk of contracting anSTI? a. Alcohol may reduceinhibitions. b. Alcohol increases risk for liverdisease. c. Alcohol lowers the bodys resistance toinfection. d. Alcohol impairs the integrity of the mucous membranes, providing a portal of entry forinfection. 16. The nurse reviews the ways to prevent condom breakage with a patient. Which patient statement indicates that more teaching isnecessary? a. Condoms should never be reused. b. I should use a water-solublelubricant. c. Before I use a condom, I should inflate it and check it for holes andleaks. d. I should make sure to leave a half inch extra space at the end of thecondom. 17. The nurse is assisting with the admission of a known intravenous drug abuser to a medical unit. In addition to drug abuse, which disorder in the patients history is most consistent with a diagnosis ofhepatitis? a. Jaundice b. Diabetesmellitus c. Bowelobstruction d. Chronicheadaches 18. The nurse is teaching a patient the importance of completing treatment for gonorrhea. On which information is the nurse basing thisteaching? a. Gonorrhea is nottreatable. b. Only men experience symptoms; women are usuallyasymptomatic. c. Men and women may be asymptomatic and still transmit theinfection. d. Treatment is associated with many serious side effects, so compliance islow. 19. The nurse is assisting in the preparation of a teaching seminar for adolescents to prevent the development of a sexually transmitted infection (STI). Which nonsexual activity should the nurse teach that may transmit a sexually transmitted infection(STI)? a. Sharing acigarette b. Borrowing ahairbrush c. Coughing andsneezing d. Sharing intravenous drugequipment 20. A patient asks for the best way to prevent contracting a sexually transmitted infection (STI). What response should the nurse make to this patientsquestion? a. Abstinence b. Oralcontraceptives c. Condom withspermicide d. Prophylactic oralantibiotics 21. A patient diagnosed with genital warts asks how they developed. Which pathogen should the nurse explain as causing genitalwarts? a. Sarcoptesscabiei b. Hepatitis A andB c. Humanpapillomavirus d. Chlamydiatrachomatis 22. The nurse is caring for a 76-year-old retired man who is undergoing evaluation for dementia. What would be an important part of the mans history to report to thephysician? a. The patient has a history ofsyphilis. b. The patient was exposed toChlamydia. c. The patient has a history of hepatitisB. d. The patient has a history of genitalwarts. 23. A patient is undergoing treatment that involves the burning of lesions with heat or chemical agents. The nurse recognizes that this patient most likely has whichcondition? a. Syphilis b. Chlamydia c. HepatitisB d. Genitalwarts 24. The nurse is providing care for a newborn. Which intervention should the nurse make to prevent development of ophthalmianeonatorum? a. Interferoninjection b. Antibioticeyedrops c. Vitamin Kinjection d. Hepatitis B virus (HBV)-immuneglobulin 25. While reviewing a medical record the nurse notes that patient has a strawberry cervix. For which sexually transmitted infection (STI) would the nurse plancare? a. Gonorrhea b. Herpessimplex c. Trichomoniasis d. Human papillomavirusinfection 26. The nurse is preparing a poster presentation identifying the frequency of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in the United States. Which STI should the nurse highlight as beingthe most commonlydiagnosed? a. Gonorrhea b. Chlamydia c. Trichomoniasis d. Humanpapillomavirus 27. While assisting a health care provider (HCP) conduct a pelvic examination, the patient complains of severe pain during the bimanual examination. For which health problem shouldthe nurse suspect this patient is going to needcare? a. Syphilis b. Gonorrhea c. Pelvic inflammatorydisease d. Human papillomavirusinfection 28. While assisting with care, the nurse counsels the patient diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection (STI) about notification of sexual partners. Which patient statement indicates the need for further teaching? (Select all thatapply.) a. I can contact my sexual partnersmyself. b. Reporting regulations are the same throughout thecountry. c. A report form will be completed in my chart that includes a list of my sexualcontacts. d. The public health authority can notify a list of sexual contacts without including myidentity. Multiple Response Identify one or more choices that best complete the statement or answer the question. 29. The nurse is assisting with teaching a patient who has been exposed to hepatitis B. Which symptoms should the nurse explain may occur before jaundice appears? (Select all thatapply.) a. Rash b. Nausea c. Confusion d. Dark-coloredurine e. Muscle or jointpain f. Elevated bloodglucose 30. The nurse is reviewing prescribed laboratory tests for a patient demonstrating manifestations of syphilis. What diagnostic tests should the nurse expect to be prescribed for this patient? (Select all that apply.) a. RPR b. NAT c. VDRL d. ELISA e. Culture f. CD4 counts 31. A 24-year-old woman diagnosed with Chlamydia has been prescribed doxycycline. What should be included in the nurses teaching about the drug treatment? (Select all thatapply.) a. Take this drug with ameal. b. Do not take with dairyproducts. c. Avoid unnecessary exposure tosunlight. d. Abstain from alcohol for at least 48 hours aftertreatment. e. Use birth control methods to ensure you do not becomepregnant. 32. The nurse is teaching a patient about the use of condoms to prevent sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Which information should the nurse include in this teaching? Select all thatapply. a. Condoms can decrease the risk of transmittingSTDs. b. Latex condoms are less likely to break than othertypes. c. Inflating the condom prior to use allows for effectiveinspection. d. Condoms should be used no more than twice and then discardedproperly. e. Use of a water-soluble lubricant with a condom increases its effectiveness in preventing the spread of anSTD. f. Use of a petroleum-based lubricant with a condom increases its effectiveness in preventing the spread of anSTD. 33. The nurse is providing care for a patient recently diagnosed with Chlamydia. Which information should the nurse recommend be included in patient teaching? (Select all thatapply.) a. Women with Chlamydia may complain of a sorethroat. b. Chlamydia is characterized by the development ofchancres. c. Ophthalmia neonatorum is seen in infants born to women withChlamydia. d. Chlamydia can be transmitted sexually and by blood and body fluidcontact. e. The risk of ectopic pregnancy is increased in women with a history ofChlamydia. f. The Chlamydia virus can lie dormant in the nervous system tissues and reactivate when an individual is under stress or has a compromised immunesystem. 34. The nurse notes that a patient is diagnosed with vulvovaginitis. What should thenurse expect when assessing this patient? (Select all that apply.) a. Vaginaledema b. Vaginaldischarge c. Areas ofecchymosis d. Dark brown vaginalbleeding e. Complaints of vaginal itching andburning 35. A patient in labor is diagnosed with mucopurulent cervicitis. For which healthproblems should the nurse anticipate providing care to the newborn? (Select all thatapply.) a. Pneumonia b. Conjunctivitis c. Irregular heartrate d. Flaccidextremities e. Cyanoticextremities 36. A patient diagnosed with syphilis reminds the HCP of having an allergy to penicillin. Which medications should the nurse expect to be prescribed for this patient? (Select all thatapply.) a. Gentamicin b. Amoxicillin c. Tetracycline d. Doxycycline e. Erythromycin 37. While providing a bath the nurse suspects that an older female patient has a Trichomonas infection. What type of discharge did the nurse observe to come to this conclusion? (Select all that apply.) a. Frothydischarge b. Foul-smellingdischarge c. Yellow-greendischarge d. Open sores on the labiamajora e. Wart-like growths on the labiaminora Chapter 52. Common Musculoskeletal Complaints Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. One of the initial steps in assessing patients with musculoskeletal complaints is to determine whether the complaint is articular or nonarticular in origin. Which of the following is an example of an articularstructure? a. Bone b. Synovium c. Tendons d. Fascia 2. You have detected the presence of crepitus on examination of a patient with a musculoskeletal complaint. Additionally, there is limited range of motion (ROM) with both active and passive movement. These findings suggest that the origin of the musculoskeletal complaintis: a. Articular b. Inflammatory c. Nonarticular d. A andB 3. Which of the following signs or symptoms indicate an inflammatory etiology to musculoskeletal pain? a. Decreased C-reactiveprotein b. Hyperalbuminemia c. Morningstiffness d. Weight gain 4. Which of the following statements concerning the musculoskeletal examination istrue? a. The uninvolved side should be examined initially and then compared to the involvedside. b. The part of the body that is causing the patient pain should be examinedfirst. c. When possible, the patient should not be asked to perform active range-of-motion (ROM) exercises to avoid causingpain. d. Radiographs should always be obtained prior to examination so as not to cause further injury to thepatient. 5. You are performing muscle strength testing on a patient presenting with musculoskeletal pain and find that the patient has complete ROM with gravity eliminated. Which numeric grade of muscle strength would you give thispatient? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 e. 5 6. Mrs. Gray is a 55-year-old woman who presents with tightness, pain, and limited movement in her right shoulder. She denies any history of trauma. Her examination reveals a 75% reduction in both active and passive ROM of the right shoulder. Mrs. Gray also is experiencing tenderness with motion and pain at the deltoid insertion. Her medical history is significant for type 1 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Her social history reveals that she is a secretary and that she is right- handed. Based on her examination and medical history, you suspect adhesive capsulitis, or “frozen shoulder.” Which clue in Mrs. Gray’s history supports thisdiagnosis? a. History ofhypertension b. Her affected shoulder is also her dominantarm. c. Her history of diabetesmellitus d. Her work as a secretary predisposes her to repetitivemotions. 7. Jennifer is an 18-year-old who comes to the emergency room after a fall during a soccergame. Jennifer explains that she fell on her left side and kept her arm out straight to break her fall. She has been experiencing severe pain and limited ROM in her left shoulder. The clinician has diagnosed Jennifer with a dislocated shoulder. Which of the following statements are true concerning shoulder dislocation? a. Posterior dislocations are more common than anteriordislocations. b. There is a risk of neurovascular and neurosensory trauma, so the clinician should check for distalpulses. c. Recurrent dislocations are uncommon and would require great force to result in injury. d. Surgery is most commonly the treatment ofchoice. 8. Mrs. Anderson is a 35-year-old woman who has been recently diagnosed with carpal tunnel syndrome. She has two young children and asks the clinician what the chances are that they alsowill develop carpal tunnel syndrome. Which of the following responses would be correct regarding the risk of developing carpal tunnelsyndrome? a. Carpal tunnel syndrome commonly occurs in families. Genetic factors are thought to account for about one-half the risk of developing carpaltunnel. b. Only people with occupations that require repeated flexion extension of the wrist, use of hand tools that require forceful gripping, or use of hand tools that vibrate are at risk for developing carpaltunnel. c. An underlying musculoskeletal disorder must be present for a person to develop carpaltunnel. d. Carpal tunnel syndrome only occurs in the presence of a hormonalimbalance. 9. Which of the following statements is true regarding the treatment of carpal tunnelsyndrome? a. The goal of treatment is to prevent flexion and extension movements of thewrist. b. Splints are used in carpal tunnel syndrome, because they allow for free movement of the fingers and thumb while maintaining the wrist in a neutralposition. c. Corticosteroid injections are discouraged in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome because of the risks for median nerve damage, scarring, andinfection. d. All of theabove 10. Sam is a 25-year-old who has been diagnosed with low back strain based on his history of localized low back pain and muscle spasm along with a normal neurological examination. As the clinician, you explain to Sam that low back pain is a diagnosis of exclusion. Which of the following symptoms would alert the clinician to the more serious finding of a herniated nucleus pulposus or ruptured disc? a. Morning stiffness and limited mobility of the lumbarspine b. Unilateral radicular pain symptoms that extend below the knee and are equal to or greater than the backpain c. Fever, chills, and elevated erythrocyte sedimentationrate d. Pathologic fractures, severe night pain, weight loss, andfatigue 11. The clinician has instructed Sam, a 25-year-old patient with low back strain, to use NSAIDs to manage his symptoms of pain and discomfort. Which of the following statements would bemost appropriate when teaching Sam about the use ofNSAIDs? a. “You should start with the lowest dose that is effective in managing your pain, because long-term use of NSAIDs can result in gastrointestinal (GI) disorders such as ulcers andhemorrhage.” b. “You should start with the lowest dose that is effective in managing your pain to avoid developing tolerance to themedication.” c. “You should take the maximum recommended dose of NSAIDs so that you will not need to take narcotics to control yourpain.” d. “It is important to take NSAIDs on an empty stomach in order toincrease absorption.” 12. Janet is a 30-year-old who has recently been diagnosed with a herniated disc at the level of L5-S1. She is currently in the emergency room with suspicion of cauda equina compression. Which of the following is a sign or symptom of cauda equina compression? a. Gastrocnemiusweakness b. A reduced or absent anklereflex c. Numbness in the lateralfoot d. Paresthesia of the perineum andbuttocks 13. Which of the following statements is true concerning the management of the client with a herniated disc? a. Muscle relaxants and narcotics can be used to control moderate pain but should be discontinued after 3 weeks ofuse. b. An epidural injection is helpful in reducing leg pain that has persisted for at least 3 weeks after the herniationoccurred. c. Intolerable pain for more than a 3-month period is an indication for surgical intervention. d. All of theabove 14. John is a 16-year-old boy who presents to the emergency room after hurting his knee in a football game. He described twisting his knee and then being unable to extend it completely. John tells the clinician that he heard a pop when the injury occurred and has been experiencing localized pain. The clinician suspects a meniscal tear. Which test would be most appropriate to assess for the presenceof a meniscaltear? a. Valgus stresstest b. McMurray circumductiontest c. Lachmantest d. Varus stresstest 15. The clinician suspects that a client has patellar instability. In order to test for this, the client is seated with the quadriceps relaxed, and the knee is placed in extension. Next the patella is displaced laterally, and the knee flexed to 30°. If instability is present, this maneuver displaces the patella toan abnormal position on the lateral femoral condyle, and the client will perceive pain. Testing for patellar instability in this way is knownas: a. Apprehensionsign b. Bulge sign c. Thumbsign d. None of theabove 16. The clinician is caring for Diane, a 22-year-old woman who presents with an injured ankle. Diane asks the clinician if she will need an x-ray. The clinician explains to Diane that an x-ray is not always necessary for an injured ankle and that the decision to obtain radiographs is dependent on the examination and Diane’s description of her injury. Which of the following clues in Diane’s examination or history would alert the clinician to the need for obtainingradiographs? a. Inability to bear weight immediately after theinjury b. Development of marked ankle swelling and discoloration after theinjury c. Crepitation with palpation or movement of theankle d. All of theabove 17. Mr. Jackson is a 65-year-old man recently diagnosed with osteoarthritis. The clinician has explained to Mr. Jackson that the goals for managing osteoarthritis include controlling pain, maximizing functional independence and mobility, minimizing disability, and preserving quality of life.Mr. Jackson explains to the clinician that his first choice would be to use complementary therapies to control his condition and asks what therapies are most effective in treating osteoarthritis. What would be the most appropriate response from the clinician? a. “Complementary therapies should be considered only if surgical interventions are notsuccessful.” b. “I am unfamiliar with the available complementary therapies for osteoarthritis and prefer to discuss more mainstream treatments, such as NSAIDs and physical therapy, to manage yourcondition.” c. “I would be happy to discuss all the treatment options available to you. Complementary therapies, such as acupuncture, acupressure, and tai-chi, are being studied for use in the treatment of osteoarthritis and have shown promise when used with standard medicaltherapy.” d. “It would be crazy to use complementary therapies to treat such a serious condition.” 18. Normal estrogen function is important for preventing osteoporosis in both men and women. Estrogen works to prevent osteoporosis in which of the followingways? a. By decreasing the erosive activity ofosteoclasts b. By promotingosteoclastogenesis c. By inhibiting osteoclastapoptosis d. All of theabove 19. Which of the following tests is considered the gold standard for definitively diagnosing osteoporosis? a. Bone alkaline phosphataselevels b. Urinary N-telopeptideassay c. Bone mass density measurement by densitometry d. Magnetic resonanceimaging 20. What is the recommended daily calcium intake for adults over the age of 50 with low bonemass? a. 1,200mg/day b. 1,000mg/day c. 1,300mg/day d. 1,500mg/day 21. Mrs. Allen is a 60-year-old woman who has been diagnosed with osteoporosis. She is very concerned about the risk of breast cancer associated with hormone replacement therapy and is wondering what other treatments are available to her. The clinician explains that bisphosphonates are another class of drugs used in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. What teaching should the clinician give Mrs. Allen in regard to takingbisphosphonates? a. Taking bisphosphonates can result in hypercalcemia, so calcium intake should be decreased while taking this class ofdrugs. b. There is potential for upper GI irritation, so these medications arecontraindicated in people with abnormalities of the esophagus or delayed esophagealemptying. c. This class of drugs can be taken at any time of the day without regard tomeals. d. None of theabove 22. Which stage of Paget’s disease is characterized by elevated numbers of osteoblasts, resulting in abnormal increases in bone remodeling and leading to an irregular deposition of collagenfibers? a. Lytic b. Mixed c. Sclerotic d. All of theabove 23. Which of the following statements concerning the treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome istrue? a. There is currently no cure for the disorder; however, patients should bemade aware that symptom relief ispossible. b. Treatment is directed toward controlling discomfort, improving sleep,and maintainingfunction. c. Fibromyalgia syndrome can be difficult to manage, requiring a variety of approaches and multiplemedications. d. All of theabove 24. One of the most frequent presenting signs/symptoms of osteoporosisis: a. Goiter b. Abnormal serumcalcium c. Elevated urine biochemicalmarkers d. Bonyfracture 25. Mrs. Thomas was seen in the office complaining of pain and point tenderness in the area of her elbow. The pain has increased following a day of gardening one week ago. A physical finding that differentiates the diagnosis and is most consistent with lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow)is: a. Ecchymosis, edema, and erythema over the lateralepicondyle b. Pain at the elbow with resisted movements at the wrist andforearm c. Inability to supinate and pronate thearm d. Inability to flex or extend the elbow againstresistance 26. A 70-year-old female has fallen 2 weeks ago and developed immediate pain in her left wrist. She thought she just bruised it but is worried because it has not improved. She has used Tylenol® and ice at home, and that has helped slightly. You examine her and find she has moderate swelling and ecchymosis but no overtly obvious deformity. Her ROM is uncomfortable and severely diminished due to the pain. No crepitus is heard or felt. Her fingers are warm; her pulse is strong; and capillary refill is less than 2 seconds. What should youdo? a. Make an immediate referral for an orthopedic evaluation without further assessment. b. Tell her that it takes time for these bruises to improve, so she should bepatient. c. Obtain a wrist x-ray and place her wrist in a splint or prescribe asplint. d. Send her to the emergency room for reduction of this obvious wristfracture. True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Osteoarthritis is primarily a noninflammatorycondition. 2. The presence of a positive rheumatoid factor is always indicative of rheumatoidarthritis. Chapter 53. Spinal Disorders 1. The nurse is caring for a home health patient who had a spinal cord injury at C5 three years ago. The nurse bases the plan of care on the knowledge that the patient will be ableto: a. feed self with setup and adaptiveequipment. b. transfer self towheelchair. c. stand erect with full legbraces. d. sit with good balance. . 2.A frantic family member is distressed about the flaccid paralysis of her son following a spinal cord injury several hours ago. What does the nurse know about thiscondition? a. It is an ominous indicator of permanentparalysis. b. It is possibly a temporary condition and willclear. c. It degenerates into a spasticparalysis. d. It will progress up the cord to cause seizures. 3.A patient with a spinal cord injury at T1 complains of stuffiness of the nose and a headache. The nurse notes a flushing of the neck and goose flesh. What should be the primary nursingintervention based on theseassessments? a. Place patient in flat position and checktemperature b. Administer oxygen and check oxygensaturation c. Place on side and check for legswelling d. Sit upright and check blood pressure 4. The nurse is aware that the characteristic gait of the person with Parkinson disease is apropulsive gait, which causes the patientto: a. stagger and need support of awalker. b. shuffle with armsflexed. c. fall over to one wide whenwalking. d. take small steps balanced on thetoes. 5. The newly admitted patient to the emergency room after a motorcycle accident has serosanguineous drainage coming from the nose. What is the most appropriate nursing responseto thisassessment? a. Cleanse nose with a soft cotton-tippedswab b. Gently suction the nasalcavity c. Gently wipe nose with absorbentgauze d. Ask patient to blow his nose . 6. How would the nurse instruct a patient with Parkinson disease to improve activitylevel? a. To use a soft mattress to relax thespine b. To walk with a shuffling gait to avoidtripping c. To walk with hands clasped behind back to helpbalance d. To sit in hard chair with arms for posture control Chapter 54. Soft-Tissue Disorders _ 1. The nurse is contributing to the plan of care for a patient who has a right fractured femur. What intervention should the nurse include in the plan of care to prevent fat emboli? a. Decrease dietary consumption offats. b. Maintain immobilization of the rightleg. c. Encourage coughing and deep breathinghourly. d. Perform passive range of motion on the rightleg. 2. A patient has an open reduction of a radial fracture and is casted. Several hours after the operation, the patient reports a throbbing pain in the arm. What nursing action is essential for the nurse to take? a. Repositionarm. b. Perform neurovascularchecks. c. Administer analgesics asordered. d. Notify the physicianimmediately. 3. The nurse is monitoring a patient with a casted left tibial fracture and a contusion of the thigh. The patient reports increasing pain in the left foot that has not been relieved by morphine injections. What should the nurse do? a. Reposition the castedleg. b. Repeat the morphine injectionnow. c. Give a higher ordered dose ofmorphine. d. Ensure physician is immediatelynotified. 4. The nurse finds a 2-day postoperative patient who had a right total hip replacement lying supine with crossed legs. What data should the nurse collect on thispatient? a. The right leg forshortening b. The right knee forcrepitation c. The left leg for internalrotation d. The left leg for loss offunction 5. The nurse is caring for a patient who had a closed reduction of the ulna with a cast applied. Later the patient reports left arm pain. What should the nurse dofirst? a. Pad the edges of thecast. b. Notify the physicianimmediately. c. Administer an analgesic asordered. d. Perform neurovascular check onfingers. 6. The nurse is reinforcing teaching provided to a patient recovering from right total hip replacement. Which patient statement indicates a correct understanding of theteaching? a. Keep legsapart. b. Lie prone inbed. c. Move right leg closer to the leftleg. d. Do not bear any weight on the leftleg. 7. A patient with a casted, fractured left leg asks why the leg has to be elevated. What should the nurse respond to thispatient? a. Decreasesswelling. b. Prevents castcracking. c. Increases yourcomfort. d. Allows the cast to dryevenly. 8. The nurse is caring for a patient who has had a right hip replacement. For which positionis the nurse attempting to achieve when a pillow is placed between the legs duringturning? a. Flexion of theknees b. Abduction of thethighs c. Adduction of the hipjoint d. Hyperextension of theknees 9. The nurse sees a neighbor fall and fracture a leg. What should the nurse do first for the neighbor? a. Assesspain. b. Transport to an emergencydepartment. c. Cover site of open fracture with cleandressing. d. Immobilize the affected limb using minimal movement. 10. The nurse is reinforcing teaching provided to a patient with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Which patient statement indicates understanding of the symptoms ofRA? a. Fatigue b. Paralysis c. Crepitation d. Shortness ofbreath 11. A patient with a 36-hour-old fractured femur is in traction and is prescribed morphine 10 mg every 3 hours as needed. The patient received a dose 3 hours ago and is now reporting a pain level of 8. The patient is stable. Which action should the nursetake? a. Holdmedication. b. Notify the registered nurse(RN). c. Give pain medication asordered. d. Give pain medication in 30minutes. 12. The nurse is caring for a patient who has a newly casted, fractured wrist. Datacollection reveals slightly puffy fingers with good capillary refill. What should the nurse do now to prevent complications? a. Notify theRN. b. Apply heat to thecast. c. Elevate the cast onpillows. d. Remove the pillow under thecast. 13. A patient with gout has been instructed on the prescribed medication allopurinol (Zyloprim). Which patient statement indicates understanding of the action of thismedication? a. Excretesproteins. b. Blocks formation of uricacid. c. Increases formation ofpurines. d. Increases metabolism ofpurines. 14. The nurse is evaluating teaching provided to a patient with gout. Which patientmenu selection indicates that additional teaching isrequired? a. Pike b. Bass c. Perch d. Sardines 15. The nurse is reinforcing teaching provided to a patient with gout. Which food should the patient state will be avoided that indicates teaching has beeneffective? a. Rice b. Beets c. Liver d. Bananas 16. The nurse is contributing to the plan of care for a patient with Pagets disease. Which outcome should the nurse identify as being appropriate for thispatient? a. Gain 5 lbweekly. b. Intake equalsoutput. c. Identify copingskills. d. Pain is relieved at a satisfactorylevel. 17. The nurse is contributing to the plan of care for a patient who has a fractured hip and is placed in Bucks (boot) traction while awaiting surgery. What is the desired outcome for placing the patient in Buckstraction? a. Restrainpatient. b. Realignfracture. c. Relieve patientpain. d. Maintain fracturereduction. 18. The nurse is reinforcing teaching for a patient who has had a total hip replacementon correct sitting positions. Which position should the nurse teach the patient toavoid? a. Crossinglegs b. Elevatinglegs c. Flexingankles d. Extendingknees 19. The nurse is contributing to the plan of care for a patient who has an upper extremity amputation. Why should the nurse keep in mind that this type of amputation can be more debilitating than a lower extremity amputation when planningcare? a. The upper extremity is morevisible. b. Prosthetic fitting is easier for theleg. c. The upper extremity is morespecialized. d. There is greater blood supply to the upperextremity. 20. The nurse observes a petechial rash and respiratory distress in a patient recovering from a fractured femur. What should these findings suggest to thenurse? a. Infection b. Pneumonia c. Fatembolism d. Pleuraleffusion 21. A patient who has a displaced mid-shaft fracture of the left femur and is in balanced suspension skeletal traction with 35 pounds of weights is experiencing calf pain with right foot dorsiflexion. Which action should the nursetake? a. Notify theRN. b. Check the tractionsetup. c. Reduce 5 pounds ofweight. d. Encourage dorsiflexion more frequently. 22. The nurse is contributing to the plan of care for a patient who is scheduled for abelow-the- knee amputation. What nursing diagnosis should be recommended for the preoperative plan ofcare? a. Anxiety b. Self-CareDeficit c. Fluid VolumeDeficit d. Ineffective AirwayClearance 23. The nurse is reinforcing teaching on positioning for a patient after a right total knee replacement. Which patient statement indicates a correct understanding of theteaching? a. Prone. b. Sidelying. c. Supine with pillow under rightknee. d. Supine with three pillows betweenlegs. 24. The nurse is reinforcing teaching provided to a patient for carpal tunnelsyndrome treatment. Which patient statement indicates a correct understanding of theteaching? a. Bedrest. b. Armsling. c. Wristsplint. d. Handexercises. 25. A patient with a fractured pelvis and a left acetabular fracture is prescribed bedrest. When the patient asks to toilet, which measure would beappropriate? a. Help patient up on a commode verycarefully. b. Turn patient onto right side, place the bedpan behind, and turnback. c. Have patient sit up as high as possible and lift self up with hands pushing on the bed, then slide the bedpanunderneath. d. Ask patient to lift straight up using a trapeze mounted above the bed and slide a bedpan underneath from the rightside. 26. The nurse is caring for a patient with gout. Which laboratory value should the nurse review which indicates that the treatment plan iseffective? a. Uric acid: 7.9mg/dL b. Creatinine: 0.8mg/dL c. Blood urea nitrogen: 15 mg/dL d. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL): 115 mg/dL 27. The nurse is reinforcing teaching provided to a patient who is postmenopausal, has lost 2 inches of height, and has osteoporosis. Which patient statement indicates correct understanding of the purpose of calcium supplements? a. To decrease boneloss b. To increase energylevels c. To decrease serumcalcium d. To increase excretion ofcalcium 28. A patient is completing instructions about complications that can occur from osteoporosis. Which complication should the patient state as evidence that teaching has beeneffective? a. Hipfracture. b. Overgrowth ofbone. c. Bone spurformation. d. Increased bonedensity. 29. The nurse is reviewing data collected during the health history for a patient with osteoporosis. What should the nurse identify as a risk factor for osteoporosisdevelopment? a. Daily use ofantacid b. Walking 1 mile daily c. Increased caffeineintake d. Increased dairy foodintake 30. The nurse reinforces medication teaching provided to a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Which medication should the patient identify as helpful to control the symptoms of the health problem? a. Digoxin. b. Ibuprofen. c. Morphine. d. Penicillin. 31. The nurse checks a patients casted right leg resting upon a pillow and finds that the cast appears too tight. What should the nursedo? a. Notify theRN. b. Administer painmedication. c. Apply an extra blanket to theleg. d. Remove the pillow under thecast. 32. The nurse is contributing to the plan of care for a patient who has a bone fracture that is splintered and has shattered into numerous fragments. Which term should the nurse use todocument this type offracture? a. Impacted b. Avulsion c. Greenstick d. Comminuted 33. The nurse reinforces teaching on prevention of osteomyelitis with a patient who has an open fracture of the right leg. Which patient statement indicates that teaching has beeneffective? a. Apply ice to rightleg. b. Keep legimmobilized. c. Increase calcium intake indiet. d. Wash hands prior to touching fracturearea. 34. An 87-year-old female with a history of osteoarthritis reports an average generalized pain score of 4 on a 0-to-10 scale while using acetaminophen prn. Which response about this pain level should the nurse make to the patient? a. Do you take a daily calciumsupplement? b. Im glad the acetaminophen is working foryou. c. Are you satisfied with this level of paincontrol? d. Research shows that acetaminophen is not really effective for osteoarthritispain. 35. A patient is diagnosed with osteomyelitis of the right lower leg. What should the nurse expect to be prescribed for this patientscare? a. Anticoagulanttherapy b. Casting of theextremity c. Fasciotomy of thewound d. Long-term antibiotic therapy MultipleResponse Identify one or more choices that best complete the statement or answer the question. 36. A patient 48 hours after surgery for a fractured femoral shaft is experiencing mental confusion, tachycardia, tachypnea, and dyspnea. The patients blood pressure is elevated and petechiae are present on the chest. After reporting the findings to the RN what should the nursedo while awaiting the physicians specific orders? (Select all thatapply.) a. Administeroxygen. b. Prepare patient for arterial blood gastests. c. Prepare patient for chest x-ray or lungscan. d. Maintain bedrest and keep movement to aminimum. e. Ask patient to move affected limb to see if pain isworse. f. Place patient in high Fowlers position or raise the head of thebed. 37. A patient asks the difference between osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. What manifestations should the nurse explain are characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis? (Select all that apply.) a. Low-gradefever b. Heberdensnodes c. Autoimmunedisease d. Activity increasespain e. Early morningstiffness f. Involvement of other majororgans 38. The nurse is collecting data from a patient suspected of developing a fat embolus froma fracture of the right femur. Which manifestations should the nurse expect? (Select all thatapply.) a. Petechiae b. Amigraine c. Tachycardia d. Mentalconfusion e. Numbness in the rightleg f. Muscle spasms in the rightthigh 39. The nurse is caring for a patient in traction. Which actions are appropriate when caring for this patient? (Select all thatapply.) a. Allow weights to hang freely inplace. b. Use assistance to reposition the patient inbed. c. Hold weights up if the patient is shifting position inbed. d. Remove weights if the patient is being moved up inbed. e. Lighten weights for short periods if the patient reportspain. 40. The nurse is contributing to the plan of care for a patient recovering from total hip replacement. Which exercises should the nurse recommend to help prevent deep veinthrombosis (DVT) formation? (Select all thatapply.) a. Footcircles b. Toetouches c. Heelpumping d. Deep kneebends e. Quadricepssetting f. Straight leg raises(SLRs) 41. A patient in the ambulatory clinic is diagnosed with a muscle strain. What actions should the nurse instruct the patient to do to treat this injury? (Select all thatapply.) a. Rest thelimb. b. Elevate thelimb. c. Apply heat for 1hour. d. Apply ice to thearea. e. Wrap with an elasticbandage. 42. The nurse is caring for a patient with a minor rotator cuff shoulder injury. What should the nurse emphasize when reviewing care with this patient? (Select all thatapply.) a. Apply ice b. Rest theshoulder c. Take NSAIDs asprescribed d. Begin out-patient physicaltherapy e. Use 2 lb hand weights forexercising 43. During a health history the nurse becomes concerned that a patient is at risk for developing osteoporosis. Which modifiable risk factors did the nurse use to come to this conclusion? (Select all that apply.) a. Smallboned b. Postmenopausal c. Cigarettesmoking d. Sedentarylifestyle e. Low calciumintake 44. The nurse is assisting in the development of an educational seminar on prevention of osteoporosis for a group of community members. Which actions should the nurse suggest be included in this presentation? (Select all thatapply.) a. Drink one cup of caffeinated coffee eachday b. Ensure an adequate intake of calcium eachday c. Participate in weight-bearing exercise everyday d. Wear well-supporting nonskid shoes at alltimes e. Consider participating in resistance exercisetraining 9. What is a sign of adislocation? a. Crepitus b. Pain andtenderness c. Increased range of motion at ajoint d. Deformity at ajoint 13. How is Duchennes muscular dystrophyinherited? a. Autosomal recessivegene b. X-linked recessivegene c. Autosomal dominant gene d. Codominantgene 14. Which of the following is true about Duchennes musculardystrophy? a. There is difficulty climbing stairs or standing up at 2 to 3 years ofage. b. It involves only the legs andpelvis. c. Skeletal muscle atrophy can be seen in the legs of atoddler. d. It cannot be detected in anycarriers. 15. The most common type of joint, which are freely movable, arecalled: a. Synarthroses b. Amphiarthroses c. Anarthroses d. Diarthroses 16. Which of the following is characteristic ofosteoarthritis? a. Inflammation and fibrosis develop at thejoints. b. Degeneration of articulating cartilage occurs in the largejoints. c. It progresses bilaterally through the smalljoints. d. There are no changes in the bone at the affectedjoints. 17. What is a typical characteristic of the pain caused byosteoarthritis? a. Decreases overtime b. Quite severe in the earlystages c. Aggravated by general muscleaching d. Increased with weight-bearing andactivity 20. What is the typical joint involvement with rheumatoidarthritis? a. Random single joints, progressing to involve otherjoints b. Bilateral small joints, symmetrical progression to otherjoints c. Abused or damaged joints first, then joints damaged by compensatorymovement d. Progressive degeneration in selectedjoints 21. What is the basic pathology of rheumatoidarthritis? a. Degenerative disorder involving the smalljoints c. Systemic inflammatory disorder due to an autoimmunereaction d. Inflammatory disorder causing damage to many organs 22. How is the articular cartilage damaged in rheumatoidarthritis? a. Enzymatic destruction by thepannus b. Inflamed synovial membrane covers thecartilage c. Fibrous tissue connects the ends of thebones d. Blood supply to the cartilage islost 23. How does the joint appear during an exacerbation of rheumatoidarthritis? a. Relativelynormal b. Enlarged, firm, crepitus withmovement c. Deformed, pale, andnodular d. Red, warm, swollen, and tender totouch 18. What limits joint movement inosteoarthritis? a. The osteophytes and irregular cartilagesurface b. The wider jointspace d. Fibrosis involving the joint capsule andligaments 19. Joints affected by osteoarthritis can sometimes affect healthy jointsby: a. causing enzymes to be released that travel to otherjoints. b. bacteria traveling from the affected join to a healthy one through thebloodstream. c. inflammation and edema affecting the entire limb. d. the affected individuals exerting stress on the normal joint to protect the damagedone. 25. Systemic effects of rheumatoid arthritis are manifestedas: a. nodules in various tissues, severe fatigue, andanorexia. b. headache, leukopenia, and highfever. c. swelling and dysfunction in manyorgans. d. progressive damage to ajoint. 26. What is a common effect of long-term use of glucocorticoids to treat rheumatoidarthritis? a. Leukocytosis b. Osteoporosis c. Severeanemia 27. Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) differs from the adult form inthat: a. only small joints areaffected. b. rheumatoid factor is not present in JRA, but systemic effects are moresevere. c. onset is more insidious inJRA. d. deformity and loss of function occur in most children withJRA. 28. Which of the following distinguishes septicarthritis? a. Multiple joints that are swollen, red, and painful at onetime b. Presence of mild fever, fatigue, andleukocytosis c. Purulent synovial fluid present in a single, swollenjoint d. Presence of many antibodies in theblood 29. Which of the following may precipitate an attack ofgout? a. A sudden increase in serum uric acidlevels b. Severehypercalcemia c. Mild trauma to thetoes d. Development of atophus 30. Where does inflammation usually begin in an individual with ankylosingspondylitis? a. Costovertebral joints with progression down thespine b. Cervical and thoracic vertebrae, causingkyphosis c. Sacroiliac joints with progression up thespine d. Peripheral joints and then proceeds to thevertebrae 31. What is a common outcome of fibrosis, calcification, and fusion of the spine inankylosing spondylitis? a. Damage to the spinal nerves and loss offunction b. Frequent fractures of longbones c. Impaired heartfunction d. Rigidity, postural changes, andosteoporosis 32. Which statement applies tomenisci? a. They are found in the hipjoints. b. They are secretory membranes injoints. c. They prevent excessive movement ofjoints. d. They are found in the shoulderjoint. 33. Which factors delay healing of bonefractures? 1. Lack of movement of thebone 2. Prolonged inflammation andischemia 3. Presence ofosteomyelitis 4. Close approximation of boneends a. 1, 2 b. 1, 3 c. 2, 3 d. 3, 4 34. What is the likely immediate result of fat emboli from a brokenfemur? a. Additional ischemia in the brokenbone b. Nonunion or malunion of thefracture c. Pulmonary inflammation andobstruction d. Abscess and infection at a distantsite 35. A sprain is a tear ina: a. ligament. b. tendon. c. skeletalmuscle. d. meniscus. Chapter 55. Osteoarthritis and Osteoporosis 1. When a patient recovering from a fractured tibia asks what callus formation is, the nurse tells her it is: a. when blood vessels of the bone arecompressed. a part of the bone healing process after a fracture when new bone is being formed over the b. fracturesite. c. the formation of a clot over the fracturesite. d. when the hematoma becomes organized and a fibrin meshwork is formed. . 2. Which patient statement indicates the need for additional teaching for a patient withrheumatoid arthritis who is taking meloxicam(Mobic)? a. I am keeping a daily record of my bloodpressure. b. I take aspirin before I go tobed. c. I know I can take meloxicam with or without regard tomeals. d. I weigh every day so I will be aware of any weight gain. 3. Which foods should the home health nurse suggest for the patient with osteoporosis to help slow thedisease? a. Leafy greenvegetables b. Foods high insodium c. Tea andcoffee d. VitaminA . 4. What should the nurse include in the teaching plan for a patient who is takingalendronate (Fosamax)? a. Take drug with anymeal b. Take drug first thing in themorning c. Drink at least 5 oz of milk before takingdrug d. Take drug with an antacid to avoid heartburn 5. What should the nurse do when a patient with osteomyelitis is admitted with an open wound that is draining? a. Enforce a low caloriediet b. Initiate drainage and secretionprecautions c. Frequently do passive ROM on theelbow d. Ambulate several times daily 16-year-old male patient presents in the emergency room with a pathologic fracture of the left femur and complains of pain on weight bearing. These are cardinal indicatorsof: a. osteogenicsarcoma. b. osteoporosis. c. rheumatoidarthritis. d. osteochondroma. . 7. How is rheumatoid arthritis distinguished fromosteoarthritis? Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune, systemic disease; osteoarthritis is a degenerative a. disease of thejoints. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune, degenerative disease; osteoarthritis is a systemic b. inflammatorydisease. c. d. People with osteoarthritis are considered to be genetically predisposed; there is no known genetic component to rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis is often caused by a virus; viruses play no part in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. 8. Which patient is most likely to developosteoporosis? a. 43-year-old African Americanwoman b. 57-year-old whitewoman c. 48-year-old African Americanman d. 62-year-old Latino woman 9. The patient, age 58, is diagnosed with osteoporosis after densitometry testing. She has been menopausal for 5 years and has been concerned about her risk for osteoporosis because her mother has osteoporosis. In teaching her about her osteoporosis, which information does the nurseinclude? Even with a family history of osteoporosis, the calcium loss from bones can be slowed by a. increased calcium intake andexercise. Estrogen replacement therapy must be started to prevent rapid progression of her b. osteoporosis. c. With a family history of osteoporosis, there is no way to prevent or slow bone reabsorption. Continuous, low-dose corticosteroid treatment is effective in stopping the courseof d. osteoporosis. 10. Calcium is a mineral found in many foods that can slow bone loss during the aging process. Which food is high incalcium? a. Oranges b. Bananas c. Spinach d. Eggs 11.A 56-year-old female patient is being seen for osteoarthritis of the knee in the clinic. Whatshould the nurse recommend when discussing strengtheningexercises? a. Jogging b. Walking rapidly on atreadmill c. Bicycling d. Aerobic exercises . 12. The characteristics of osteoarthritis that should be included in a teaching plan would includethat osteoarthritis (select all thatapply): a. will cause the formation of Heberdennodes. b. can involve otherorgans. c. results from wear andtear. d. may affect only one side of thebody. e. may cause constitutional symptoms of fatigue andfever. f. will cause marked erythema and edema of hands. . Chapter 56.Common Endocrine/Metabolic Complaints Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A patient is 66 inches in height, weighing 200 pounds, and newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM). Her fasting plasma glucose level is 215 mg/dL. What is the best initialtreatment? a. No treatment at thistime b. Diet and exercise for 6-weektrial c. Diet, exercise, and oralmedication d. Diet, exercise, and exogenousinsulin 2. The clinician suspects that a client seen in the office has hyperthyroidism. Which of the following tests should the clinician order on the initialvisit? a. High sensitivity thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and freeT4 b. Free T4 and serumcalcium c. Free T3 andT4 d. TSH and thyroxinantibodies 3. A patient with type 2 diabetes asks the clinician why she needs to exercise. In order to answer her, the clinician must understand that exercise has what effect on the patient with type 2diabetes? a. Reduces postprandial bloodglucose b. Reduces triglycerides and increases high-density lipoprotein(HDL) c. Reduces totalcholesterol d. All of theabove 4. A patient with type 1 diabetes comes to the clinic complaining of feeling nervous and clammy. He states that he took his insulin this morning but was late for work and did not eat breakfast. Which action should the clinician takefirst? a. Check his bloodsugar. b. Have him drink 4 ounces ofjuice. c. Call 911. d. Ask him about his usual eatinghabits. 5. A patient with type 2 diabetes comes to the clinic after reading about metformin in a magazine. Which of the following conditions that the patient also has would be a contraindication totaking metformin? a. Ketoacidosis b. Cirrhosis c. Hypoglycemicepisodes d. All of theabove 6. A 25-year-old patient presents to the clinic with fatigue, cold intolerance, weight gain, and constipation for the past 3 months. On physical examination, the clinician notices a sinus bradycardia; muscular stiffness; coarse, dry hair; and a delay in relaxation in deep tendon reflexes. Which of the following tests should be orderednext? a. Serumcalcium b. TSH c. Electrolytes d. Urine specificgravity 7. The clinician has been doing diabetic teaching for a patient with type 1 diabetes. Which of the following statements by the patient would indicate that teaching has beeneffective? a. “As long as I don’t need glasses, I don’t have to worry about goingblind.” b. “I know I need to have my eyes checked everyyear.” c. “My optometrist checks myeyes.” d. “I will see my eye doctor when my vision getsblurry.” 8. A 64-year-old man with type 2 diabetes presents to the clinic with the complaint of “my feet feel like they are on fire.” He has a loss of vibratory sense, +1 Achilles reflex, and a tack embedded in his left heel. Which of the following would be an appropriate treatment? a. Tricyclicantidepressants b. Capsaicincream c. Vitamin B12injections d. Insulin 9. After removing a tack from a type 2 diabetic’s heel and evaluating the site for infection, what is the best plan for thispatient? a. Suggest she use a heating pad to improvecirculation. b. Refer to a podiatrist for a foot care treatmentplan. c. Send her for acupuncturetreatments. d. All of theabove 10. Joyce is seen in the clinic complaining of vague symptoms of nervousness and irritability. She says that her hair will not hold a permanent wave anymore. On physical examination, the clinician finds an irregular heartbeat and brisk reflexes. The differential diagnosis should include which of the followingconditions? a. Myxedema b. Thyrotoxicosis c. Cushing’ssyndrome d. Pan-hypopituitarism 11. The patient is prescribed radioactive iodine (RAI) and asks the clinician how this drug works. The clinician’s response should include which of the followingdata? a. RAI prevents the peripheral conversion of T4 toT3. b. RAI binds freeT4. c. RAI destroys thyroidtissue. d. RAI reduces freely circulatingiodine. 12. A patient is diagnosed with hypothyroidism. Which of the following electrocardiogram changes should the clinician expect as a manifestation of thedisease? a. Sinusbradycardia b. Atrialfibrillation c. Supraventriculartachycardia d. Uwaves 13. After 6 months of Synthroid therapy, the clinician should expect which of the following in the repeat thyroidstudies? a. ElevatedTSH b. NormalTSH c. LowTSH d. UndetectableTSH 14. Which of the following laboratory findings should the clinician expect in a patient with untreated Graves’disease? a. ElevatedTSH b. ElevatedT4 c. Elevated thyrotropin-releasing hormone(TRH) d. All of theabove 15. The clinician prescribes glipizide (Glucotrol) for a diabetic patient. Which statement made by the patient would indicate that your teaching has beeneffective? a. “I’ll take my pill at least 30 minutes beforebreakfast.” b. “I’ll take my Glucotrol before bedtime.” c. “It is important to take my medication right after Ieat.” d. “Since I only like to eat two meals a day, I can take the pill between mymeals.” 16. A diabetic patient asks the clinician why he needs to check his blood sugar at home even when he feels good. Which of the following responses would be mostappropriate? a. “Control of glucose will help postpone or delaycomplications.” b. “Regularly checking blood sugar will help establish aroutine.” c. “Monitoring glucose will promote a sense ofcontrol.” d. All of theabove 17. How often should the clinician examine the feet of a person withdiabetes? a. Once ayear b. Every 6months c. Every 3months d. Everyvisit 18. The clinician sees a patient who is 5 feet tall and weighs 150 pounds. How would the clinician classify thispatient? a. Overweight b. Mild obesity c. Moderateobesity d. Morbid obesity 19. Mr. S presents in the clinic with pain, tenderness, erythema, and swelling of his left great toe. The clinician suspects acute gout. Which of the following should the clinician expect in the initial test results for this patient? a. Elevated uric acidlevel b. Elevated blood ureanitrogen c. Decreased urinepH d. Decreased C-reactiveprotein 20. Mr. W, 53 years old, is seen in the clinic with concerns about his left foot. He has a 40-year history of type 1 diabetes with “fairly good” control on twice-daily insulin. He denies injury but states that he tripped a few months ago and that his foot is sore when he walks. Physical examination reveals an edematous, erythremic, and warm foot. There is a superficial ulcer on the plantar surface. Which of the following is the most likelydiagnosis? a. Fallenarch b. Arthritis c. Charcotjoint d. Sprainedankle 21. Which of the following tests should you order to confirm Mr. W’sdiagnosis? a. Bone scan b. Computed tomography (CT)scan c. X-ray of thefoot d. Culture of theulcer 22. A vegetarian patient with gout asks the clinician about food he should avoid. The clinician should advise the patient to avoid which of the followingfoods? a. Rice b. Carrots c. Spinach d. Potatoes 23. The clinician should question the patient with suspected gout about use of which of these medications? a. Low-doseaspirin b. Thiazidediuretics c. Ethambutol d. All of theabove 24. The clinician finds numerous nodules on the thyroid of a 65-year-old woman. The clinician suspects thyroid cancer. Which of the following data would be most significant for thispatient? a. A history of tonsillectomy in the1940s b. Recent exposure tomumps c. Vegetariandiet d. Allergy toiodine 25. Which of the following is essential for diagnosing thyroidcancer? a. Fine needleaspiration b. Thyroidultrasound c. CTscan d. Magnetic resonanceimaging 26. Which of the following are common signs of type 2DM? a. Anorexia b. Recurrent yeastinfection c. Weight gain d. Elevated HDLcholesterol 27. Which of the following medications can causehyperglycemia? a. Prednisone b. Metformin c. Synthroid d. Cephalexin 28. Which of the following is diagnostic for diabetesmellitus? a. A1C 7.0 on oneoccasion b. Fasting blood sugar (FBS) of 100 mg/dL on twooccasions c. Random glucose of 200 mg/dL on twooccasions d. Two-hour post-load plasma glucose of 300 mg/dL on oneoccasion 29. Which of the following medications for type 2 diabetes mellitus should not be prescribed during pregnancy? a. Insulin b. Metformin c. Glucotrol d. Precose 30. A 35-year-old woman presents with symptoms of hypoglycemia. There is no history of diabetes mellitus. Which of the following should be included in the differentialdiagnosis? a. Anxietydisorder b. Pheochromocytoma c. Psychosis d. All of theabove True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Metformin is the first line of pharmacologic treatment for type 2DM. 2. Fruit juice with added sugar is the treatment of choice for anyone experiencinghypoglycemia. 3. Lifestyle modification is the treatment of choice for metabolicsyndrome. 4. A BMI of 29 kg/m2 is consideredobesity. 5. Urine-free cortisol is one of four diagnostic tests recommended for Cushing’ssyndrome. Chapter 57. Glandular Disorders 1. Why would a patient with hyperthyroidism be prescribed the drug methimazole(Tapa-zole)? a. To limit the effect of the pituitary on thethyroid b. To destroy part of the hyperactive thyroidtissue c. To stimulate the pinealgland d. To block the production of thyroidhormones 2.To which diet should a patient with Cushing syndrome adhere? a. Lesssodium b. Morecalories c. Lesspotassium d. More carbohydrates 3.A patient has returned to his room after a thyroidectomy with signs of thyroid crisis. During thyroid crisis, exaggerated hyperthyroid manifestations may lead to the development of the potentially lethal complicationof: a. severe nausea andvomiting. b. bradycardia. c. delirium withrestlessness. d. congestive heart failure. The purpose of the use of radioactive iodine in the treatment of hyperthyroidism isto: a. stimulate the thyroidgland. b. depress thepituitary. c. destroy some of the thyroidtissue. d. alter the stimulus from the pituitary. 5. Which precaution(s) should the nurse take when caring for a patient who is being treatedwith radioactive iodine 131(RAIU)? a. Initiate radioactive safetyprecautions b. Avoid assigning any young woman to the patient c. Wait three days after dose before assigning a pregnant nurse to care for thispatient d. Advise visitors to sit at least 10 feet away from the patient 6. Why would a patient with hyperthyroidism be prescribed the drug methimazole(Tapa-zole)? a. To limit the effect of the pituitary on thethyroid b. To destroy part of the hyperactive thyroidtissue c. To stimulate the pinealgland d. To block the production of thyroidhormones 7. What is the postoperative position for a person who has had athyroidectomy? a. Prone b. Semi-Fowler c. Side-lying d. Supine 8. What extra equipment should the nurse provide at the bedside of a newpostoperative thyroidectomypatient? a. Large bandagescissors b. Tracheotomytray c. Ventilator d. Water-sealed drainage system . 9. As the nurse is shaving a patient who is 2 days postoperative from a thyroidectomy, the patienthas a spasm of the facial muscles. What should the nurse recognize thisas? a. Chvosteksign b. Montgomerysign c. Trousseausign d. Homanssign 10.A patient has undergone tests that indicate a deficiency of the parathyroid hormone secretion. She should be informed of which potentialcomplication? a. Osteoporosis b. Lethargy c. Laryngealspasms d. Kidneystones . 11.A 27-year-old patient with hypothyroidism is referred to the dietitian for dietary consultation. What should nutritional interventionsinclude? a. Frequent small meals high incarbohydrates b. Calorie-restrictedmeals c. Caffeine-richbeverages d. Fluid restrictions 12. What instructions should be included in the discharge instructions for a 47-year-old patientwith hypothyroidism? a. Taking medication whenever symptoms causediscomfort b. Decreasing fluid and fiberintake c. Consuming foods rich iniron d. Seeing the physician regularly for follow-up care Regular checkups are essential, because drug dosage may have to be adjusted from time to time. 13. How should the nurse administer insulin to preventlipohypertrophy? a. At roomtemperature b. At bodytemperature c. Straight from therefrigerator d. After rolling bottle between hands to warm . 14.A patient with a history of Graves disease is admitted to the unit with shortness of breath. The nurse notes the patients vital signs: T 103 F, P 160, R 24, BP 160/80. The nurse also notes distended neck veins. What does the patient most likelyhave? a. Pulmonaryembolism b. Hypertensivecrisis c. Thyroidstorm d. Cushingcrisis 15. What is the master gland of the endocrinesystem? a. Thyroid b. Parathyroid c. Pancreas d. Pituitary 16. What information should be obtained from the patient before an iodine-131test? a. Presence of metal in thebody b. Allergy to sulfadrugs c. Status of possiblepregnancy d. Use of prescription drugs for hypertension 17. The patient being treated for hypothyroidism should be instructed to eat well-balanced meals including intake of iodine. Which of the following foods containsiodine? a. Eggs b. Pork c. White bread d. Skinlesschicken 18. The nurse is caring for a patient who is receiving calcium gluconate for treatment of hypoparathyroid tetany. Which assessment would indicate an adverse reaction to thedrug? a. Increase in heartrate b. Flushing of face andneck c. Drop in bloodpressure d. Urticaria 19. The adrenal cortex secretes glucocorticoids. The most important is cortisol. What is it involved in? (Select all thatapply.) a. Glucosemetabolism b. Releasing androgens andestrogens c. Providing extra reserve energy duringstress d. Decreasing the level of potassium in the bloodstream e. Increasing retention of sodium in the blood stream Chapter 58. Diabetes Mellitus 1. Which diagnostic test for diabetes mellitus provides a measure of glucose levels for the previous8 to 12weeks? a. Fasting blood sugar(FBS) b. Oral glucose tolerance test(OGT) c. Glycosylated hemoglobin(HbA1c) d. Postprandial glucose test (PPBG) 2. Which test will furnish immediate feedback for a newly diagnosed diabetic who is not yet under control? a. Fasting blood sugar(FBS) b. Glycosylated hemoglobin(HgbA1c) c. Oral glucose tolerance test(OGTT) d. Clinitest 3. The patient is a 20-year-old college student who has type 1 diabetes and normally walks each evening as part of an exercise regimen. The patient plans to enroll in a swimming class. Which adjustment should be made based on thisinformation? a. Time the morning insulin injection so that the peak action will occur during swimmingclass. b. Delete normal walks on swimming classdays. c. Delay the meal before the swimming class until the session isover. Monitor glucose level before, during, and after swimming to determine the need for d. alterations in food or insulin. 4. What is a long-term complication of diabetesmellitus? a. Diverticulitis b. Renalfailure c. Hypothyroidism d. Hyperglycemia 5.In diabetes insipidus, a deficiency of which hormone causes clinical manifestations? a. antidiuretic hormone(ADH) b. follicle-stimulating hormone(FSH) c. thyroid-stimulating hormone(TSH) d. adrenocorticotropic hormone(ACTH) 6. What should the nurse caution a type I diabetic about excessiveexercise? a. It can increase the need for insulin and may result inhyperglycemia. b. It can decrease the need for insulin and may result inhypoglycemia. c. It can increase muscle bulk and may result in malabsorption ofinsulin. d. It can decrease metabolic demand and may result in metabolic acidosis. 7. The nurse caring for a 75-year-old man who has developed diabetes insipidus following a head injury will include in the plan of care provisionsfor: a. limiting fluids to 1500 mL aday. b. encouraging physicalexercise. c. protecting patient frominjury. d. discouraging daytime naps. . 8. The physician orders an 1800-calorie diabetic diet and 40 units of (Humulin N) insulin U-100 subcutaneously daily for a patient with diabetes mellitus. Why would a mid-afternoon snack of milk and crackers begiven? a. To improve nutrition b. To improve carbohydrate metabolism c. To prevent an insulinreaction d. To prevent diabetic coma . insulin reaction would include information about: a. abdominal pain andnausea. b. dyspnea andpallor. c. flushing of the skin andheadache. d. hunger and a trembling sensation. 10 The nurse discovers the type 1 diabetic (IDDM) patient drowsy and tremulous, the skin is cool and moist, and the respirations are 32 and shallow. These are signsof: a. hypoglycemic reaction; give 6 oz of orangejuice. b. hyperglycemic reaction; give ordered regularinsulin. c. hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic reaction; squeeze glucagon gel in buccalcavity. d. hypoglycemic reaction; give ordered insulin. 11.What instructions should a nurse give to a diabetic patient to prevent injury to the feet? a. Soak feet in warm water everyday. b. Avoid going barefoot and always wear shoes withsoles. Use of commercial keratolytic agents to remove corns and calluses are preferred to cutting c. off corns andcalluses. d. Use a heating pad to warm feet when they feel cool to thetouch. . 12. The physician prescribes glyburide (Micronase, DiaBeta, Glynase) for a patient, age 57, when diet and exercise have not been able to control type 2 diabetes. What should the nurse include inthe teaching plan about thismedication? a. It is a substitute for insulin and acts by directly stimulating glucose uptake into thecell. b. It does not cause the hypoglycemic reactions that may occur with insulinuse. c. d. It is thought to stimulate insulin production and increase sensitivity to insulin at receptor sites. It lowers blood sugar by inhibiting glucagon release from the liver, preventing gluconeogenesis. 13. The nurse is administering long-acting insulin once a day, which provides insulin coverage for24 hours. Thisinsulin is . Lantus is a long-acting synthetic (recombinant DNA origin, human-made) human insulin. It is used once a day at bedtime and works around the clock for 24 hours. 14. Another term for hyperglycemicreactionis . 15. Only insulin can be administered intravenously. Chapter 59. Metabolic Disorders MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What kind of control mechanism is indicated when increased blood glucose levelsstimulate increased secretion of insulin? a. Control by releasinghormones b. Control by tropichormones c. Negative feedbackcontrol d. Hypothalamus/hypophysiscoordination 2. What is the most common cause of endocrinedisorders? a. Malignantneoplasm b. Infection c. Congenitaldefect d. Benigntumor 3. Choose the statement that applies to type 1 diabetesmellitus. a. Onset often occurs duringchildhood. b. Relative insufficiency of insulin or insulin resistancedevelops. c. It can be treated by diet, weight control and exercise, or oralhypoglycemics. d. Complications rarelyoccur. 4. Why does polyuria develop with diabetesmellitus? a. Increased thirst andhypoglycemia b. Ketoacidosis c. Osmotic pressure due toglucose d. Diabeticnephropathy 5. What is the cause of diabeticketoacidosis? a. Excess insulin in thebody b. Loss of glucose in theurine c. Failure of the kidney to excrete sufficientacids d. Increased catabolism of fats andproteins 6. What is a precipitating factor for diabeticketoacidosis? a. Skipping ameal b. Anorexia c. Seriousinfection d. Insulinoverdose 7. Which of the following may cause insulin shock todevelop? b. Missing an insulindose c. Eating excessively largemeals d. Sedentarylifestyle 8. Which of the following indicates hypoglycemia in adiabetic? a. Deep, rapidrespirations b. Flushed dry skin andmucosa c. Thirst andoliguria d. Staggering gait, disorientation, andconfusion 9. Which of the following are signs of diabetic ketoacidosis in an unconsciousperson? a. Pale moistskin b. Thirst and poor skinturgor c. Deep rapid respirations and fruity breathodor d. Tremors and strong rapidpulse 10. Immediate treatment for insulin shock mayinclude: a. administration ofbicarbonates. c. inducedvomiting. d. consumption of large amounts ofwater. 11. What causes loss of consciousness in a person with diabeticketoacidosis? a. Toxic effects of excessiveinsulin b. Excessive glucose in theblood c. Metabolicacidosis d. Lack of glucose in braincells 12. Which of the following does NOT usually develop as a complication ofdiabetes? a. Osteoporosis b. Nephropathy c. Impotence d. Peripheralneuropathy 13. How do many oral hypoglycemic drugsact? a. To replace insulin in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus(IDDM) b. To transport glucose into bodycells d. To stimulate the pancreas to produce moreinsulin 14. Diabetes may cause visual impairment through damage to the lens; this is referred toas: a. cataracts. b. maculardegeneration. c. myopia. d. strabismus. 15. Which of the following applies to diabeticmacro-angiography? 1. It affects the small arteries andarterioles. 2. It is related to elevated serumlipids. 3. It leads to increased risk of myocardial infarction and peripheral vasculardisease. 4. It frequently causes damage to thekidneys. a. 1, 3 b. 1, 4 c. 2, 3 d. 2, 4 16. Why is amputation frequently a necessity indiabetics? a. Necrosis and gangrene in the feet andlegs c. Severe dehydration in thetissues d. Elevated blood glucose increasing bloodviscosity 17. A type of diabetes that may develop during pregnancy and disappear after delivery iscalled: a. temporary maternaldiabetes. b. fetaldiabetes. c. acute developmentaldiabetes. d. gestationaldiabetes. 18. Which one of the following develops hypoglycemia morefrequently? a. Type 1 diabeticpatients b. Type 2 diabeticpatients c. Patients with a poor stressresponse d. Patients with a regular exercise and mealplan 19. Which of the following hormonal imbalances causes Addisonsdisease? a. Increasedglucocorticoids b. Decreasedglucocorticoids d. Deficit of T3 and T4 20. Which of the following hormonal imbalances causesmyxedema? a. Increasedglucocorticoids b. Decreasedglucocorticoids c. Deficit ofADH d. Deficit of T3 and T4 21. Which of the following hormonal imbalances causes diabetesinsipidus? a. Increasedinsulin b. Decreasedglucocorticoids c. Deficit ofADH d. Deficit of T3 and T4 22. What is caused byhyperparathyroidism? a. Hypocalcemia b. Tetany c. Bonedemineralization 23. What is caused by hypocalcemia due tohypoparathyroidism? 1. Skeletal muscle twitching orspasm 2. Weak cardiaccontraction 3. Increased secretion of parathyroid hormone(PTH) 4. Decreased serum phosphatelevel a. 1, 2 b. 1, 3 c. 2, 3 d. 3, 4 24. Which of the following applies toacromegaly? a. It occurs in infants andchildren. b. It causes excessive longitudinal bonegrowth. c. It results from excessive secretion of growth hormone(GH). d. It does not change soft tissuegrowth. 25. Which of the following may causegoiter? 1. Hyperthyroidism 2. Hypothyroidism 3. Lack of iodine in thediet a. 1, 4 b. 2, 3 c. 1, 2, 3 d. 1, 2, 3, 4 26. Which signs are typical of Gravesdisease? a. Facial puffiness, bradycardia, andlethargy b. Exophthalmos andtachycardia c. delayed physical and intellectualdevelopment d. Goiter and decreased basal metabolic rate(BMR) 27. Characteristics of Cushings syndrome include all of the followingEXCEPT: a. Heavy body and roundface b. Atrophied skeletal muscle in thelimbs c. Staring eyes with infrequentblinking d. Atrophy of the lymphnodes 28. Which of the following is an effect of long-term glucocorticoidtherapy? a. Decreased secretion from the adrenal cortexgland c. Hypotension and poorcirculation d. Increased number of hypersensitivityreactions 29. Which of the following is an effect of Addisonsdisease? a. Elevated blood glucoselevels b. High bloodpressure c. Low serum potassiumlevels d. Poor stressresponse 30. What is the most common cause of type 1 diabetesmellitus? a. Increased glucose production in theliver b. Destruction of pancreatic cells by an autoimmunereaction c. Increased resistance of body cells to insulinaction d. Chronicobesity 31. Why does glucosuria occur indiabetics? a. Excess ketoacids displace glucose into thefiltrate. b. Excess water in the filtrate draws more glucose into theurine. d. Sufficient insulin is not available for glucosereabsorption. 32. Which of the following are common early signs of a pituitaryadenoma? 1. Persistentheadaches 2. Hemianopia 3. Hypertension 4. Papilledema a. 1, 4 b. 2, 3 c. 1, 2 d. 1, 3, 4 33. Which of the following does NOT apply to inappropriate ADHsyndrome? a. The cause is excess ADHsecretion. b. Severe hyponatremiaresults. c. Excessive sodium isretained. d. Fluid retentionincreases. 34. What is/are the effect(s) of thyrotoxiccrisis? a. Hyperthermia and heartfailure c. Toxic goiter andhypometabolism d. Decreased stressresponse 35. Which of the following conditions may precipitate or exacerbatehyperglycemia? a. Hypothyroidism b. Cushingsdisease c. Addisonsdisease d. Growth hormonedeficit 36. Which of the following conditions may causeimmunosuppression? a. Gravesdisease b. Acromegaly c. Cushingsdisease d. Diabetesinsipidus 37. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic coma (HHNC) more frequently develops in patients with: a. type 1diabetes. b. type 2diabetes. d. hyperparathyroidism. 38. Which of the following is recommended for immediate treatment of hypoglycemicshock? 1. If conscious, immediately give sweet fruit juice, honey, candy, orsugar. 2. If unconscious, give nothing by mouth (require intravenous glucose50%). 3. Treat immediately withinsulin. 4. Give large quantity of clear fluids for shock. a. 1, 2 b. 1, 3 c. 2, 3 d. 1, 3, 4 39. All these tissues use glucose without the aid of insulinEXCEPT: a. liver. b. digestivesystem. c. exercising skeletalmuscle. d. brain. 40. Differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes include which of thefollowing? a. Type 1 diabetes weight gain is common, and type 2 weight loss oftenoccurs. Type 1 diabetes may be controlled by adjusting dietary intake and exercise, but type 2 c. diabetes requires insulinreplacement. Type 1 diabetes occurs more frequently in children and adolescents, and type 2 diabetes d. occurs more often inadults. 41. Complications of diabetes mellitusinclude: a. peripheralneuropathy. b. frequentinfections. c. cataracts. d. A, B, andC. 42. Which of the following often causeshyperparathyroidism? a. A malignant tumor in the parathyroidglands b. End-stage renalfailure c. Osteoporosis d. Radiation involving the thyroid gland and neckarea 43. Dwarfism is causedby: a. excessive levels of somatotropin(GH). c. excessive levels ofinsulin. d. excessive levels of parathyroidhormone. 44. Which of the following results from a deficit of antidiuretic hormone(ADH)? a. Inappropriate ADHsyndrome b. Gigantism c. Diabetesinsipidus d. Myxedema 45. Goiters occur more frequently in persons living inthe: a. Great Lakes or mountainousregions. b. southwest UnitedStates. c. temperateregions. d. areas bordering theoceans. 46. Which of the following is caused by Gravesdisease? a. Hypermetabolism b. Decreased size of thyroidgland d. Decreased blood levels of T3, T4, and TSH 47. Goiters may be causedby: a. hypothyroid conditionsonly. b. either hypothyroid or hyperthyroidconditions. c. hyperthyroid conditionsonly. d. fungal infections such ascandidiasis. 48. Severe impairment of all aspects of growth and development, including difficulty feeding, mental retardation, and stunted skeletal growth, are associatedwith: a. myxedema. b. Cushingssyndrome. c. diabetesinsipidus. d. cretinism. e. Gravesdisease. 49. A benign tumor of the adrenal medulla that secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine iscalled: a. pheochromocytoma. b. Cushingssyndrome. d. Addisonsdisease. 50. The anterior pituitary gland secretes all of the following hormonesEXCEPT: a. prolactin(PRL). b. glucagon. c. adrenocorticotropic hormone(ACTH). d. growth hormone(GH). Chapter 60. Common Hematologic and Immunological Problems Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Sandra is 42 years old and has just been diagnosed with leukemia. She is complaining of bone and joint pain. Which type of leukemia is most likely theculprit? a. Acute lymphocyticleukemia b. Acute myelogenousleukemia c. Chronic myelogenousleukemia d. Chronic lymphocyticleukemia 2. Which type of bone marrow transplant is obtained from an identicaltwin? a. Autogenic b. Autologous c. Allogeneic d. Syngeneic 3. During treatment for anaphylaxis, what site is used for the initial injection ofepinephrine? a. IV b. Abdomen c. Upper lateralthigh d. Deltoid 4. After the initial treatment for anaphylaxis, which medication should be added to prevent late-phase anaphylacticreactions? a. Albuterol b. Diphenhydramine c. An H2blocker d. Corticosteroids 5. When analyzing synovial fluid, if it is opaque, white, or translucent; has 5,000 leukocytes/Ml; 80% polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN); and a low red blood cell count, it may be indicative of which of the followingconditions? a. This is a normalresult. b. Scleroderma c. Rheumatoidarthritis d. Sickle celldisease 6. Which of the following disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs is a folic acidantagonist? a. Methotrexate(Rheumatrex) b. Etanercept(Enbrel) c. Rituximab(Rituxan) d. Anakinra(Kineret) 7. Which statement about HIV postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) for health-care workers is the most accurate? a. PEP should be started within hours ofexposure. b. PEP should be started within 72 hours ofexposure. c. Renal and hepatic function tests should be done 6 weeks after beginningPEP. d. PEP will prevent potential hepatitis C infection ifpresent. 8. Which household solution should be used to clean a bathroom if sharing with a friend who hasHIV? a. 100%bleach b. 50% bleach and 50%vinegar c. Nine parts H2O to one partbleach d. The friend must have his or her ownbathroom. 9. Reuben, age 24, has HIV and just had a routine viral load test done. The results show a falling viral load. What does thisindicate? a. A favorable prognostictrend b. Diseaseprogression c. The need to be more aggressive with Reuben’smedications d. The eradication of theHIV 10. If the international normalized ratio (INR) result is above the therapeutic range in a patient with atrial fibrillation on warfarin, what might the cliniciando? a. Stop the warfarin for 1 week, and then repeat theINR. b. Withhold one or more days of anticoagulanttherapy. c. Restart therapy at a lower doseimmediately. d. The prothrombin time and INR should be reevaluated within 1 month of the dosageadjustments. 11. Which of the following is identified as an eating disorder in which a person craves food substitutes, such as clay, ice chips, and cotton, and is considered an objective finding associated with severe iron deficiency? a. Ferritin b. Porter’ssyndrome c. Hypochromasia d. Pica 12. As a rule of thumb, the estimated level of hematocrit is how many times the value of the hemoglobin? a. Two b. Three c. Four d. Five 13. What is the most common cause of microcyticanemia? a. Anemia of chronicdisease b. Sideroblasticanemia c. Iron-deficiencyanemia d. Thalassemia 14. The cardinal subjective symptom of sickle cell crisis is which of thefollowing? a. Pain b. Nausea c. Light-headedness d. Palpitations 15. In the United States, what is the second most common connective tissue disease and the most destructive to thejoints? a. Osteoarthritis b. Systemic lupus erythematosus(SLE) c. Rheumatoidarthritis d. Sjögren’ssyndrome 16. Which blood test is a nonspecific method and most helpful for evaluating the severity and course of an inflammatoryprocess? a. Erythrocyte sedimentationrate b. White blood cellcount c. Polymorphonuclearcells d. C-reactive protein(CRP) 17. Infectious mononucleosis results from an acute infection with which of thefollowing? a. Epstein-Barrvirus b. Acute HIVinfection c. Guillain-Barré d. Hepatitis 18. What is the most common cause of generalized musculoskeletal pain in women ages 20 to55? a. Chronic fatigue syndrome(CFS) b. Anemia c. Fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) d. Sports-relatedinjuries 19. After returning from visiting his grandchildren in England, George, age 59, complains of a flulike illness, including fever, chills, and myalgia. He reports having discovered a rash or red spot that grew in size on his right leg. What disease are youconsidering? a. A viralsyndrome b. Lymedisease c. Rocky Mountain spottedfever d. Relapsingfever 20. Dryness of the eyes and mouth is typical of whichcondition? a. Sjögren’ssyndrome b. CFS c. FMS d. Hypothyroidism 21. Triggering factors for acute exacerbations of which of the following conditions include exposure to ultraviolet (UV)-B and UV-Arays? a. Rheumatoidarthritis b. Scleroderma c. SLE d. Sjögren’ssyndrome 22. The current goal of treatment for a patient with HIV infection is which of thefollowing? a. Viral suppression of HIV to undetectable levels in the peripheralblood b. Compete eradication of thevirus c. Encouraging the person to have no contact with uninfectedindividuals d. Completeabstinence 23. The most cost-effective screening test for determining HIV status is which of thefollowing? a. Westernblot b. Enzyme-linked immunosorbentassay c. Venereal Disease Research Laboratorytest d. Viralload 24. An important complication of antiretroviral (ARV) therapy in patients with advanced AIDS is which of thefollowing? a. Immune reconstitution inflammatorysyndrome b. Improvement in opportunisticinfections c. Restoration of immune system to preinfectionstatus d. Progression toAIDS 25. Which drug category of ARV therapy is generally effective in crossing the blood–brain barrier and may be useful in managing HIV-associateddementia? a. Nucleoside reverse transcriptaseinhibitors b. Proteaseinhibitors c. Integraseinhibitors d. Nonnucleoside reverse transcriptaseinhibitors 26. Spontaneous bruising may be seen with platelet counts below whatlevel? a. 100,000cells/mL b. 75,000cells/mL c. 50,000cells/mL d. 30,000cells/ml 27. Which type of the following is characterized by fatigue on awakening that may improve with exercise? a. Functionalfatigue b. Fatigue with an organicorigin c. Fatigue of chronicanemia d. Fatigue of depression andanxiety 28. Early rheumatoid disease is characterizedby: a. Pain and swelling in both small and large peripheraljoints b. Rigid joints with diminished range ofmotion c. Joint swelling and immobility onrising d. A cardiac rub or pulmonary frictionrub 29. Which test is diagnostic of rheumatoidarthritis? a. Rheumatoidfactor b. ESR c. CRP d. Anti-CCPtiters 30. What is the mainstay of management for infectiousmononucleosis? a. Antivirals b. Symptomcontrol c. Corticosteroids d. Isolation 31. CFS tends to occur in whichindividuals? a. Active, highly functionaladults b. Depressed middle-agedpersons c. Individuals with a depressed immunesystem d. Individuals who arehypochondriacs 32. The exanthem of Lyme diseaseis: a. Erythemainfectiosum b. Laterothoracicexanthem c. Erythemamigrans d. Morbilliexanthem 33. If left untreated, this condition will progress to complaints that include multiple jointarthritis. a. Sjögren’ssyndrome b. HIV/AIDS c. Guillain-Barré d. Lymedisease 34. Keratoconjunctivitis sicca is a classic sign of whichcondition? a. SLE b. Sjögren’ssyndrome c. CFS/FMS d. Lymedisease 35. Which person is four times more likely to develop SLE than aCaucasian? a. Persons of Africandescent b. Asians c. Hispanics d. Middle EasternJews Chapter 61. Hematologic Disorders MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the process by which certain cells engulf and digest microorganisms and cellulardebris? a. Erythrocytosis b. Hematocrit c. Phagocytosis d. Hemostasis KEY: Nursing Process Step: Assessment MSC: NCLEX: Physiological Integrity 2. The nurse explains that because it is a reliable and predictable indicator of the bodys level of infection orrecoverythe is a common diagnostictool. a. Hemoglobin b. Hematocrit c. Mean cell volume(MCV) d. Differential 3. The nurse assessing a differential sees an increase in immature neutrophils (bands) and is aware that thisindicates: a. a significanthemorrhage. b. aplasticanemia. c. an overwhelming bacterialinfection. d. beginning recovery from an infection. cells and T cells fit under whichclassification? a. Erythrocytes b. Basophils c. Lymphocytes d. Monocytes 5. The nurse explains that in the event of an invasion of an allergen, the basophils release astrong vasodilator, whichis: a. lysozyme. b. prothrombin. c. hematocrit. d. histamine. 6. The presence of excess bands in the peripheral blood that indicate severe infection iscalled: a. shift to theleft. b. shift to theright. c. bone marrowaspiration. d. thrombocytosis. 7.A patient who had a Schilling test shows a 20% excretion of the radioactive vitamin B12. What would thisindicate? a. The patient has a low reserve of iron and has iron deficiencyanemia. b. The patient has a normal finding and does not have perniciousanemia. c. The patient has a deficiency of thrombocytes and has a clottingdisorder. d. The patient has an excess of RBCs and has polycythemia. In an adult, where are erythrocytes continuouslyproduced? a. Yellow bonemarrow b. Lymphaticsystem c. Spleen d. Red bonemarrow 9. What does the elevation in the eosinophil count to 10%indicate? a. Anemia b. Allergy c. Infection d. Hypoxia 10. What would a nurse include in a teaching plan for a home health patient with a hemoglobin of8.4 mg? a. Exercising for periods of 30 minutesdaily b. Limiting fluidintake c. Alternating activity with restperiods d. Avoiding the use of oxygen 11. Approximately how much blood is stored in the spleen that can be released in ahypovolemic emergency? a. 100mL b. 300mL c. 500mL d. 1000 mL . 12.The nurse caring for a patient with pernicious anemia should make provisions for: a. frequent iceddrinks. b. lightweightblanket. c. a fan to circulate theair. d. reverse isolation. 13. When instructing the patient taking an oral liquid iron preparation, what should the nurseinclude? a. Information relative to taking the iron withmilk b. Information relative to the bowel movement color changing to darkred c. Information relative to taking preparation through a straw to prevent staining ofteeth d. Information relative to taking a drug with meals or a snack 14. When the 14-year-old African American boy comes into the emergency room in sickle cellcrisis, what should be the primary focus ofcare? a. Instruct patient about transfusionprocedure b. Starting of IVfluids c. Paincontrol d. Relief of dyspnea 15. The mother of a 4-year-old child with leukemia says to the nurse, I dont understand why he is crying about his legs hurting. The nurses most informative response would be based on the information that bone pain is relatedto: a. Elevated WBCs indifferential b. Long periods ofinactivity c. Splenomegaly d. Bone marrow congested with white cells . 16.What must a patient undergo before a bone marrow transplant? a. A thorough nutritional plan to support newmarrow b. Total body irradiation to kill all the marrowcells c. A physical therapy program to strengthen thebody d. Inhalation therapy to reduce possible pathogens in the lungs The 9-year-old child with leukemia who is on palliative care has drawn a picture of a boy under a huge black cloud that has lightning coming out of it. Which of the following would be an appropriate intervention for thenurse? a. What is this pictureabout? b. Are you afraid oflightning? c. I bet this is a picture of you, isntit? d. Is it about to rain in your picture? 18. The home health nurse recommends to the mother of a 12-year-old child with leukemia that the child shouldhave: a. the series for prevention of hepatitisB. b. an annual influenzavaccine. c. an annual pneumococcalvaccine. d. vitamin B12 19. Which patient statement from a 15-year-old girl with thrombocytopenia would requiremore assessment to report to the chargenurse? a. I think these red spots on my skin are goingaway. b. I am so bored lying in bed I couldscream. c. My bowel movement is brown andstinks. d. I have this really weird Coke-colored urine. 23-year-old male patient with hemophilia A says, How can I keep my children from having hemophilia A? Which of the following is the most informativeresponse? a. You need to select a very dependable mode of birthcontrol. b. You can only pass hemophilia B to yoursons. Your daughter may be a carrier and her children may have hemophilia A. Your son is not at c. risk. d. Your sons should have coagulation studies. 24 The nurse caring for a child with hemophilia who is hospitalized with hemarthrosis should include which of the following in the plan ofcare? a. Splint the affected leg to maintain anatomicalignment b. Apply warm compresses to reduce hemorrhage in thejoint c. Use analgesiasparingly d. Encourage vigorous ROM exercises several times a day to keep knee flexible 22. In caring for a patient with multiple myeloma, what should the nurse include in the dailycare? a. Provisions for limiting fluid intake to less than 1000mL/day b. Provisions for close supervision and assistance whenambulating c. Provisions for straining allurine d. Provisions for limiting use of an analgesic . 23. The nurse is aware that a person with Hodgkin disease, who has two or more abnormal lymph nodes on the same side of the diaphragm and involvement of extranodal involvement on the same side of the diaphragm, would bein: a. stage I b. stageII c. stageIII d. stage IV . 24. The nurse explains that a positron emission tomography (PET) has been orderedto: a. assess bone marrowdepression. b. measure bonedensity. c. radiate and destroy diseased lymphnodes. d. measure lymph node response to therapy. . 25. Which of the following foods would the nurse recommend to a person with iron deficiency anemia as an excellent meat source forerythropoiesis? a. Dark meat ofchicken b. Curedham c. Porkchops d. Processedmeat . 26.The peripheral smear is a diagnostic test that: a. assesses the level ofhemoglobin. b. measures antibodyproduction. c. examines the shape and structure ofRBCs. d. identifies infection. . 27. The typical medical treatment of polycythemia vera involves repeated phlebotomies and medications such as busulfan (Myleran) in orderto: a. stimulate bonemarrow. b. inhibit bone marrowactivity. c. increasehemoglobin. d. reducegout. . 28. Which of the following would the nurse explain as the most common type of leukemiathat affectschildren? a. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia(CLL) b. Acute myeloid leukemia(AML) c. Acute lymphocytic leukemia(ALL) d. Chronic myeloid leukemia(CML) 29. The nurse is aware that persons of the Jehovahs Witness faith accept which types ofblood transfusions? a. No type of bloodtransfusion b. Blood that has been blessed by their religiousleader c. Transfusions only for persons who have not yet beenbaptized d. Autologous blood transfusions 30. Which mandatory practice is the most effective and significant nursing practice to preventthe spread ofinfection? a. Strict and frequent handwashing by all people having contact with thepatient b. Placement of patients in private rooms with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA)filtration c. Administration of combinations of prophylacticantibiotics d. Creation of a sterile environment for the patient with the use of laminar airflow rooms 31.What is the average life span of an erythrocyte? a. 7 days b. 60 days c. 120 days d. Up to severalyears 32. Because older adults suffer from conditions such as colonic diverticula, hiatal hernia, and ulcerations that can cause occult bleeding, the nurse should assess for symptomsof: a. leukemia. b. iron deficiencyanemia. c. sickle cellanemia. d. polycythemia. 33. The nurse explains that the treatment of hemophilia A has been revolutionized with the adventof the useof: a. corticosteroids. b. large doses oftestosterone. c. recombinant factorVIII. d. transfusion with packed red cells. 34. From which location would the bone marrow sample come in the aspiration of a 25-year-old patient? a. Sternum b. Posterior superior iliaccrest c. Posterior iliaccrest d. Femur MULTIPLE RESPONSE 35. What are the most likely matches for a bone marrow transplant to a 10-year-old withleukemia? (Select all thatapply.) a. Uncle b. Self c. Mother d. Brother e. Sister f. Father 36. The spleen is a highly vascularized organ located in the left upper quadrant of theabdominal cavity. What are the main functions of the spleen? (Select all thatapply.) a. Serve as reservoir forblood b. Destroy worn-outRBCs c. Promotephagocytosis d. Responsible for development of Tlymphocytes e. Continuously produce RBCs duringlifetime 37. The nurse examines the complete blood count (CBC) to assess (select all thatapply): a. hematocrit. b. red cellcount. c. differential white cellcount. d. plasmalevel. e. blood type. f. hemoglobin. 38. Which of the following are necessary factors that support healthy erythropoiesis? (Select all that apply.) a. Dietarymagnesium b. Healthy bonemarrow c. Adequate oxygensource d. VitaminB12 e. Aminoacids f. VitaminB2 39. The nurse caring for a patient in the emergency room with suspected internal injuries willassess for hypovolemic shock, which is evidenced by (select all thatapply): a. irritability. b. restlessness. c. slow boundingpulse. d. decreasedrespirations. e. pallor. f. hypotension. 40. Which of the following are B symptoms of a patient with Hodgkin disease? (Select all that apply.) a. Hematuria b. Nightsweats c. Severediarrhea d. Weight gain fromedema e. Fever f. Persistent dry cough COMPLETION 41. are leukocytes that destroy and remove cellular waste, bacteria, and solid particles. 42. The person with aplastic anemia is saidtobe because all three major blood elements (RBCs, WBCs, and platelets) are diminished orabsent. Persons with aplastic anemia are deficient in all three of the major blood elements, a condition known as pancytopenia. 43. The nurseclarifiesthat replaces iron stores needed for red blood cellproduction. Ferrous sulfate replaces iron stores needed for red blood cell production. 44.Neutrophilsrelease , an enzyme that destroys certain bacteria. 45. The Reed-Sternberg cell is the hallmark diagnosticindicatorfor . OTHER 46. Arrange the process of hemostasis in sequence. (Separate letters by a comma and space as follows: A, B, C,D) a. Release of clotting factor from injuredtissue b. Formation ofthrombin c. Formation offibrin d. Trapping of RBC andplatelets e. Clot f. Release ofthromboplastin 47. Outline the sequence of the process that stimulates the increase in the production of red blood cells. (Separate letters by a comma and space as follows: A, B, C,D) a. Kidneys release erythropoieticfactor b. Increase in red blood cellproduction c. Enzyme stimulates red bonemarrow d. Oxygen delivery increased to thetissues e. Oxygen delivery decreased to the tissues f, Decrease in red blood cell production Chapter 62. Immunological Disorders MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is an example ofimmunocompetence? a. A child that is immune to measles because of aninoculation b. A person who has seasonal allergies everyfall c. When the symptoms of a common cold disappear in 1day d. A neonate having a natural immunity from maternalantibodies 2. An anxious patient enters the emergency room with angioedema of the lips and tongue, dyspnea, urticaria, and wheezing after having eaten a peanut butter sandwich. What should be the nurses first intervention? a. Apply cool compresses tourticaria b. Provide oxygen per non-rebreathingmask c. Cover patient with a warmblanket d. Prepare for venipuncture for the delivery of IV medication . 3. What is the etiology of autoimmune diseases basedon? a. Reaction to asuperantigen b. Immune system producing no antibodies atall c. T cells destroying Bcells d. B and T cells producing autoantibodies 4 patient is admitted with a secondary immunodeficiency from chemotherapy. The nursing planof care should include provisionsfor: a. infectioncontrol. b. supportingself-care. c. nutritionaleducation. d. maintaining high fluid intake. system is activated which: a. toughens the cellwall. b. generates more Tcells. c. attractsphagocytes. d. makes the antigen resistant. 6.How does normal aging change the immune system? a. Depresses bonemarrow b. T cells becomehyperactive c. B cells show deficiencies inactivity d. Increase in the size of thethymus . 7. What would the nurse recommend for a 94-year-old home health patient with deteriorated cell- mediatedimmunity? a. Avoiding the influenzavaccine b. Getting pneumoniavaccine c. Having skin tests for allantigens d. Taking large doses of beta-carotene . 8.A patient who works in a plant nursery and has suffered an allergic reaction to a bee sting is stabilized and prepared for discharge from the clinic. During discussion of prevention and management of further allergic reactions, the nurse identifies a need for additional teaching based on whichcomment? a. I need to think about a change in myoccupation. b. I will learn to administer epinephrine so that I will be prepared if I am stungagain. c. I should wear a Medic-Alert bracelet indicating my allergy to insectstings. d. I will need to take maintenance doses of corticosteroids to prevent reactions to further stings. . 9. What is the substance released by the T cells that stimulates the lymphocytes to attackan inflammation? a. Lymphokine b. Epinephrine c. Bcells d. Histamine 10. Immediately after the nurse administers an intradermal injection of a suspected antigen during allergy testing, the patient complains of itching at the site, weakness, and dizziness. Which action by the nurse is most appropriateinitially? a. Elevate the arm above theshoulder b. Administer subcutaneousepinephrine c. Apply a warm compress toarea d. Apply a local anti-inflammatory cream to the site 11. Which person is most at risk for a hypersensitivityreaction? a. 26-year-old receiving his second desensitizationinjection b. 35-year-old starting back on birth controltablets c. The 52-year-old started on a new series of Pyridium forcystitis d. The 84-year-old receiving penicillin for an annually recurring respiratory infection 12. The nurse recommends to the busy mother of three that the antihistamine fexofenadine(Allegra) would be more beneficial than diphenhydramine (Benadryl) becauseAllegra: a. isinexpensive. b. contains a stimulant for an energyboost. c. does not dry out the mucousmembranes. d. does not induce drowsiness. 13. The patient who had an asthma-like reaction to a desensitization shot was medicated with a subcutaneous injection of epinephrine. What effect should the nurse assure the anxious patient this willhave? a. Causevasodilation b. Producebronchodilation c. Cause productivecoughing d. Reduction of pulse rate 14. Health care facilities have reduced the incidence of serious latex reactionsby: a. Having local and injectable corticosteroids on hand foremployees b. Desensitizing staff who areallergic c. Supplying extra handwashing stations in thehalls d. Using only powder-free gloves 15. What should the nurse include to assess for in the plan of care for a patient undergoing plasmapheresis? a. Hypotension b. Hypersensitivity c. Urticaria d. Flank pain . 16.A patient is undergoing immunotherapy on a perennial basis. With this form of treatment, what should the patientreceive? a. Larger doses eachweek b. Higher concentrations eachweek c. Increased amounts and concentrations in 6-weekcycles d. The same amount and concentration each visit What is the term for transplantation of tissue between members of the samespecies? a. Allograft b. Autograft c. Isograft d. Homograft 18. In which patient should the nurse be most concerned about immunodeficiencydisorder? a. The patient taking desensitization injections(immunotherapy) b. The patient on long-term radiation therapy forcancer c. The overweightpatient d. The patient recently diagnosed with lupus erythematosus 19. What is the purpose of plasmapheresis in the treatment of rheumatoidarthritis? a. To add corticosteroids to relievepain b. To remove pathologic substances present in theplasma c. To remove waste products such as urea andalbumin d. To add antinuclear antibodies 20. The nurse explains that when the patient received tetanus antitoxin with the antibodies in it,the patientreceiveda type ofimmunity. a. Activenatural b. Passivenatural c. Activeartificial d. Passiveartificial 21. Because the older adult has decreased production of saliva and gastric secretions, they are atrisk for: a. mouthulcers. b. fissures in corners of themouth. c. gastrointestinalinfections. d. bloating. 22.What is the major negative effect of cell-mediated immunity? a. Depression of bonemarrow b. Rejection of transplantedtissue c. Activation of the Tcells d. Stimulation of the Bcells 23.What is B-cell proliferation dependent on? a. Presence of NK (natural killer)cells b. Complementsystem c. Antigenstimulation d. Lymphokines What timeframe must blood be transfused within once it has been removed fromrefrigeration? a. 2 hours b. 4 hours c. 6 hours d. 3 hours 25. The LPN/LVN has arrived at the patients bedside with a unit of packed cells to be connected to an IV that is infusing. When the RN arrives, what is the first thing the nurses mustdo? a. Check to ensure that the donor and recipient numbers match according topolicy b. Request the patient to sign the card on the packedcells c. Immediately administer the packedcells d. Check the patients ID bracelet and then administer the packed cells right arm for 35 minutes. He is complaining of chills, itching, and shortness of breath. What should be the nurses initial action? a. Cover with a warmblanket b. Take the patientstemperature c. Elevate the head of thebed d. Stop the transfusion and continue with saline 29 Which symptom would be classified as a mild transfusionreaction? a. Orthopnea b. Tachycardia c. Hypotension d. Wheezing 28. What should the nurse do because of the increasing strength of the dose in the injections for immunotherapy? a. Observe the patient for at least 20 minutes afteradministration b. Take the vital signs every 10 minutes for anhour c. Have the patient lie down quietly for anhour d. Place a warm compress on the area to speed its absorption MULTIPLE RESPONSE (Select all that apply.) a. Peanuts b. Avocados c. Milk d. Bananas e. Tomatoes f. Potatoes 30. Which of the following provide the body with innate immunity? (Select all thatapply.) a. Skin and mucousmembranes b. Lungs c. Heart d. Tears andsaliva e. Natural intestinal and vaginalflora f. Stomach acid Chapter 63. Infectious Disorders 1. How do antiviral drugsact? a. They interfere with cell walldevelopment. b. They decrease cell membranepermeability. c. They destroy new, immature viralparticles. d. They reduce the rate of viralreplication. 2. Which statement applies toyeasts? a. They are usually considered to bepathogenic. b. They seldom contain a distinctnucleus. c. They may cause opportunistic infection in thebody. d. They are normally not found in large numbers in residentflora. 3. Fungi reproduceby: 1. budding. 2. extension ofhyphae. 3. binaryfission. 4. production ofspores. a. 1, 2 b. 2, 4 c. 1, 2, 4 d. 2, 3, 4 4. Which of the following is NOT classified as a protozoan agent ofdisease? a. Plasmodiumvivax b. Trichomonasvaginalis c. Tineapedis d. Entamoeba histolytica 5. Which of the following is a characteristic ofrickettsia? a. It is a very small gram-negative intracellularmicrobe. b. It exists in threeforms. c. It causes sexually transmitteddisease. d. It reproduces bybudding. 6. Entamoeba histolytica is transmitted by which of thefollowing? a. Mosquitoes(bites) b. Inhaling contaminatedparticles c. Sexualintercourse d. Cysts infeces 7. Which of the following is a characteristic of resident or normal flora(microflora)? a. It exists in all areas of thebody. b. Different species inhabit various areas of thebody. c. It is of no benefit to the humanhost. d. It consists only ofbacteria. 8. Which of the following is normally consideredsterile? a. Urine b. Pharynx c. Distalurethra d. Vagina 9. The term nosocomial infectionmeans: a. transmission involves an insect or animalhost. b. acquired in a hospital or medicalfacility. c. transmitted by afomite. d. spread by direct contact with secretions from an openlesion. 10. Transmission of microbes by direct contactincludes: a. touching a contaminatedcountertop. b. sexualintercourse. c. drinking contaminatedwater. d. inhaling dust-bornemicrobes. 11. What does the term carriermean? a. A person with active infection who acts as a reservoir formicrobes b. Animals, insects, objects, or surfaces contaminated bypathogens c. An individual who is contagious through infected secretions on thehands d. An asymptomatic person whose body harbors pathogens and can transmit them toothers 12. Opportunistic infection may develop when: a. pathogens enter the body but cannot colonize the site ofentry. b. an imbalance occurs in the normal residentflora. c. host resistance increases, and the balance of resident flora isrestored. d. contaminated food or water is unknowinglyingested. 13. Host resistance is promoted by all of the followingEXCEPT: a. prescribedimmunizations. c. vitamin and mineralsupplements. d. appropriate inflammatory or immuneresponse. 14. Which of the following factors would NOT increase the virulence of a specificmicrobe? a. Secretion ofendotoxin b. Presence of a bacterialcapsule c. Production ofinterferons d. Secretion of invasiveenzymes 15. That time in the course of an infection when the infected person may experience a headache or fatigue and senses he or she is coming down with something is referred to as which of thefollowing? a. Subclinicalperiod b. Eclipseperiod c. Prodromalperiod d. Presymptomaticperiod 16. The principle of Universal Precautions is basedon: a. using disinfectants at all times to eliminatecross-infections. b. not touching any open or bleedinglesions. d. assuming that all body fluids from all individuals are possible sources ofinfection. 17. The incubation period refers to the time periodbetween: a. entry of the pathogen into the body and the first signs of infectiousdisease. b. the onset of the prodromal period and the peak of the acuteinfection. c. the onset of clinical signs and signs of recovery frominfection. d. the acute period and establishment of chronicinfection. 18 What does bacteremia referto? e. Numerous pathogens circulating and reproducing in theblood f. Uncontrolled sepsis throughout thebody g. Multiple infections, primary and secondary, established in thebody h. Microbes present in theblood 18. Which of the following is a local sign ofinfection? a. Fever andleukocytosis b. Headache andanorexia c. Pain, erythema, andswelling 19. What are culture and sensitivity tests usedfor? a. To determine the type of microbe present in anexudate b. To provide a specific medium that supports maximum microbialgrowth c. To identify the causative microbe and the effective antimicrobial agent forit d. To provide living host cells for microbes requiring such forreplication 20. A broad-spectrum bactericidal agent would be expectedto: a. destroy many gram-positive and gram-negativebacteria. b. destroy all pathogenic microbes in contact with theagent. c. reduce the replication of manybacteria. d. inhibit the growth of most spores and acid-fastbacteria. 21. How does penicillin act as a bactericidalagent? a. It interferes with cell-wallsynthesis. b. It blocks proteinsynthesis. c. It increases cell membranepermeability. d. It prevents DNAreplication. 22. Secondary infection may occur with administration of antibacterial drugs becausethe: a. patient is allergic to thedrug. b. balance of species in the resident flora isupset. c. mucosa of the stomach isirritated. d. infecting microbes spread to adjacentareas. 23. All of the following are mechanisms of antiviral drug actionEXCEPT: a. interference with attachment to hostcell. b. block assembly of viralparticles. c. interference withmitosis. d. shedding of proteincoat. 24. Secondary bacterial infections occur frequently during influenza epidemics primarilybecause: a. antiviral drugs lower hostresistance. b. the virus causes extensive tissue inflammation andnecrosis. c. respiratory droplets transmitinfections. d. the viral infection is usuallyself-limiting. 25. The primary pathological effect of influenza virusis: a. destruction of the mucosa in the lower respiratorytract. c. destruction of leukocytes and macrophages in thelungs. d. inflammation and necrosis of the upper respiratoryepithelium. 25 What does leukocytosis frequentlyindicate? b. Immunosuppression c. Bone marrowdamage d. Presence of bacterialinfection e. An allergic or autoimmunereaction 26. When an infection or inflammation is suspected, what does leucopenia oftenindicate? a. Bacterialinfection b. Viralinfection c. Allergicreaction d. Septicemia 27. Which of the following statements applies toChlamydia? a. The microbe exists as a chain ofcells. b. It causes a commonSTD. d. It is excreted infeces. 28 Which of the following microbes is classified as an obligate intracellularparasite? c. Fungus d. Bacterium e. Virus f. Protozoa 28. Which of the following are characteristics of influenzavirus? 1. It is an obligate intracellularparasite. 2. It containsRNA. 3. It usually causes nausea andvomiting. 4. There are three subtypes: A, B,C. a. 1, 4 b. 1, 3 c. 2, 3, 4 d. 1, 2, 4 32. The widespread necrosis of respiratory mucosa caused by an influenza infection often gives rise to: b. secondaryinfections. c. asthma. d. emphysema. 33 Prions cannot be cultured in a PETRI plate of mediabecause: a. they take so long togrow. b. they require extensive amounts of specializednutrients. c. they are proteinaceous particles, not livingorganisms. d. they are viruses that dont grow on conventionalmedia. 33. Which of the following statements applies to Influenza AH1N1? a. It alters human chromosomes to causemanifestations. b. It usually causes severe respiratory distress and highfever. c. Infection is common in theelderly. d. It contains genetic material from avian, swine, and humanviruses. 34. Which of the following does NOT directly determine the virulence of amicrobe? a. Capacity foropportunism c. Ability tomutate d. Invasivequalities 35. Which of the following is a function ofinterferons? a. They block the invasion of pathogenicbacteria. b. They reduce the inflammatory response to localinfection. c. They increase host cell resistance to viralinvasion. d. They may facilitate the spread of some cancercells. 36. Inflamed tissue is likely to become infectedbecause: a. the immune system is not effective in inflamedtissue. b. the increased fluid and protein in the inflamed area supports microbialgrowth. c. phagocytes cannot penetrate the inflamedareas. d. capillaries are less permeable in the affectedarea. 37. When an infectious disease is occurring globally at a higher rate than usual, it may be designated asa/an: a. sporadicoccurrence. b. epidemic. d. emergingdisease. 38. Which of the following is the primary difference between an antiseptic and adisinfectant? a. Antiseptic is used on living tissue, whereas disinfectant is designed for nonlivingsurfaces. b. Antiseptic is much stronger than the potency of adisinfectant. Antiseptic often causes allergic skin reactions, whereas disinfectant is always c. hypoallergenic. d. Antiseptic is effective against endospores; disinfectants are not effective againstendospores. 39. Drugs that are designed to inhibit or slow down growth of microbes but not necessarily kill them areconsidered: a. ineffective. b. bacteriostatic. c. narrow-spectrum. d. bactericidal. Chapter 64. Common Psychosocial Complaints Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The effectiveness of benzodiazepines in treating anxiety disorders suggests that which of the following neurotransmitters plays a role inanxiety? a. Acetylcholine b. Gamma-aminobutyric acid(GABA) c. Dopamine d. Serotonin 2. The criteria for diagnosing generalized anxiety disorder in the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edition (text revision) state that excessive worry or apprehension must be present more days than not for atleast: a. 1 month b. 3months c. 6months d. 12 months 3. A patient presents to the clinician after experiencing four episodes in the last month of sweating, palpitations, chest pain, nausea, and shaking. Each episode lasted about 10 minutes. The patient is now becoming very fearful of future events and has been reluctant to leave the house. Theclinician suspects panic disorder but wants to rule out any possible medical causes. Which of the following medical conditions can mimic the symptoms of a panicattack? a. Pheochromocytoma b. Hyperthyroidism c. Cardiacarrhythmias d. All of theabove 4. Which of the following is considered first-line treatment for panicdisorders? a. Benzodiazepines b. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors(SSRIs) c. Tricyclicantidepressants d. Cognitive behavioraltherapy 5. Which of the following symptoms is not part of the diagnostic criteria for post-traumatic stress disorder(PTSD)? a. Hypersomnolence b. Bluntedfeelings c. Loss of interest in significantactivities d. Intrusive recurrent recollections of theevent 6. Which of the following neuroendocrine abnormalities is implicated indepression? a. Decrease in adrenalsize b. Increased cortisol and corticotrophin-releasinghormone c. An exaggerated response of thyrotropin (TRH) to infusion of thyroid-releasing hormone d. Increased inhibitory response of glucocorticoids todexamethasone 7. The clinician has chosen to prescribe an SSRI instead of a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) for a patient fitting the diagnostic criteria for depression. Which of the following is not true concerning SSRIs in comparison to tricyclicantidepressants? a. SSRIs are more effective thanTCAs. b. SSRIs take less time to work thanTCAs. c. SSRIs have a more favorable side-effect profile thanTCAs. d. SSRIs are not lethal inoverdose. 8. After discontinuing fluoxetine, how long must a person wait before starting a monoamine oxidase inhibitor? a. 2weeks b. 3weeks c. 4weeks d. 5weeks 9. It is important to educate patients with depression and their family members about reporting signs of increasing depression and suicidal thoughts. This is especially true during which timeperiod? a. Before the initiation oftreatment b. 1 to 2 weeks after the initiation oftreatment c. When switching to a differentmedication d. 1 to 2 weeks after tapering offmedications 10. A patient is experiencing extrapyramidal side effects from his antipsychotic medications. The clinician would most likely take which of the following approaches to treating these sideeffects? a. Give the patient a “drug holiday” until the symptoms resolve and then restart the medication. b. Switch the patient to a differentantipsychotic. c. Treat the patient withanticholinergics. d. Treat the patient withanticonvulsants. 11. According to Kübler-Ross, the stages of grief occur in whichorder? a. Anger, denial, depression, bargaining,acceptance b. Anger, denial, bargaining, acceptance,depression c. Denial, anger, depression, bargaining,acceptance d. Denial, anger, bargaining, depression,acceptance 12. The clinician is educating a patient about the effects of marijuana. The patient stated she has been smoking for years and believes the use does not interfere with her life. What is a significant long- term sequelae of marijuana use that the clinician should educate this patient about? a. Memoryimpairment b. Sexualdysfunction c. Dry mouth d. There are no long-term consequences of marijuanause. 13. Cocaine acts as a stimulant by blocking the reuptake of whichneurotransmitter? a. GABA b. Acetylcholine c. Dopamine d. Serotonin 14. What blood alcohol level corresponds with the signs of stupor and confusion? a.0.05 b. 0.1 c. 0.2 d. 0.3 15. Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep occurs how frequently during non-REMsleep? a. Every 30minutes b. Every 60minutes c. Every 90minutes d. Every 180minutes 16. Which of the following is a laboratory finding commonly found in patients with anorexianervosa? a. Hypercholesterolemia b. Hypermagnesmia c. Leukocytosis d. DecreasedTRH 17. Which of the following is the only drug for bulimia approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration? a. Sertraline b. Fluoxetine c. Citoprolam d. Imipramine 18. Which of the following would be important to monitor in a child receiving methylphenidate for treatment of attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder(ADHD)? a. Liverfunction b. Vision c. Growthparameters d. Renalfunction 19. It is important for the clinician to discuss the long-term effects of sexual assault withsurvivors. Which of the following is the most common long-term effect of sexual assault? a. Depression b. Obsessive-compulsivedisorder c. Substanceabuse d. PTSD 20. Women are at the highest risk for developing postpartum depression for up to how long after childbirth? a. 2weeks b. 1month c. 3months d. 6months 21. Which is the most prevalent psychiatric condition in the UnitedStates? a. Depression b. Anxiety c. Substance-relatedaddictions d. Gambling 22. What is recorded as clinical category two of the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edition (textrevision)? a. Clinical disorder or focus of clinicalattention b. Personality or environmentalproblems c. Environmental and psychosocialstressors d. Global assessment offunctioning 23. Which of the following may be used to evaluate a person’s suiciderisk? a. CAGE b. SANE c. SADPERSONAS d. DIGFAST 24. Assessing for adherence with prescribed medications and developing a plan for what to do if they are stopped is a major treatment issue for which of the following diagnosticgroups? a. ADHD b. Bipolar c. Depression d. Anxiety 25. Bipolar disorder requires differential diagnosis from all of the followingexcept? a. Substance abuse and medicationeffects b. Medical and neurologicaldisorders c. Cluster B personality disorders anddepression d. Obsessive-compulsivedisorder True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. The use of benzodiazepines in the patient with generalized anxiety disorder and comorbid depression can exacerbate depressivesymptoms. 2. Depressive episodes associated with bipolar disorder are treated the same as major depressive disorder. 3. Women in abusive relationships have a greater chance of being killed by their batterers when they leave the relationship than women whostay. 4. Adults must show childhood onset of symptoms to receive a diagnosis ofADHD. 5. Parkinson’s disease and dementing illnesses may commonly manifest depressivesymptoms. 6. The best predictor of suicide risk is a history of suicideattempts. 7. A no-suicide contract can prevent a suicideattempt. 8. Depression is the most chronic disabling and economically catastrophic medical disorder of the severe mentalillnesses. 9. Clozapine (Clozaril) requires laboratory monitoring at specified frequencies with results reported to a nationalregistry. 10. When combined with certain other medications, serotonin-specific antidepressants can have significant liver P450-interactioneffects. Chapter 65. Substance Use Disorders MULTIPLE CHOICE 1.A 60-year-old man was admitted for cholecystitis that resulted in a cholecystectomy. On his third day of hospitalization, he begins to sweat profusely, tremble, and has a blood pressure of 160/100. Based on these findings, what focused assessment should the nursecomplete? a. Cardiacproblems b. Respiratoryproblems c. Withdrawalproblems d. Circulatoryproblems . 2. What age of onset of alcohol consumption is most predictive of alcoholaddiction? a. 8 or younger b. 10 or younger c. 12 or younger d. 14 or younger . 3. Alcohol is involved in motor vehicle accidents, suicides, and homicides. Approximately howmany deaths each year are related to alcoholconsumption? a. 50,000 b. 70,000 c. 80,000 d. 100,000 4. What stage of dependence is described by a patient when he tells the nurse that he has tried tostop his drug habit, but he does not feel normal withoutit? a. Early b. Prodromal c. Middle d. Late 5. What must a patient in the late stages of dependence do in order torecover? a. Gain insight into theaddiction b. Receive treatment for substanceabuse c. Pledge to lead a completely differentlifestyle d. Seek a nondrug-oriented support system 6. What is the best response by a nurse when a patient inquires how alcohol acts so quickly onhis system? a. Alcohol is digestedquickly. b. Alcohol is converted to glycogenimmediately. c. Alcohol is metabolized into ethanolrapidly. d. Alcohol is excreted in urine slowly. 7. The nurse reminds a group of high school students that most states have laws limitingblood alcohol levels of drivers. What is the legal blood alcohol serum level in moststates? a. 0.08% b. 0.20% c. 0.40% d. 0.50% 8.A pregnant adolescent tells the nurse that she only drinks a little. How many drinks per day can cause an adverse effect in aninfant? a. One drink aday b. Two drinks aday c. Three drinks aday d. Four drinks aday . 9. The nurse assesses an alcoholic patient carefully for signs of withdrawal. How soon aftercessation of alcohol intake do withdrawal symptoms usuallyappear? a. 3 hours b. 4 hours c. 5 hours d. 6 hours 10. The nurse is performing an initial assessment on an alcoholic patient. Which of thefollowing actions by the nurse would best ensure honestanswers? a. Not asking personalquestions b. Having a nonjudgmentalattitude c. Including thefamily d. Promising the patient not to tell anyone . 11. During the detoxification period, what does the nurse aim to achieve whendesigning interventions? a. Enroll the patient in Alcoholics Anonymous(AA) b. Keep the patient safe from aspiration andseizure c. Help the patient interact in nonaddictiveactivities d. Help the patient gain insight into the addiction . 12. What should the entire health team focus on during the rehabilitationphase? a. Establishing a supportsystem b. Seeking and maintainingemployment c. Abstaining from druguse d. Addressing the problems related to addiction 13. What should the nurse do to decrease the patients disorientation at night during thedetoxification period? a. Place the patient in a room with another recoveringpatient b. Instruct the patient to orient himself to his surroundings atbedtime c. Wake the patient up every 4 hours to eat a smallsnack d. Use nightlights and remove extra furniture from the room . 14. The nurse explains that Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) consists of abstinent alcoholics who help other alcoholics become and stay sober. What is the foundation ofAA? a. Psychotherapy b. A 12-stepprogram c. Treatmentcenter d. Individual counseling . 15. What severe side effect will occur if an alcoholic patient consumes alcohol while taking disulfiram(Antabuse)? a. Nausea b. Blackouts c. Headaches d. Hypertension 16. If the patient tells the nurse, Im not an alcoholic. I can stop whenever I want to, what shouldbe the nurses most therapeuticresponse? a. Well, why dontyou? b. Hasnt alcohol use interfered with youremployment? c. A positive attitude like that is a goodstart. d. What would you call alcoholism? 17. When a patient denies any problems related to addiction, what is the nurses most therapeutic response? a. What do you call thishospitalization? b. How can anybody help you if you dont see aproblem? c. Would your family agree that you have noproblems? d. Can you think of any time your behavior created an unpleasant situation in your life? . 18.Which drug is often used in date rape? a. Dalmane b. Xanax c. Narcan d. Rohypnol 19.A patient seems bewildered when he confides in the nurse that all of his friends and leisure time have been centered on a drug culture. Which would be the best response by thenurse? a. What other sort of activities might youenjoy? b. You will need to get newfriends. c. Returning to those activities will get you back here and introuble. d. You need to get a hobby. . 20. When a patient is admitted with an overdose of an opioid narcotic, the nurse should anticipatean order for which drug to reverse the effects of thenarcotic? a. Clonidine b. Narcan c. Orlaam d. Methadone 21. The nurse concludes that a significant goal of the care plan for an alcoholic patient has beenmet when the patient makes whichstatement? a. I drink because Imlonely. b. All my difficulties are related to mydrinking. c. I wouldnt need to drink if I had my familyback. d. My drinking helps me cope with the stress of myjob. 22. While creating a methadone protocol for a patient rehabilitating from heroin addiction, thenurse explains that the patient will take methadone for what length oftime? a. Daily for the rest of hislife b. Daily until stabilized, then gradually reduce the dose tozero c. Weekly for at least 6 months, then decrease the dose to once amonth d. Monthly for 6 to 10 months, then decrease the dose to zero . 23.A 22-year-old patient presents in the emergency department with the characteristics of severe Parkinson disease. The nurse should suspect an overdose of whatdrug? a. Marijuana b. Cocaine c. Amphetamines d. Valium . 24.A college student has brought his hallucinating roommate to the college clinic. The young man says his roommate has been experimenting with phencyclidine (PCP). How long should the nurse expect the hallucinations tolast? a. 30 to 60minutes b. 1 to 4 hours c. 4 to 6 hours d. 6 to 12hours . 25. The mother of a young woman being treated for amphetamine overdose asks the nurse whenthe manifestations will subside. What would be the most correct answer by thenurse? a. Usually in 8 to 10hours. b. She will snap out of it in a day ortwo. c. Usually in about 2 hours, but the effects will return in 2 to 3days. d. The manifestations may be permanent. . 26. What nursing intervention should be included in the plan of care for a baby born to adrug- addictedmother? a. Swaddle the babyclosely b. Place the baby in a brightly litarea c. Hold and rock the babyfrequently d. Place the baby in a busy part of the nursery forstimulation . 27. What is the greatest problem with lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)use? a. The drug isaddictive. b. The drug stimulates drug-seekingbehavior. c. The drug causesflashbacks. d. The drug sets off hypertensive episodes. . 28. What should the nurse do to decrease the damage of bruxism seen in a patient who hasbeen abusing the drugecstasy? a. Turn the patient to his rightside b. Elevate the head of the bed 30degrees c. Provide the patient with apacifier d. Administer a muscle relaxant ). 29. What should the nurse do when suspecting a co-worker of abusing drugs while atwork? a. Confront theabuser b. Report observations to asupervisor c. Call the state board ofnursing d. Discuss the problem with another co-worker . MSC: NCLEX: Health Promotion and Maintenance 30. Which statement describes the impaired nurse who is in a peer assistanceprogram? a. The nurse has a revoked nursinglicense. b. The nurse does not have to notify heremployer. c. The nurse will be allowed to work as a nurse undersupervision. d. The nurse will be reported to the Healthcare Integrity and Protection Data Bank. , MULTIPLE RESPONSE 31. During the initial intake assessment of a drug user, the nurse should attempt to obtainwhich subjective data? (Select all thatapply.) a. Usual pattern ofuse b. Specificdrug c. Previousarrests d. Amount of drugused e. Time of lastuse , 32. The nurse should assess a patient for which criteria of addiction? (Select all thatapply.) a. Excessive use of thesubstance b. Increase in socialfunction c. Uncontrollableconsumption d. Increase in economicfunction e. Psychological disturbances . 33.A nurse suspects her a co-worker is abusing drugs. Which of the following symptoms, noticed in the co-worker, would contribute to thesuspicions? a. Spending more time withco-workers b. Frequently absent from theunit c. Rapid changes in mood andperformance d. Increased somaticcomplaints e. Patients report they did not receive their medications . COMPLETION 34. When assessing an alcoholic patient, the nurse notes short-term memory loss, painful extremities, footdrop, and muttered incoherent responses to questions. The nurse recognizes these symptoms as most likely related to a condition caused by long-term alcohol abuse, which isknown as syndrome. . 35. The nurse uses the CAGE questionnaire to assess a patient. The nurse suspects the patient is an alcoholic if there are affirmativeanswersfor items on the questionnaire. . 36. The nurse cautions that a person who chronically abuses drugs may experience mental impairment. The area of the brain that can be affected and permanently damaged isthe . Chapter 66. Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders The nurse is caring for a client in an inpatient mental health setting. The nurse notices that when the client is conversing with other clients, he repeats what they are saying word for 1. word. The nurse interprets this finding and documents it as which of thefollowing? A) Echopraxia B) Neologisms C) Tangentiality D) Echolalia While caring for a hospitalized client with schizophrenia, the nurse observes that the client is listening to the radio. The client tells the nurse that the radio commentator is speaking 2. directly to him. The nurse interprets this finding as which of thefollowing? A) Autisticthinking B) Concretethinking C) Referentialthinking D) Illusionalthinking A client has been diagnosed with schizophrenia. Assessment reveals that the client lives alone. His clothing is disheveled, his hair is uncombed and matted, and his body has a strange odor. During an interview, the clients family voices a desire for the client to live with them when he is discharged. Based on the assessment findings, which nursing 3. diagnosis would be thepriority? A) Ineffective Role Performance related to symptoms ofschizophrenia. B) Social Isolation related to auditoryhallucinations. C) Dysfunctional Family Processes related topsychosis. D) Bathing Self-Care Deficit related to symptoms ofschizophrenia. The nurse is caring for an elderly client who has been taking an antipsychotic medication for 1 week. The nurse notifies the physician when he observes that the client has muscle rigidity that resembles Parkinsons disease. Which agent would the nurse expect the 4. physician toprescribe? A) Anticholinergic B) Anxiolytic C) Benzodiazepine D) Beta-blocker The nurse is caring for a hospitalized client who has schizophrenia. The client has been taking antipsychotic medications for 1 week when the nurse observes that the clients eyes 5. are fixed on the ceiling. The nurse interprets this finding as which of thefollowing? A) Akathisia B) Oculogyriccrisis C) Retrocollis D) Tardivedyskinesia A hospitalized client with schizophrenia is receiving antipsychotic medications. While assessing the client, the nurse identifies signs and symptoms of a dystonic reaction. Which 6. agent would the nurse expect toadminister? A) Diphenhydramine(Benadryl) B) Propranolol(Inderal) C) Risperidone(Risperdal) D) Aripiprazole(Abilify) The nurse is caring for a client who has been receiving treatment for schizophrenia with chlorpromazine for the past year. It would be essential for the nurse to monitor the client for 7. which of thefollowing? A) Weight loss B) Torticollis C) Hypoglycemia D) Tardivedyskinesia A client hospitalized for treatment of schizophrenia has been receiving olanzapine (Zyprexa) for the past 2 months. The nurse would be especially alert for which of the 8. following? A) Weight loss B) Hypertension C) Diarrhea D) Diabetes The nurse is caring for a client who has been taking clozapine (Clozaril) for 2 weeks. The client tells the nurse, My throat is sore, and I feel weak. The nurse assesses the clients vital signs and finds that the client has a fever. The nurse notifies the physician, expecting an 9. order to obtain which laboratorytest? A) A white blood cellcount B) Liver functionstudies C) Serum potassiumlevel D) Serum sodiumlevel A client is being released from the inpatient psychiatric unit with a diagnosis of 10. schizophrenia and treatment with antipsychotic medications. After teaching the clientand family about managing the disorder, the nurse determines that the teaching was effective when they state which of the following should be reported immediately? A) Elevatedtemperature B) Tremor C) Decreased bloodpressure D) Weight gain A nurse is preparing an in-service program for a group of psychiatricmental health nurses about schizophrenia. Which of the following would the nurse include as a major reason for 11. relapse? A) Lack of familysupport B) Accessibility to communityresources C) Non-adherence to prescribedmedications D) Stigmatization of mentalillness While assessing a client with schizophrenia, the client states, Everywhere I turn, the government is watching me because I know too much. They are afraid that I might go public with the information about all those conspiracies. The nurse interprets this 12. statement as indicating which type ofdelusion? A) Grandiose B) Nihilistic C) Persecutory D) Somatic The nurse is interviewing a client with schizophrenia when the client begins to say, Kite, 13. night, right, height, fright. The nurse documents this as which of thefollowing? A) Clangassociation B) Stiltedlanguage C) Verbigeration D) Neologisms A nurse is providing care to a client just recently diagnosed with schizophrenia during an inpatient hospital stay. Throughout the day, the nurse observes the client drinking from the water fountain quite frequently as well as carrying cans of soda and bottles of water with him wherever he goes. Upon entering the clients room, the nurse sees numerous empty cups that had been filled with fluids on his table and in the trash can. The room has an 14. odor of urine. The nurse suspects which of thefollowing? A) Diabetesmellitus B) Disordered waterbalance C) Tardivedyskinesia D) Orthostatichypotension A group of nursing students is reviewing the various theories related to the etiology of schizophrenia. The students demonstrate understanding of the information when they 15. identify which neurotransmitter as being responsible for hallucinations anddelusions? A) Dopamine B) Serotonin C) Norepinephrine D) Gamma-amino butyric acid(GABA) After teaching a class on antipsychotic agents, the instructor determines that the teaching was successful when the class identifies which of the following as an example of a 16. second-generation antipsychoticagent? A) Fluphenazine(Prolixin) B) Thiothixene(Navane) C) Quetiapine(Seroquel) D) Chlorpromazine(Thorazine) When assessing a client for possible disordered water balance, the nurse checks the clients urine specific gravity. Which result would lead the nurse to suspect that the client is 17. experiencing severe disordered waterbalance? A) 1.020 B) 1.011 C) 1.005 D) 1.002 A client with schizophrenia tells the nurse, Im being watched constantly by the FBI 18. because of my job. Which response by the nurse would be mostappropriate? A) Tell me more about how you are beingwatched. B) It must be frightening to feel like youre always beenwatched. C) Youre not being watched; its all in yourmind. D) You are experiencing a delusion because of yourillness. A nurse is working with a group of clients diagnosed with schizophrenia in a community 19. setting. Which of the following would least likely be apriority? A) Improving the quality oflife B) Instillinghope C) Managingpsychosis D) Preventingrelapse A client with schizophrenia is prescribed clozapine because other prescribed medications have been ineffective. After teaching the client and family about the drug, the nurse 20. determines that the teaching was successful when they state which of thefollowing? A) He needs to have an electrocardiogram periodically when taking thisdrug. B) Well need to make sure that he has his blood count checked at leastweekly. C) He might develop toxic levels of the drug if he smokescigarettes. D) We need to watch to make sure that he doesnt lose too muchweight. Which of the following would be most important for the nurse to keep in mind when establishing the nursepatient relationship with a client with schizophrenia to promote 21. recovery? A) The relationship typically develops over a short period oftime. B) Decisions about care are the responsibility of interdisciplinaryteam. C) Short, time-limited interactions are best for the client experiencingpsychosis. D) Typically, clients with schizophrenia readily engage in a therapeutic relationship. A nurse is developing a teaching plan for a client with schizophrenia. Whichmethod 22. would the nurse use to be mosteffective? A) Engaging the client the trial and errorlearning Having the client write down information after directly being given the correct B) information C) Asking the client questions that encourage the client to guess at the correctanswer D) Using visual aids that are very colorful and full of descriptive graphicimages Assessment of a client with schizophrenia reveals that he is hearing voices that tell him that people are staring at him and illusions. When developing the plan of care for this 23. client, which nursing diagnosis would be mostappropriate? A) Disturbed thoughtprocesses B) Risk for self-directedviolence C) Disturbed sensoryperception D) Ineffectivecoping A nursing instructor is preparing a class lecture about schizophrenia and outcomes focusing on recovery. Which of the following would the instructor include as a major 24. goal? A) Continuity ofcare B) Shorter in-patientstays C) Immediate crisisstabilization D) Socialengagement experiencing an anticholinergic crisis. Which of the following would the nurse most likely 25. have assessed? Select all thatapply. A) Dilated reactivepupils B) Blurredvision C) Ataxia D) Coherentspeech E) Facialpallor F) Disorientation Answer Key 1. D 2. C 3. D 4. A 5. B 6. A 7. D 8. D 9. A 10. A 11. C 12. C 13. A 14. B 15. A 16. C 17. D 18. B 19. C 20. B 21. C 22. B 23. C 24. A 25. B, C,F A client who has a major depressive episode tells the nurse that for the past 2 weeks, he has been hearing voices and at times thinks that someone is following him. History reveals that he had these alternating symptoms before along with times when he has experienced neither of these symptoms and has been able to function adequately. The nurseinterprets 1. these findings as suggesting which of thefollowing? A) Paranoidschizophrenia B) Undifferentiatedschizophrenia C) Brief psychoticdisorder D) Schizoaffectivedisorder A nursing instructor is developing a class lecture that compares and contrasts schizoaffective disorder with schizophrenia. When describing one of the differences between these two diagnoses, which of the following would the instructor include as 2. reflecting schizoaffectivedisorder? A) It is episodic innature. B) It involves difficulties withself-care. C) It has less severehallucinations. D) It is associated with a lower suiciderisk. The nurse is caring for a client who was diagnosed with schizoaffective disorder. Based on the nurses understanding of this disorder, the nurse develops a plan of care to address which 3. issue as the toppriority? A) Suicide B) Aggression C) Substanceabuse D) Eatingdisorder A family member of a client diagnosed with schizoaffective disorder asks a nurse what 4. causes the disorder. Which response by the nurse would be mostappropriate? A) Dysfunctional family dynamics has been identified as a stronglink. B) Research has suggested that the cause is predominatelygenetic. C) Dopamine, a substance in the brain, appears to beunderactive. D) Studies have indicated that birth order is strongly associated with thisdisorder. The nurse is caring for a client who was just admitted with a diagnosis of schizoaffective disorder with depression. Which agent would the nurse anticipate as being prescribed for 5. thisclient? A) Lithium B) Haloperidol C) Chlorpromazine D) Clozapine The nurse is assessing a newly admitted client diagnosed with schizoaffective disorder. The nurse assesses the clients level of anxiety and reactions to stressful situations, obtaining this 6. information for whichreason? A) To help determine the clients outcomes aftertreatment B) To help identify whether or not the clients mental competency isintact C) To act as a predictor of the clients risk for a suicideattempt D) To provide a basis for evaluating the clients socialskills The nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with a delusional disorder. While assessing this 7. client, which of the following would the nurse expect tofind? A) History of chronic majordepression B) Consistently disrupting behaviorpatterns C) Verbalization of bizarredelusions D) Living with one or more delusions for a period oftime The nurse is preparing to interview a client who has a delusional disorder. Which of the 8. following would the nurseexpect? A) Cognitiveimpairment B) Normalbehavior C) Labileaffect D) Evidence of motorsymptoms The nurse is preparing to document information obtained from a client diagnosed with a delusional disorder who is experiencing somatic delusions. Which of the following would 9. the nurse most likelydocument? A) Disorientation B) Reduced attentionspan C) Above averageintelligence D) Bodycomplaints A client with schizoaffective disorder is prescribed clozapine to treat her symptoms. 10. 10. A) Which of the following instructions would the nurse provide? Keep a record of how often and how long you experience the side effect of dry mouth. B) Monitor your urinary output and notify your doctor if your urine changescolor. C) Keep an eye on your weight, and if you gain weight rapidly, notify yourdoctor. D) If you experience any drowsiness, discontinue taking thismedication. After teaching a group of students about the epidemiology of schizoaffective disorder, the instructor determines that the teaching was successful when the students state which of the 11. following? A) The disorder occurs often inchildren. B) It is more likely to occur inwomen. C) Most persons are AfricanAmericans. D) The disorder is rare in familyrelatives. A client with schizoaffective disorder is having difficulty adhering to the medication regimen that requires the use of several agents. The client also is experiencing several side effects contributing to this nonadherence. The physician plans to change the clients 12. medication. Which agent would the nurse anticipate that the physician wouldprescribe? A) Lithium B) Aripiprazole C) Clozapine D) Olanzapine While interviewing a client diagnosed with a delusional disorder, the client states, I have this really strange odor coming out of my mouth. I stop to brush my teeth almost every hour and then rinse with mouthwash every half hour to get rid of this smell. Ive seen so many doctors, and they cant tell me whats wrong. The nurse interprets the clients 13. statement as reflecting which type ofdelusion? A) Erotomanic B) Grandiose C) Somatic D) Jealous Chapter 67. Mood Disorders A client diagnosed with bipolar disorder and experiencing mania is admitted to the inpatient psychiatric setting. During the acute phase of mania, which medication would the nurse 1. expect to most likelyadminister? A) Lithium carbonate(Lithium) B) Haloperidol lactate(Haldol) C) Fluoxetine(Prozac) D) Paroxetine(Paxil) A client asks the nurse if he needs to alter any of his activities because he is taking lithium 2. carbonate. Which of the following responses would be mostappropriate? A) Increase your salt intake if an activity causes you to perspireheavily. B) Wear sunscreen when you are going to be outdoors in the summertime. C) Drink less fluid than usual now because you are taking thisdrug. D) No changes are necessary for strenuous activities you dooutdoors. The nurse is assessing a client with bipolar disorder who is experiencing mania. The client states, Im just so beautiful. Everyone just stops and stares at how gorgeous I am. Men constantly want to have sex with me. The nurse interprets these statements as indicative of 3. which type ofmood? A) Irritable B) Elevated C) Expansive D) Euphoric The nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client with bipolar disorder. The nurse 4. would most likely expect to find a history of which of thefollowing? A) Panicdisorder B) Schizophrenia C) Delusionaldisorder D) Posttraumatic stressdisorder A nurse is developing a presentation for families who have members that have been diagnosed with bipolar disorders. When describing this condition to the group, which of the 5. following would the nurse most likelyinclude? A) As the person ages, the episodes tend to decrease overtime. B) Environmental stressors are a key cause of thesedisorders. C) The risk for suicide is high with either depression ormania. D) Risk-taking behaviors are more common with a depressiveepisode. A client is to receive lithium therapy as part of the treatment plan for bipolar disorder. When reviewing the clients medication history, which agents would alert the nurse to the 6. possibility that a decrease in lithium dosage may be needed? Select all thatapply. A) Lisinopril B) Hydrochlorothiazide C) Indomethacin D) Caffeine E) Aspirin A client with bipolar disorder is receiving divalproex sodium as part of the treatment plan. When monitoring the clients blood level for this drug, which level would alert the nurse to 7. the need to change thedosage? A) 30ng/mL B) 55ng/mL C) 75ng/mL D) 115ng/mL A client with bipolar disorder having experienced a depressive episode is prescribed lamotrigine. After teaching the client about this medication, the nurse determines that the 8. teaching was successful when the client states which of thefollowing? A) I need to notify my physician if I develop a skinrash. B) I need to have my blood tested about once amonth. C) I have to watch how much salt I use everyday. D) This drug can affect my liver function. A nurse is preparing to administer medications to a female client with bipolar disorder who is experiencing acute mania. Which of the following would be most appropriate for the 9. nurse todo? A) Tell the client firmly that she must take hermedication. B) Allow the client to participate in the treatmentdecision. C) Restrain the client before administering themedication. D) Notify the physician about the clients refusal of themedication. the client reports a fine hand tremor. Which action by the nurse would be most 10. appropriate? A) Immediately obtain a specimen to determine the clients blood druglevel. B) Suggest that the client take the medication with meals orsnacks. C) Assist the client in minimizing exposure tostressors. D) Encourage the client to elevate the affected hand on apillow. A clients blood level of carbamazepine is increased. When reviewing the clients 11. medication history, which of the following would alert the nurse to a possibleinteraction? A) Phenobarbital B) Primidone C) Phenytoin D) Diltiazem A client is brought to the emergency department by his brother. The client has a history of bipolar disorder for which he is taking divalproex. The brother reports that he watched his brother take the medication about 2 hours ago. He stated, A little while ago, he got very disoriented and agitated. The nurse suspects toxicity based on assessment of which of the 12. following? Select all thatapply. A) Tachypnea B) Bradycardia C) Hypotension D) Nystagmus E) Vomiting A client with bipolar disorder has a lithium drug level of 1.2 mEq/L. Which of the 13. following would the nurse expect to assess? Select all thatapply. A) Metallictaste B) Ataxia C) Diarrhea D) Slurredspeech E) Fasciculations F) Muscleweakness The nurse is preparing a teaching plan for the family of a client who has been diagnosed with bipolar disorder. After teaching them about potential indicators for relapse, the nurse determines that the teaching was effective when they identify which of the following as 14. suggesting mania? Select all thatapply. A) Avoidingpeople B) Sleeping more thanusual C) Talking faster thanusual D) Being hungry all thetime E) Reading several books atonce A client with bipolar disorder has had a history of multiple episodes and states, Im so frustrated with whats happened because of these episodes. Which of the following would 15. the nurse encourage to help support this clientsrecovery? A) Codependence B) Hope C) Self-control D) Independent decisionmaking Answer Key 1. B 2. A 3. C 4. A 5. C 6. A, B,C 7. A 8. A 9. B 10. C 11. D 12. C, D,E 13. A, C,F 14. C, D,E 15. B Chapter 68. Anxiety, Stress, and Trauma-Related Disorders The nurse is planning a presentation to a group of nursing students on the topic of anxiety 1. disorders. Which of the following would the nurse include when describing panicdisorder? A) Individuals may believe they are having a heart attack when a panic attackoccurs. B) People with panic attacks often have fewer attacks if they also haveagoraphobia. C) Typically, individuals experience this disorder after the age of 30years. D) Persons rarely have an underlying comorbid condition ofdepression. A client comes to the emergency department because he thinks he is having a heart attack. Further assessment determines that the client is not having a heart attack but is having a panic attack. When beginning to interview the client, which question would be most 2. appropriate for the nurse touse? A) Are you feeling much better now that you are lyingdown? B) What did you experience just before and during theattack? C) Do you think you will be able to drivehome? D) What do you think caused you to feel thisway? A client with a panic disorder has been prescribed a benzodiazepine medication. Which of 3. the following would the nurse emphasize as a risk associated with using thismedication? A) Dietaryrestrictions B) Withdrawalsymptoms C) Agitation D) Fecalimpaction A female client is diagnosed with panic disorder. The client tells the nurse that she hasnt left her house in more than a month because she was afraid of another attack. She visited the mental health clinic today only because her son brought her. Which nursing diagnosis 4. would be a priority for thisclient? A) Powerlessness related to symptoms ofanxiety B) Decisional Conflict related to fear of leaving thehouse C) Ineffective Family Coping related to symptoms ofanxiety D) Social Isolation related to fear of recurrence of anxietysymptoms The nurse has instructed a client with panic disorder about how to use the technique of positive self-talk. The nurse determines that the client has understood the instructions when 5. the client verbalizes which statement to use during an impending panicattack? A) I am feeling very nervous rightnow. B) I can handle this anxiety; it will be overshortly. C) I am taking medication to eliminate thesesymptoms. D) Relax your muscles, relax yourmuscles. A client who has been diagnosed with panic disorder visits the clinic and experiences a panic attack. The client tells the nurse, Im so nervous. My hands are shaking, and Im sweating. I feel as if Im having a stroke right now. Which of the following would the nurse 6. dofirst? A) Stay with the client while remainingcalm. B) Move the client to a safeenvironment. C) Tell the client that the attack will soonpass. D) Teach the client deep breathing techniques to calmher. A client with obsessive-compulsive disorder has been taking fluoxetine for 1 month. The client tells the nurse, These pills are making me sick. I think Im getting a brain tumor 7. because of the headaches. Which response by the nurse would be mostappropriate? A) Lets talk about how often you have been performing the ritualslately. B) Tell me how many times you have washed your handstoday. C) Have you been practicing your deep breathing and relaxationexercises? D) These medications have side effects that can cause increasedheadaches. A nurse who has worked with a client diagnosed with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) when he was an inpatient on the psychiatric unit sees the client in the waiting room of the outpatient psychiatric clinic. The client motions to the nurse to come over so he can tell the nurse how things have been going since he was discharged. While talking with the client, the nurse determines that the clients therapy has been effective when the client states which 8. of thefollowing? I am still experiencing quite a bit of stress at home and at work; things are different at A) home than they were in thehospital. When my mother-in-law comes over now, I go out to my workshop and work on one B) of myprojects. C) Im still drinking coffee; I cant quit after drinking it all theseyears. D) Ive learned having a beer after I get home from work helps merelax. The nurse is caring for a client who is being treated in the emergency department for a 9. panic attack. Which of the following nursing interventions would be mostappropriate? A) Demonstrate empathy for the client by trying to mimic the clients state of anxiety. Tell the client that you must leave to go report his symptoms to the psychiatriston B) duty. Tell the client this is an acute exacerbation with a positive prognosis and low C) morbidity. D) Stay with the client, emphasizing that he is safe and that you will remain withhim. A nurse determines that a client who is experiencing anxiety is using relief behaviors. The 10. nurse determines that the client is experiencing which degree ofanxiety? A) Mild B) Moderate C) Severe D) Panic A group of students is reviewing information about anxiety disorders in preparation for a class examination. The students demonstrate understanding of the material when they state 11. which of thefollowing? A) Anxiety disorders rank second to depression in psychiatric illnesses beingtreated. B) Women experience anxiety disorders more often than domen. C) Most anxiety disorders tend to be short term with individuals achieving fullrecovery. D) Anxiety disorders are more common in children than inadolescents. While interviewing a client, the client reports an intense fear of spiders, stating, I cant be near them. I get so upset. I start to sweat and hyperventilate if I see one. The nurse 12. documents this finding as which of thefollowing? A) Algophobia B) Entomophobia C) Arachnophobia D) Cynophobia After teaching a class about the biochemical theories associated with panic disorder, the instructor determines a need for additional teaching when the students identify which 13. neurotransmitter as beingimplicated? A) Dopamine B) Serotonin C) Norepinephrine D) Gamma-aminobutyric acid(GABA) A nurse is preparing an in-service presentation about panic disorders and associated theories related to the cause. When describing the cognitivebehavioral concepts associated 14. with panic disorders, which of the following would the nurse expect toaddress? A) Personallosses B) Conditionedresponse C) Earlyseparation D) Dysfunctional familycommunication A nurse is developing the plan of care for a client with panic disorder that will include pharmacologic therapy. Which of the following would the nurse most likely expect to 15. administer? A) Benzodiazepine B) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor(SSRI) C) Monoamine oxidase inhibitor(MAOI) D) Tricyclic antidepressant(TCA) A client with panic disorder who has been prescribed sertraline in conjunction with alprazolam comes to the clinic for a follow-up. The client states, I stopped taking the alprazolam about 2 days ago. I was feeling really sleepy and tired. Which of the following 16. would alert the nurse to suspect possible withdrawal? Select all thatapply. A) Metallictaste B) Irritability C) Dry, flushedskin D) Tremor E) Muscleflaccidity A client with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is using cue cards to help restructure thought patterns. Which statements would be appropriate to include on a cue card? Select 17. all thatapply. A) These are the OCDthoughts. B) Trustmyself. C) Keep onchecking. D) Safety is thekey. E) I did it right the firsttime. A client is diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and is to receive medication therapy. Which of the following agents might the nurse expect to be 18. prescribed? Select all thatapply. A) Clomipramine B) Lithium C) Sertraline D) Fluvoxamine E) Paroxetine F) Alprazolam A woman diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder comes to the clinic with her husband. During the visit, the husband states, Shes always checking and rechecking to 19. make sure that all of the appliances are turned off before we go out. Itsnerve-wracking. We can never get out of the house on time. Isnt checking once enough? An understanding of which of the following would the nurse need to incorporate into the response? A) The client is attempting to exert control over thesituation. B) The client performs the ritual to relieve anxietytemporarily. C) The womans behavior reflects a need forsafety. D) The woman is attempting to use thought stopping to decrease herbehavior. A group of students is reviewing information about the etiology of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). The students demonstrate understanding of this information when they 20. identify which of the following as representing the psychoanalytic theory for thisdisorder? A) Inaccurate environmental dangerassessment B) Exposure to multiple stressful lifeevents C) Kindling caused byoverstimulation D) Unresolved unconsciousconflicts A nurse is developing a teaching plan for a client with generalized anxiety disorder, focusing on nutrition. Which of the following would the nurse encourage the client to 21. avoid? Select all that apply. A) Coffee B) Ginseng C) Milkproducts D) Citrusjuices E) Agedcheese The nurse is assessing a client with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Which of the 22. following would the nurse categorize as reflecting intrusion? Select all thatapply. A) Irritability B) Difficultysleeping C) Flashbacks D) Short-term memorydeficits E) Dissociation A group of students is reviewing information about social phobia in preparation for an oral class presentation on this topic. Which of the following would the students expect to 23. include when describing a person with this condition? Select all thatapply. A) Fear that others will judge themnegatively B) Openly speak up in crowds to reducefear C) Are insensitive to otherscriticism D) Demonstrate a distorted view of their ownstrengths E) Exaggerate personalflaws A group of students is reviewing the signs and symptoms associated with anxiety. The students demonstrate an understanding of the information when they identify which of the 24. following as cognitive symptoms? Select all thatapply. A) Edginess B) Feelings ofunreality C) Difficultyconcentrating D) Tunnelvision E) Apprehensiveness F) Speechdysfluency A client is diagnosed with generalized anxiety disorder and is prescribed medication therapy. Which agent would the nurse expect to administer to the client to obtain the 25. quickest relief from anxietysymptoms? A) Buspirone B) Venlafaxine C) Alprazolam D) Imipramine Chapter 69. Obsessive-CompulsiveDisorders 1. When planning care for a female patient diagnosed with obsessive and compulsivebehavior, Nurse Barbara and case manager Marc must recognize that theritual: A. Assists the patient to understand their inability to deal withreality. B. Helps the patient to be in control of theiranxiety. C. Helps the patient control the obsessive and compulsivebehavior. D. Is used to manipulate others. . 2.A patient is frequently late for appointments because he goes back to his room numerous times to assure himself that none of his belongings have been stolen. What does this behaviorrepresent? a. Senselessbehavior b. Controlledrepetition c. Obsessive-compulsive d. Anxietytension . 3.A 14-year-old survivor of a school shooting screams and dives under a table when firecrackers go off. What does this behavior represent? a. Phobia b. Post-traumatic stressdisorder c. Obsessive-compulsivedisorder d. Disordered thinking . 4. The nurse is working with the family of a patient with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Which concept should the nurse incorporate in the teachingplan? a. The thoughts, images, and impulses arevoluntary. b. The family should pay immediate attention tosymptoms. c. The thoughts, images, and impulses tend to worsen withstress. d. OCD is a chronic disorder that does not respond to treatment. . 5. The nurse has identified a nursing diagnosis of disturbed thought processes for a patient with obsessive-compulsive disorder. What abilities displayed by the patient would be related to an appropriate outcome for this problem? Select all thatapply. a. Can identify when obsessions areworsening b. Speaks of obsessions as being embarrassingbehaviors c. Describes lessening anxiety when compulsive rituals areinterrupted d. Plans to ignore obsessive thoughts and so minimizes resultingstress e. Limits time focusing on obsessive thoughts to 15 minutes, 4 times a day . 6. A patient checks and rechecks electrical cords related to an obsessive thought that the house may burn down. The nurse and patient explore the likelihood of an actual fire. The patient states this event is not likely. This counseling demonstrates principlesof: a. flooding. c. relaxationtechnique. b. desensitization. d. cognitive restructuring. . 7. 26. A nurse assesses an individual who commonly experiences anxiety. Which comment by this person indicates the possibility of obsessive-compulsivedisorder? a. I check where my car keys are eighttimes. b. My legs often feel weak andspastic. c. Im embarrassed to go out inpublic. d. I keep reliving a car accident. . Chapter 70. Behavioral Disorders Related to Physical/Physiological Disturbances The nurse is preparing to assess a client with a paranoid personality trait. The nurse integrates knowledge of this condition, anticipating that the clients affect and behavior will 1. most likely be which of thefollowing? A) Angry andhostile B) Flirtatious andseductive C) Fearful andanxious D) Friendly andopen The nurse is caring for a client with schizoid personality trait. When developing the plan of 2. care for the client, which of the following would the nurse most likelyinclude? A) Social skillstraining B) Anger managementtraining C) Relaxationtechniques D) Coping skillstraining A nursing instructor is preparing a teaching plan for a class of nursing students about antisocial personality disorder. Which of the following would the nurse include as a term 3. often used to describe the behaviors associated with this condition? Select all thatapply. A) Psychopath B) Manipulator C) Criminality D) Sociopath E) Psychotic A nurse is reading a journal article about the various theories associated with the development of antisocial personality disorder. The article mentions difficult temperament as a possible theory. The nurse demonstrates understanding of this concept when identifying which of the following as a key behavior associated with a difficult 4. temperament? Select all thatapply. A) Aggression B) Inattention C) Hyperactivity D) Impulsivity E) Depression F) Paranoia A nurse is developing a plan of care for a client diagnosed with an antisocial personality disorder who has been admitted to the inpatient psychiatric unit. Which of the following 5. would the nurse most likely include? Select all thatapply. A) Developing a therapeuticrelationship B) Bargaining about the unitrules C) Holding the client responsible forbehavior D) Discouraging client from discussingthoughts E) Using a firm, lecture-like approach forteaching A nurse is working with the family of a client who has been diagnosed with antisocial personality disorder. Which of the following would be most important for the nurse to focus 6. on when teaching the family about thisdisorder? A) Angermanagement B) Boundarysetting C) Medicationtherapy D) Self-responsibility A group of nursing students is reviewing information about antisocial personality disorder. The students demonstrate understanding of this disorder when they state which of the 7. following? A) The disorder occurs more frequently inwomen. B) The individual must be at least 18 years ofage. C) The disorder is found primarily in Asianindividuals. D) Alcohol abuse disorder rarely accompanies thisdisorder. A nurse is providing care to a client with antisocial personality disorder. As part of the plan of care, the client is to participate in a problem-solving group. The nurse understands that 8. this intervention is effective based on whichrationale? A) It requires the client to developattachments. B) It sets up specific boundaries for theclient. C) It helps reinforceself-responsibility. D) It avoids confrontation about dysfunctionalpatterns. The nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client diagnosed with antisocial personality disorder. The nurse notes that the client has had numerous episodes involving irritability, aggressiveness, and impulsivity and has exhibited callousness toward others. Based on this 9. information, which nursing diagnosis would the nurse most likely identify as apriority? A) Risk for Other-DirectedViolence B) Risk forSelf-Injury C) Risk forSuicide D) Risk for Self-DirectedViolence A client is brought into the emergency department because of complaints from the neighbors that the client was acting strangely. The nurse assesses the client and suspects schizotypal personality disorder based on assessment of which of the following? Select all 10. thatapply. A) Magicalbeliefs B) Hallucinations C) Paranoia D) Avoidance of eyecontact E) Meticulousdress A nurse is assessing a client diagnosed with avoidant personality disorder. Which of the 11. following would the nurse most likely expect to find? Select all thatapply. A) Shyness B) Feelings ofinadequacy C) Feelings ofsuperiority D) Perfectionism E) Detailoriented A group of nursing students is reviewing information about schizoid personality trait. The students demonstrate understanding of the information when they identify which disorder 12. as the most common comorbiddisorder? A) Depression B) Substanceabuse C) Avoidant personalitydisorder D) Anxiety A nurse is interviewing a client and suspects that the client may have narcissistic 13. personality disorder. Which client statement would help support the nursessuspicions? A) I have a very important position in life; everyone I know wants to be likeme. B) My wife is poisoning my food so she can get rid of me and marry herboss. C) I like to work alone because then I can let my thoughtswander. D) Im always the life of the party, making new friends all thetime. A nurse is developing a teaching plan for a client with an impulse-control disorder. The nurse is planning to explain the emotional aspects associated with the behavior as part of the plan. Which of the following would the nurse describe as occurring first before the 14. individual commits theact? A) Remorse B) Tension C) Regret D) Pleasure A nurse is reading an article about a young girl who developed gastrointestinal symptoms from a hair ball because of a ritual that she engaged in. The girl would pull out hair over several hours to relieve tension and anxiety and then eat the hair. The nurse most likely is 15. reading an article about which of thefollowing? A) Kleptomania B) Trichotillomania C) Pyromania D) Intermittent explosivedisorder A nurse is working with a client who is a compulsive gambler. Which of the following 16. would the nurse emphasize as crucial for relapse prevention? Select all thatapply A) Medicationtherapy B) Familyinvolvement C) Identification oftriggers D) Angermanagement E) Milieumanagement A nursing instructor is describing depressive and negativistic personality traits to a group of nursing students. The instructor determines that the teaching was successful when the students identify which of the following as characteristic of negativistic personality traits? 17. Select all thatapply. A) Anhedonia B) Hostility C) Pessimism D) Oppositionality E) Guilt The nurse is assessing a client who is diagnosed with borderline personality disorder. 1. Which client statement indicates the client is at risk for self-injuriousbehavior? A) I have felt so down lately. I dont enjoy doing anythinganymore. B) I do what I do because others tell me to doso. C) When I feel extremely anxious, it is like my mind goes somewhereelse. D) It is almost as if as soon as I think of doing something, I immediately doit. A woman with borderline personality disorder has been admitted to the inpatient unit because she has been engaging in wrist cutting. The clients sister is visiting, and the sister asks the nurse to explain why her sister sometimes does this to herself. Which response by 2. the nurse would be mostappropriate? A) Sometimes the self-injurious behavior is undertaken to relievestress. B) Self-injurious behavior often calms and sedates people with thisdiagnosis. C) Sometimes they do it to avoid the onslaught of delusionalthinking. D) The self-mutilation often slows the mood swings your sisterexperiences. The nurse has explained some of the biologic theories of causation to a client diagnosed with borderline personality disorder and his family. The nurse determines that the client and 3. family have understood the instructions when they state which of thefollowing? A) The disorder may be caused by increased serotoninactivity. B) The disorder is caused by decreased dopamine activity in mybrain. C) A frontal lobe dysfunction may be causing thiscondition. D) A decrease in hormonal substances increases the risk for thisillness. The nurse is assessing a client who has borderline personality disorder. Which of the 4. following would be apriority? A) Nutritionpatterns B) Personal hygienepractices C) Physicalfunctioning D) Somaticcomplaints A client diagnosed with borderline personality disorder tells the nurse that she frequently 5. spaces out. Which response by the nurse would be mostappropriate? A) Do you feel stressed most of thetime? B) Does this frighten you when ithappens? C) Whats happening around you when thisoccurs? D) Do you feel as if you are out of yourbody? The nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with borderline personality disorder. The nurse has instructed the client about using the communication triad. The nurse determines that the 6. client has understood this technique when he states which of thefollowing? A) I should start by stating my feelings as an Istatement. B) Maybe I should start by describing the situation that has meupset. C) I should first tell the other person what Id like to be different about thesituation. D) I should begin by telling the other person what has triggered myemotion. A client with borderline personality disorder tells the nurse, Im afraid to get on a train because well probably get into a wreck. Which response by the nurse would be most 7. appropriate? A) Have you had a bad experience riding atrain? B) What are the chances of that actuallyhappening? C) Now you know that wonthappen. D) Have you thought about going byautomobile? A nursing instructor is preparing a class discussion on personality disorders and characteristics. Which term would the instructor include to differentiate personality 8. disorders from normal personality? Select all thatapply. A) Inflexible B) Shortterm C) Pervasive D) Unstable overtime E) Distressing A group of nursing students is reviewing possible risk factors for development of borderline personality disorder. The students demonstrate understanding of the information when they 9. identify which of the following as a risk factor? Select all thatapply. A) Childhood sexualabuse B) Parentalloss C) Substanceabuse D) Familyhistory E) Genetics A nurse is observing a client diagnosed with borderline personality disorder on the 10. inpatient unit. Which of the following would the nurse most likelynote? A) Actively participating in several differentgroups B) Openly verbalizingfeelings C) Participating in relationships in which the client hascontrol D) Adhering to the personal boundaries ofothers A nurse is assessing a client with borderline personality disorder. Which questionwould 11. be most appropriate to assess the clients level ofimpulsivity? A) What things bother you and make you feelhappy? B) Have you ever felt sorry after acting as you did on the spur of themoment? C) How do you view other people aroundyou? D) Have you ever felt like you were separated from yourbody? As part of a clients treatment plan for borderline personality disorder, the client is engaged in dialectical behavior therapy. As part of the therapy, the client is learning how to control and change behavior in response to events. The nurse identifies the client as learning 12. which type ofskills? A) Emotion regulationskills B) Mindfulnessskills C) Distress toleranceskills D) Self-managementskills professional relationship. Which of the following would be most effective for the nurse to 13. do? Select all that apply. A) Punish the client with seclusion for violating establishedboundaries. B) Respond to the clients arrogance in a neutral, nonconfrontationalmanner. C) Discuss the purpose of the limits in the therapeuticrelationship. D) State the parameters of the limits and boundariesclearly. E) Ensure that any established limits are maintainedconsistently. A nurse is engaged in role-playing with a client with borderline personality disorder to assist the client in learning how to communicate effectively. Which of the following 14. would the nurse encourage the client to use? Select all thatapply. A) Mestatements B) Validating perceptions withothers C) Paraphrasing beforeresponding D) Listeningpassively E) Compromising A nurse is assisting a client with borderline personality disorder in how to manage transient psychotic episodes that involve auditory hallucinations. The teaching is planned for times when the client is free of these symptoms. Which of the following would the 15. nurse instruct the client to dofirst? A) Use skills to tolerate painfulfeelings. B) Practice deep abdominalbreathing. C) Identify early internal cues ofdistress. D) Refer to cards listing potentialsymptoms. Chapter 71. Neurodevelopmental Disorders MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The nurse is discussing the differences between a patient with a neurosis and one with a psychosis. What is true of the patient experiencing aneurosis? a. The patient experiences a flight fromreality. b. The patient usually needshospitalization. c. The patient has insight that there is an emotionalproblem. d. The patient has severe personality deterioration. . 2. When the patient with a psychosis is thought to be a danger to self or others, by whatmethod should the patient be admitted to thehospital? a. Probating b. Nursesrequest c. Physiciansorder d. Familyrequest 3. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Psychiatric Disorders, V (DSM-V), is used by most hospitals and is the current tool used to examine mental health and illness. What approach does the DSM-V use to classify mentaldisorders? a. Holisticsystem b. Hierarchicalsystem c. Multiaxialsystem d. Evaluationsystem 4. When all five axes of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Psychiatric Disorders, V, areused, it provides what type of assessment approach to comprehensivecare? a. Personalized b. Individualized c. Holistic d. Organic . 5.A young man with malaria spikes a temperature of 105 F and begins to hallucinate. Howshould the nurse assessthis? a. Delirium b. Psychoticbreak c. Possiblestroke d. Anxietydisorder 6.A patient admitted for delirium demonstrates increased disorientation and agitation only during the evening and nighttime. What is the term applied to this type ofdelirium? a. Disorderedthinking b. Schizophrenia c. Dementia d. Sundowning syndrome 7. Dementia is an organic mental disease secondary to whatproblem? a. Chemicalimbalance b. Emotionalproblems c. Circulatoryimpairment d. Cerebraldisease 8.A profound, disabling mental illness is characterized by bizarre, nonreality thinking. What is the illness? a. Manicdepressive b. Schizophrenia c. Paranoia d. Bipolar 9.A patient believes himself to be the president of the United States and that terrorists are trying to kidnap him. The nurse records these observations as which type ofbehavior? a. Absentbehavior b. Positivebehavior c. Negativebehavior d. Falsebehavior 10. The patient talks with his dead brother and arranges furniture so that his brother will have a place to sit. How should the nurse document thisbehavior? a. Disorderedthinking b. Anhedonia c. Hallucination d. Alogia 11. What is the prognosis for a schizophrenic patient who is exhibiting positivebehaviors? a. Guarded b. Poor c. Good d. Repeatable 12.The nurse cautions a patient to watch his step. What response indicates concrete thinking? a. The patient fixedly begins to watch hisfeet. b. The patient immediately examines hiswatch. c. The patient begins to watch the nursesfeet. d. The patient stands rigidly in one place without moving. 13 The nurse asks a patient with schizophrenia if he had any visitors on Sunday. Which response indicates looseassociation? a. No. b. Yes! I had 90 visitors who came from every state in theunion. c. Sunday is the Sabbath. Do we have visitors on theSabbath? d. We visited Yellowstone Park lastsummer. 14. The nurse is caring for a patient with a diagnosis of catatonic schizophrenia. What behavioris consistent with thisdiagnosis? a. Talks excitedly about goinghome b. Suspiciously watches thestaff c. Stands on one foot for 15 minutes d. States he has a cat under his bed that talks to him 15. What is the term used for the beginning stage of schizophrenia, characterized by a lack ofenergy and complaints of multiple physicalproblems? a. Prepsychotic b. Residual c. Acute d. Prodromal . 16. For the past 3 weeks, the nurse has observed a patient interacting with staff and other patients, helping decorate the dining room for a party, and leading the singing in the activity room. Today,the patient tearfully refuses to dress or get out of bed. The nurse recognizes these behaviors as evidence of which psychiatricdisorder? a. Unipolardepression b. Dysthymicdisorder c. Hypomanicepisode d. Bipolardisorder . 17. The nurse recognizes that researchers have identified that hereditary factors account forwhat percentage of mooddisorders? a. 10% to 15% b. 20% to 30% c. 35% to 50% d. 60% to 80% . 18.A home health nurse has a patient who is taking lithium. What should be included in the teaching plan? a. Examine her skin closely foreruptions b. Take her blood pressure twice a day to check forhypertension c. Have her drug blood level checked everymonth d. Avoid aged cheese and red wine . 19. The nurse alters the care plan for a patient with depression to include what type ofactivity? a. Domino game with three otherpatients b. Ping-Pong game with one otherpatient c. Group outing to viewwildflowers d. Magazine to read alone 20. The nurse is assessing a female patient who has become rapidly and exceedingly anxiousbecause her fingernail polish is chipped. What type of anxiety should the nurse conclude that the patient is exhibiting? a. Signalanxiety b. Generalanxiety c. Anxietytraits d. Panicdisorder . 21. The home health nurse assesses a patient who creates elaborate excuses for not leavinghome. Further questioning reveals the patient had not left home for 6 months. How should this be documented? a. Mania b. Depression c. Agoraphobia d. Anxiety . 22. When a patient demonstrates accelerated heart rate, trembling, choking, and chest pain along with acute, intense, and overwhelming anxiety, the nurse should recognize that the patient is most likely experiencing whatcondition? a. Terror b. Fright c. Fear d. Panic . 23. When a patient is experiencing a panic attack, how should the nurse best assist thepatient? a. Assist with realityorientation b. Aid in decision making c. Assist with rationalthought d. Coach in deepbreathing . 24.A patient is frequently late for appointments because he goes back to his room numerous times to assure himself that none of his belongings have been stolen. What does this behaviorrepresent? a. Senselessbehavior b. Controlledrepetition c. Obsessive-compulsive d. Anxietytension . 25.A 14-year-old survivor of a school shooting screams and dives under a table when firecrackers go off. What does this behavior represent? a. Phobia b. Post-traumatic stressdisorder c. Obsessive-compulsivedisorder d. Disordered thinking . 26. What should the nurse preparing a patient for a scheduled appointment forelectroconvulsive therapy (ECT) remind the patient todo? a. Drink plenty of fluids before ECT to ensure adequatehydration. b. Bring a change of clothes in case ofincontinence. c. Be prepared for visual disturbances after thetreatment. d. Arrange for transportation to and from the appointment. . 27. The nurse is told that a patient believes he was born into the wrong body. What is thecorrect terminology for the desire to have the body of the oppositesex? a. Homosexuality b. Transsexualism c. Heterosexuality d. Bisexuality . 28. The patient complains of recurrent, multiple physical ailments for which there is no organic cause. How should the nurse assessthis? a. Obsessive-compulsivedisorder b. Phobia anxietydisorder c. Somatoformdisorder d. Delusional disorder . 29. What disorder is a severe form of self-starvation that can lead todeath? a. Bulimianervosa b. Anorexianervosa c. Teenagenervosa d. Obesitynervosa . 30. The patient is concerned about confidentiality and asks the nurse not to tell anyone what issaid. What is the best response by thenurse? a. I am required to report any intent to hurt yourself orothers. b. Conversations between patient and nurse areconfidential. c. What we say can be secret. What I write in the chart is available to the healthteam. d. I cant help you unless you trust me. . 31. What is the term for a long-term and intense form of psychotherapy developed by SigmundFreud that allows a patients unconscious thoughts to be brought to thesurface? a. Adjunctive b. Behavior c. Psychoanalysis d. Cognitive . 32. What is the typical schedule for electroconvulsive therapy(ECT)? a. 3 treatments over 2weeks b. 6 treatments over 2months c. 8 treatments over severalweeks d. 10 treatments over several weeks . 33.A patient who is taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) asks the nurse about the addition of St. Johns wort to help with his depression. What would be the best response of thenurse? a. That is a great idea. Alternative therapies can be veryhelpful. b. You will feel better sooner if you includephenylalanine. c. Did you know that St. Johns wort can raise your blood pressuredramatically? d. You will need to drink lots of water. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 34. Adjunctive therapies are used for which reasons? (Select all thatapply.) a. To increaseself-esteem b. To promote positive interaction c. To enhance realityorientation d. To stimulatecommunication e. To increase energy 35. What are considered warning signs of suicide? (Select all thatapply.) a. Talking aboutsuicide b. Increased interactions with friends andfamily c. Drug or alcoholabuse d. Difficulty concentrating on work orschool e. Personality changes . COMPLETION 36. The nurse recognizes that a woman who has experienced physical abuse and has inadequate income to care for herself and her family would be categorizedunderAxis . . 37. The nurse instructs a patient who has just been prescribed a protocol of fluoxetine HCl(Prozac) that thedrugtakes to weeks to takeeffect. . 38. The nurse explains that an alternative therapy that uses essential oils and scented candles to helpa patient relax and focuses on the atmosphere of themomentis . . Chapter 72. Common Urgent Care Complaints Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which type of heat-related illness involves a core body temperature of at least 104.9°F, acute mental status changes, absent sweat, andtachypnea? a. Heatcramps b. Heatsyncope c. Heatexhaustion d. Heatstroke 2. What percentage of burns is involved using the rule of nines if both front legs areburned? a. 9% b. 18% c. 24% d. 36% 3. Which drug commonly prescribed for burns is active against a wide spectrum of microbial pathogens and is the most frequently used agent for partial- and full-thickness thermalinjuries? a. Clotrimazole cream(Lotrimin) b. Mafenide acetate(Sulfamylon) c. Silvernitrate d. Silver sulfadiazine(Silvadene) 4. A sunscreen with a sun-protection factor of at least what number will block most harmful ultraviolet radiation? a. 4 b. 8 c. 10 d. 15 5. Which clinical feature is the first to be affected in increased intracranialpressure? a. Decrease in level ofconsciousness b. Headache c. Nausea d. Widening pulsepressure 6. What is the normal number for the Glasgow ComaScale? a. 7 b. 9 c. 10 d. 15 7. Which diagnostic test is the best to diagnose a subduralhematoma? a. History b. Positron emissiontomography c. Magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) d. Computed tomography (CT)scan 8. Patients with a spontaneous pneumothorax should be counseled that up to what percentage may experience a reoccurrence at somepoint? a. 10% b. 20% c. 30% d. 50% 9. Most adult poisoningsare: a. Intentional andself-inflicted b. Accidental c. Caused by someone wishing to do harm to theperson d. Not attributed to anyreason 10. Which method is used to remove heavy metals, such as lead, that are ingested aspoisons? a. Chelation b. Dialysis c. Gastriclavage d. Bowelirrigation 11. If a previously frostbitten area becomes frostbitten again after it has healed, what mightoccur? a. Permanent tissue damage may occur, resulting in necrosis to that bodypart. b. The area will be supersensitive. c. The area is prone to a repeatfrostbite. d. The area is as susceptible as any otherarea. 12. What percentage of all visits to the emergency department (ED) are related towounds? a. 5% b. 12% c. 18% d. 24% 13. Which solution should be used when irrigating lacerated tissue over a wound on thearm? a. Dilute povidone-iodinesolution b. Hydrogen peroxide(H2O2) c. Saline solution infused with anantibiotic d. Saline irrigation or soapywater 14. Which type of burn injury results in destruction of the epidermis with most of the dermis, yet the epidermal cells lining hair follicles and sweat glands remainintact? a. Superficialburns b. Superficial partial-thicknessburns c. Deep partial-thicknessburns d. Full-thicknessburns 15. Which carboxyhemoglobin (COHb) level correlates with the clinical symptoms of confusion, lethargy, and ST-segment depression on theelectrocardiogram? a. Less than10% b. 20%COHb c. 30%COHb d. 40% to 60%COHb 16. Which causes the greatest percentage of mammalianbites? a. Dogs b. Cats c. Humans d. Rodents 17. Which arthropod bite can contain cytotoxic and hemolytic toxins that may destroytissue? a. Tick b. Brown reclusespider c. Wasp d. Stingingcaterpillar 18. Which of the following characteristics separates anaphylaxis from a vasovagalreaction? a. Bradycardia b. Extremediaphoresis c. Severebronchoconstriction d. Hypotension 19. Delayed serum sickness–type reactions in response to multiple bee, wasp, or fire ant stings can be managed with which of thefollowing? a. A corticosteroid such as prednisone (Deltasone), 60 to 100 mg, tapered over2 weeks b. An oral antihistamine, such as hydroxyzine, for 2weeks c. An H2 blocker such as cimetidine for 1week d. 0.1 mg (1 mL of 1:10,000 solution epinephrine) in 10 mL of normal saline and administer as a slow intravenous push over 10minutes 20. After a head injury, what is it called when air enters into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)–filled spaces within thehead? a. Pneumocephalus b. Hemotympanum c. Battle’ssign d. Raccoonsign 21. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) may leak through the cribriform plate region of the skull following a head injury and cause which of thefollowing? a. Ear CSFotorrhea b. Leakage of CSF from theeye c. Nasal CSFrhinorrhea d. Leakage of CSF from themouth 22. Which classic feature of an epidural hematoma may distinguish it from other skullhematomas? a. Unilateralhemiparesis b. Loss ofspeech c. Temporary hearingloss d. A brief loss of consciousness, then a brief “lucid” moment, followed by momentary unconsciousness minutes after theinjury 23. A patient with a basilar skull fracture may experience an impaired downward gaze or diplopia from which affected cranialnerve? a. CNII b. CNIII c. CNIV d. CNV 24. A history of overuse or excessive force, as opposed to a fall, hyperextension, or the twisting of a joint, is more likely related to which musculoskeletalinjury? a. Asprain b. Astrain c. A partialfracture d. Afracture 25. In a healthy adult, the process of remodeling after a fracture of the humerus takes howlong? a. Approximately 4weeks b. 2months c. 3months d. 4months 26. A patient who sustains blunt chest trauma and/or penetrating chest trauma must have which of the following imagingexaminations? a. Upright chest x-rayfilm b. Supine chestx-ray c. Lateral chestx-ray d. MRI 27. Josie, age 30, has a pneumothorax. It may be treated conservatively without a chest tube if it is deflated by whatpercentage? a. 30% b. 45% c. 60% d. All pneumothoraxes require a chest tube. 28. Hepatic necrosis with jaundice may occur after ingesting massive doses of whichmedication? a. Phenobarbital b. Diazepam c. Ritalin d. Acetaminophen 29. Pink, cherry red tissues and skin may result from which type ofpoisoning? a. Arsenic b. Lead c. Carbonmonoxide d. Strychnine 30. In which type of burn is the injury more extensive than it appears, and the cardiac conduction system may be affected, leading to sudden death orarrhythmias? a. Chemicalburns b. Electricalburns c. Radiationburns d. Thermalburns 31. Eddie, age 4, presents to the ED with a live insect trapped in his ear canal causing a lot ofdistress. What should be your first step? a. Remove the insect withtweezers. b. Immobilize the insect with 2%lidocaine. c. Sedate Eddie withdiazepam. d. Shine a light in the ear for the insect to “find its wayout.” 32. When giving discharge instructions to a patient with a laceration injury to his lower leg, which is the most importantone? a. Recommend isometric exercises to prevent a deep vein thrombosis(DVT). b. Recommend cleansing the wound every 4 hours to prevent aninfection. c. Keep the leg elevated at waist level to prevent anyedema. d. Keep the leg completely immobile to prevent extension of thelaceration. 33. Cerebellar function may be assessed by performing whichexamination/test? a. Gagreflex b. Pupillaryresponse c. Romberg’stest d. Apley’stest 34. In the epithelialization phase of wound healing, the wound will have only what percent of its normal tensile strength at 3weeks? a. Less than 15% b. 15% to 20% c. 25% to40% d. Greater than 50% 35. Which of the following statements is true about antibiotic prophylaxis for mostwounds? a. It is not indicated for most wounds and does not affect the infectionrate. b. Antibiotics should always be ordered for awound. c. Antibiotics need to be ordered for at least 2weeks. d. Antibiotics should be ordered only if sutures are inplace. Chapter 73. Common Injuries A patient sustained injuries in a motor vehicle accident and is in the Emergency Department. A CT scan of the head and neck have been ordered. What part of the survey is 1. this? A) Primary B) Secondary C) Tertiary D) Initial A patient who is in the Emergency Department was attacked in a parking lot and suffered several stab wounds to various areas on the chest and abdomen; BP 100/60, heart rate 108, respiratory rate 20, pulse oximetry 98%. In order to counteract the blood loss and restore 2. circulating volume for this patient, what priority intervention will the nurseperform? A) Start lactated Ringers at 150mL/hr. B) Start dopamine at 5mcg/kg/min. C) Start an albumin infusion wideopen. D) Start a unit of uncrossmatchedblood. The nurse is assigned to a patient in the Emergency Department who exhibits paradoxical chest movement. What intervention by the nurse can help improve oxygenation in this 3. patient? A) Elevate the head of the bed 30degrees. B) Splint the chest with 3-inch surgicaltape. C) Turn the patient with the injured sidedown. D) Place the patient in the proneposition. A patient has been involved in a motor vehicle accident. The patient, who was driving, was unrestrained by a seat belt when hitting the car in front of him. The patient is complaining of midsternal pain, restlessness, and difficulty breathing. What is the priority nursing 4. diagnosis for thispatient? A) Anxiety B) Impaired gasexchange C) Impairedcirculation D) Pain A patient has suffered a mild pulmonary contusion from a jet ski accident. What nursing 5. interventions are appropriate for this patient? Select all thatapply. A) Maintenance of chesttubes B) Frequent pulse oximetrymonitoring C) Assessment of lung sounds every 2hours D) Continuous epiduralanalgesia E) Maintainance of ventilatorysupport A patient sustained an injury to the right arm after falling off a motorcycle. The patient is complaining of severe pain and is unable to feel the fingers of the right hand. Radial pulse 6. is absent. What is the priority intervention by thenurse? A) Elevate the right arm above the level of theheart. B) Notify thephysician. C) Apply ice packs to the affectedarea. D) Place the patient in Trendelenburgposition. The nurse is caring for a patient with deep vein thrombosis of the left lower extremity. The patient exhibits a decrease in pulse oximetry readings from 98% to 86%, shortness of breath with a respiratory rate of 34, and is now disoriented to place. The nurse recognizes that 7. these findings are caused by whatcomplication? A) Pulmonaryedema B) Cardiactamponade C) Pulmonaryembolus D) Tensionpneumothorax The nurse is assigned to care for a patient who was admitted 2 days previous after a four- wheeler accident. The patient sustained a closed fracture to the left femur and had an open reduction with internal fixation the same day. What is a priority for the nurse to assess for 8. thispatient? A) White bloodcount B) Urinaryoutput C) Cardiacoutput D) Pulseoximetry A patient has been brought into the Emergency Department via ambulance with resuscitation efforts being performed. It is unlikely that the patient will survive the severe injuries sustained. Two adult children of the patient are present and are requesting to be 9. with the patient at this time. What is the best response by thenurse? I dont think you should see your loved one like this. Wouldnt you rather remember A) him the way hewas? Our hospital doesnt allow more than one family member in with a patient. One of you B) can come in and one of you will have to wait in the waitingarea. You may come in with your parent and I will have someone stay with you to explain C) what ishappening. D) 10. 10. I have been through this many times and I promise you, it is a sight that you dont want to remember. The nurse is caring for the patient with chest tubes. Which observation by the nurse is a priority concern? A) 250 mL/hr of blood in drainage collectionsystem B) Pulse oximetry of94% C) Blood pressure of104/62 D) 30 mL/hr of urineoutput A patient is admitted to the emergency department after he was hit by a car. The car was going about 30 mph and was braking at the time of impact. The patient was struck just above the right knee, fell forward over the hood of the car, striking his anterior chest, and then slipped off the hood of the car and hit the pavement head first. Based on the mechanism of injury and transfer of force, what injuries does the nurse most expect? 11. Select all thatapply. A) Fracture of left femur and damage to leftknee B) Fractures of thoracic and lumbarspine C) Fractured ribs and cardiac and lungcontusion D) Bilateral radial and humerusfractures E) Closed head injury and cervical spinefracture F) Bilateral clavicle and scapularfractures The patient has received a gunshot wound. To help predict the amount of damage, what 12. information does the nursecollect? A) Location of theshooting B) Information about theshooter C) Type of weapon and caliber ofbullet D) Whether the injury involved afelony A patient was in a serious motor vehicle crash. At the scene, what is the highest priority of 13. care? A) Extrication from thevehicle B) Cervical spineprotection C) Establishing two large-bore intravenouslines D) Collecting information about thecrash On initial admission of a trauma victim to the emergency department, the nurse completes a primary survey. The patient is awake and tachypneic, is using accessory muscles of respiration, has unequal chest expansion, and is very anxious. There are absent breath sounds on the right and cyanosis on 100% oxygen, and the trachea is deviated to the left. 14. What action takes the highest priority during the primarysurvey? A) Jaw thrustmaneuver B) Suctioning the oralpharynx C) Chest tubeinsertion D) Assisting ventilation with bag-maskdevice A patient has been admitted to the emergency department after being in a severe motor vehicle crash. The patient was a passenger and had a lap and seat belt in place. The patient is lethargic and moaning. Initial exposure and head-to-toe examination reveals scattered minor abrasions and contusions and bruising over the upper abdomen. The patient moans more when the abdomen is palpated, and the abdomen is rigid. Heart rate is 110, capillary refill is greater than 4 seconds, and blood pressure is 140/88 mm Hg. What is the nursing 15. priority ofcare? A) Administer intravenous opioid forpain. B) Increase rate of intravenouscrystalloid. C) Obtain CT of theabdomen. D) Prepare for immediate endotrachealintubation. As part of a major trauma, a patient has suffered a flail chest injury. What hallmark sign of 16. flail chest does the nurse expect tofind? A) Flail segment elevation duringinhalation B) Evidence of rib fractures on chestradiograph C) Flail segment depression duringinhalation D) Hypoxemia evident on arterial bloodgases A patient is admitted to the CCU after experiencing blunt trauma to the chest. Among other injuries, the patient has a flail chest on the left and several extremity fractures. About 12 hours after admission, the patient is tachypneic and complaining of shortness of breath. Breath sounds are present bilaterally with scattered fine crackles. Chest radiograph shows an ill-defined, patchy, ground-glass area of density on the left. If the patient hasa 17. pulmonary contusion, what is the nursingpriority? A) Monitor pulse oximetry and arterial blood gasesclosely. B) Place an oral endotracheal tubeimmediately. C) Increase the amounts of intravenous crystalloidadministration. D) Obtain sputum culture and sensitivity and Gramstain. A patient has suffered severe blunt trauma to the abdomen with bruising, diffuse pain, 18. guarding, and rigidity evident. Damage to which structure is mostlikely? A) Stomach B) Bladder C) Largeintestine D) Liver As part of a multiple trauma injury, the patient has suffered a closed fracture of the radius. What nursing assessment finding indicates a significant complication warranting 19. immediatetreatment? A) Swelling and pain over thefracture B) Loss of pulses distal to thefracture C) Ecchymosis over thefracture D) Deformity offorearm A patient has experienced multiple fractures, including pelvic and long bone fractures. After 72 hours, the patient complains of tachypnea and dyspnea and is found to have cyanosis, tachycardia, confusion, and fever. Laboratory analysis reveals a normal complete blood count except for thrombocytopenia and progressive respiratory 20. insufficiency. What is the nursing carepriority? A) Administer oxygen and monitor pulseoximetry. B) Initiate low-molecular-weight heparintherapy. C) Obtain cultures of all bodysubstances. D) Initiate fall and seizureprecautions. During a motor vehicle accident, a patient sustained blunt trauma to the head and face, resulting in hairline skull fracture and a LeFort III maxillofacial fracture. The patient also has bruising across the chest and upper abdomen and multiple small superficial bleeding abrasions and lacerations. On admission to the emergency department, what is the nursing 21. carepriority? A) Apply direct pressure to bleedingareas. B) Assess neurologicstatus. C) Perform endotrachealintubation. D) Administer tetanus boosterimmunization. As part of a multiple trauma injury, a patient developed hemorrhagic hypovolemic shock, necessitating fluid resuscitation with massive amounts of intravenous crystalloid fluids and blood products as well as extensive surgical repair under general anesthesia. Twenty- four hours later, the patient develops hypoxia unresponsive to oxygen therapy and diffuse white, ground-glass infiltrates of the lung fields on a chest radiograph. Development of 22. this complication has what effect on the patientsrecovery? A) Significantly greater chance ofdeath B) No change in outcomeexpectations C) Outcome depends ontreatment. D) Lower chance ofdeath Chapter 74. Toxic Exposures MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is likely to result from leadpoisoning? a. Damage to the brain and peripheralnerves b. Inflammation and fibrosis in thelungs c. Variouscancers d. Displacement of oxygen fromhemoglobin 2. During the development of hyperthermia, the state of heat exhaustion is indicatedwhen: a. body core temperature is veryhigh. b. skeletal muscle spasmsoccur. c. hypovolemia and faintingoccur. d. the cool-down process is toorapid. 3. What is/are signs ofhypothermia? a. Systemicvasodilation b. Lethargy andconfusion c. Nausea andcramps d. Rapid but strongpulse 4. Which of the following types of cells are most likely to be damaged by exposure toradiation? a. Bone andcartilage b. Skeletal and smoothmuscle c. Peripheral and centralneurons d. Epithelial tissue and bonemarrow 5. Which of the following events would most likely cause a person to faint and experiencedifficulty breathing? a. Exposure to gammarays b. Eating fish containingmercury c. An insectsting d. Inhalation of asbestosparticles 6. Bites and stings cause disease in which threeways? a. Injection of toxins, transmission of infectious agents, or allergicreactions b. High fever and chills, transmission of infectious agents, or nausea andvomiting c. Bone marrow damage, extensive skin rashes, or allergicreactions d. Injection of neurotoxins, transmission of infectious agents, or kidneydamage 7. Which statement applies to foodpoisoning? 1. It results from consuming contaminated food andwater. 2. It often causes gastroenteritis, including vomiting anddiarrhea. 3. Outbreaks occur frequently ininstitutions. 4. It is often caused by Escherichia coli, normally found in thestomach. a. 1, 3 b. 2, 4 c. 1, 2, 3 d. 1, 3, 4 8. Institutions frequently have outbreaks of infection associated with poultry productscontaminated by: a. E. coli b. Salmonella c. Listeria d. HIV 9. The amount of radiation absorbed by the body is measured inrads,or . a. radiation-absorbeddoses. b. roentgen-absorbeddoses. c. radiation-emissionnumber. d. radiation ionizingrate. 10. The term pica refersto: a. the consumption of nonfood substances such asclay. b. diffuse edema and degeneration of neurons in thebrain. c. particulates in the respiratorytract. d. high levels of mercury in theblood. 11. Inhalants canbe: a. a particulate such asasbestos. b. gaseous, such as sulfurdioxide. c. a solvent, such asbenzene. d. A, B, andC 12. Choose the correct effects of exposure of the ears to very coldtemperatures: a. Loss ofsensation b. Lethargy andconfusion c. Vascularocclusions d. A andC 13. During the development of hyperthermia, the stage of heat stroke is markedby: a. shock andcoma. c. diaphoresis and decreasing bodytemperature. d. dizziness, fainting, andheadache. 14. Which of the following is a potential effect of a bite orsting? a. Immediate heartfailure b. Anaphylaxis c. Severe nausea, vomiting, anddiarrhea d. Bone marrowdamage 15. Bites from both wild and domesticated animals maycause: a. anaphylaxis. b. Shigellaoutbreaks. c. rabies. d. severe pain andheadache. 16. Which of the following is consideredcarcinogenic? a. Lead b. Carbonmonoxide d. Mercury 17. Illness in institutions may be traced back to food handlerswho: a. are carriers ofpathogens. b. do not practice adequate hand-washing orsanitization. c. bring in pathogens from home or thecommunity. d. A, B, andC 18. A common illness for tourists in developing countries is travelers diarrhea, often causedby: a. Salmonella b. Shigella c. E. coli d. Listeria 19. Radiation damage may occur from repeated exposureto: a. ultravioletrays. b. X-rays. c. radioactivesubstances. d. A, B, andC 20. Two types of eye damage that can be caused by a laser beamare: a. chemical andstructural. b. thermal burn and photochemicaldamage. c. tissue necrosis and vascularocclusions. d. formation of deep lesions in the optic nerve and in thesclera. Chapter 75. Environmental Exposures A nurse from the ICU is participating in the hospitals disaster response preparedness team. One issue that proves difficult for the team to agree on is a statement regarding the standard of medical care observed during a disaster. Which of the following do you think the nurse 1. should recommend to theteam? The goal should be to provide the highest care possible, with limited resources and A) equipment. The lack of resources should not diminish the standard of care that the hospital B) provides. C) The medical staff should tend to the needs of the most critically illfirst. If electrical power should be lost to the facility, patients on life support should be D) given lowestpriority. A nurse learns that local law enforcement officials have informed the hospital that an imminent terrorist attack has been threatened in a building just down the street from the 2. hospital. Which of the following are appropriate responses? Select all thatapply. Explain to the patients in the ICU that a terrorist attack is expected and that their care A) may beinterrupted. Begin making preparations to move all ICU patients to other hospital facilities in the B) area in the event of anattack. Review the hospitals disaster plan and make sure that it is distributed to the rest of the C) medicalstaff. D) Determine what her specific role in the disaster planis. Not be concerned because federal deployable medical teams will likely be sent to the E) hospital in the event of anattack. Check the number of ventilators available in the ICU to determine whether more F) would be needed in the event of anattack. The nurse is at the bedside of her 90-year-old patient, Ruth, who is comatose and on life support in the ICU, when she begins to feel the room shaking violently. The power suddenly fails and emergency generators have not started yet. The nurse provides bag-mask resuscitation for Ruth while she waits for the power to be restored. Moments later, the ICU is inundated with patients injured by the collapse of a nearby apartment building as a result of the earthquake. The nurse is called to help. Kevin has been impaled by a metal rod through the chest, is in a state of shock, and will die without immediate intervention. Gwyneth has compound fractures of the femur and a dislocated shoulder, is in pain, but is responsive. Mason is unconscious and unresponsive. Based on the START triage 3. categories, whom should the nurse assist first in thissituation? A) Ruth B) Kevin C) Gwyneth D) Mason A patient arrives at the ICU after being injured by car bomb that exploded 20 feet away. The patient sustained only primary blast injuries. Which of the following are injuries he 4. might have sustained? Select all thatapply. A) Perforated eardrum caused by a sudden change in atmosphericpressure B) Laceration from a shard of glass that struck thepatient C) Concussion as a result of his body being thrown against a brickwall D) Hemorrhagic contusion of thelungs E) Gastrointestinalhemorrhage F) Blunt force trauma from a piece of metal shrapnel that struck the patientshead A group of patients, colleagues from the same office, arrive at the ICU with symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. It is determined that they are suffering from radiation exposure as a result of an inconspicuous device placed in the office that leaked radiation over a period of days. The nurse suspects that which of the following was used in this 5. terroristattack? A) Radiological dispersaldevice B) Improvised nucleardevice C) Nuclearweapon D) Simple radiologicaldevice A patient arrives at the ICU with symptoms of radiation exposure. While in the ICU, he begins gasping for air and clutching his throat with his hand. What intervention should take 6. priority at thispoint? A) Perform CPR on the patient to restore normal respiratoryfunction. B) Evaluate the degree of radiation exposure in the patient using a Geiger counter. Undress the patient and have him shower and wash with soap todecontaminate C) himself. D) Administer potassiumiodide. A woman arrives at the ICU after being the victim of a terrorist attack in a nearby shopping center involving a gas that spewed from a metal canister. The woman complains of a burning sensation in her eyes, mouth, and throat, and the nurse observes blistering on her face and arms. What chemical agent should the nurse suspect, and what intervention should 7. sheimplement? A) Vesicant agent; applylotion B) Nerve agent; administerbenzodiazepine C) Vesicant agent; soap and waterblot D) Nerve agent; provide ventilatorysupport A worker at a local chemical plant arrives at the ICU following an industrial accident involving a gas leak. The patient shows signs of pulmonary edema and bronchospasm. What chemical should the nurse suspect is involved, and what intervention would be most 8. appropriate? A) Nitrogen mustard; soap and waterblot B) Chlorine; airway management and ventilatorysupport C) Tear gas; irrigation of eyes withwater D) Cyanide; sodiumnitrate A man presents to the ICU with a severe case of H1N1 viral infection. What would be the 9. most appropriate intervention for thispatient? A) Administer an H1N1vaccine. B) Administer anantibiotic. C) Administer an antiviralagent. D) Administer potassiumiodide. A young man arrives at the ICU after being held hostage while a passenger on a commercial airplane. He sustained a bullet wound in his chest and has undergone surgery to repair his lung. He is now receiving an analgesic for his pain. The nurse observes that the patient frequently complains that he is sick to his stomach and has no appetite. His sleep is regularly interrupted by nightmares, and he is prone to outbursts of anger and 10. grief. What is the most likely cause of thesesymptoms? B) Reaction to severepain C) Post-traumatic stressdisorder D) Delirium resulting from aninfection The nurse is caring for a group of patients from the same workplace who have similar symptoms of cough, respiratory distress, and nausea and vomiting. What should the nurse 11. suspect? A) Food poisoning at localrestaurant B) Mass exposure to an inhaledagent C) Allergic response to a new cleaningagent D) Acute asthma exacerbationsyndrome The nurse is part of a planning committee developing a disaster response plan for a hospital that serves as the major trauma center for the local area. The committee has identified that the most likely cause of a disaster in the community is a devastating tornado that significantly damages most major structures, including hospitals of all sizes, in the 12. community. What component of the plan is least likely to berealistic? A) Transfer all noncritical patients to smaller hospitals in thecommunity. B) Provide for secure storage of emergency supplies andequipment. C) Agree with other hospitals in town to share supplies andequipment. D) Interface with the city disaster management plan and commandcenter. The nurse is preparing to assist with triage of victims from a large mass casualty incident. The patients are sorted into categories at the door of the facility. What category will 13. receive carelast? A) Minimal B) Delayed C) Immediate D) Expectant The nurse is assisting with triage in the emergency department. A large group of patients from a mass casualty incident arrive. These patients have been classified at the scene as 14. minimal, delayed, immediate, and expectant. What is the best nursingapproach? A) Use the classifications from the scene to determine the order oftreatment. B) Reassess and reclassify patients quickly to determine the order oftreatment. C) Treat the patients in the order they arrive at the emergencydepartment. D) After the first 20 patients, refer all others to another emergency care facility. The nurse is caring for a patient who was exposed to a high dose of externalradiation. 15. What is the least likely nursingaction? B) Assess radiological measurements with a Geigercounter. C) Remove clothing and shower patient as soon aspossible. D) Assist in removing penetrating radioactivematerials. The nurse is caring for a patient who has been exposed to radiation. The patient has been increasingly unstable, with decreasing lymphocytes, leukocytes, thrombocytes, and erythrocytes, along with shock, diarrhea, and altered level of consciousness for some weeks. Today, there is clear evidence of worsening shock, subnormal body temperature, and increased intracranial pressure. The family asks what the patients prognosis is. The 16. 16. A) B) best nursing response is based on what rationale? Increased intracranial pressure following other symptoms is a sign of impending death. The symptoms listed are typical of the latent phase of recovery, which lasts several weeks. C) Full recovery from radiation exposure can take many weeks tomonths. D) The absence of fever indicates the patient has entered the latent phase of recovery. The nurse is caring for a patient with a suspected cyanide exposure. The patient isanxious 17. and hyperventilating. What is the nursing priority ofcare? A) Give antiseizuremedications. B) Send toxicologyscreen. C) Give cyanideantidote. D) Obtain history ofexposure. The nurse is assisting with the initial care and assessment of a group of patients with a massive topical toxic chemical exposure. What is the best way to decontaminate these 18. patients? A) Use an antidote to the chemical ofexposure. B) Use an alkaline substance for an acidcontaminant. C) Soap-and-water shower first for mostchemicals D) Administer 100% oxygen under positivepressure. A worker in a tanning factory comes to the emergency department with itchy, papular lesions on his hands and arms. Some of the lesions have black eschar in the center and 19. some are vesicular. What biological exposure is mostlikely? A) Cutaneousanthrax B) Pulmonaryanthrax C) Cutaneoussmallpox D) Pneumonicplague A patient and his family have been exposed to probable anthrax spores through contaminated postal contents within the past 8 hours. Upon arrival at the emergency department, all members of the family are anxious and say they are afraid of dying. The 20. best nursing response is based on whatrationale? A) There is no treatment for anthrax exposure and their fears arerealistic. B) A vaccine given in the first 3 days after exposure will stop thedisease. C) Antibiotic therapy is very effective for cutaneousanthrax. D) A toxicology screen is necessary to determine whether there really was anexposure. Chapter 76. Sports Physicals MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A patient is being assessed for range-of-joint movement. The nurse asks him to move his arm in toward the center of his body. This movement iscalled: a. Flexion. b. Abduction. c. Adduction. d. Extension. . 2. A patient tells the nurse that she is having a hard time bringing her hand to her mouth when she eats or tries to brush her teeth. The nurse knows that for her to move her hand to her mouth, shemust perform whichmovement? a. Flexion b. Abduction c. Adduction d. Extension . 3. The functional units of the musculoskeletal system arethe: a. Joints. b. Bones. c. Muscles. d. Tendons. 4. When reviewing the musculoskeletal system, the nurse recalls that hematopoiesis takes place in the: a. Liver. b. Spleen. c. Kidneys. d. Bone marrow. 5. Fibrous bands running directly from one bone to another that strengthen the joint and helpprevent movement in undesirable directions arecalled: a. Bursa. b. Tendons. c. Cartilage. d. Ligaments. 6. The nurse notices that a woman in an exercise class is unable to jump rope. The nurse is aware that to jump rope, ones shoulder has to be capableof: a. Inversion. b. Supination. c. Protraction. d. Circumduction. 7. The articulation of the mandible and the temporal bone is known asthe: a. Intervertebralforamen. b. Condyle of themandible. c. Temporomandibularjoint. d. Zygomatic arch of the temporal bone. . 8. To palpate the temporomandibular joint, the nurses fingers should be placed in the depression of theear. a. Distal to thehelix b. Proximal to thehelix c. Anterior to thetragus d. Posterior to the tragus . 9. Of the 33 vertebrae in the spinal column, thereare: a. 5lumbar. b. 5 thoracic. c. 7 sacral. d. 12 cervical. . 10. An imaginary line connecting the highest point on each iliac crest wouldcrossthe vertebra. a. Firstsacral b. Fourthlumbar c. Seventhcervical d. Twelfth thoracic . 11. The nurse is explaining to a patient that there are shock absorbers in his back to cushion the spine and to help it move. The nurse is referring tohis: a. Vertebralcolumn. b. Nucleuspulposus. c. Vertebralforamen. d. Intervertebral disks. . 12. The nurse is providing patient education for a man who has been diagnosed with a rotator cuff injury. The nurse knows that a rotator cuff injury involvesthe: a. Nucleuspulposus. b. Articularprocesses. c. Medialepicondyle. d. Glenohumeral joint. 13. During an interview the patient states, I can feel this bump on the top of both of my shouldersit doesnt hurt but I am curious about what it might be. The nurse should tell the patient that it ishis: a. Subacromialbursa. b. Acromionprocess. c. Glenohumeraljoint. d. Greater tubercle of the humerus. . 14. The nurse is checking the range of motion in a patients knee and knows that the knee iscapable of whichmovement(s)? a. Flexion andextension b. Supination andpronation c. Circumduction d. Inversion and eversion . 15. A patient is visiting the clinic for an evaluation of a swollen, painful knuckle. The nurse notices that the knuckle above his ring on the left hand is swollen and that he is unable to remove his wedding ring. This joint iscalledthe joint. a. Interphalangeal b. Tarsometatarsal c. Metacarpophalangeal d. Tibiotalar .) 16. The nurse is assessing a patients ischial tuberosity. To palpate the ischial tuberosity, the nurse knows that it is best to have thepatient: a. Standing. b. Flexing thehip. c. Flexing theknee. d. Lying in the supine position. . 17. The nurse is examining the hip area of a patient and palpates a flat depression on theupper, lateral side of the thigh when the patient is standing. The nurse interprets this finding asthe: a. Ischialtuberosity. b. Greatertrochanter. c. Iliaccrest. d. Gluteus maximus muscle. . 18. The ankle joint is the articulation of the tibia, fibula,and: a. Talus. b. Cuboid. c. Calcaneus. d. Cuneiform bones. . 19. The nurse is explaining the mechanism of the growth of long bones to a mother of a toddler. Where does lengthening of the bonesoccur? a. Bursa b. Calcaneus c. Epiphyses d. Tuberosities 20. A woman who is 8 months pregnant comments that she has noticed a change in her posture and is having lower back pain. The nurse tells her that during pregnancy, women have a posture shift to compensate for the enlarging fetus. This shift in posture is knownas: a. Lordosis. b. Scoliosis. c. Ankylosis. d. Kyphosis. . 21. An 85-year-old patient comments during his annual physical examination that he seems to be getting shorter as he ages. The nurse should explain that decreased height occurs with agingbecause: a. Long bones tend to shorten withage. b. The vertebral columnshortens. c. A significant loss of subcutaneous fatoccurs. d. A thickening of the intervertebral disks develops. . 22. A patient has been diagnosed with osteoporosis and asks the nurse, What is osteoporosis? The nurse explains that osteoporosis is definedas: a. Increased bonematrix. b. Loss of bonedensity. c. New, weaker bonegrowth. d. Increased phagocytic activity. . 23. The nurse is teaching a class on preventing osteoporosis to a group of perimenopausalwomen. Which of these actions is the best way to prevent or delay bone loss in thisgroup? a. Taking calcium and vitamin Dsupplements b. Taking medications to preventosteoporosis c. Performing physical activity, such as fastwalking d. Assessing bone density annually 24. A teenage girl has arrived complaining of pain in her left wrist. She was playing basketballwhen she fell and landed on her left hand. The nurse examines her hand and would expect a fracture if the girl complains ofa: a. Dullache. b. Deep pain in herwrist. c. Sharp pain that increases withmovement. d. Dull throbbing pain that increases with rest. . 25. A patient is complaining of pain in his joints that is worse in the morning, better after he moves around for a while, and then gets worse again if he sits for long periods. The nurse should assess for other signs of whatproblem? a. Tendinitis b. Osteoarthritis c. Rheumatoidarthritis d. Intermittent claudication 26. A patient states, I can hear a crunching or grating sound when I kneel. She also states that it is very difficult to get out of bed in the morning because of stiffness and pain in my joints. The nurse should assess for signs of whatproblem? a. Crepitation b. Bone spur c. Loosetendon d. Fluid in the knee joint 27. A patient is able to flex his right arm forward without difficulty or pain but is unable to abduct his arm because of pain and muscle spasms. The nurse shouldsuspect: a. Crepitation. b. Rotator cufflesions. c. Dislocatedshoulder. d. Rheumatoid arthritis. . 28. A professional tennis player comes into the clinic complaining of a sore elbow. The nursewill assess for tenderness atthe: a. Olecranonbursa. b. Annularligament. c. Base of theradius. d. Medial and lateral epicondyle. . 29. The nurse suspects that a patient has carpal tunnel syndrome and wants to perform the Phalen test. To perform this test, the nurse should instruct the patientto: a. Dorsiflex thefoot. b. Plantarflex thefoot. c. Hold both hands back to back while flexing the wrists 90 degrees for 60 seconds. Hyperextend the wrists with the palmar surface of both hands touching, and wait for60 d. 30. An 80-year-old woman is visiting the clinic for a checkup. She states, I cant walk as much asI used to. The nurse is observing for motor dysfunction in her hip and should ask herto: a. Internally rotate her hip while she issitting. b. Abduct her hip while she is lying on herback. c. Adduct her hip while she is lying on herback. d. Externally rotate her hip while she is standing. . 31. The nurse has completed the musculoskeletal examination of a patients knee and has founda positive bulge sign. The nurse interprets this finding toindicate: a. Irregular bony margins. b. Soft-tissue swelling in thejoint. c. Swelling from fluid in theepicondyle. d. Swelling from fluid in the suprapatellar pouch. . 32. During an examination, the nurse asks a patient to bend forward from the waist and notices that the patient has lateral tilting. When his leg is raised straight up, the patient complains of a pain going down his buttock into his leg. The nursesuspects: a. Scoliosis. b. Meniscustear. c. Herniated nucleuspulposus. d. Spasm of paravertebral muscles. 33. The nurse is examining a 3-month-old infant. While the nurse holds his or her thumbs on the infants inner mid thighs and the fingers on the outside of the infants hips, touching the greater trochanter, the nurse adducts the legs until the his or her thumbs touch and then abducts the legs until the infants knees touch the table. The nurse does not notice any clunking sounds and is confident to recorda: a. Positive Allistest. b. Negative Allistest. c. Positive Ortolanisign. d. Negative Ortolani sign. Chapter 77. Primary Care of Older Adults MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. When discussing aging, to whom does the term older adulthoodapply? a. Age 55 andabove b. Age 65 andabove c. Age 70 andabove d. Age 75 andabove 2. When the nurse discusses prevention of cardiac disease, falls, and depression with a group of older adults, the benefits of what are important tostress? a. Nutrition b. Medications c. Exercise d. Sleep 3. When was the Social Security Act, which was the first major legislation providingfinancial security for older adults,passed? a. 1930 b. 1935 c. 1940 d. 1945 4. When assessing the skin of an older adult patient who is complaining of pruritus, what shouldthe nurse advise the patient to avoid to reduce further drying of herskin? a. Perfumedsoap b. Hard-milledsoap c. Antibacterialsoap d. Lotion soap 5. Because thin skin and lack of subcutaneous fat predisposes the older adult to pressure ulcers, the nurse alters the care plan to include turning the bedfast patient howoften? a. Once everyshift b. Every 4hours c. Eachevening d. Every 2hours . 6. At mealtime, the older adult seems to be eating less food than would be adequate. Compared tothe younger adult, what is a requirement for the olderadult? a. More fluids b. Lesscalcium c. Fewercalories d. Morevitamins . 7. The older patient informs the nurse that food has no taste and therefore the patient has noappetite. What is this most likely causedby? a. Tastelessfood b. Overuse ofsalt c. Lack ofvariety d. Loss of tastebuds . 8. An older adult is having difficulty swallowing. What position should the nurse recommend toaid inswallowing? a. Chinparallel b. Chinupward c. Chindown d. Chin to theside nurse suggest to fulfill calcium needs? a. Ryebread b. Yogurt c. Apples d. Raisins 10. The older adult patient complains to the nurse about nocturia. This problem is most likelyrelated to: a. loss of bladdertone. b. decrease intestosterone. c. decrease in bladdercapacity. d. intake of caffeine. 11. The older adult female patient is concerned about incontinence when she sneezes. What isthe correct terminology for this type ofincontinence? a. Urgeincontinence b. Stressincontinence c. Overflowincontinence d. Functional incontinence 12.A change of aging related to the circulatory system includes decreased blood vessel elasticity. For what should the nurseassess? a. Confusion b. Tachycardia c. Hypertension d. Retained secretions . 13. What should be suggested to a patient to aid with the pain ofclaudication? a. Rest b. Exercise c. Crosslegs d. Stand 14. The nurse recommends a breathing technique to help a patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) to empty the lungs of used air and to promote inhalation ofadequate oxygen. What is this method of breathingcalled? a. Pursed-lipbreathing b. Increasedinspiration c. Vitalcapacity d. Decreased expiration respiratory infections. For what is this patient at increased risk? a. COPD b. Bronchitis c. Pneumonia d. Atelectasis . 16. The nurse recognizes that an older adult patient with COPD has a higher incidence ofdeveloping which age-related skeletal change that will alter the ability to exchange aireffectively? a. Osteoporosis b. Arthritis c. Kyphosis d. Osteomyelitis 17. What is a major difference between rheumatoid arthritis andosteoarthritis? a. Rheumatoid arthritis isdegenerative. b. Rheumatoid arthritis only affects patients over 40 years ofage. c. Rheumatoid arthritis isinflammatory. d. Rheumatoid arthritis is curable. 18. For what is the older adult patient at increased risk because of age-related changes inthe musculoskeletalsystem? a. Fractures due to poor uptake ofcalcium b. Heart attacks due to increased effort toambulate c. Respiratory failure due tokyphosis d. Falls related to posturechanges . 19. The nurse is assisting an older adult patient out of bed when suddenly the patient begins tofall. What is the likely cause of thefall? a. Fever b. Orthostatichypotension c. Dehydration d. A decrease in venous return 20. To help prevent falls related to muscle weakness, what type of exercises should be selectedfor the agingpatient? a. Daily b. Running c. Weight-bearing d. Aerobic . 21. What is the best test to identify the risk of osteoporosis in postmenopausalwomen? a. Skeletalx-ray b. Bone densityscan c. Calcium bloodlevel d. CATscan recognize as the probable cause? a. Urinaryincontinence b. Arthriticjoints c. Kyphosis d. Mucosaldrying 23. What is age-related vision change caused by the loss of elasticity of the lenscalled? a. Nearsightedness b. Cataracts c. Presbyopia d. Blepharitis . 24. When communicating with an older adult patient who has difficulty hearing, how should the nurse change herspeech? a. Speak veryloudly b. Speakrapidly c. Lower the tone of thevoice d. Raise the tone of the voice 25. Which symptom of diabetes distorts tactilesensation? a. Proprioception b. Loss of visualacuity c. Progressiveparesis d. Peripheral neuropathy 26. What is the result of a slowing of the impulse transmission in the nervoussystem? a. Hypertension b. Hearingdeficit c. Decrease in tactilesensations d. Longer reaction time 27. What is the most common cause ofdementia? a. Multi-infarct b. Medications c. Alzheimerdisease d. Parkinsondisease 28.What is one positive aspect of Parkinson disease? a. The disease does not alter ability tocommunicate b. Anti-Parkinson drugs have few sideeffects c. Intellectual function is notimpaired d. Involuntary movements can be controlled . 29. When should family members of a stroke victim expect to see some of theneurologic involvementdisappear? a. Within 2 to 3weeks b. Within 1 to 2months c. Within 3 to 6months d. Within 6 to 9 months 30. When communicating with an older adult patient, the nurse becomes aware of the fact thatthe patient is well satisfied with his accomplishments over a lifetime and has no regrets concerning aging. Which of Eriksons developmental stages has the patientachieved? a. Acceptance b. Withdrawal c. Egointegrity d. Interaction Chapter 78. Palliative Care and Pain Management Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following statements is true regardingpain? a. If a patient complains of pain but has no physical signs, he or she is most likely exhibiting drug-seekingbehaviors. b. Acute pain is more intense and severe than chronicpain. c. Pain is a subjective experience related to actual or potential tissuedamage. d. All of theabove 2. Which of the following would be a cause of visceralpain? a. Bone metastases b. Intra-abdominalmetastases c. Musculoskeletalinflammation d. Postsurgical incisionalpain 3. According to the World Health Organization’s analgesic ladder, which drug combination would be most appropriate in an opiate-naïve patient who presents with moderatepain? a. Ibuprofen/imipramine b. Naproxen/morphine c. Aspirin/fentanyl d. Indomethacin/hydrocodone 4. A 75-year-old man is being treated as an outpatient for metastatic prostate cancer. Which of the following statements is true regarding the management of pain with opioids in theelderly? a. Opioids with a long half-life, such as methadone, are a good choice, because they stay in the system longer, and patients do not have to remember to take multiple pills. b. Serum creatinine is the best measurement of renal function in the elderly and should be done prior to the initiation of treatment withopioids. c. Renal clearance of medications is faster in the elderly, so higher dosages of medications are needed to adequately controlpain. d. None of theabove 5. A patient had a transdermal fentanyl patch placed 2 hours ago and is not getting any painrelief. What would be the most appropriate intervention? a. Remove the current patch and replace with a new fentanyl patch at a higherdose. b. Prescribe a short-acting opioid for breakthroughpain. c. Remove the patch and switch to a different intravenousopioid. d. Tell the patient not to worry, as it takes about 12 hours for the patch’s effects to be felt, and he will have relief at thattime. 6. A patient is preparing to be discharged to home with hospice. She is on a morphine patient- controlled analgesia (PCA) in the hospital. She is concerned as to whether she can stay onher morphine PCA at home even when she is not able to give herself boluses. What would be an appropriate response from theclinician? a. “We are unable to prescribe a PCA for use at home. If you are comfortable on the PCA, you should remain in thehospital.” b. “It would be possible for your nurse or another trained family member to activate the dosing button when you are unable to doso.” c. “A PCA is not an appropriate method of pain medication delivery once you are unable to use the dosing button. I will switch you to another form of paincontrol.” d. “You should not be concerned about your pain management at home. It will be taken care of foryou.” 7. A patient taking PO hydromorphone for pain control has developed dysphagia. The clinician decides to switch the patient to IV hydromorphone. What ratio of IV:PO hydromorphone does the clinician need to know to calculate the properdose? a. 1:1 b. 1:2 c. 1:5 d. 1:7 8. A patient is receiving long-acting oxycodone for pain control. The clinician thinks that he also will benefit from a short-acting oxycodone for breakthrough pain. How will the clinician figure out what the dose of short-acting oxycodone shouldbe? a. The short-acting dose should be 10% to 20% of the total 24-hour long-actingdose. b. The short-acting dose should be 40% to 50% of the total 24-hour long-actingdose. c. The short-acting dose should be 10% to 20% of each long-actingdose. d. The short-acting dose should be 40% to 50% of each long-actingdose. 9. A patient is being switched from hydromorphone to methadone in an attempt to achieve better pain control. How much should the dose of methadone be reduced when calculating the equianalgesic dose of the twodrugs? a. 0% b. 20% c. 50% d. 90% 10. If a patient requires six rescue doses for breakthrough pain in a 24-hour period, what would be an appropriateintervention? a. Increase the dose of the baseline long-actingmedication. b. Increase the dose of the rescue short-actingmedication. c. Switch to a different short-acting rescuemedication. d. Do nothing, because this is appropriate, and the patient’s pain is wellcontrolled. 11. A patient with bone metastases from prostate cancer inquires whether he is a candidate for radiopharmaceuticals. Which of the following conditions would exclude him as acandidate? a. Karnofsky performance status of65 b. Pathologicfracture c. Life expectancy of 5months d. Hypocalcemia 12. Which of the following is the best description ofdyspnea? a. An oxygen saturation of less than90% b. Respiratory rate greater than24 c. A psychological state resulting in the feeling of airhunger d. A subjective feeling ofbreathlessness 13. What would be an appropriate dose of morphine to give an opioid-naïve patient to manage tachypnea associated withdyspnea? a. 5 mg PO every 4hours b. 15 mg PO every 4hours c. 30 mg PO every 4hours d. 40 mg PO every 4hours 14. Glycopyrrolate (Robinul) is one drug of choice to manage which of the following conditions that can contribute todyspnea? a. Copioussecretions b. Cough c. Anxiety d. Effusion 15. Which characteristic of delirium helps to distinguish it fromdementia? a. Abruptonset b. Impairedattention c. Affectivechanges d. Delusions 16. Which of the following classes of drugs should be used as first-line therapy for treatment of delirium? a. Benzodiazepines b. Antipsychotics c. Anticonvulsants d. Antidepressants 17. Which of the following is a role of the advanced practice nurse in palliative cancercare? a. Detecting cancer in asymptomatic patients or those with specificsymptoms b. Arranging for follow-up care, including psychosocial and spiritualsupport c. Identifying and managing complications ofcare d. All of theabove True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Patients who are receiving life-prolonging therapies do not qualify for palliativecare. 2. Some anticonvulsant drugs can be used as an adjuvant treatment for mildpain. 3. Oxygen has shown no benefit in alleviating dyspnea in patients withouthypoxemia. Chapter 79. Ethical and Legal Issues of a Caring-Based Practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which statement about the American Nurses Association Code of Ethics isaccurate? a. The state’s legal requirements exceed those of the Code ofEthics. b. The primary purpose of the Code is to show physicians that nurses are professional. c. The Code was formulated by physicians for allnurses. d. The Code sets forth the values and ethical principles that guide clinicaldecisions. 2. Which ethical principle reflects respect for all persons and theirself-determination? a. Autonomy b. Beneficence c. Justice d. Veracity 3. When may confidentiality be overridden? a. When personal information is available on thecomputer b. When a clinician needs to share information with a billingcompany c. When an insurance company wants to know the results of a breast cancer genetest d. When a patient has a communicabledisease 4. In an outpatient setting, what is the most common reason for a malpracticesuit? a. Failure to treat acondition b. Failure to diagnosecorrectly c. Ordering the wrongmedication d. Failure to managecare 5. Which type of liability insurance covers only situations in which the incident occurred and the claim was made while the policy was ineffect? a. Claims made policy b. Occurrencepolicy c. An employment coveragepolicy d. A “tail”policy 6. Which insurance plan was the first to allow members to choose nurse practitioners as their primary care provider and pay them the same rate as physicians for the samecare? a. Blue Cross/BlueShield b. Medicare/Medicaid c. The Oxford HealthPlan d. United HealthInsurance 7. Constructing a decision tree is helpful in analyzing ethical dilemmas, because a decisiontree: a. Shows the bestsolution b. Explains the ethicalprinciples c. Delineates the legalparameters d. Allows all the options to beconsidered 8. In the consensus model for Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN) regulation, the “C” of LACErepresents? a. Commitment b. Consensus c. Certification d. Collaboration 9. The main mechanism for avoiding a lawsuitinvolves: a. Good liabilityinsurance b. A collaboratingphysician c. Gooddocumentation d. Open communicationskills 10. Paternalism in healthcare: a. Assumes the physician knows what isbest b. Is neverwarranted c. Is in effect after an informed consent issigned d. Requires a courtorder 11. The Nurse Practice Act of each state is responsiblefor: a. Establishing the legalstandards b. Promoting high-quality nursingcare c. Protecting the public from unethical nursingpractice d. Exceeding the requirements of the Code of Ethics forNurses 12. Deontologyis: a. The greatest amount of happiness or the least amount of harm for the greatest number b. The consideration of consequences and the calculation ofbenefits c. The belief that the ends justify themeans d. The principle ofuniversalizability 13. A situation that requires informed consentinvolves: a. Therapeuticprivilege b. An emergencysituation c. Invasiveprocedures d. The therapeutic use ofplacebos 14. Which ethical principle is the foundation on which health carerests? a. Autonomy b. Nonmaleficence c. Beneficence d. Justice 15. The Joint Commission mandates that all health-care organizationshave: a. A mechanism in place for the consideration of ethicalissues b. An Ethicscommittee c. A resident parishnurse d. Legal counsel who is knowledgeable aboutethics 16. The relationship between ethics and law is suchthat: a. What is ethical is alsolegal b. What is unethical is alsoillegal c. Legal actions may be both ethical andunethical d. There is no relationship between the law andethics 17. An APRN’s scope of practice includes all of the following statementsEXCEPT: a. The scope of practice defines the duties and responsibilities of theAPRN b. The scope of practice delineates the permissible boundaries of the professional practice c. The scope of practice is defined by statute, rule, or a combination of thetwo d. Each APRN defines his/her own scope of practice and includes it in theirprotocol 18. Which board administers and defines advanced nursing practice in allstates? a. The Board ofNursing b. The Board ofMedicine c. The Board ofPharmacy d. It is different for eachstate. 19. Three components must be present to establish malpractice. Which one does NOTapply? a. The APRN must be paid for the services inquestion. b. The provider must have a duty to thepatient. c. The standard of care must have been deviated from orbreached. d. Harm or damages must have occurred as a result of the duty and a breach of the standards ofcare. 20. The Institute of Medicine stresses interprofessional collaboration between physicians andAPRNs. Which statement supports this? a. The physician supervises theAPRN. b. The physician sponsors theAPRN. c. There is a collegial relationship between the twoproviders. d. The physician pays the APRN’ssalary. Chapter 80. The Business of Advanced Practice Nursing Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Identify the primary challenge for insurance carriers in today’s health deliverymodel. a. Preventingillness b. Screening fordisease c. Educating thepublic d. Reducing health-carespending 2. Medicare benefits were offered to U.S. beneficiaries beginning in 1965. What was the service added with the Medicare D plan in2006? a. Health-carescreening b. Health-careeducation c. Pharmaceuticalcoverage d. Durable medical equipmentcoverage 3. With the growing shortage of primary care physicians, the demand for advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs) will increase between 2014 and 2016from: a. 5 to 15million b. 15 to 35million c. 20 million to 30million d. 30 million to 40million 4. Maintaining optimum cash flow is a basic fundamental concept in all businesses. Cash flow is impacted at the initial request for appointment and is affected by practices thatinclude: a. Billing within 15 days ofservices b. Beneficiary verification ofpatient c. Timely processing ofdenials d. Identifying payment below contractrate 5. Patients require insurance counseling prior to accessing health-care services for the following reason: a. Many patients do not understand policy benefits and paymentresponsibility. b. Services may change across the beneficiaryyear. c. Copayments and deductibles may have already been met by thepatient. d. Coding may need to be adjusted to meet the terms of the patient’sbenefits. 6. Health-care billing is a significant reason for bankruptcy in the United States. The following provision of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) legislation was included to reduce this fromoccurring with insuredpatients: a. Consumer assistanceprograms b. Preventative care optionsstandardized c. Young adult coverage (under 26years) d. Elimination of lifetimelimits 7. Accounting keeps track of the financial state of a business. The accounting report that demonstrates the growth in assetsis: a. Net incomestatement b. Balancesheet c. Cash flowstatement d. Operatingstatement 8. Medicare advantage plans, also called Medicare HMO Plans, are plans approved by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) as alternative carriers for Medicare beneficiaries. Which of the following is not a characteristic of theseplans? a. Offer additionalbenefits b. Offer lowercopayments c. Follow Medicare benefitrules d. Follow the Commercial Carriersrules 9. Current procedural terminology (CPT) coding offers the uniformed language used for reporting medical services and procedures performed by physician and nonphysician practitioners. Clinicians are paid based on calculated resource costs that, in turn, are based on practice components. Whichof the following is a part of the components used to calculate the per CPT code paymentrate? a. Clinician educationloans b. Clinician practice liability and malpracticeexpense c. Clinician reported cost reductionefforts d. Clinician volume of patientstreated 10. Beginning in 2014, all medical practices will be required by the CMS to adopt a certified electronic medical record software system for documenting and billing for medical services. What is a primary reason for this implementationmandate? a. Allows CMS to audit all medical practices’performance b. Standardizes the billing rules for allclinicians c. Reduces the duplication of services noted in the currentsystem d. Reduces costs related to multiple billingsystems 11. All health-care practices should develop a compliance plan. Compliance plans offer practice safeguards that prevent which of thefollowing? a. Malpracticeclaims b. Conflict of interestclaims c. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Actviolations d. Occupational Safety and Health Administrationviolations 12. Clinicians who learn how to code and document Evaluation and Management and clinician services will be more successful in gaining timely payment for care delivery. Which of the following CMS practices is designed to financially penalize clinicians who do not bill according to CMSguidelines? a. Audits andprobes b. Add-oncodes c. Modifiercodes d. HACguidelines 13. Each state has criteria defining the level of collaboration required between the APRN and an oversight physician. Which is among the questions an APRN should seek when selecting a practice setting? a. List of practice limitations as anAPN b. Standard hourly rate as officestaff c. Expectation for net revenuegeneration d. Standard benefit package offered to officestaff 14. Identify one of the primary reasons for an APRN to develop a businessplan? a. To monitor monthly actual expense to budgetedexpense b. To reduce the likelihood of litigationaction c. To identify the marketing needed to grow the APRNpractice d. To assure accreditation standards aremet 15. Despite the growth in the numbers of advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs) over the last decades, the role of the profession is often not understood by the public. What actions should APRNs undertake to market their services to thepublic? a. Request that the physician act as an APRNspokesperson. b. Increase articles in nursing professional journals about the APRNrole. c. Personally seek out the news media to communicate theirvalue. d. Rely on patients to communicate their benefits toneighbors. Chapter 81. The 15-Minute Hour: Practical Approaches to Behavioral Health for Primary Care Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. According to World Health Organization data on 1,500 patients in 15 separate world sites, how many patients presenting with medical/somatic complaint had a psychiatricproblem? a. Fully one-third of allpatients b. One-quarter of allpatients c. One-half of allpatients d. 60% of allpatients 2. Integrating mental health techniques and approaches, such as the 15-minute hour, into the primary care patient encounter is important for a number of reasons. Theseinclude: a. Decreasing the patient’s stress and increasing yourreimbursement b. Encouraging coping strategies and increasing professionalsatisfaction c. Assisting patients in reliving traumaticexperiences d. Decreasing care clinicianstress 3. Valliant (1979) discusses the “ubiquity of stress.” Ubiquity of stress maintainsthat: a. In a current and rapidly changing society, stress can be viewed as apositive. b. Eustress iscounterproductive. c. The overwhelmed can functionallyregress. d. Dream therapy has been found to be an effective treatment of overwhelmingstress. 4. Basic human needs are identifiedas: a. Autonomy and feeling valued byothers b. Exhilaration andproductivity c. Spirituality d. Career success and materialrewards 5. Commonalities among psychotherapeutic techniques include thefollowing: a. Dream therapy, listening, andreflection b. Psychodrama, group psychotherapy, and 12-stepprograms c. Self-helpgroups d. Obtaining external perspective and participation in a helpingrelationship 6. The goals of the 15-minute hour approachinclude: a. Enhance self-esteem, expand behavioral repertoire, prevent dire consequences, and reestablish premorbid levels offunctioning b. Emerge with a higher level of functioning and commitment to long-term psychotherapy c. Accept need for antidepressant therapy and psychiatric referral; share concerns with primary careclinician d. Improve family functioning and sexual performance as well as accept need for antidepressantmedication 7. BATHEing the patient refersto: a. A technique used in primary care to get the patient to accept the need for psychological or psychiatricreferral b. A technique used to facilitate culturalunderstanding c. A technique used to performpsychotherapy d. A technique that is a quick screen for psychiatric issues and interventions for psychologicalproblems 8. BATHEing the patient is an advanced practice nursing intervention that allows the practitionerto: a. Develop a therapeutic relationship without “owning” the patient’sproblem b. Conduct psychological counseling within the context of the primary careencounter c. Focus on the “process” and not theassessment d. Make the patient and familyhappier 9. The BATHE technique was developed more than 20 years ago and has been used extensively in primary care and family practice. The new “Positive BATHE”stresses: a. A belief that all things are possible through positiveaffirmations b. A belief that one should only refer to practitioners who embrace the viewpoint of positivepsychology c. Personal accomplishment, thankfulness, autonomy, and general positiveeffect d. The patient’s problems andconcerns 10. Which of the following scenarios best demonstrates the relationship between physical health and distress? a. A patient’s high calorie diet contributes to his diagnosis of type 2diabetes. b. A patient with an elevated HbA1C reports that he was recently evicted from his home. c. A patient with depression reports an increase in suicidalthoughts. d. A patient reports feeling “numb” after learning her malignant tumor isinoperable. 11. One benefit of BATHEing a patient isthat: a. It allows providers an in-depth exploration of patient’s presentingproblems. b. It assumes that ambivalence is a normal part of the changeprocess. c. It utilizes the therapeutic relationship to help patients in a time-sensitiveapproach. d. It can be done only with extensive training in therapeutictechnique. 12. One benefit of motivational interviewing (MI)is: a. It assumes that ambivalence is a normal part of the changeprocess. b. It can be utilized during routine officevisits. c. It is a therapeutic technique which is not necessarily timeintensive. d. All are benefits ofMI. 13. Which is not a basic principle ofMI? a. People often continue behaviors with negative consequences for reasonsunknown to theprovider. b. The patient is the expert on his/herbehavior. c. Providers are obligated to inform each patient of the negative consequences of theirbehaviors. d. Helping patients understand ambivalence for change is often more powerful than directinstruction. 14. The primary purpose of the “Positive BATHE” is intended to help patientsby: a. Focusing on autonomy andaccomplishment b. Creating a stronger therapeuticalliance c. Helping the patient change negativebehaviors d. Engaging the patient during the psychosocialassessment Chapter 82. Putting Caring into Practice: Caring for Self Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The World Health Organization defines self-careas: a. An important global activity for all health-careproviders b. A set of deliberate actions that all individuals, families, and communities should engage in to maintain goodhealth c. Essential to efficacious advanced practice nursing (APRN)practice d. An awareness by the APRN of their self-care behaviors as related to diet, activity, and mentalattitude 2. Nurse theorist Dorothea Orem defines self-care activitiesas: a. Attainment of professional self-developmentgoals b. Ability to persevere throughhardship c. Striving to attain balance and harmony in one’slife d. Comprising activities that are performed independently by an individualto promote and maintain well-being throughoutlife 3. Self-care and personal development are built into the standards of practiceof: a. The American Holistic NursesAssociation b. The American NursesAssociation c. The American Association of NursePractitioners d. The American Academy ofNursing 4. There are many pressures inherent in primary care practice today for APRNs. These pressures include all of thefollowing: a. Electronic medical record, the Affordable Care Act, and the implementation of socializedmedicine b. Patient care outcomes being tied to reimbursement, role diffusion with physicians and physicianassistants c. Uncertainty, the team approach to care, and the need for patient-centeredcare d. Availability of medical information on the internet, educational programs for patients, and Medicare drugbenefits 5. A new era of health care leadsto: a. Greater opportunity for independent practice, yet increased legal risk in accountability forpatients b. Lowered reimbursement for all health-care services andproviders c. Decrease in status for health-careproviders d. No ability to individualizecare 6. Compassion fatigue is another side-effect of today’s health-care delivery system. This termmeans: a. The APRN feels sudden guilt and distress when he or she cannot rescue or save an individual, such as when bad health habits persist despite the best efforts of the APRN. b. This happens over time related to the need to see increasing numbers of patients in busy primary carepractices. c. This may persist over time, even when the APRN transfers to a new and different setting. d. Patients’ problems and circumstances can be so overwhelming that theAPRN needs to set severe boundaries to maintain safefunction. 7. Another term used, burn out, is differentiatedby: a. Numbness of feelings leading to substanceabuse b. How novice APRNs feel at the end of the day in primarycare c. Feelings of aloneness, desperation, anddespair d. A gradual response to the inability to achieve one’s goals with patients in the work setting; it is characterized by frustration and diminishingmorale 8. The following statement istrue: a. APRNs are often sensitive to patients’ deficiencies but not theirown. b. APRNs always respond appropriately to patients, families, and teammembers. c. APRNs are well-equipped from their APRN educational programs to care forself. d. Relicensure in some states mandates continuing education units inself-care. 9. Self-compassion is the ability to be compassionate to one’s self and is positively correlated with emotional intelligence. Emotional intelligence is definedas: a. Being highly attuned to the needs ofothers b. The ability to engage inself-care c. Being aware of self, having the capacity to self-regulate, possessing motivation, empathy, and socialskills d. The holistic integration of self-care and self-developmentpractices 10. APRNs need to develop their own self-management plans. Two key elements of self-management plans are: a. Taking vacations and keeping up with new knowledge and developments in medicine b. Resilience and positiveintentionality c. Family support and a healthydiet d. Being physically and emotionally“fit” 11. The term resilienceimplies: a. Ability to look to a higher power to get you through acrisis b. Response to difficult and adverse circumstances through positively adjusting to stressors c. That the APRN can weather anyemergency d. Learning to set appropriateboundaries 12. Qualities associated with resilienceinclude: a. Hope, self-efficacy, andoptimism b. Stick-to-it-ness, belief in a higherpower c. Education, self-regulation, and use of activity to decreasestress d. Ability to take vacations and the availability of support systems and a secure work environment 13. Patsy, a 42-year-old experienced APRN, is orienting a new APRN to the Minute Clinic, where she has worked for more than 5 years. Patsy loves her work and was concerned when the new APRN, Sue, expressed her dissatisfaction with this setting. “I hate the idea of being here on my own, with no back-up and support after orientation” was one of Sue’s concerns. Sue confessed that this was the only job she could find. Patsy felt good in her independent role and felt she had worked to create a positive atmosphere for her patients at all times. She derived joy and satisfaction from her ability to do this for her patients. Patsy found Sue’s endless complaints debilitating. Patsy demonstrated resiliency by using which of the followingstrategies? a. Patsy distanced Sue by listening to her as little aspossible. b. Patsy openly shared her positive feelings about the work environment and took a risk by sharing with Sue that she found her endless complainingdraining. c. Patsy spoke privately with their supervisor, Pamela, stating that she did not think Sue could be successful in thisenvironment. d. Patsy requested that Sue be assigned to a different APRN fororientation. 14. The qualities of resilience that Patsy demonstrated when responding to Sueinclude: a. Protecting her own positive attitude by lessening her contact with Sue, a negative person b. The ego strength to admit failure in her ability to orient Sue, a destructiveperson c. Protecting her organization by sharing Sue’s deficiencies with theirsupervisor d. Asserting her positive approach and basic optimism by initiating an honest discussion with Sue and having the emotional insight to recognize Sue’s negative effect onher 15. According to nurse theorist Jean Watson, a focus on positive intentionality—holding caring thoughts, loving kindness, and open receptivity—enhances caring energy, which leads tohealing. How can the APRN bring this to theirpractice? a. Spiritual readings, centering oneself before patient encounters, engagingin behaviors that help build positiveenergy b. Review of materials on primary care before going into the work environment to increase one’s confidence, leading to caringenergy c. Travel to sacredplaces d. Helping the poor and homeless—volunteering at a domestic violence shelter, for example—in addition to one’s regularpractice [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 530 pages

Reviews( 1 )

by efeltman · 3 years ago
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 28, 2020
Number of pages
530
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 28, 2020
Downloads
1
Views
136




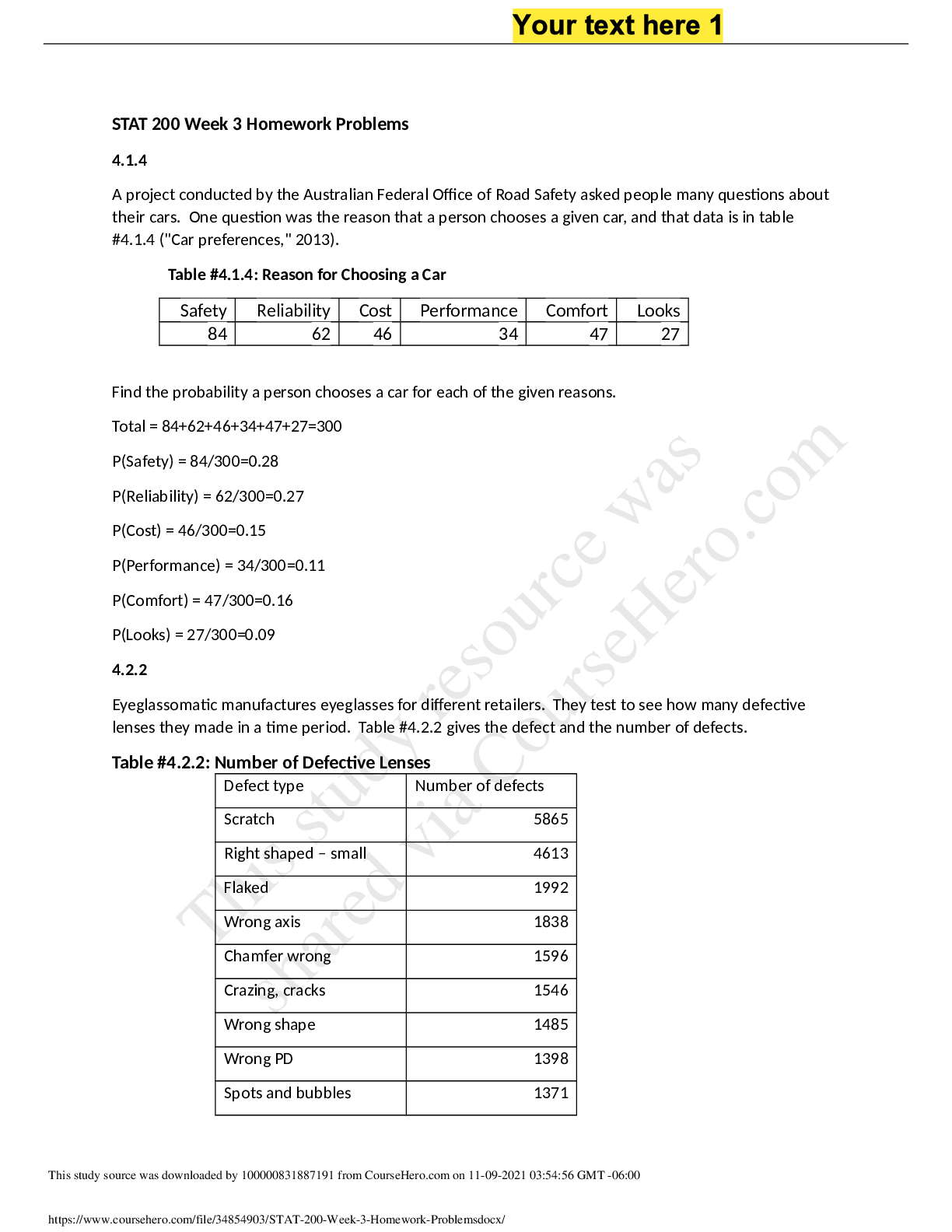




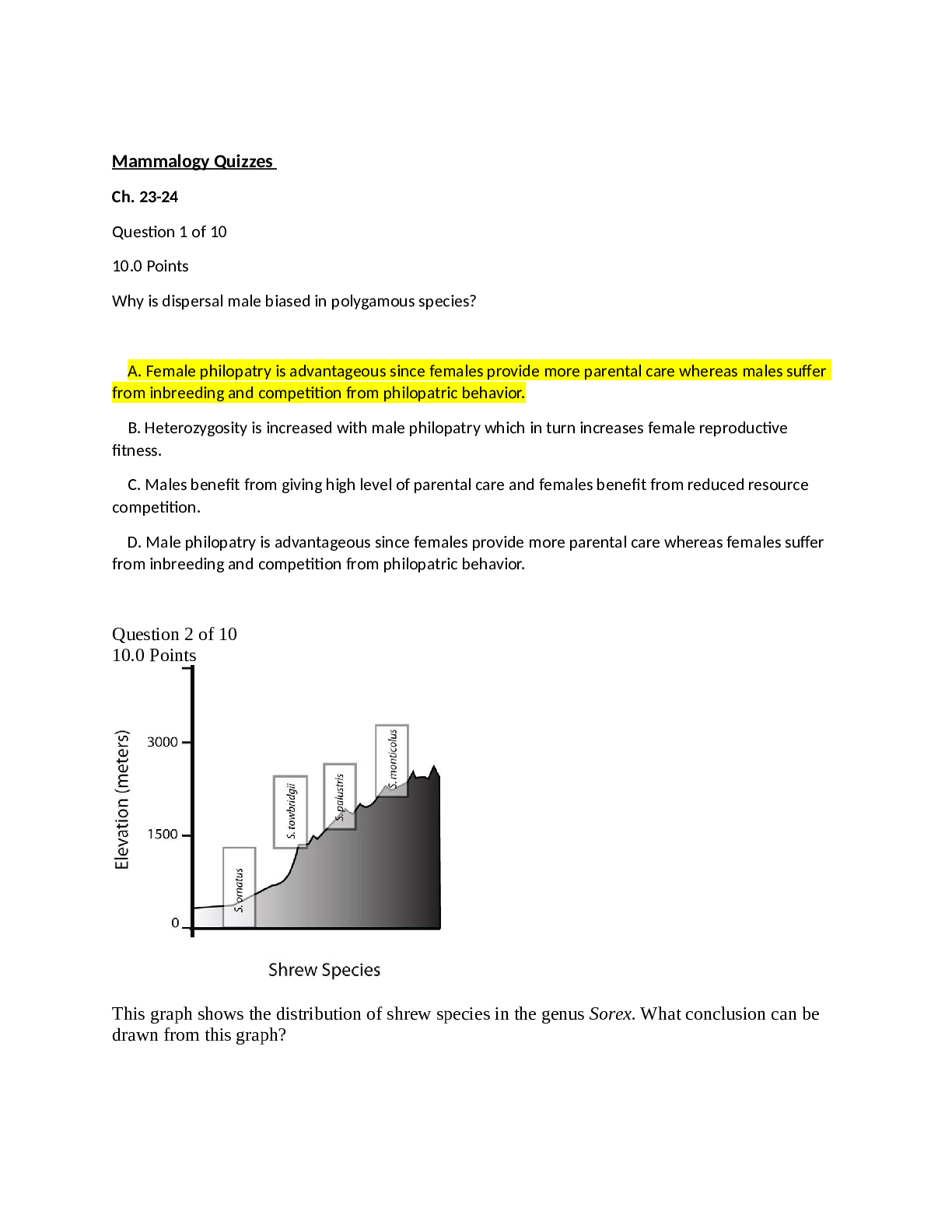
.png)

.png)


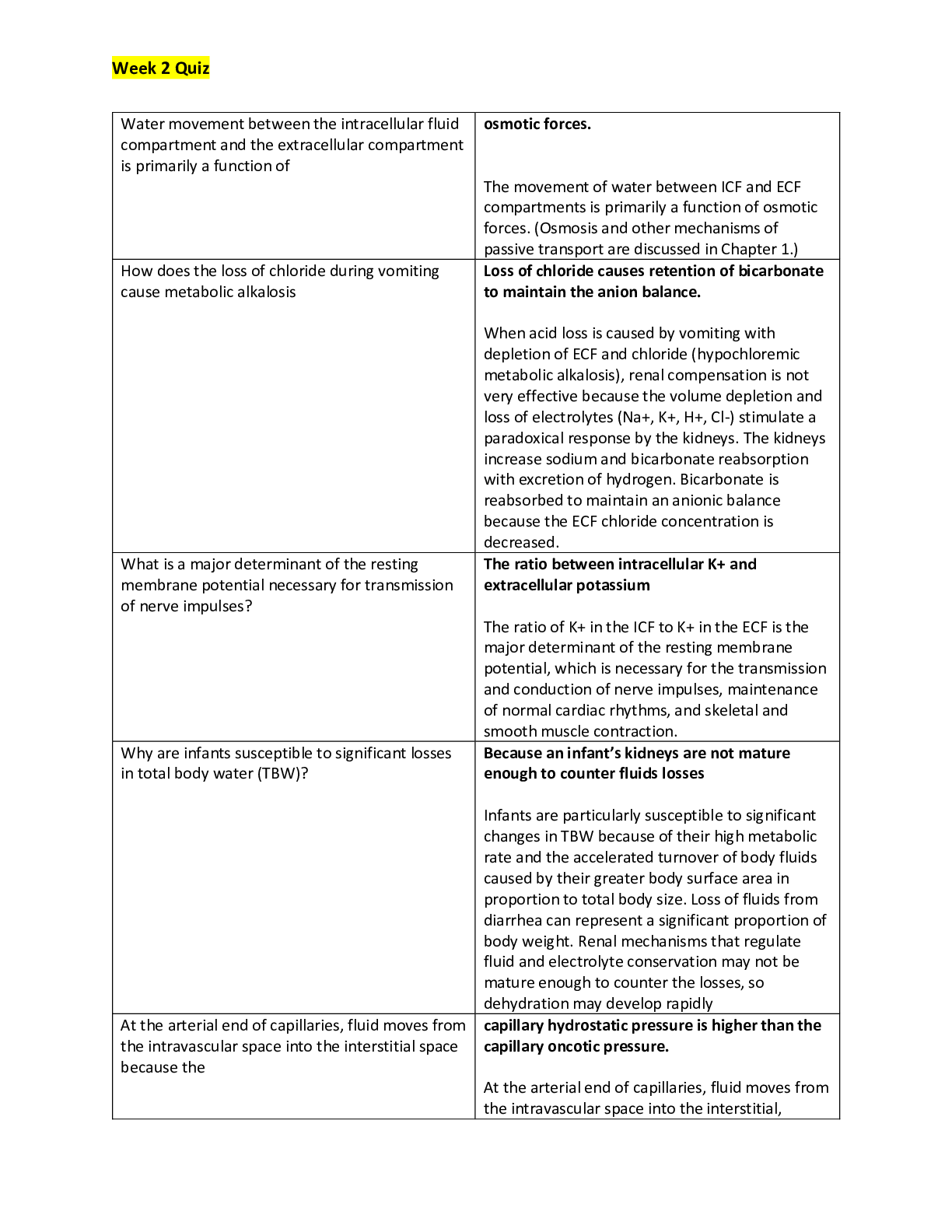


 (1).png)
.png)


















