BioChemistry > EXAM REVIEW > University of South Florida: BIO CHEMIST 3053. Biochemistry-Gift-2-Spring-2021. Possible Questions: (All)
University of South Florida: BIO CHEMIST 3053. Biochemistry-Gift-2-Spring-2021. Possible Questions: BLUE Possible Answers: From Previous GIFT: Yellow Highlight Notes: GREEN.
Document Content and Description Below
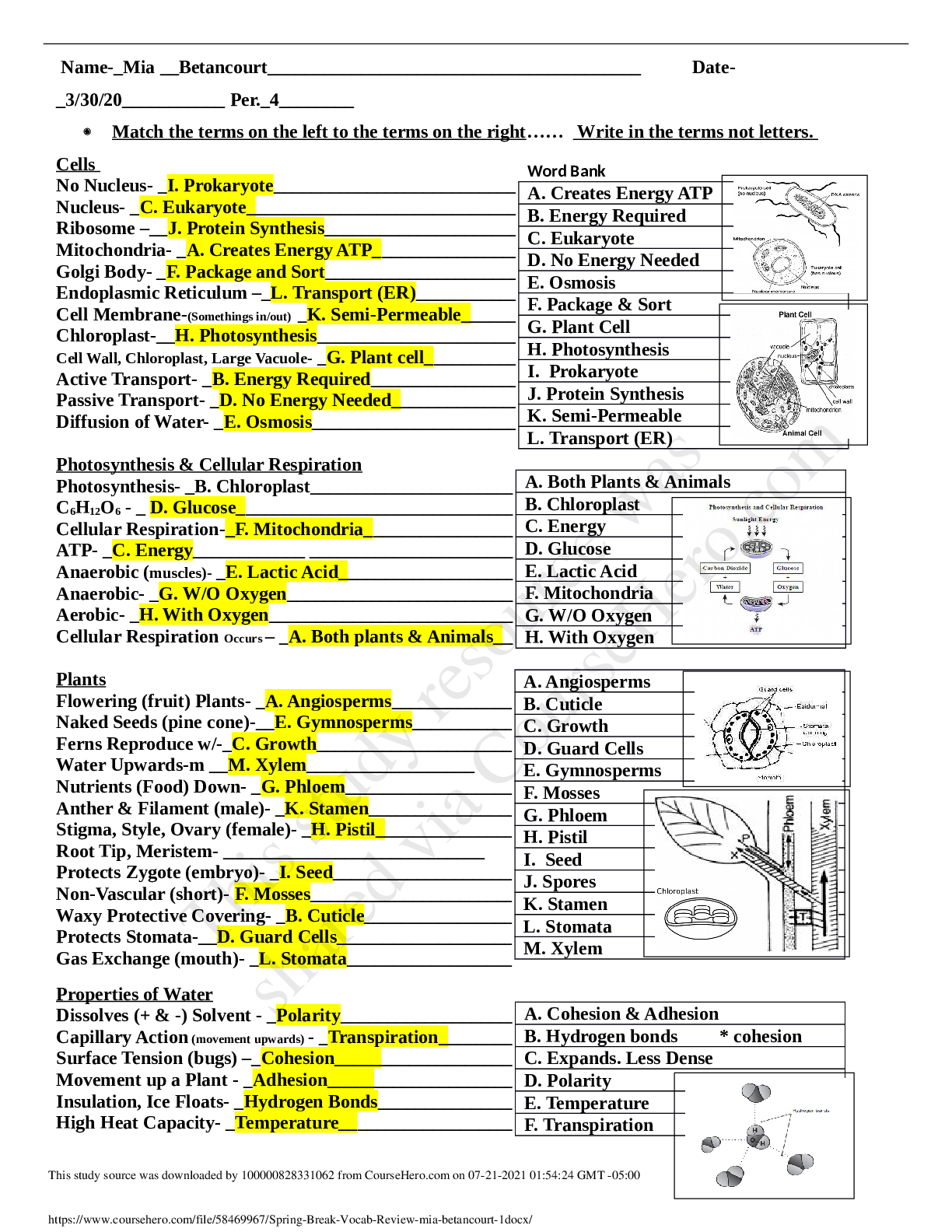
Old Biochem Exam 2 Biochemistry 3053 GIFT 2 Possible Questions: BLUE Possible Answers: From Previous GIFT: Yellow Highlight Notes: GREEN 1. Which enzyme is considered [REDACTED]? Part of TCA and ETC? ... Rate limiting: 1. Which enzyme is considered part of TCA and ETC? A. Malate dehydrogenase B. Citrate synthase C. Isocitrate dehydrogenase D. NADH- ubiquinone oxidoreductase 2. A solution at pH [REDACTED] contains a weak acid, HA. The pKa of the acid is [REDACTED]. What is the ratio of [A- ]:[HA]? pH=7 pKa=6.5 pH= pka + log ([A- ]/[HA]) 7= 6.5 + log ([A- ]/[HA]) log ([A- ]/[HA])= 0.5 ([A- ]/[HA])= 100.5 = 3.162271766017 ratio of [A- ]:[HA]= 3.16:1 3. In mitochondria, what is the expected pH [REDACTED]? In mitochondria, what is the expected pH of the matrix compared to the intermembrane space? 4. When Compound C [REDACTED] electrons [REDACTED] Compound D, [REDACTED] When Compound C gives electrons to Compound D, then Compound D is the oxidant and Compound C is the reductant. When Compound C removes electrons from Compound D, then Compound C is the oxidant and Compound D is the reductant 5. When Compound C [REDACTED] electrons [REDACTED] Compound D, [REDACTED] When Compound C gives electrons to Compound D, then Compound D was reduced and Compound C was oxidized. When Compound C removes electrons from Compound D, then Compound C is reduced and Compound D was oxidized 6. What provides the energy to the ATP Synthase for the formation of ATP? - ADP + Pi + H+out ⇌ ATP + H2O + H+in When protons flow back down their concentration gradient (from the intermembrane space to the matrix) 7. Which of the following describe cristae? - Cristae do not have pores for movement of proteins - Their proteins are not found in outer membrane - Cristae does not seal inner membrane - Cristae does not anchor f1f0 ATP synthase - THEY INCREASE SURFACE AREA OF INNER MEMBRANE 8. (True / False) The amino acid [REDACTED] at pH 7.4 has [REDACTED] charged groups. - Amino acid T at pH 7.4 has two charged groups but net charge of 0 - Amino acid H at pH 7.4 has two charged groups but net charge of 0. - Amino acid E at pH 7.4 has two charged groups but net charge of 0 -(True / False) The amino acid [aspartic acid or glutamic acid] at pH 7.4 has [a negative (T/F) The amino acid [aspartate] at pH 7.4 has [three] charged groups T Congratulations! Due to your success in Dr. Daniel’s Biochemistry class. You have been selected by NASA to do the biochemical write up on a new organism recovered from a Martian probe! During your analysis you have discovered a brand new electron transport chain! The organism appears to use electron transport as its primary source of energy rather than ATP. This leaves you with a couple of questions to answer: During analysis, your technician reports a new electron transport chain (always check your technician’s work! Analyze this carefully!): Ickygreenone + H+ + 2e- → Ickygreenol [REDACTED] V -0.2 V Barsool → Barsoom + H+ + 2e- [REDACTED] V 0.03 V Because the reactions are not originally in the same form we would flip the bottom reaction to have the oxidized form accepting electrons to become the reduced form so we can determine which half reaction is the stronger reductant This would give: Ickygreenone + H+ + 2e- → Ickygreenol (-0.2 V) Barsoom + H+ + 2e- → Barsool (-0.03 V) Both half reactions are now in the same form so we can confirm that the top reaction is the most negative of the two half reactions and the stronger reductant **If we want to solve for ΔE0 we would flip the top reaction to make the electrons flow, which would give: Ickygreenol → Ickygreenone + H+ + 2e- (0.2 V) Barsoom + H+ + 2e- → Barsool -0.03 V (-0.03 V) **to determine, reductant, oxidant, reduced, and oxidized you would look at the half reactions when they are in the same form (before the stronger reductant becomes flipped) So this: Ickygreenone + H+ + 2e- → Ickygreenol (-0.2 V) Barsoom + H+ + 2e- → Barsool (-0.03 V) 9. Which species is the reductant for the proposed ETC? Reductant relates to oxidized so Ickygreenol and Barsool are the reductants The stronger reductant would be Ickygreenol because it is the most negative **Smaller Ev value is more negative 10. Which species is the oxidant for the proposed ETC? Oxidant relates to being reduced so Ickygreenone and Barsoom are the oxidants because they have gained electrons ← this is just how I understand it The stronger oxidant would be Barsoom because it is the most “positive” **Larger Ev value is more positive 11. Which series of voltages represents the correct voltages to trace the electron flow for the free energy calculation? If this is what we originally had: Ickygreenone + H+ + 2e- → Ickygreenol (0.5 V) Barsoom + H+ + 2e- → Barsool (1.25 V) Then 0.5 would be flipped because it is the most “negative” out of the two voltages This means the top equation has the strongest reductant This would give: Ickygreenol → Ickygreenone + H+ + 2e- (-0.5 V) Barsoom + H+ + 2e- → Barsool (1.25 V) If this is what we originally had: Ickygreenone + H+ + 2e- → Ickygreenol (-0.5 V) Barsoom + H+ + 2e- → Barsool (-1.25 V) Then -1.25 would be flipped because it is the most “negative” out of the two voltages This means the bottom equation is the strongest reductant This would give: Ickygreenone + H+ + 2e- → Ickygreenol (-0.5 V) Barsool → Barsoom + H+ + 2e- (1.25 V) a) -0.5V and -1.25V b) +0.5V and -1.25V c) -0.5V and +1.25V d) +0.5V and +1.25V 12. What is the free energy from the electron transport chain presented (Faraday constant is 23)? ***Use the equation ΔG॰= (-n)(F)Ecell ½ O2 + 2H+ + 2e- → H2O (0.82 V) Dehydroascorbate + 2e- → Ascorbate (0.08 V) Both half reactions are in the same form, in order for electrons to flow we need to flip the stronger reductant The stronger reductant would be the bottom half reaction because it is more “negative” We get: ½ O2 + 2H+ + 2e- → H2O (0.82 V) + Ascorbate → Dehydroascorbate + 2e- (-0.08 V) --------------- ΔE = 0.74 V 0 ΔG = - nFΔE 0 ΔG = - 2 (23) (0.74) = - 34.04 13. From one run of the proposed electron transport chain, how many ATP equivalents in energy could theoretically be generated? Theoretical amount of ATP is 7.3 kcal/mol 34.04/7.3 ≈ 4.7 ≈ 4 ATP ← round down- if you round up you are creating energy that you don’t have 14. (True/False) Amino Acid E converts directly to Oxaloacetate. The amino acids have the same number of carbons as the intermediate that they convert into. Alanine (A) ---> Pyruvate (Both have 3 carbons) Glutamate (E) ---> Alpha-Ketoglutarate (Both have 5 carbons) Oxaloacetate would be Aspartate (D) (Both have 4 carbons) (True/False) Given metabolic pathways in the class so far, malate] can be directly converted to pyruvate in one step by a single enzyme, malate dehydrogenase. 15. What is the material on the right (Figure 1)? a. Citrate b. Succinate c. Malate d. Acetyl CoA e. Oxaloacetate 16. What is the rate limiting enzyme of [REDACTED]? -Palmitate Biosynthesis: Acetyl CoA Carboxylase -TCA: Isocitrate Dehydrogenase -Glycolysis: Phosphofructokinase 17. What is the material on the right (Figure 2)? a. Citrate b. Succinate c. Malate d. Acetyl CoA e. Oxaloacetate 18. What is the material on the right (Figure 3)? Succinate 19. What is the material on the right (Figure 4)? or Malate acetyl coA 20. The asterisk shows a radiolabeled carbon (Figure 5). This structure is a glycolytic intermediate that will be converted to enter the TCA cycle. What [REDACTED] product that will be radiolabeled? Radiolabeling gets rid of the problem that succinate's symmetry creates. Analogy: tagging a ball with neon paint and releasing it into a dark room with other balls. Even with the lights off, the neon paint still lets you see which ball was "labelled". [is the last] product that will be radiolabeled ← succinate if the radiolabeled carbon was removed during oxidative decarboxylation; oxaloacetate If the radiolabeled carbon stayed on during the oxidative decarboxylation and made it to the end of one round of the TCA cycle If the carbon is in acetyl coA before it enters the TCA then it will be in oxaloacetate after one round If the carbon is in oxaloacetate before it enters the TCA then there will be a 50% chance it will be in oxaloacetate after one round and a 50% chance that it will be lost as CO2 21. Ammonium has a pKa of 9.25. [REDACTED] mL of [REDACTED] M HCl is added to [REDACTED] L of a [REDACTED] M buffer solution of this ammonium at pH 10.0. The resulting solution is at pH: Ammonium has a pKa of 9.25. 45 mL of 1.00 M HCl is added to 75 mL of a 1.00 M buffer solution of this ammonium at pH 10. The resulting pH is: a. 7.4 b. 8.0 c. 8.5 d. 9.0 e. This is an explosive reaction The Neutralization cookbook has an in depth explanation of this^ Neutralization Cookbook Step 1: pH=pka + log[ A - /HA ] 10=9.25 + log [A-/HA] 0.75= log [A-/HA] [A-/HA] =100.75= 5.62 [A-]=5.62/6.62 [HA]= 1/ 6.62 Step 2: moles of weak acid & conjugate base Molarity-->moles Mol A- : 0.075 L buffer (5.62 mol/6.62 L)=0.06367 mol A- buffer solution Mol HA: 0.075 L buffer (1 mol/ 6.62 L)= 0.011329 mol HA buffer solution Step 3: moles of acid and base added to the buffer 0.045 L x (1 mol/L)= 0.045 mol H+ (HCl) Step 4: Change in amounts of A- and HA [0.0637 mol A- buffer] - [0.045 mol HCl] =0.0187 mol A [0.0113 mol HA buffer] + [0.045 mol HCl] =0.0563 mol HA You would add to the acid because you are adding acid (HCl) which creates more acid You would subtract from the base because you are adding acid (HCl) which creates less base Step 5: New pH determination pH=pKa + log [A-/HA] pH= 9.25 + log [0.0187 mol A-/0.0563 mol HA] 9.25 + [0.332149201] pH= 8.77 ≈ 9 22. In a test organism that possesses a normal TCA cycle, you determine that [REDACTED] is elevated compared to control samples. Which enzymatic failure could best explain this observation? -L-malate; enzymatic failure is Citrate Synthase 23. What type of reaction does the [REDACTED] step of TCA perform? (Hint: consider all products made, including side products) What type of reaction does the [rate-limiting] step of the TCA perform? a. Phosphoryl transfer b. Carboxylation c. Reduction d. Oxidative decarboxylation e. Hydrolysis What type of reaction does the [sixth] step of the TCA perform? a. Phosphoryl transfer b. Carboxylation c. Oxidation d. Oxidative decarboxylation e. Hydrolysis What type of reaction does the [seventh] step of the TCA perform? a. Phosphoryl transfer b. Carboxylation c. Reduction d. Oxidative decarboxylation e. Hydration 24. Which enzyme activity in TCA makes a [REDACTED]? -is powered by thioester bond cleavage and makes a nucleotide triphosphate (GTP) as a product? Which enzyme activity in TCA makes a [NADH as a product]? a) Citrate synthetase b) Malate dehydrogenase c) Succinate dehydrogenase d) Aconitase Enzymes that make NADH as a product in the TCA cycle: malate dehydrogenase, isocitrate dehydrogenase, and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. Which enzyme activity in TCA makes a [FADH2 as a product]? a) Citrate synthetase b) Malate dehydrogenase c) Succinate dehydrogenase d) Aconitase Which enzyme activity in TCA makes a [symmetrical molecule] 25. (A = True / B = False) It is reasonable to say that: [REDACTED] TCA [REDACTED] ATP [REDACTED]. It is reasonable to say that TCA does not make ATP directly. 26. The asterisk shows a radiolabeled carbon (Figure 6), after one round of TCA where is this carbon found? 2. From the TCA quiz: Acetyl CoA is combined with oxaloacetate to start the TCA cycle. By the time this one cycle completes, how many carbons from the acetyl CoA were removed? The answer is 0 I’m guessing if the Acetyl CoA has the radiolabeled carbon then it would be found on oxaloacetate after one round of TCA 27. [REDACTED] can become what amino acid? - Pyruvate > alanine (A) - Alpha ketoglutarate > glutamate (E) - Oxaloacetate > Aspartate (D) **Know the one letter abbreviations in a previous gift that is how the answer choices were Alpha ketoglutarate can become what amino acid? a. G b. E c. N d. Q e. K Pyruvate can become what amino acid? a. G b. A c. N d. Q e. K Oxaloacetate can become what amino acid? a. G b. A c. N d. Q e. D 28. Which of the following amino acids are likely [REDACTED] at physiological pH? (Select all that apply) Figure 6 -Positive: Lysine (K), Arginine ( R) -Negative: Glutamate (E), Aspartate (D) 29. Using glycolysis, suppose [REDACTED] moles of glucose are converted to [REDACTED] of pyruvate, how many moles of ATP are made? (Hint: Read this question carefully) - 1 mol of glucose > 1 mol of pyruvate = 2 mols of ATP made - 1 mol of glucose > 2 mol of pyruvate = 4 mol of ATP made If there is complete conversion of glucose to 2 moles of pyruvate then 4 moles of ATP will be made - however many moles of pyruvate x2 30. A mad-scientist wishes to make a glycolysis inhibitor to treat gerbilitis, why is this a bad idea? (Select all that apply) - Expect toxicity to eye, toxicity to red blood cells, and kidney Medulla (all of which rely on glycolysis) - All of the above From the Glycolysis ICA: Please never make a drug that targets kinases or glycolytic enzymes. Why is this such a bad idea? Because kinases and glycolytic enzymes are involved in glycolysis and if glycolysis is not functional then the rest of the pathways will not function correctly 31. [REDACTED] What does the regulation of hexokinase protect against? D. Depletion of Pi. a) Protection from depletion of NADH b) Protection from depletion of NAD+ c) Protection from depletion of ADP d) Protection from depletion of Pi . e) Protection from accumulation of fructose-1,6,-bisphosphate (True/False) Given metabolic pathways in the class so far, [pyruvate] can be directly converted to [acetyl CoA] in one step by a single enzyme. False pyruvate dehydrogenase complex that is made up of three enzymes is required to convert pyruvate to acetyl CoA (True/False) Given metabolic pathways in the class so far, [1 molecule fructose-1,6-bisphosphate] can be directly converted to [2 molecules G3P] in one step by a single enzyme. This is false because fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is not directly converted into 2 molecules of G3P. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate converts into 1 molecule of G3P and 1 molecule of Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate, then triose phosphate isomerase converts dihydroxyacetone phosphate into G3P 32. Which of the following [REDACTED] enzymatic reactions is freely reversible by the same enzyme in cellular conditions? Glycolytic: -Glyceraldehyde 3 Phosphate to Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate (Enzyme: Triose Phosphate Isomerase) Glycolytic enzymatic reactions that are freely reversible - Glucose-6-phosphate ↔ fructose-6-phosphate (phosphoglucose isomerase) - Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate ↔ dihydroxyacetone phosphate ↔ glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (aldolase) - Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate ↔ dihydroxyacetone phosphate (triosephosphate isomerase) - Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate ↔ 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) - 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate ↔ 3-phosphoglycerate (phosphoglycerate kinase) - 3-phosphoglycerate ↔ 2-phosphoglycerate (phosphoglycerate mutase) - 2-phosphoglycerate ↔ phosphoenolpyruvate (enolase) 33. What is the name of the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of the correct answer to the previous question? -Triose phosphate isomerase if you go with the highlighted one 34. If [REDACTED] is [REDACTED] in cells, what is the effect on the glycolysis pathway in those cells? [ATP]-[ elevated] - PFK produces 1,6 bisphosphate so if it is inhibited then it is not going to produce 1,6 bisphosphate and the levels will decrease [citrate] [elevated]- It inhibits PFK, PFK produces 1,6 bisphosphate so if it is inhibited then it is not going to produce fructose 1,6 bisphosphate [fructose 2,6 biphosphate] [elevated] this will activate PFK, which produces Fructose 1,6 bisphosphate, some Fructose 1,6 bisphosphate molecules will bind to pyruvate kinase, which will activate the enzyme and produce pyruvate Levels of fructose 1,6 bisphosphate will increase [AMP] [elevated] this will activate PFK, which produces Fructose 1,6 bisphosphate, some Fructose 1,6 bisphosphate molecules will bind to pyruvate kinase, which will activate the enzyme and produce pyruvate 35. Which of the following structures is the product made by the [REDACTED] of glycolysis? [The rate limiting step of glycolysis] Rate limiting step of glycolysis is with PFK - product made is fructose 1-6 - bisphosphate Pyruvate kinase [last step] phosphophenol pyruvate → 36. Which enzyme in glycolysis [REDACTED]? [is the first one to produce ATP]- [ is the first one to use ATP [the first one to produce NADH] 37. [REDACTED-chemical reaction] of [REDACTED-substrate] produces: [Dehydration] of [2-phosphoglycerate] produces [Oxidation] of [succinate] produces [Hydration] of fumarate produces [Oxidative decarboxylation] of [isocitrate] produces 38. Consider a [REDACTED] inhibitor. What would be the changes expected in a Lineweaver-Burk Plot? (Select all that apply) x intercept= - K1m y intercept= slope= V m1ax VKmmax [uncompetitive] Km and vmax both decrease--y int increases, x int decreases [non-competitive (or allosteric)] Km unchanged, vmax decreases -- y int increases, slope steepens [competitive] Km increases, vmax unchanged -- steeper slope, y int unchanged 39. During anaerobic conditions … a. Glycolysis risks failing due to lack of a key metabolite b. Lactate dehydrogenase begins to function c. NADH is consumed by the reduction of pyruvate to lactate d. All of the above complete the statement e. None of the above complete the statement 40. [REDACTED] increases in the cell, what would we expect? -[Fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate] a. Decreased activity of hexokinase b. Decreased activity of lactate dehydrogenase c. Increased activity of pyruvate kinase d. Immediate conversion of dihydroxyacetone phosphate to glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate e. Decreased activity of pyruvate kinase 41. Which of the following [REDACTED] inhibits [REDACTED]? -[allosterically] inhibits [phosphofructokinase] a. AMP b. Fructose-2,6-bisphophate c. Glucose d. Hydroxyl e. Citrate Which of the following [allosterically] inhibits [pyruvate kinase] a. AMP b. Fructose-2,6-bisphophate c. Glucose d. Hydroxyl e. alanine 42. How is [REDACTED] converted to [REDACTED]? [Glyceraladehyde 3 phosphate] [ 1,3 biphosphoglycerate] Inorganic phosphate and NAD+ a. ATP is used provide phosphate b. Pi is used to provide phosphate c. Phosphate is transferred from fructose-2,6-bisphosphate d. NADH provides the phosphate e. This reaction does not occur in glycolysis, the question is invalid 43. How is [REDACTED]phosphate converted to [REDACTED]phosphate -[glucose-6-phosphate] converted to [fructose-6-phosphate] a. Isomerization b. Decarboxylation c. Oxidative decarboxylation d. Phosphoryl transfer e. Reductive carboxylation 44. Which of the following is a cause of [REDACTED]? -[hemolytic anemia] a. Failure of glucose kinase b. Failure of phoshphofructokinase c. Failure of triosephosphate isomerase d. Failure of pyruvate kinase e. Failure of lactate dehydrogenase 45. Does this span of amino acids possess a residue typically used phosphorylation: [REDACTED] The only ones that will are Serine(S), Tyrosine (Y), and Threonine (T). This is because they have terminal hydroxyl groups. - D-K-H-F-W-Q-N a) No, it does not b) Yes, it contains a Lys. c) Yes, it contains a Ser. d) Yes, it contains an Asp. e) Yes, it contains a Thr. Short Answer Question PATHWAY TRACE For this trace, we’re going through a couple of pathways. Starting with this material: [REDACTED] go to this: [REDACTED] You must also NAME the starting material and ending material! Use every box, do not add boxes, do not remove boxes. Do not change clues. (Boxes in gray are not graded. 10 points total) Hint to trace: Two food group Glucose to (amino acid D or amino acid E or amino acid A) **Sugar to Dairy (Glucose to lactate) Aline-----> Pyruvate via the enzyme transamase Glutamate-----> Alpha keto gluterate via the enzyme transamase Aspartate-----> oxaloacetate via the enzyme transamase Glutamate------> glutamine via the enzyme glutamine synthase [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 22 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 31, 2021
Number of pages
22
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 31, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
53







.png)