*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > South University, Savannah NSG 6320 AGNP BOARD EXAM QUESTIONS Health Promotion Assessment Already Pa (All)
South University, Savannah NSG 6320 AGNP BOARD EXAM QUESTIONS Health Promotion Assessment Already Passed
Document Content and Description Below
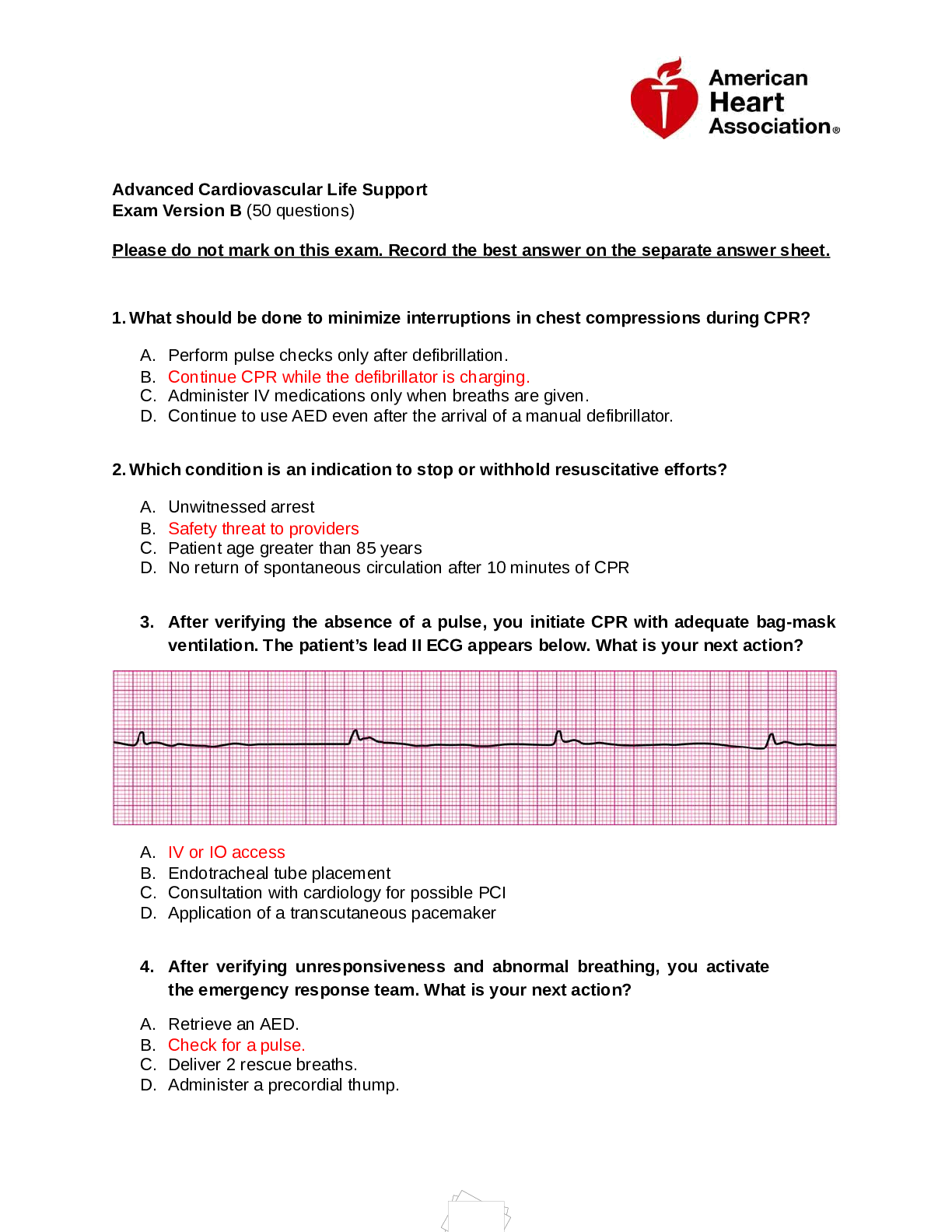
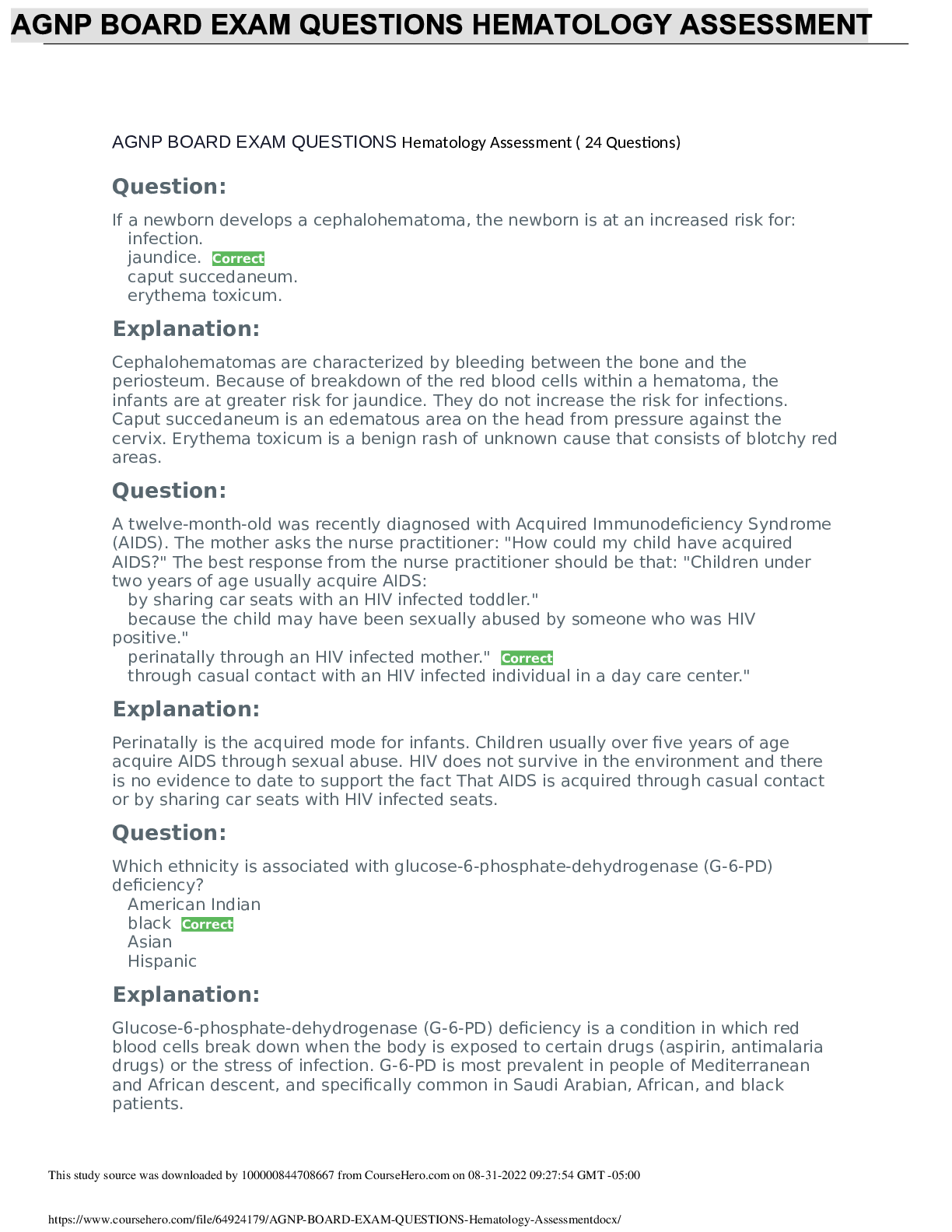
AGNP BOARD EXAM QUESTIONS Health Promotion Assessment (51 Questions) Question: According to the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, older adults should be screened for colorectal cancer with sigmo... idoscopy every: year. 2 years. 5 years. Correct 10 years. Explanation: The Task Force recommends screening with colonoscopy every 10 years, sigmoidoscopy every 5 years with high-sensitivity fecal occult blood tests (FOBTs) every 3 years, or FOBTs every year beginning age 50 years through age 75 years. Recommends against routine screening for adults ages 76 to 85 years, due to moderate certainty that the net benefit is small. Question: Which topic should be a priority when providing anticipatory guidance to an 8-year-old child? Screening for scoliosis Advising the parent to protect the child from sunburn with sunscreen Recommending that the child receive another varicella vaccine now Assessing child care arrangements for before and after school Correct Explanation: School age children may not want to go to daycare, but are not old enough to stay home unsupervised. Help the parent to problem solve. Scoliosis is screened in 10-12- year-old children. Applying sunscreen should start at an earlier age than 8 years. Varicella vaccine is first given between 12 and 15 months and repeated at 4-6 years (before entering elementary school - kindergarten). Question: All of the following strategies are useful for assessing older adults at high risk for falls except: reviewing the medication history. obtaining a functional history. assessing immunization history. Correct conducting an environmental assessment. Explanation: Strategies for assessing older adults at high risk for falls include: obtaining a detailed fall history, medication review, and history of relevant risk factors (such as acute and chronic medical problems ). Other assessments should include: gait, balance, mobility, and lower extremity joint function, neurologic function, lower extremity muscle strength, cardiovascular status, visual acuity, and examination of the feet and footwear . A functional and environmental assessment as well as implementing multifactorial / multicomponent interventions to address identified risks will help to prevent falls. Question: Higher level self-care functioning activities are referred to as: activities of daily living. instrumental activities of daily living. Correct necessary activities of daily living. required activities of daily living. Explanation: Activities of daily living (ADLs) consist of basic self-care abilities: bathing, dressing, toileting, transferring, continence, and feeding. Higher level functions are referred to as the instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs) and include: using the telephone, shopping, preparing food, laundry, and taking medicine. Question: Which of the following would help a 9-year-old develop a sense of industry? Providing large plastic blocks for him to build things Helping him make a collection of several objects Correct Encouraging running for short distances Explaining the workings of his heart Explanation: The school age child likes to collect things and keep them as memoirs. Large plastic blocks are characteristic of preschoolers and would not accomplish this task. Running short distances is a more appropriate activity for this child. Explaining how the heart works requires more cognitive abilities than a 9-year-old may have. Question: Which technique would be least effective in gaining the cooperation of a toddler during a physical exam? Tell the child that another child the same age was not afraid. Correct Allow the child to hold and touch the equipment when possible. Permit the child to sit on the parent's lap during the examination. Give the child immediate praise for holding still or doing what was asked. Explanation: Telling the child that another child the same age was not afraid would not be an effective technique as a toddler is unable to process that concept. The other choices are appropriate techniques. Question: The first sign of puberty in a male is: increased vertical height. a change in voice. testicular enlargement. Correct facial hair. Explanation: Puberty begins sexual maturity. It is a process that usually occurs between ages 10 and 14 for girls, and ages 12 and 16 for boys. It causes physical changes, and affects boys and girls differently. In boys, puberty usually begins with the testicles and penis getting bigger. Then hair grows in the pubic area and armpits. Question: At what age would a baby first be expected to locate an object hidden from view? At 4 months of age At 9 months of age Correct At 13 months of age At 20 months of age Explanation: Around 9 months of age, infants are first able to find an object hidden from view, also known as object permanence. The other choices are not age appropriate. Question: The 10 minute geriatric screener is a tool used to assess: smoking habits. alcohol consumption. functionality. Correct dementia. Explanation: The 10-Minute Geriatric Screener is a tool used for functional assessment in the older adult and assesses: vision, hearing, leg mobility, urinary incontinence, nutrition and weight loss, memory, depression, and physical disability. Question: Part of the nutritional assessment includes anthropometric measurements. These measurements include all of the following except: height and weight. blood pressure, pulse, and respiration. Correct body mass index (BMI). basal metabolic rate (BMR). Explanation: Anthropometric measurements are a set of noninvasive, quantitative techniques for determining an individual's body fat composition by measuring, recording, and analyzing specific dimensions of the body: height, weight, BMI, BMR, distribution of body fat, and skin fold thickness. Vital signs are considered physiologic measurements. Question: The first sign of puberty in females is: appearance of body odor. increased energy and appetite. occurrence of first menses. appearance of breast buds. Correct Explanation: Breast buds are the first sign of puberty in girls. Body odor comes later as the apocrine glands develop. Menses first occurs about 1 year following the appearance of breast buds. Increased energy and appetite do not relate to the signs of puberty. Question: Sarcopenia is: cancer of the muscle sheath. loss of lean body mass and stre [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 24 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 22, 2022
Number of pages
24
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 22, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
64

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)