*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > South University, Savannah NSG 6320 AGNP BOARD EXAM QUESTIONS Hematology Assessment Already Passed (All)
South University, Savannah NSG 6320 AGNP BOARD EXAM QUESTIONS Hematology Assessment Already Passed
Document Content and Description Below
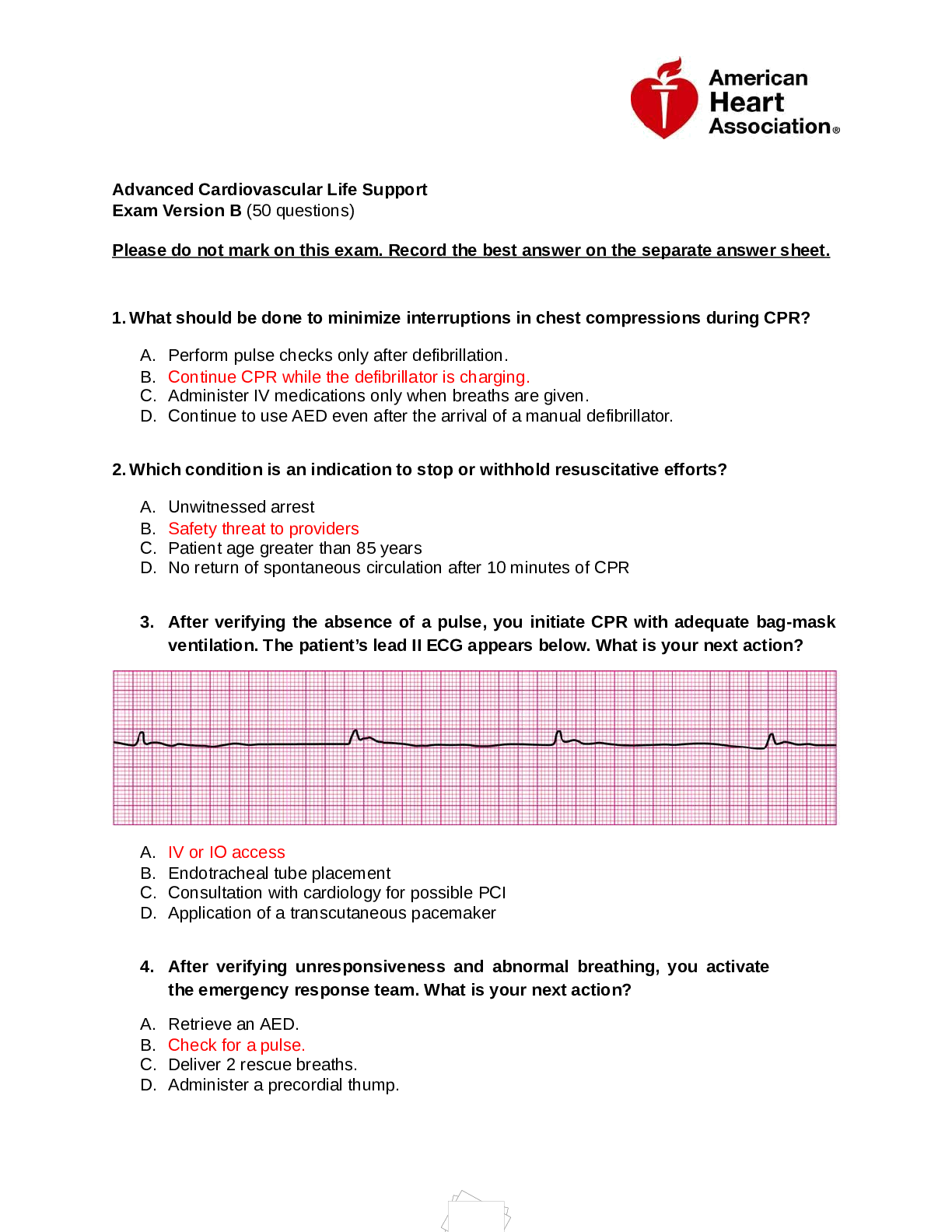
AGNP BOARD EXAM QUESTIONS Hematology Assessment ( 24 Questions) Question: If a newborn develops a cephalohematoma, the newborn is at an increased risk for: infection. jaundice. Correct caput succ... edaneum. erythema toxicum. Explanation: Cephalohematomas are characterized by bleeding between the bone and the periosteum. Because of breakdown of the red blood cells within a hematoma, the infants are at greater risk for jaundice. They do not increase the risk for infections. Caput succedaneum is an edematous area on the head from pressure against the cervix. Erythema toxicum is a benign rash of unknown cause that consists of blotchy red areas. Question: A twelve-month-old was recently diagnosed with Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS). The mother asks the nurse practitioner: "How could my child have acquired AIDS?" The best response from the nurse practitioner should be that: "Children under two years of age usually acquire AIDS: by sharing car seats with an HIV infected toddler." because the child may have been sexually abused by someone who was HIV positive." perinatally through an HIV infected mother." Correct through casual contact with an HIV infected individual in a day care center." Explanation: Perinatally is the acquired mode for infants. Children usually over five years of age acquire AIDS through sexual abuse. HIV does not survive in the environment and there is no evidence to date to support the fact That AIDS is acquired through casual contact or by sharing car seats with HIV infected seats. Question: Which ethnicity is associated with glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase (G-6-PD) deficiency? American Indian black Correct Asian Hispanic Explanation: Glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase (G-6-PD) deficiency is a condition in which red blood cells break down when the body is exposed to certain drugs (aspirin, antimalaria drugs) or the stress of infection. G-6-PD is most prevalent in people of Mediterranean and African descent, and specifically common in Saudi Arabian, African, and black patients. This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 04-22-2022 05:28:26 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/64924179/AGNP-BOARD-EXAM-QUESTIONS-Hematology-Assessmentdocx/ Question: The blood lead level that requires further testing and monitoring in children is: 3 mcg/dL. 5 mcg/dL. Correct 7 mcg/dL. 9 mcg/dL. Explanation: In children, a blood lead level of 5 mcg/dL or 0.24 µmol/L or greater requires further testing and monitoring. The source of lead must be found and removed. A lead level greater than 45 mcg/dL or 2.17 µmol/L in a child's blood usually indicates the need for chelation. Question: Which of the following foods contains the LEAST amount of folic acid? Dairy Correct Green leafy vegetables Liver Fruits Explanation: Dairy foods such as cheese, milk and yogurt do not contain folic acid unless they have been specifically fortified to include this vitamin. Foods high in folic acid include green leafy vegetables, meat from animal sources, fruits, nuts, liver, and foods containing yeast. Question: Which assessment finding is consistent with pernicious anemia? Facial palsy Nuchal rigidity Priapism Peripheral neuropathy Correct Explanation: Pernicious anemia is associated with B12 deficiency. Vitamin B12 deficiency may lead to nerve damage attributable to pathology in the peripheral and optic nerves, posterior and lateral columns of the spinal cord (subacute combined degeneration), and in the brain. This can cause tingling and numbness in the hands and feet, muscle weakness, and loss of reflexes. Patients may feel unsteady and experience equilibrium problems and ataxia. Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause weakened bones and may lead to hip fractures. Vitamin B 12 deficiency does not cause facial palsy; however, vitamin B12 has been used in the treatment of Bell's Palsy. Nuchal rigidity and priapism are not associated with vitamin B12 deficiency. Question: The infant with the lowest risk of developing elevated levels of bilirubin is the one who: is feeding poorly or whose feedings are delayed for several hours. has developed a cephalhematoma. is the second birth to an Rh negative mother. This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 04-22-2022 05:28:26 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/64924179/AGNP-BOARD-EXAM-QUESTIONS-Hematology-Assessmentdocx/ breast feeds within the first hour of life. Correct Explanation: The infant who is fed early will be less likely to retain meconium and reabsorb bilirubin from the intestines back into the circulation. Additionally, lack of adequate intestinal flora hinders excretion of conjugated bilirubin so by feeding soon after birth, this speeds up the development of bacteria and creation of good intestinal flora. The other choices are all examples of situations that increase the risk for jaundice in the newborn. Question: Patients who develop pica have a deficiency in: folic acid. lead. magnesium. iron. Correct Explanation: Pica is characterized by an appetite for substances that are nonnutritive, such as ice, starch, or clay. This finding is associated with iron deficiency anemia. Note: Pica is considered an eating disorder in the DSM-5 criteria. Question: Which of the following symptoms is associated with iron deficiency anemia? Atrophic glossitis Correct Oral candida Melanoglossia Transient lingual papillitis Explanation: Atrophic glossitis occurs when a large number of papillae are lost, resulting in changes to the tongue’s color and texture. This type of glossitis typically turns the tongue dark red and is a symptom of iron deficiency anemia. Oral candida is a white paste on the tongue. The most common type of oral candida is Candida albicans fungus. Melanoglossia is a medical condition in which the tongue becomes blackened. This is usually caused by a bacterial infection or allergic reaction. Transient lingual papillitis is a common painful inflammatory condition affecting one or several fungiform papillae on the tongue. Question: Folic acid deficiency is an example of which type of anemia? Normocytic Macrocytic Correct Microcytic Hemolytic Explanation: Macrocytic anemia is characterized by larger than normal red blood cells. Vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies are examples of macrocytic anemias. Normocytic anemia is caused by acute blood loss, chronic disease, or failure to produce adequate red blood This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 04-22-2022 05:28:26 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/64924179/AGNP-BOARD-EXAM-QUESTIONS-Hematology-Assessmentdocx/ cells. Chronic renal failure (decreased production of erythropoietin) or liver failure causes normocytic anemia. Microcytic anemia usually occurs in iron deficiency anemia. Hemolytic anemia can be autoimmune, hereditary or mechanical. It can result (because of cell fragmentation) in a microcytic anemia, a normochromic anemia, or (because of premature release of immature red blood cells from the bone marrow), a macrocytic anemia. Question: Which situation would put the patient at the LEAST risk for developing lead toxicity? Being a plumber Residing in a home built before 1988 Correct Having a history of gout Living near a busy highway. Explanation: Risks for lead toxicity may include an occupation as a plumber, having a history of gout, living near a busy highway or hazardous waste dump, and residing in a home built before 1978. Question: Which patient is most likely to carry the alpha thalassemia anemia trait? A 45-year-old black man A 32-year-old Filipino man Correct A 24-year-old Italian woman A 19-year-old Greek woman Explanation: Alpha thalassemia minor is a disease that occurs among the Asian population. Beta thalassemia is commonly found in patients of Mediterranean descent (Italian, Greek). Question: Hemophilia type A is a deficiency of factor: VIII. Correct IX. XI. IV. Explanation: Hemophilia is an inherited disorder in which a person lacks adequate clotting factors. Type A is a lack of clotting factor VIII (90% of cases). Type B is a lack of clotting factor IX. Type C is a lack of clotting factor XI. Question: A child with sickle cell anemia presents with a history of sudden onset of rapid breathing with left upper quadrant (LUQ) tenderness upon palpation. The child is most likely experiencing a (an): aplastic crisis. sequestration crisis. Correct vaso-occlusive crisis. This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 04-22-2022 05:28:26 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/64924179/AGNP-BOARD-EXAM-QUESTIONS-Hematology-Assessmentdocx/ hemarthrosis crisis. Explanation: Sequestration occurs when RBC's are trapped or sequestered in the spleen causing it to enlarge; therefore, there would be tenderness in the LUQ and the child may have tachypnea as well. Aplastic crisis occurs when RBC production is decreased. Symptoms include pallor, decreased hemoglobin and decreased RBCs. Vaso-occlusion usually involves pain but no increase in spleen size. Hemarthrosis is usually seen in hemophilia and where there is joint involvement, but not spleen involvement. Question: The nurse practitioner differe [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 8 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 22, 2022
Number of pages
8
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 22, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
53

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)