Computer Networking > EXAM > Business Data Networks and Security, 11e (Panko) Chapter 4 Network Security (2019 Latest) Already Gr (All)
Business Data Networks and Security, 11e (Panko) Chapter 4 Network Security (2019 Latest) Already Graded {A+}
Document Content and Description Below
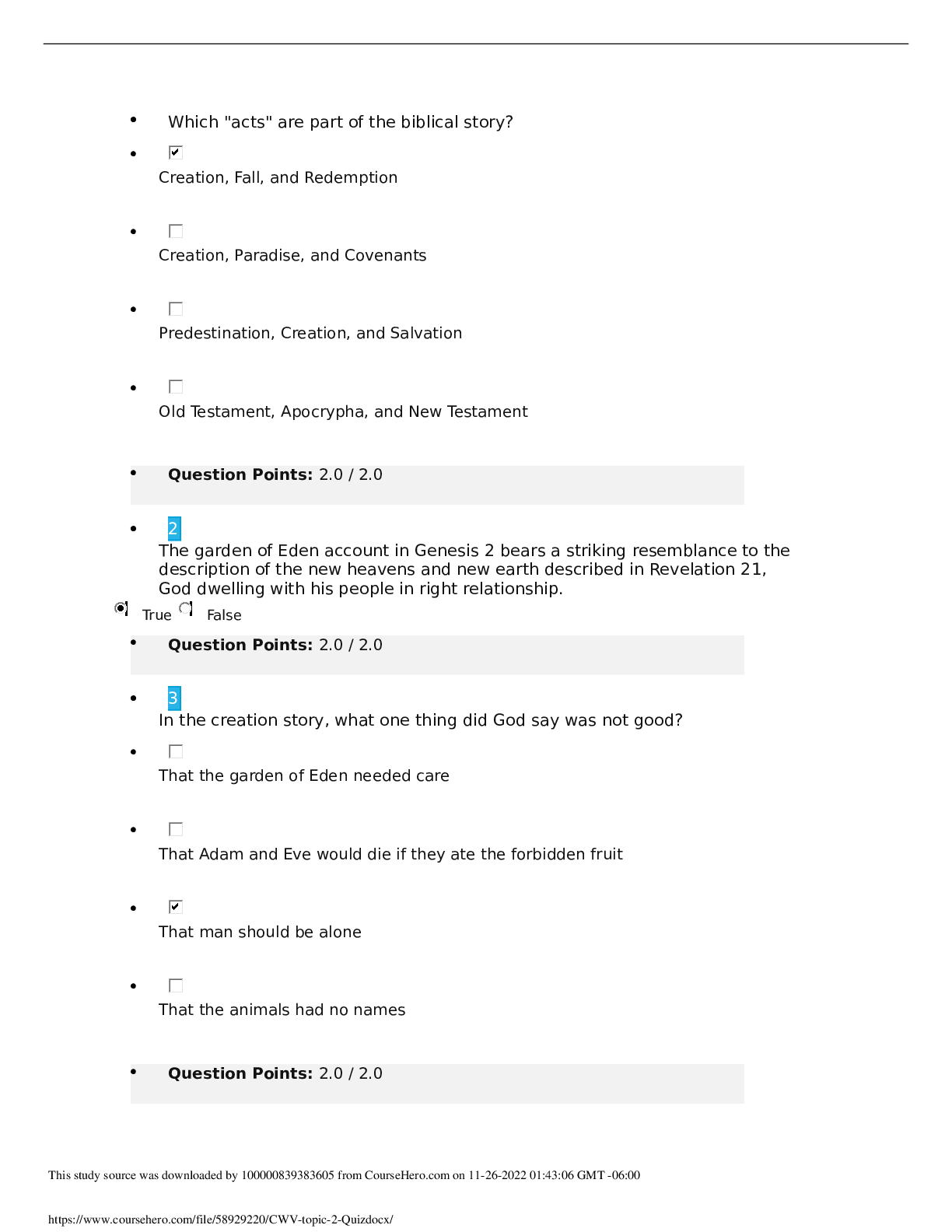
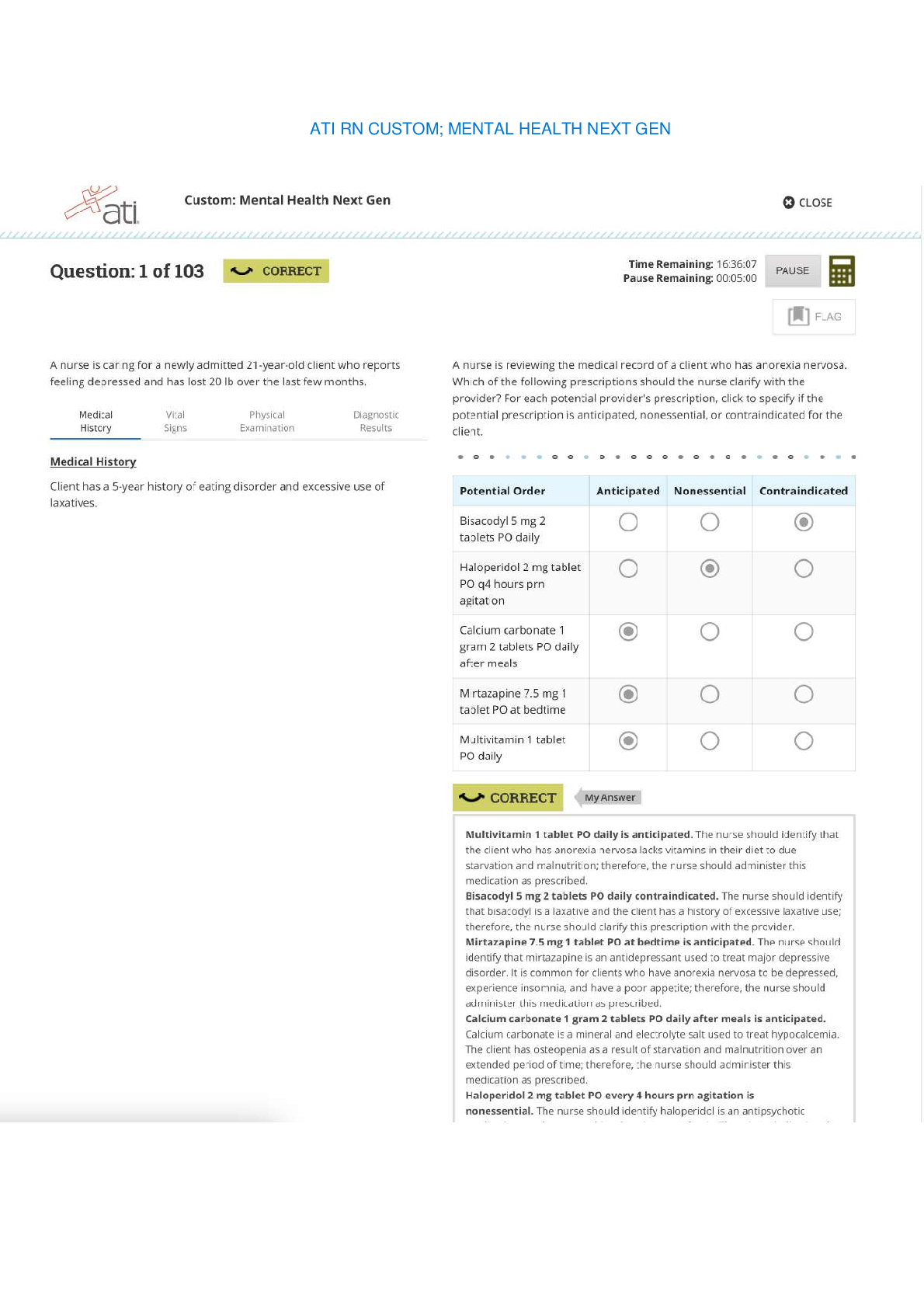
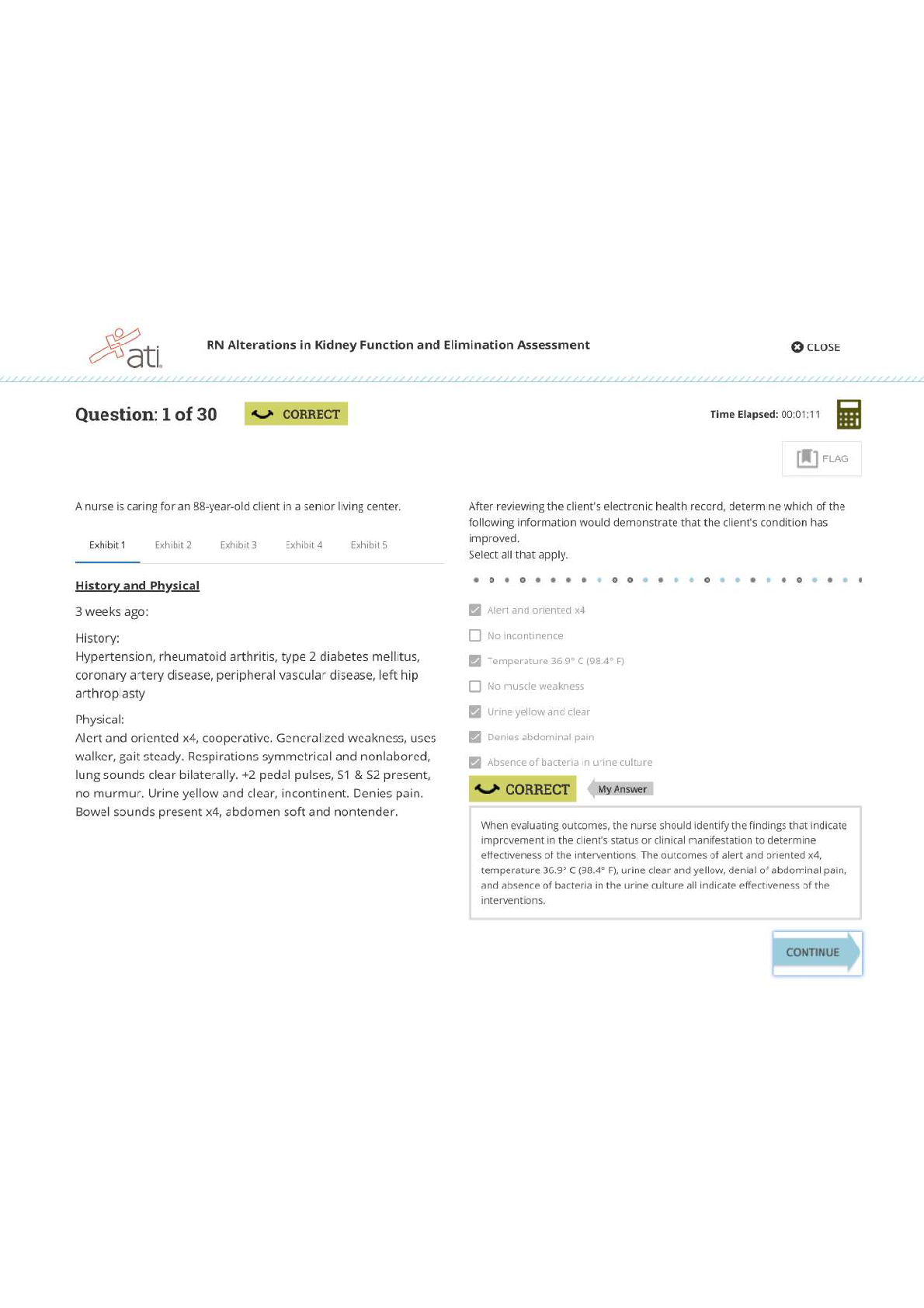
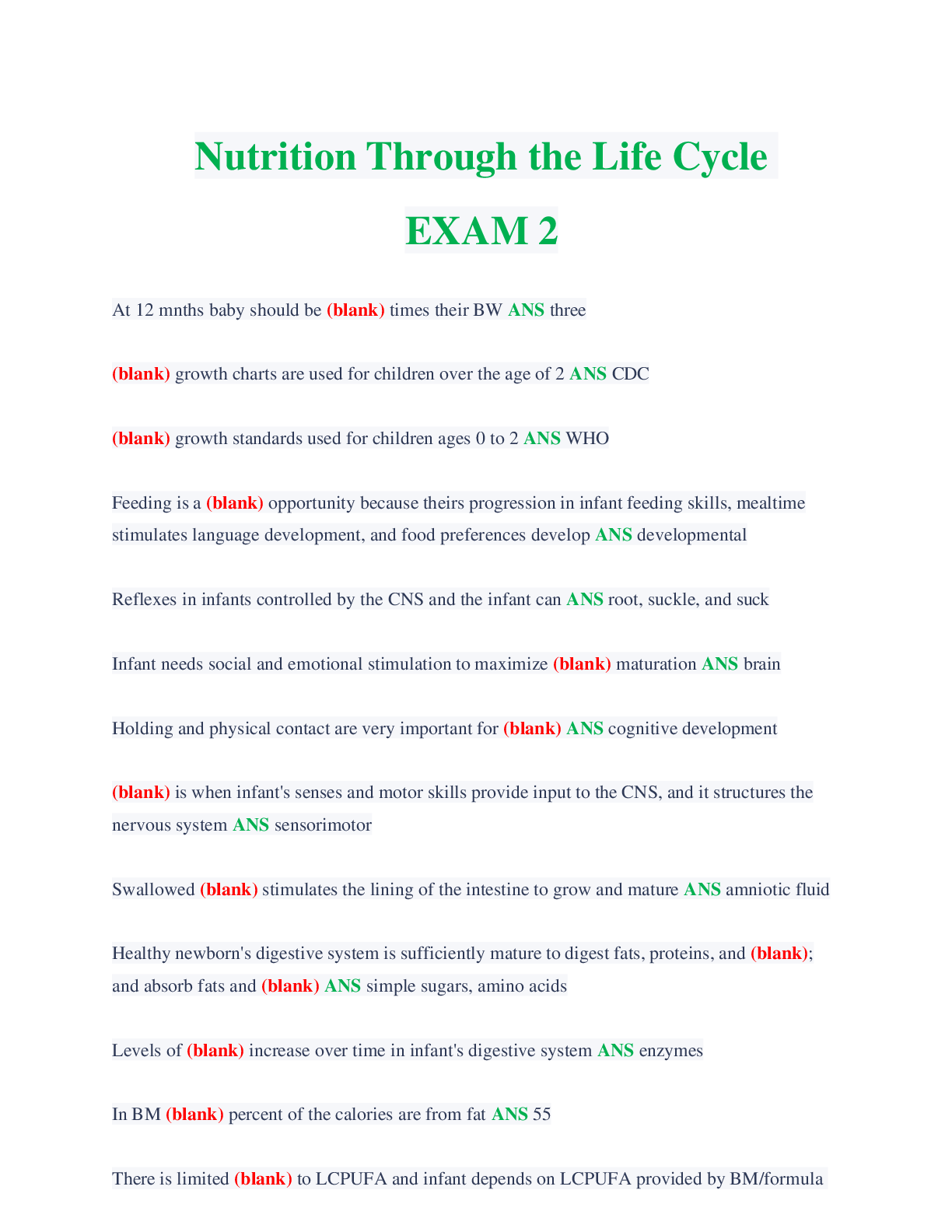
1) The Target attackers probably first broke into Target using the credentials of a(n) ________. A) low-level Target employee B) Target IT employee C) Target security employee D) employee in a fir... m outside Target Difficulty: Basic Question: 1a Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 2) How did the Target attackers obtain the stolen information? A) Directly from the POS terminals B) From the vendor service server C) From the POS software download server D) none of the above. Difficulty: Deeper Question: 1c Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 3) The Target attackers sold stolen card information to ________. A) crimeware shops B) card shops C) card counterfeiters D) all of the above Difficulty: Basic Question: 1c Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 4) Which of the following probably suffered the most financial damage from the Target breach? A) Target B) banks C) consumers D) retailers Difficulty: Basic Question: 2a Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 5) Which of the following were able to recoup most of the money they lost from Target? A) credit card companies B) retailers C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 2b Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 6) For consumers who suffered credit card fraud because of the Target breach and acted quickly, which of the following is true? A) They received no compensation. B) They received compensation from Target. C) The credit card companies did not charge them for fraudulent purchasers. D) The United States Treasury compensated them from an insurance fund. Difficulty: Basic Question: 2c Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 7) In ________ thinking, the opponent is primarily an intelligent attacker. A) networking B) security C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 3 Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 8) The general term for evil software is ________. A) virus B) worm C) malware D) all of the above Difficulty: Basic Question: 4a Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology9) ________ is the most frequent type of company attack. A) DoS B) Hacking C) Ransomware D) Malware Difficulty: Basic Question: 4b Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 10) ________ is the general name for a security flaw in a program. A) A virus B) Malware C) A security fault D) A vulnerability Difficulty: Basic Question: 5a Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 11) ________ is a flaw in a program that permits a specific attack or set of attacks. A) Malware B) A security error C) A vulnerability D) A security fault Difficulty: Basic Question: 5a Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 12) Users typically can eliminate a vulnerability in one of their programs by ________. A) installing a patch B) using an antivirus program C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Deeper Question: 5b Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 13) Vulnerability-based attacks that occur before a patch is available are called ________ attacks. A) indefensible B) stealth C) malware D) zero-day Difficulty: Basic Question: 5c Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 14) What kind of attack is most likely to succeed against a system with no technological vulnerabilities? A) malware B) social engineering C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 6a Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 15) A spear phishing attack is usually aimed at ________. A) an individual B) a group C) everyone D) all of the above Difficulty: Basic Question: 6c Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 16) ________ are full programs. A) Viruses B) Worms C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 7a Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 17) Which of the following attach themselves to other programs? A) viruses B) worms C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 7a Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 18) Viruses and worms propagate through ________. A) social engineering B) exploiting vulnerabilities C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 7b Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 19) Which of the following sometimes uses direct propagation between computers? A) viruses B) worms C) Trojan horses D) downloaders Difficulty: Basic Question: 7c Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 20) Which of the following can spread very rapidly? A) directly-propagating viruses B) directly-propagating worms C) both A and B Difficulty: Basic Question: 7d Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 21) Malware programs that masquerade as system files are called ________. A) viruses B) scripts C) root malware D) Trojan horses Difficulty: Basic Question: 7e Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 22) Trojan horses can spread by ________. A) e-mailing themselves to victim computers B) directly propagating to victim computers C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Deeper Question: 7f Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 23) Pieces of code that are executed after the virus or worm has spread are called ________. A) vulnerabilities B) exploits C) compromises D) payloads Difficulty: Basic Question: 8a Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 24) In a ________ attack, the attacker encrypts some or all of the victim's hard drive. A) virus B) DoS C) ransom D) lock Difficulty: Basic Question: 8b Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 25) ________ is the general name for malware on a user's PC that collects sensitive information and sends this information to an attacker. A) A keystroke logger B) Anti-privacy software C) Spyware D) Data mining software Difficulty: Deeper Question: 8c Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 26) ________ is a program that can capture passwords as you enter them. A) A keystroke logger B) Data mining software C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 8d Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 27) In which type of attack does the attacker gather extensive sensitive personal information about its victim? A) identity theft B) credit card number theft C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 8e Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 28) Which is more harmful to the victim? A) identity theft B) credit card number theft C) both A and B are about equally harmful Difficulty: Basic Question: 8f Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 29) Hacking is defined as using a computer resource without authorization or in excess of authorization. Difficulty: Deeper Question: 9a Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 30) Which of the following meets the definition of hacking? A) to intentionally use a computer resource without authorization B) to intentionally use a computer on which you have an account but use it for unauthorized purposes C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 9b Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 31) If you see a username and password on a Post-It note that anyone can see on a monitor, is it hacking if you use this information to log in? A) yes B) no C) We cannot say from the information given. Difficulty: Basic Question: 9b Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 32) You accidentally discover that you can get into other e-mail accounts after you have logged in under your account and only spend a few minutes looking at another user's mail. Is that hacking? A) yes B) no C) We cannot say from the information given. Difficulty: Deeper Question: 9c Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 33) You click on a link expecting to go to a legitimate website but are directed to a website that contains information you are not authorized to see. You exit without looking around. is that hacking? A) yes B) no C) We cannot say from the information given. Difficulty: Deeper Question: 9d Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 34) You are concerned with the security of a site you use and run a vulnerability test against it. The test reveals a security threat. Is this hacking? A) yes B) no C) We cannot say from the information given. Difficulty: Deeper Question: 9d Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 35) DoS attacks attempt to ________. A) hack a computer B) reduce the availability of a computer C) steal information from a computer D) delete files on a computer Difficulty: Basic Question: 10a Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 36) In a DDoS attack, a ________ sends messages directly to the victim. A) botmaster B) bot C) command and control server D) all of the above Difficulty: Deeper Question: 10b Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 37) Attack programs that can be remotely controlled by an attacker are ________. A) bots B) sock puppets C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 10c Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 38) In distributed DoS attacks, the attacker sends messages directly to ________. A) bots B) the intended victim of the DoS attack C) a DOS server D) none of the above Difficulty: Deeper Question: 10e Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 39) Which of the following can be upgraded after it is installed on a victim computer (choose the most specific answer)? A) Trojan horses B) bots C) viruses D) worms Difficulty: Basic Question: 10f Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 40) Advanced persistent threats are ________. A) inexpensive for the attacker B) extremely dangerous for the victim C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 11a Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 41) ________ attacks typically extend over a period of months. A) DDoS B) Malware C) APT D) Spear phishing Difficulty: Basic Question: 11b Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 42) Who mounts APTs today? A) national governments B) cybercriminals C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Deeper Question: 11d Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 43) What type of attacker are most attackers today? A) disgruntled employees and ex-employees B) career criminals C) hackers motivated by a sense of power D) cyberterrorists Difficulty: Basic Question: 12a Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 44) ________ attackers are often well-funded. A) Disgruntled employee B) Cybercriminal C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 12b Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 45) Employees often attack ________. A) for revenge B) for money C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 13a Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 46) Why are employees especially dangerous? A) They are technically sophisticated. B) They are trusted. C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Deeper Question: 13b Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 47) Who are the most dangerous types of employees? A) financial employees B) manufacturing employees C) IT security employees D) former employees Difficulty: Basic Question: 13c Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 48) In general, what should an employer do whenever an employee leaves the firm? A) Their accounts should be disabled instantly B) They should be given no prior notice that they are being released C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Deeper Question: 13e Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 49) In terms of security thinking, "insiders" include ________. A) employees B) many contractors working for the company C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 13f Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 50) Cyberwar attacks are made by ________. A) major cybercriminal gangs B) national governments C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 15a Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 51) In general, what type of attackers do the most damage? A) criminal attackers B) hackers driven by curiosity C) employees and ex-employees D) national governments Difficulty: Basic Question: 15b Objective: Describe the threat environment. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 52) Using encryption, you make it impossible for attackers to read your messages even if they intercept them. This is ________. A) authentication B) confidentiality C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 16a Objective: Explain how to protect dialogues cryptographically. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 53) A specific encryption method is called a ________. A) code B) schema C) key method D) cipher Difficulty: Deeper Question: 16b Objective: Explain how to protect dialogues cryptographically. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 54) In encryption, what must be kept secret? A) the cipher B) the key C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Deeper Question: 16c Objective: Explain how to protect dialogues cryptographically. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 55) In most encryption, keys must be at least ________ long to be considered safe. A) 128 bits B) 128 bytes C) 1,280 bits D) 1,280 bytes Difficulty: Deeper Question: 16d Objective: Explain how to protect dialogues cryptographically. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 56) Electronic signatures provide message-by-message ________. A) authentication B) confidentiality C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Deeper Question: 17a Objective: Explain how to protect dialogues cryptographically. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 57) Electronic signatures also provide ________ in addition to authentication. A) message integrity B) message encryption C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Deeper Question: 17a Objective: Explain how to protect dialogues cryptographically. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 58) Secured packets typically receive ________. A) confidentiality B) authentication C) message integrity D) all of the above Difficulty: Basic Question: 17b Objective: Explain how to protect dialogues cryptographically. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 59) The messages of VPNs ________. A) share the same transmission lines used by other VPNs B) are encrypted C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Deeper Question: 18a Objective: Explain how to protect dialogues cryptographically. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 60) SSL/TLS is used for ________. A) Web applications B) almost all applications C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Deeper Question: 18b Objective: Explain how to protect dialogues cryptographically. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 61) Using SSL/TLS for Web applications is attractive because SSL/TLS ________. A) is essentially free to use B) offers the strongest possible cryptographic protections C) both A and B Difficulty: Basic Question: 18b Objective: Explain how to protect dialogues cryptographically. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 62) Requiring someone prove his or her identity is ________. A) confidentiality B) authentication C) authorization D) both B and C Difficulty: Basic Question: 19a Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 63) In authentication, the ________ is the party trying to prove his or her identity. A) supplicant B) verifier C) true party D) all of the above Difficulty: Deeper Question: 19b Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 64) In authentication, ________ are the general name for proofs of identity. A) credentials B) authorizations C) digital certificates D) all of the above Difficulty: Basic Question: 19c Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 65) The supplicant claims to be ________. A) the true party B) an impostor C) either A or B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 19d Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 66) The supplicant is ________. A) the true party B) an impostor C) either A or B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 19f Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 67) Authentication should generally be ________. A) as strong as possible B) appropriate for a specific resource C) the same for all resources D) different for every different resource Difficulty: Deeper Question: 19g Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 68) Traditionally, we have told users that passwords ________. A) should have a mix of characters (uppercase and lowercase letters, digits, other keyboard characters) B) should be easy to remember C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 20a Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 69) For reusable passwords, NIST now recommends ________. A) that passwords be easy to remember B) that passwords should be changed monthly C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Deeper Question: 20b Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 70) For reusable passwords, NIST now recommends ________. A) that passwords be easy to remember B) that passwords be long phrases instead of being about 8-12 characters long C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Deeper Question: 20b Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 71) NIST guidelines for reusable passwords permit ________. A) entirely lower-case passwords B) the use of the same password at different sites C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Deeper Question: 20d Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 72) For sensitive assets, reusable passwords ________. A) should be especially long B) should contain a truly complex mixture of characters C) should be difficult to remember D) should not be used Difficulty: Deeper Question: 20e Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 73) Biometrics, and other new authentication methods, are being created with the goal of getting rid of reusable passwords. Difficulty: Basic Question: 20f Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 74) Using bodily measurements for authentication is ________. A) illegal B) biometrics C) mandatory for good security D) all of the above Difficulty: Basic Question: 21b Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 75) Fingerprint recognition is generally acceptable for ________. A) laptops B) corporate databases C) resources involving private information about customers D) all of the above Difficulty: Basic Question: 21c Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 76) Iris scanning is attractive because of its ________. A) low cost B) precision C) both A and B Difficulty: Basic Question: 21d Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 77) Facial recognition is controversial because ________. A) it can be fooled very easily B) it can be used surreptitiously C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 21e Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 78) In digital certificate authentication, the supplicant encrypts the challenge message with ________. A) the supplicant's private key B) the verifier's private key C) the true party's private key D) none of the above Difficulty: Deeper Question: 22a Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 79) In digital certificate authentication, the verifier decrypts the challenge message with ________. A) the supplicant's private key B) the true party's private key C) the supplicant's public key D) the true party's public key Difficulty: Deeper Question: 22b Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 80) In digital certificate authentication, the verifier gets the key it needs directly from the ________. A) supplicant B) verifier C) true party D) certificate authority Difficulty: Basic Question: 22d Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 81) The digital certificate provides the ________. A) private key of the supplicant B) private key of the true party C) public key of the supplicant D) none of the above Difficulty: Deeper Question: 22d Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 82) Which form of authentication depends on the supplicant proving that she knows something only the true party should know? A) reusable password authentication B) iris scanning C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 23b Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 83) Digital certificate authentication fails if the supplicant ________. A) is the true party B) learns the true party's private key C) learns the true party's public key D) either B or C Difficulty: Deeper Question: 23c Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 84) A debit card is secure because it requires two credentials for authentication–the card itself and a PIN. This is called ________. A) segmentation B) redundancy C) two-factor authentication D) none of the above Difficulty: Basic Question: 23d Objective: Explain authentication alternatives. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 85) When a firewall identifies an attack packet, it ________. A) discards the packet B) copies information about the packet into a log file C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 24a Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 86) A firewall will drop a packet if it ________. A) is a definite attack packet B) is a highly probable attack packet C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Deeper Question: 24b Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 87) Firewall log files should be read ________. A) every month B) every day C) every week D) usually only when a serious attack is suspected Difficulty: Basic Question: 24c Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 88) Stateful packet inspection firewalls are attractive because of their ________. A) low cost for a given traffic volume B) ability to base rules on specific application programs C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 25a Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 89) When a packet that is part of an ongoing connection arrives at a stateful inspection firewall, the firewall usually ________. A) drops the packet B) drops the packet and notifies an administrator C) passes the packet D) passes the packet, but notifies an administrator Difficulty: Deeper Question: 25c Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 90) When a packet that is not part of an ongoing connection and that does not attempt to open a connection arrives at a stateful inspection firewall, the firewall ________. A) drops the packet B) passes the packet C) opens a new connection D) does not approve the connection Difficulty: Deeper Question: 25c Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 91) How will a stateful packet inspection (SPI) firewall handle a packet containing a TCP segment that contains an acknowledgement? A) process it through the Access Control List (ACL) B) pass it if it is part of an approved connection C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Deeper Question: 25c Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 92) SPI firewalls are attractive because of their ________. A) ability to do antivirus filtering B) ability to filter complex application content C) QoS guarantees D) low cost Difficulty: Deeper Question: 25d Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 93) ________ is the dominant firewall filtering method used on main border firewalls today. A) ACL filtering B) Application content filtering C) Stateful packet inspection D) NGFW Difficulty: Basic Question: 25e Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 94) In SPI firewalls, ACLs are used for packets in the ________ state. A) connection-opening B) ongoing communication C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 26a Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 95) In an SPI firewall, all rules except the last will permit the connection. The last will ________. A) also permit the connection B) deny the connection C) either A or B D) none of the above Difficulty: Basic Question: 26a Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 96) SPI firewalls are being replaced in large part because they are limited in their ability to detect ________. A) NAT B) piggybacking C) port spoofing D) none of the above Difficulty: Deeper Question: 27a Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 97) Which type of firewall filtering collects streams of packets to analyze them as a group? A) SPI B) NGFW C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Deeper Question: 27b Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 98) Which type of firewall filtering looks at application-layer content? A) stateful packet inspection B) NGFW C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 27b Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 99) NGFWs ________. A) can implement different rules for different applications B) base server decisions on port numbers C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 27b Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 100) Which type of firewall is more expensive per packet handled? A) SPI B) NGFW C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 27d Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge 101) If a packet is highly suspicious but not a provable attack packet, an ________ may drop it. A) SPI firewall B) IDS C) NGFW D) none of the above Difficulty: Deeper Question: 28a Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 102) Which of the following is the most frustrating to use? A) IDSs B) opaque filtering C) SPI firewalls D) NGFW firewalls Difficulty: Deeper Question: 28b Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 103) Compared to NGFWs, IDSs ________. A) look for different threats B) look for the same threats C) look for the same threats but do so differently D) none of the above Difficulty: Deeper Question: 28c Objective: Describe firewall protections. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 104) ________ look at ________, while ________ mostly look at ________. A) Antivirus programs; packets; firewalls; packets B) Antivirus programs; files; firewalls; files C) Antivirus programs; packets; firewalls; files D) Antivirus programs; files; firewalls; packets Difficulty: Deeper Question: 29a Objective: Describe the role of antivirus protection. AACSB: Applying Information Technology, Application of Knowledge, Analytical Thinking 105) Antivirus programs are designed to detect ________. A) viruses B) worms C) both A and B D) neither A nor B Difficulty: Basic Question: 29b Objective: Describe the role of antivirus protection. AACSB: Applying Information Technology 106) In antivirus filtering, the best ways to filter currently use ________. A) application awareness B) stateful inspection C) signature detection D) behavioral detection Difficulty: Basic Question: 29c Objective: Describe the role of antivirus protection. AACSB: Applying Information Technology [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 27 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 19, 2019
Number of pages
27
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 19, 2019
Downloads
0
Views
50






















 Chapter 5 Ethernet (802.png)