Finance > Class Notes > FIN 111 EXAM STUDY NOTES (All)
FIN 111 EXAM STUDY NOTES
Document Content and Description Below
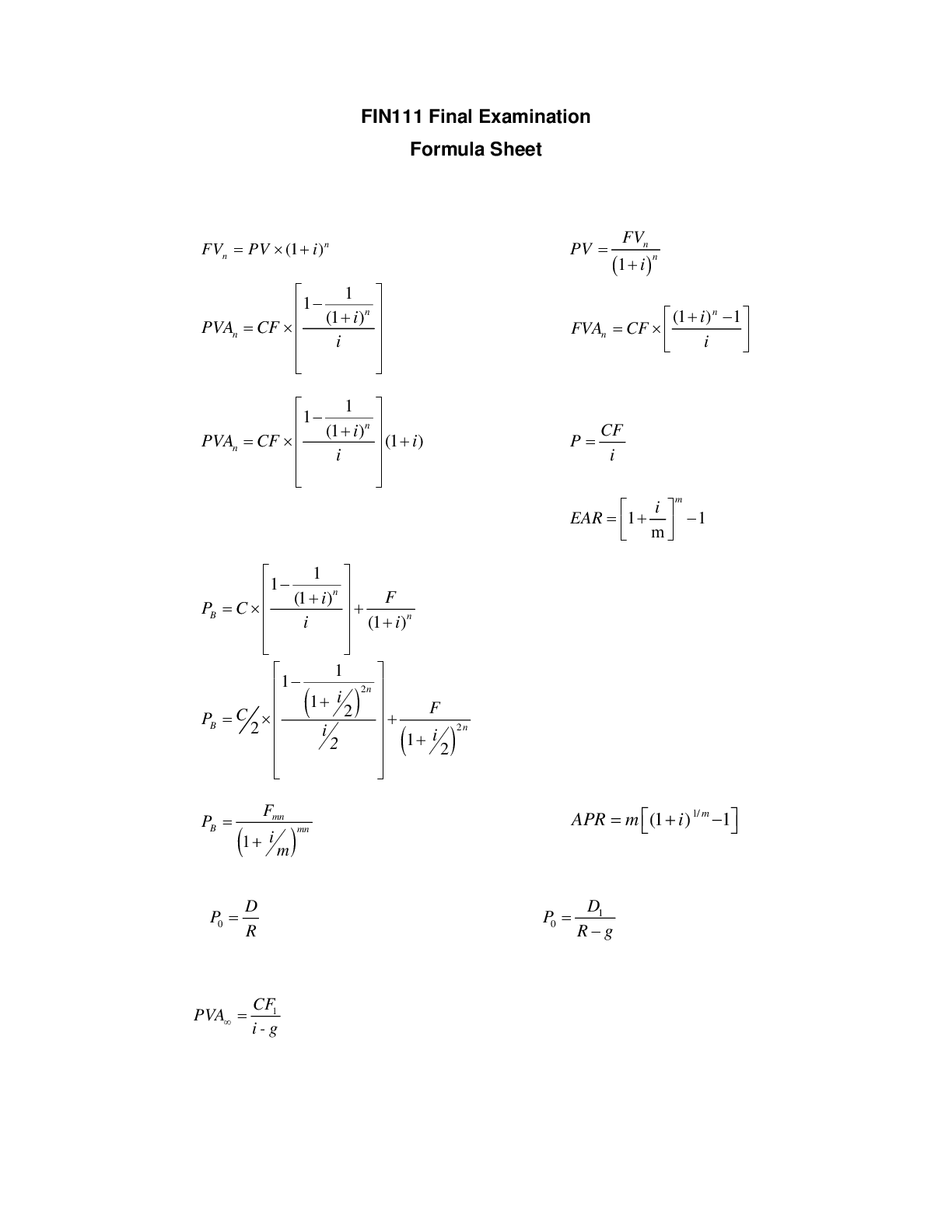
FIN 111 EXAM STUDY NOTES Role of the Financial Manager: the role of the financial manager is to help maximise the owners/shareholders wealth. Three Types of Financial Management decisions:... - Capital budgeting: A list of productive assets that may be purchased over a budget cycle. A good decision is one which benefits are worth more to the company than the cost of the asset. - Financing: Determining how the company should finance or ay for assets. Productive assets are financed by long term borrowing, equity investments or both. - Working capital management: determining how day to day financial matters should be managed so that the company can pay its bills and how surplus cash should be invested. Inventory levels are also an important decision in this type of management. Three major forms of business organisations: - Sole trader: business owned by one person. Simplest type of business to start and least regulated. Sole traders keep 100% of profit and do not need to share decision making authority. Disadvantages include unlimited liabilities. Also traders need to invest in business from their own wealth. Partnership: Consist of two or more owners who have joined together legally to manage a business. Advantages similar to sole traders with the addition, partners have access to more capital, pooling of knowledge, expertise and skills. Disadvantages include disputes between partners, each partner responsible for business debts and liabilities of other partners as well as unlimited liabilities. Corporations: A company is an independent legal entity able to do business in its own rights. Companies can sue and be sued, enter into contracts, issue debt, borrow money and own assets. The owners of companies are its shareholders. Starting a company is costly and must beregistered with ASIC. Advantages include limited liability. Goal of Financial Management: To maximise the current value of the company’s shares. To do this, managers must make investments and financing decisions so that total value cash inflows exceed total value cash out flows by the greatest possible amount Agency problems: An agency relationship arises when one party, the principal, hires another party, the agent, to perform some service on behalf of the principal. - Agency costs: Agents can be bound legally and ethically to act in the interest of the principal. When agents are guilty of dishonesty, fraud, or deception it can have a huge impact in share prices. - Conflict of interest: When an agents interest are different from the principal’s. Conflict of interest can be resolved by complete disclosure. Alternatively, the conflicted party can withdraw from servicing the interests of one of the parties. - Information Asymmetry: occurs when one party in a business transaction has information that is unavailable to other parties in the transaction. Actions based on the principles that do not pass the golden rule test or that cannot be publicly advocated are not likely to be fair. Roles of a Financial System: - To facilitate the flow of funds: Financial institutions allow the flow of funds from savers or Surplus Spending Units (SSUs) to borrowers or Deficit Spending Units (DSUs). Financial institutes are financial intermediaries because they are in between parties that want to sell and buy financial instruments. Money is the medium of exchange used in the financial system. Surplus Spending units (SSUs) – a unit whose income exceeds planned spending Deficit Spending units (DSUs) – a unit whose spending exceeds its receipts - To provide the mechanism to settle transactions: The payment system permits the settlement of transactions. An effective payment system is characterized by its efficiency, in terms of speed, cost and stability. - To generate and disseminate information: Efficient financial markets provide sufficient economic and financial information to enable participants to make informed investment decisions. This information needs to be available in a timely fashion to all market participants so that all have equal opportunity to act. - To provide the means to transfer and manage risk: Risk relates to uncertainty and the chance of an unexpected outcome being achieved. Financial systems manage the risks they are exposed to including insurance products, and securitisation. - To provide ways of dealing with incentive problems: The three key incentive problems of financial contracts are: * Information asymmetry * Moral hazards * Agency problems The financial system manages these problems through various devices that align the interests of principals and agents, as well as implementing a regulatory environment that promotes this and penalises those who breach their duties. Benefits of Financial Intermediaries - Denomination Divisibility: Financial intermediaries are able to produce a wide range of denominations from $1 to many millions. They do this by pooling the funds of many individuals and investing them in direct securities of varying sizes. - Currency Transformation: Financial intermediaries help finance the global expansion of Australian companies by buying financial claims denominated in one currency and selling denominations in another currency. - Maturity Flexibility: Financial intermediaries create securities with a wide range of maturities so that they buy direct claims issued by DSUs and issue indirect securities with precisely the maturities desired by SSUs. - Credit risk Diversification: By purchasing a wide variety of securities financial intermediaries are able to spread the risk. Portfolio diversification is an application of ‘not putting all eggs in one basket’. - Liquidity: Many of the financial commodities produced by intermediaries are highly liquid. Financial Intermediaries tailor characteristics of the indirect securities they issue to the desires of SSUs. They engage in one or more distinct types of intermediation to earn a profit. Types of Financial Intermediaries - Banks: including commercial banks, the largest and most diversified intermediaries. Liabilities are in the form of deposit accounts. Assets in the forms of loans. Westpac NAB Commonwealth - Building Societies: Authorized Deposit taking Institutions (ADI). They accept retail deposits and produce loans with a traditional emphasis in home loan lending. Newcastle Permanent - Credit unions: ADI with traditional Co-op in which membership is based on common bond such as profession, trade union, local communities. First choice credit union Central West credit union - Foreign bank representatives: A company organized under the laws of a foreign country. In Australia Foreign banks are required to confine their deposit taking activities to the wholesale markets. - General and Life Insurers: General and life insurers sell protection against loss of property, or loss of income from premature death or retirement. -Friendly societies: Also known as mutual societies, a financial organisation owned by its members not shareholders. Originally set up to provide insurance style services. Services include education bonds, funeral, accident and sickness benefits. Money Market corporations: Merchant or investment banks. Provide specialist advise on various financial matters including mergers, acquisitions, fund raising and risk management. - Finance Companies and Securitises: Make loans to consumers and small businesses. Not ADI. Obtain funds by selling debentures and other capital market instruments to investors. Superannuation entities: Obtain funds from employer and employee contributions during employees’ working years and provide financial resources that can be used in a variety of ways in retirement. Types of Financial Markets - Primary and secondary Markets: Primary markets are ones in which claims are first sold as new issues. Secondary markets are ones where participants buy and sell previously issued financial claims. - Over the Counter Money Markets: Stock exchange where securities transactions have no central location. Stocks are bought over the phone or on the internet rather than the floor ofstock exchange. Strict rules must be followed by dealers in the market. Regulated by ASIC. - Capital Markets: Markets in which goods are financed with stock or long term debt instruments. Types of Risk - Credit Risk: Possibility that the borrower will fail to make either interest or principal payments in the amount and at the time promised. Managed by careful credit analysis, diversification, and monitor customer over life of loan. - Interest Rate Risk: Risk that changes in interest rates will cause an assets price and realised yield to differ from the purchase price and initially expected yield. - Liquidity Risk: The risk that a financial institution will be unable to generate sufficient cash inflow to meet required cash out flow. - Foreign Exchange Risk: The fluctuations in the earnings or value of a financial institution that arises from changes in exchange rates. - Political Risk: Country or sovereign risks that can result in financial claims of foreigners being repudiated or becoming unenforceable because of changes on a government, or in government policy in a country. Reputational Risk: The potential that negative publicity will cause a decline in the customer base, costly litigation or revenue restrictions. - Environmental Risk: The actual or potential threat of adverse impacts on the value from changes in the environment and or organisational impacts on the environment. Main sources and uses of Funds for Commercial Banks Sources: - Deposits: Banks offer deposit accounts products to businesses and public sector clients called transaction or savings accounts. Basic medium of exchange and account for 60% of bank liabilities. - Bill Acceptance: By accepting a bill, a bank guarantees funding to the client. Bills can be bank funded or client issuing bill in the money market. - Debt Liabilities: Short and long term instruments that raise funds from public debt issues. Common forms are commercial papers, medium to long term debentures and unsecured notes. - Foreign Currency Liabilities: Provide banks with opportunity to diversify their funding base and often at a lower cost when large amounts are being raised. - Loan Capital: Long term, subordinated notes and debentures some of which can be converted into common stock. - Shareholders’ Equity: The residual interest in assets after deducting liabilities. Financial institutions are required to keep sufficient shareholders equity to meet their obligations towards customers. Uses - Personal and housing finances: Loans to individuals that usually have terms up to five years for purchases of cars, holidays and consumables. Also mortgages that finance construction, purchase and remodelling of both residential and commercial facilities. - Commercial Lending: Loans to commercial industrial firms constitute both long and short term loans. Can comprise of bridging loans, seasonal loans and long term asset loans. - Lending to government Liquidity management of Commercial Banks - Asset Management: Maintaining sufficient cash and non-cash assets that can be quickly converted into cash with minimal value loss. - Liability Management: Acquiring liquidity from the liability side of the balance sheet. Importance of Banks ‘Off Balance Sheet’ Business: - Contingent Assets: As asset in which the possibility of an economic benefit depends solely upon future events that can’t be controlled by the company. Due to uncertainty these are not placed on the balance sheet but can be found in the company’s financial statement notes. - Contingent Liabilities: A potential obligation that may be incurred depending on the outcome of a future event. A contingent liability is recorded only if the contingent is probable and the amount of liability can be estimated. Examples: • Loan commitments • Letters of credit • Loan brokerage • Securitisation • Derivative securities Bank Capital management - Provides a Financial cushion: Banks are able to continue to operate even if they suffer temporary operating issues. - Helps maintain public confidence: adequate capital helps maintain public confidence in soundness and safety of individual banks and the banking systems. - Provides some protection to depositors: Adequate capital provides protection in terms of a source from which their deposits may be recouped in the event of bank failure. - Serves as a source of funds for expansion: Capital is a source of funds for bank growth and an addition of new products, services and/ or facilities. Non-Bank Financial Institutions - Building societies • ADI • Regulated by APRA • Assets = residential mortgage • Capital: owned by members - Credit Unions • ADI • Regulated by APRA • Assets: Loans to members • Liabilities: Members saving accounts • Capital: Mutual institutions that do not hold shareholders’ equity - Finance Companies • Not ADI • Regulated by ASIC • Consumer lending o Personal loans o Real estate lending o Business lending Wholesale Financing Retail financing Lease Financing • Liabilities: • Highly Leveraged • Commercial papers • Debentures • Unsecured notes Advantages of Consumer Credit • Increase current purchasing power • Transaction efficiency • Indicates good financial standing with external parties • Reduces cost of holding cash • Reduces record keeping Disadvantages of Consumer Credit • Likelihood of overspending • Reduction in quality of lifestyle if misused • Adverse legal outcomes • Court action • Bankruptcy Types of Consumer Credit • Housing loans • Credit cards • HECS/HELP • Personal loans • Motor vehicle finance • Revolving lines of credit • Leasing finance • Fully drawn advance • Bridging loans Time Value of Money Definition: The difference in value between a dollar in hand today and a dollar promised in the future. A dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 16 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 15, 2021
Number of pages
16
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 15, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
96





.png)