*NURSING > EXAM > NURSING NR508 Advanced Pharmacology Mid-Term Exam (Latest 2020) Chamberlain College Of Nursing (All)
NURSING NR508 Advanced Pharmacology Mid-Term Exam (Latest 2020) Chamberlain College Of Nursing
Document Content and Description Below
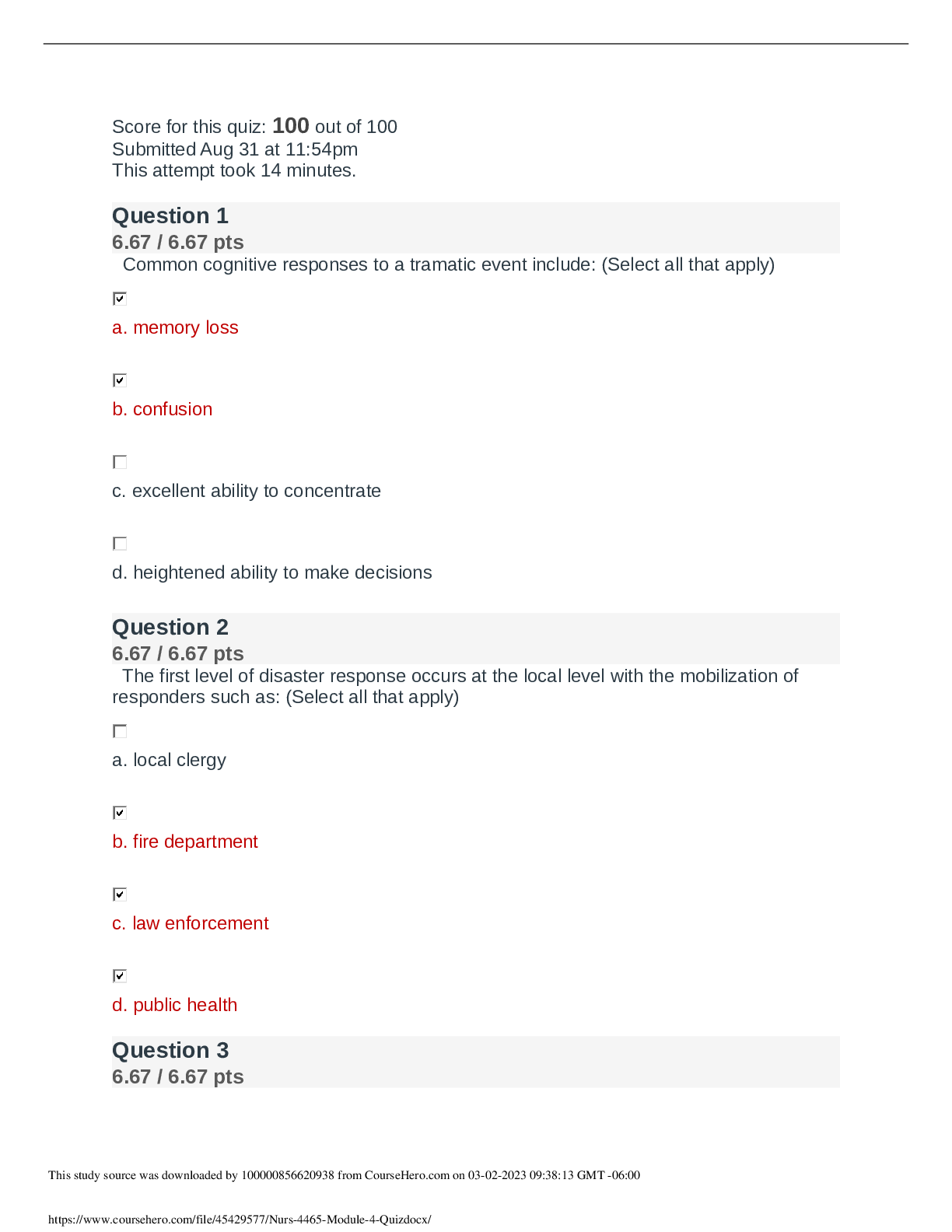
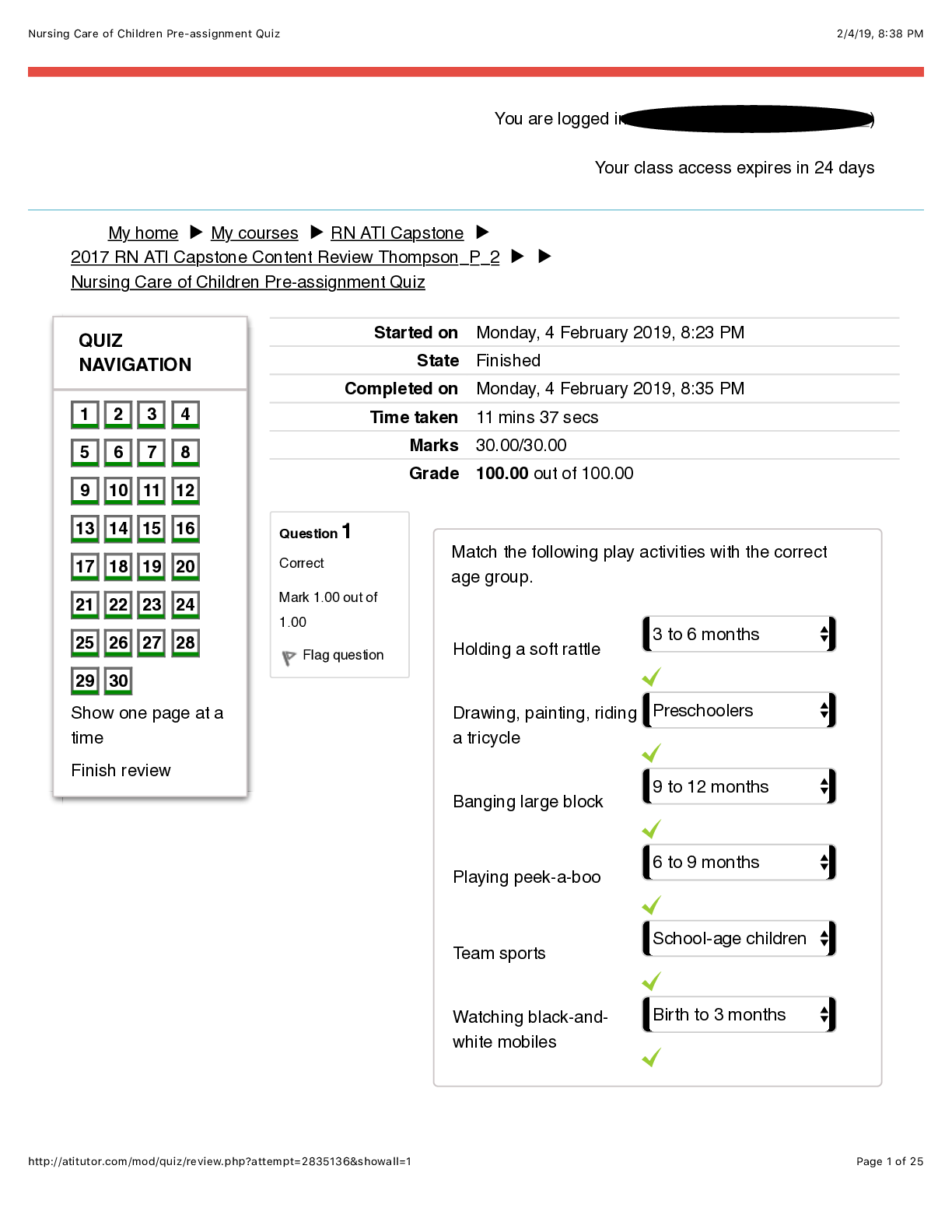
1. A patient asks a primary care NP whether over-the-counter drugs are safer than prescription drugs. The NP should explain that over-the-counter drugs are: (Points : 2) generally safe when ... label information is understood and followed. safer because over-the-counter doses are lower than prescription doses of the same drug. less safe because they are not well regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). not extensively tested, so claims made by manufacturers cannot be substantiated. Question 2.2. A woman who is being treated with radiotherapy for breast cancer asks her primary care nurse practitioner (NP) about using dietary supplements to improve her chance of recovery. The NP should tell her that: (Points : 2) vitamin E is not harmful but has not been shown to change outcomes. no supplements have been shown to alter outcomes or response to therapy. folic acid and other B vitamins may improve ability to tolerate chemotherapy. vitamin C, taken at least 6 days per week, may lower her risk of cancer recurrence. Question 3.3. A patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus takes metformin (Glucophage) 1000 mg twice daily and glyburide (Micronase) 12 mg daily. At an annual physical examination, the BMI is 29 and hemoglobin A1c is 7.3%. The NP should: (Points : 2) begin insulin therapy. change to therapy with colesevelam (Welchol). add a third oral antidiabetic agent to this patient’s drug regimen. enroll the patient in a weight loss program to achieve better glycemic control. Question 4.4. A patient comes to the clinic to discuss weight loss. The primary care NP notes a BMI of 32 and performs a health risk assessment that reveals no obesity-related risk factors. The NP should recommend: (Points : 2) orlistat (Xenical). surgical intervention. changes in diet and exercise. changes in diet and exercise along with short-term phentermine. Question 5.5. Which of the following statements is true about the prescribing practices of physicians? (Points : 2) Older physicians tend to prescribe more appropriate medications than younger physicians. Antibiotic medications remain in the top five classifications of medications prescribed. Most physicians rely on a “therapeutic armamentarium” that consists of less than 100 drug preparations per physician. The dominant form of drug information used by primary care physicians continues to be that provided by pharmaceutical companies. Question 6.6. A primary care NP is aware that many patients in the community use herbal remedies to treat various conditions. The NP understands the importance of: (Points : 2) learning about the actions, uses, doses, and toxicities of these agents. prescribing these agents when possible to ensure safe dosing. counseling patients to stop using herbal products to avoid toxic side effects. teaching patients that these products are unregulated and unsafe to use. Question 7.7. A patient who is at risk for DVT tells the primary care NP she has just learned she is pregnant. The NP should expect that this patient will use which of the following anticoagulant medications? (Points : 2) Aspirin Heparin Dabigatran Warfarin Question 8.8. As primary care nurse practitioners (NPs) continue to develop their role as prescribers of medications, it will be important to: (Points : 2) attain the same level of expertise as physicians who currently prescribe medications. learn from the experiences of physicians and develop expertise based on evidence-based practice. maintain collaborative and supervisorial relationships with physicians who will oversee prescribing practices. develop relationships with pharmaceutical representatives to learn about new medications as they are developed. Question 9.9. A patient with a previous history of myocardial infarction (MI) who takes nitroglycerin for angina develops hypertension. The primary care NP is considering ordering an ACE inhibitor. Preliminary laboratory tests reveal decreased renal function. The NP should: (Points : 2) begin therapy with a low-dose ACE inhibitor. choose an ARB instead. add a low-dose thiazide diuretic to the drug regimen. order a renal perfusion study before starting treatment. Question 10.10. A 40-year-old woman tells the primary care nurse practitioner (NP) that she does not want more children and would like a contraceptive. She does not smoke and has no personal or family history of cardiovascular disease. She has frequent tension headaches. For this patient, the NP should prescribe: (Points : 2) condoms. tubal ligation. monophasic combined oral contraceptive pill (COCP). low-estrogen COCP. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 4 pages
Instant download
.png)
Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 27, 2020
Number of pages
4
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 27, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
32



.png)



.png)


















 – CHAMBERLAIN COLLEGE OF NURSING.png)



 – Chamberlain College of Nursing.png)





