*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > South University, Savannah NSG 6320 AGNP BOARD EXAM QUESTIONS CARDIOVASCULAR PRESCRIBING Already Pas (All)
South University, Savannah NSG 6320 AGNP BOARD EXAM QUESTIONS CARDIOVASCULAR PRESCRIBING Already Passed
Document Content and Description Below
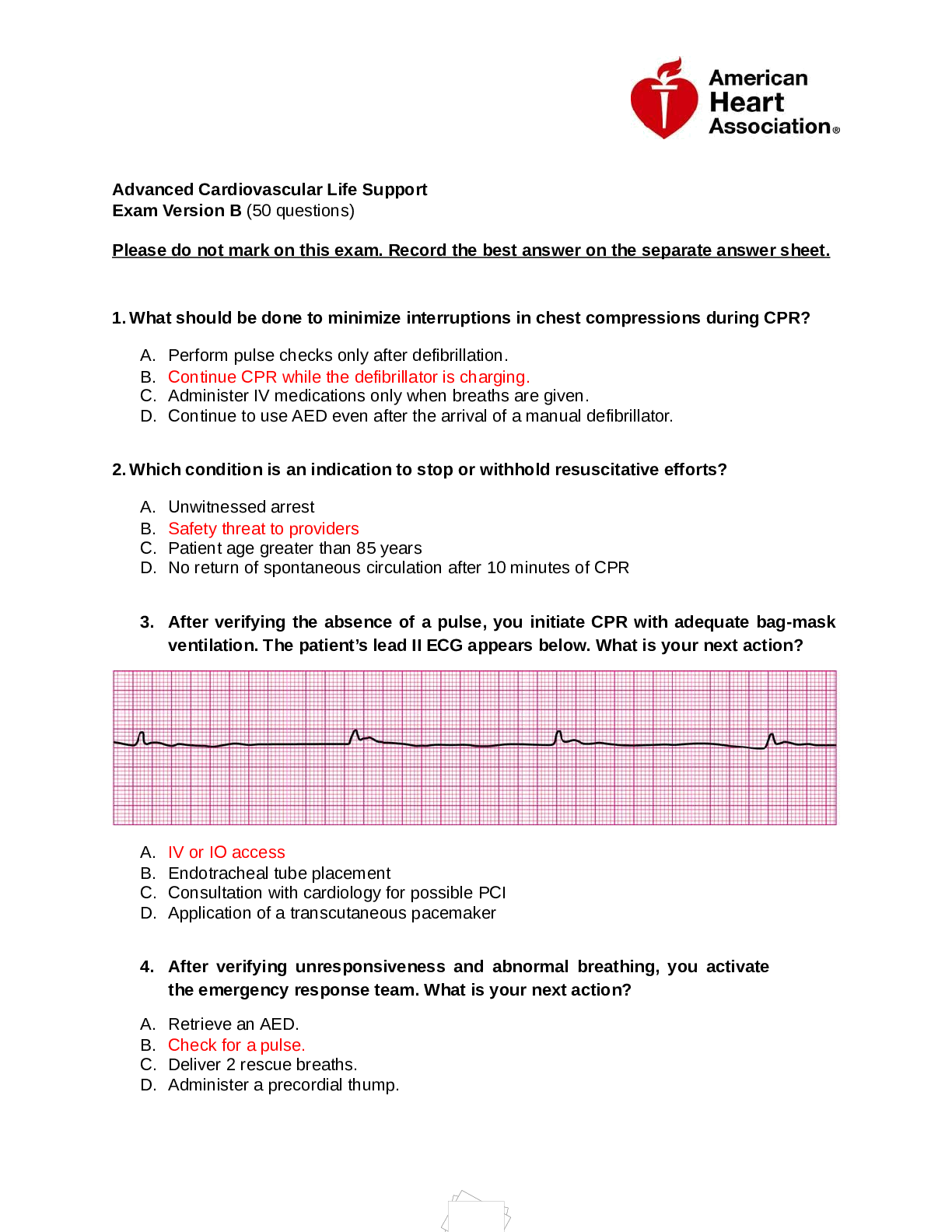
AGNP BOARD EXAM CARDIOVASCULAR PRESRIBING (113 QAND A) Question: Signs and symptoms of digitalis toxicity include: constipation and muscle spasms. bradycardia and tinnitus. headache and dizziness... . blurred vision and persistent diarrhea. Correct Explanation: Signs and symptoms of digitalis toxicity include: confusion, irregular pulse, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fast heart beat, and visual changes (blurred vision, blind spots, greenyellow color disturbances, halo effect). Regardless of route of administration, digoxin levels should be checked at 12-24 hours after the last dose. However, depending on the clinical situation, wait at least 6-8 hours after the last dose to check levels. Question: A side effect of beta-blockers that is more common in children than adults is: decreased appetite. muscle weakness. vivid dreams. a cough that produces mucus. Correct Explanation: Side effects of beta-blockers that are more common in children than adults may include a mucusproducing cough, difficulty breathing, or tightness in the chest. Beta-blockers are not recommended as initial therapy in children due to potential adverse outcomes including increased bronchial obstruction and airway reactivity in children with asthma. Question: Spironolactone (Aldactone) is highly protein bound and has a duration of: 6 hours. 12 hours. 24 hours. 48 hours. Correct Explanation: Spironolactone (Aldactone) is greater than 90% protein bound, has a half-life elimination of 1.4 hours and a duration of 48-72 hours. It is classified as an aldosterone receptor antagonist. This class blocks the effects of aldosterone, which increases sodium reabsorption by the kidneys. Question: Nonselective beta-blockers block the stimulation of: beta-1 receptors in the heart. beta-2 receptors in the lungs. both beta-1 receptors in the heart and beta-2 receptors in the lungs. Correct neither beta-1 receptors in the heart nor beta-2 receptors in the lungs. Explanation: Nonselective beta-blockers (i.e., propranolol [Inderal]) block the stimulation of both beta-1 receptors in the heart and beta-2 receptors in the lungs. Selective beta-blockers (i.e. metoprolol [Lopressor]) specifically block beta-1 receptors, but may also block beta-2 receptors at higher doses. Because they also block beta-2 receptors in the lungs, nonselective beta-blockers are contraindicated in patients with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Question: Dabigatran (Pradaxa), an anticoagulant, is also classified as a: direct factor Xa inhibitor. direct thrombin inhibitor. Correct indirect thrombin inhibitor. factor V inhibitor. Explanation: Dabigatran (Pradaxa) is a direct thrombin inhibitor (DTI). Medications in this class inactivate circulating and clotting thrombin (factor IIa). They prevent thrombin (central to the generation of a thrombus) from attaching fibrinogen to fibrin. DTIs bind directly to thrombin and do not require a cofactor such as antithrombin to exert their effect. They can inhibit both soluble thrombin and fibrin-bound thrombin. Key advantages of using DTIs instead of heparin is that they: produce a more predictable anticoagulant effect due to their lack of binding to other plasma proteins; exert an antiplatelet effect; and do not cause immune-mediated thrombocytopenia. Question: The brand name for candesartan cilexetil is: Atacand. Correct Avandia. Benicar. Cozaar. Explanation: The brand name for candesartan cilexetil is Atacand. The generic name for Avandia is rosiglitazone; Benicar is olmesartan medoxomil (an ARB); Cozaar is losartan. Candesartan, olmesartan and losartan are classified as angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) and are used in the treatment of hypertension. Notice that they all end in "sartan." Rosiglitazone is a thiazolidinedione and is used in the treatment of diabetes. Question: Gemfibrozil (Lopid), for the treatment of hypertriglyceridemia, is classified as a: bile acid sequestrant. nicotinic acid. fibric acid. Correct statin. Explanation: Gemfibrozil (Lopid) is a fibric acid. It is indicated in the treatment of hypertriglyceridemia and mixed dyslipidemia. Fibric acid derivatives, also known as fibrates, are the recommended treatment for very high triglyceride levels (>500 mg/dL). Fibrates lower serum triglyceride levels by reducing the liver's production of VLDL (triglyceride-carrying particle circulating in the blood) and by speeding up the removal of triglycerides from the blood. Gemfibrozil should not be used concurrently with statins. Question: In patients with normal renal function, the diuretic that has the greater antihypertensive effect is: osmotic diuretics. thiazide diuretics. Correct loop diuretics. potassium-sparing diuretics. Explanation: Among patients with normal renal function, thiazide diuretics, particularly chlorthalidone (Thalitone), have a greater antihypertensive effect than the loop diuretics. This may be related to the longer duration of action of thiazides compared to most loop diuretics. Diuretics lower blood pressure, at least initially, by inducing sodium and fluid loss. Other thiazide diuretics include hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide) and methyclothiazide. Question: An adverse effect of statin therapy for the treatment of hyperlipidemia is: hypertension. myalgia. Correct hypoglycemia. edema. Explanation: Statins may cause myalgia. The pain may be experienced as a soreness, fatigue or weakness in the muscles. The pain can be a mild discomfort, or it can be severe enough to make daily activities difficult. Other common side effects include diarrhea, arthralgia and nasopharyngitis. Question: Nitroglycerin sublingual (Nitrostat) tablets should be stored: in a dark bottle, with the patient carrying all tablets at all times. in a dark container in the refrigerator, with only a small quantity kept with the patient. Correct in a tightly capped medicine bottle at room temperature. in a tightly sealed bag or container in a purse or wallet. Explanation: Nitroglycerin sublingual (Nitrostat) tablets are both heat- and light-sensitive. They should be stored in a tightly capped dark bottle in the refrigerator. Only a small supply should be carried by the patient. Nitroglycerin tablets in an opened bottle should be discarded after 12 months. Question: Patients taking warfarin (Coumadin) therapy should: increase intake of vitamin K-enriched foods. avoid intake of vitamin K-enriched foods. maintain a consistent intake of vitamin K-enriched foods. Correct decrease intake of vitamin K-enriched foods. Explanation: Patients who are anticoagulated with warfarin (Coumadin) generally are sensitive to fluctuations in vitamin K intake. Adequate INR control requires a consistent intake of vitamin K. The goal of monitoring vitamin K intake is to maintain a moderate, constant level of intake rather than to eliminate vitamin K from the diet. Reducing vitamin K intake can cause the INR to increase, and increasing vitamin K can cause the INR to decrease, making it more difficult to control. Question: Non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers (i.e. verapamil) may be safely used in patients with: heart failure. bradycardia. second-degree AV block. chronic stable angina. Correct Explanation: Non-dihydropyridine CCBs (non-DHP CCB; i.e. verapamil [Calan] and diltiazem [Cardizem]) have negative chronotropic and inotropic effects. Therefore, they slow down heart rate and decrease force of ventricular contractions. Non-DHP CCBs are contraindicated in patients with heart failure who have reduced ejection fraction, sick sinus syndrome, and second- or thirddegree atrioventricular block. Since non-DHP CCBs increase myocardial blood flow by dilating coronary arteries, they are beneficial in patients with chronic stable angina. Additionally, they can be given for rate control (tachycardia) or for the control of angina (chronic, stable) when left ventricular systolic function is normal. In general, the long-acting form of Non-DHP CCBs are recommended over the short-acting forms. Question: The generic name for Lopressor is: atenolol. metoprolol tartrate. Correct carvedilol. bisoprolol. Explanation: The generic name of Lopressor is metoprolol tartrate. The brand name for atenolol is Tenormin; carvedilol is Coreg; and bisoprolol is Zebeta. All of these drugs are classified as beta-blockers and end in "lol". Question: A patient is taking isosorbide dinitrate (Isordil) at 8 am, 2 pm and 9 pm and reports that the medication is no longer effective. The nurse practitioner knows that: this is the correct time interval and the dose should be increased. the dosing interval should be chan [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 47 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 22, 2022
Number of pages
47
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 22, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
73

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)