Chemistry > GIZMOS > Gizmo: Student Exploration - Temperature and Particle Motion - 2022 | Student Exploration Gizmo - Te (All)
Gizmo: Student Exploration - Temperature and Particle Motion - 2022 | Student Exploration Gizmo - Temperature and Particle Motion - Graded A+
Document Content and Description Below
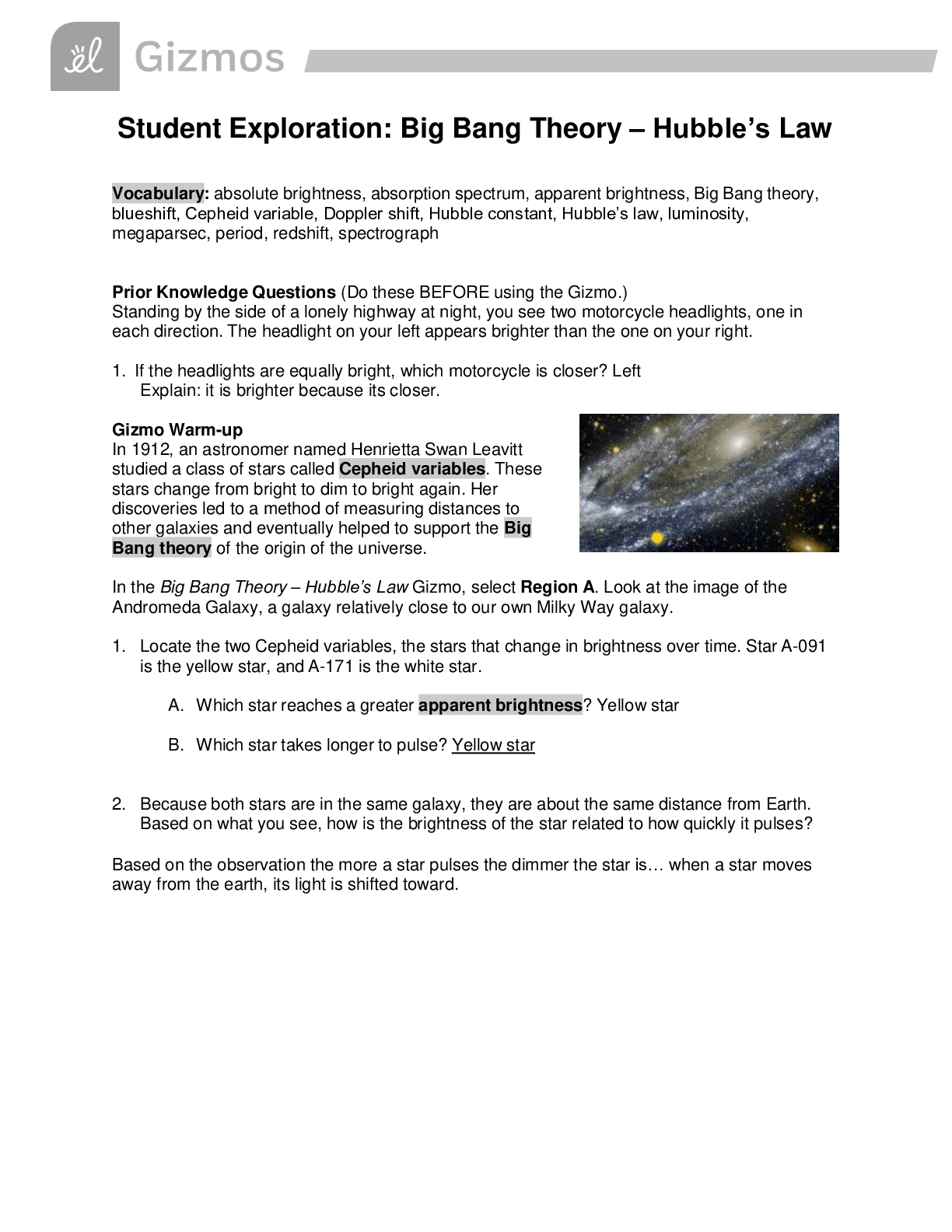
Lab Gizmo Temperature and Particle Motion Gizmo Packet Pages 82-85 Name: Janelle Mosquera Student Exploration: Temperature and Particle Motion Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the ... Gizmo.) 1. Why is hot air hot? This is because there is more heat in the air 2. Why is cold air cold? There is an absence of heat in the air. 3. Air consists of tiny particles called molecules. How do you think the molecules move in hot and in cold air? I think molecules in hot air move faster and the molecules in cold air move slower. Gizmo Warm-up The Temperature and Particle Motion Gizmo illustrates how the molecules of gas move at different temperatures. In this Gizmo, temperature is measured on the Kelvin scale, which measures temperature from absolute zero, the coldest possible temperature (-273.15 °C). Each unit on the Kelvin scale is equivalent to 1 °C: 273.15 K = 0 °C, and 373.15 K = 100 °C. 1. Describe the motion of the hydrogen molecules: The molecules are moving fast 2. Are all of the molecules moving at the same speed? No, some are moving slower than others Question: How is the temperature of a gas related to the motion of gas molecules? 1. Observe: Move the Temperature slider back and forth. Focus on the particle motion at left. What do you notice? Cooler temperatures cause the molecules to move slowly and the warmer temperatures cause the molecules to move quicker. This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 04-15-2022 00:17:04 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/77595841/Temp-and-particle-motion-gizmodocx/ 2. Analyze: The temperature of a substance is a measure of the average kinetic energy of its particles (kinetic energy is the energy of motion). The kinetic energy (KE) of a particle is equal to its mass times the square of its velocity, divided by two: KE = mv2 / 2 A. Based on the formula for kinetic energy, how will the temperature change if you increase the average velocity of the molecules in a gas? The temperature will increase. B. How will the temperature change if you increase the mass of the gas molecules? The temperature will increase. 3. Predict: Oxygen molecules are sixteen times as massive as hydrogen molecules. At the same temperature, which type of molecule would you expect to move faster? Explain. I would expect the hydrogen molecules to move faster because they are smaller than the oxygen molecules, allowing them to move quicker. 4. Check: Test your prediction by choosing Oxygen from the Select a gas menu. What do you see? The hydrogen molecules are moving faster than the hydrogen molecules did. 5. Explain: Based on the definition of temperature given above, explain why oxygen molecules move more slowly than hydrogen molecules at the same temperature. This is because the oxygen molecules are heavier, and they weigh down so the molecules and don't allow the same amount of moving ability as the hydrogen moles have. Question: How are particle velocities distributed? 1. Observe: Move the Temperature slider back and forth. This time focus on the graph at right. What do you notice about the shape of the graph? The shape of the graph is a low line, its height doesn’t go up much. 2. Analyze: Look at the left side of the graph as you raise the temperature from 50 to 1,000 K. A. Even at the highest temperatures, are there still a few slow particles? Yes This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 04-15-2022 00:17:04 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/77595841/Temp-and-particle-motion-gizmodocx/ B. At what temperature do you see the widest variety of particle velocities? 750 ºc C. In general, is the Maxwell-Boltzmann curve a symmetrical or an asymmetrical curve? It is a symmetrical curve. 3. Estimate: Because particles have a range of velocities at any given temperature, it is useful to calculate the average velocity. Physicists express the average velocity in three ways: most probable velocity (vp), mean velocity ( ), and root mean square velocity (vrms). A. Estimate the most probable velocity by looking at the peak of the curve. What is your estimate? 1298 ºc B. Turn on Show most probable velocity. What is the actual value? 1284 ºc C. Base on the shape of the curve, do you think most of the particles are moving faster or slower than the most probable velocity? I think they’re moving faster than the most probable velocity. 4. Predict: The mean velocity is the average velocity of all of the particles. Based on the shape of the curve an [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 4 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 15, 2022
Number of pages
4
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 15, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
215





.png)















.png)