*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NRNP 6566 Week 7 Knowledge Check (100% Correct) Verified Answers (All)
NRNP 6566 Week 7 Knowledge Check (100% Correct) Verified Answers
Document Content and Description Below
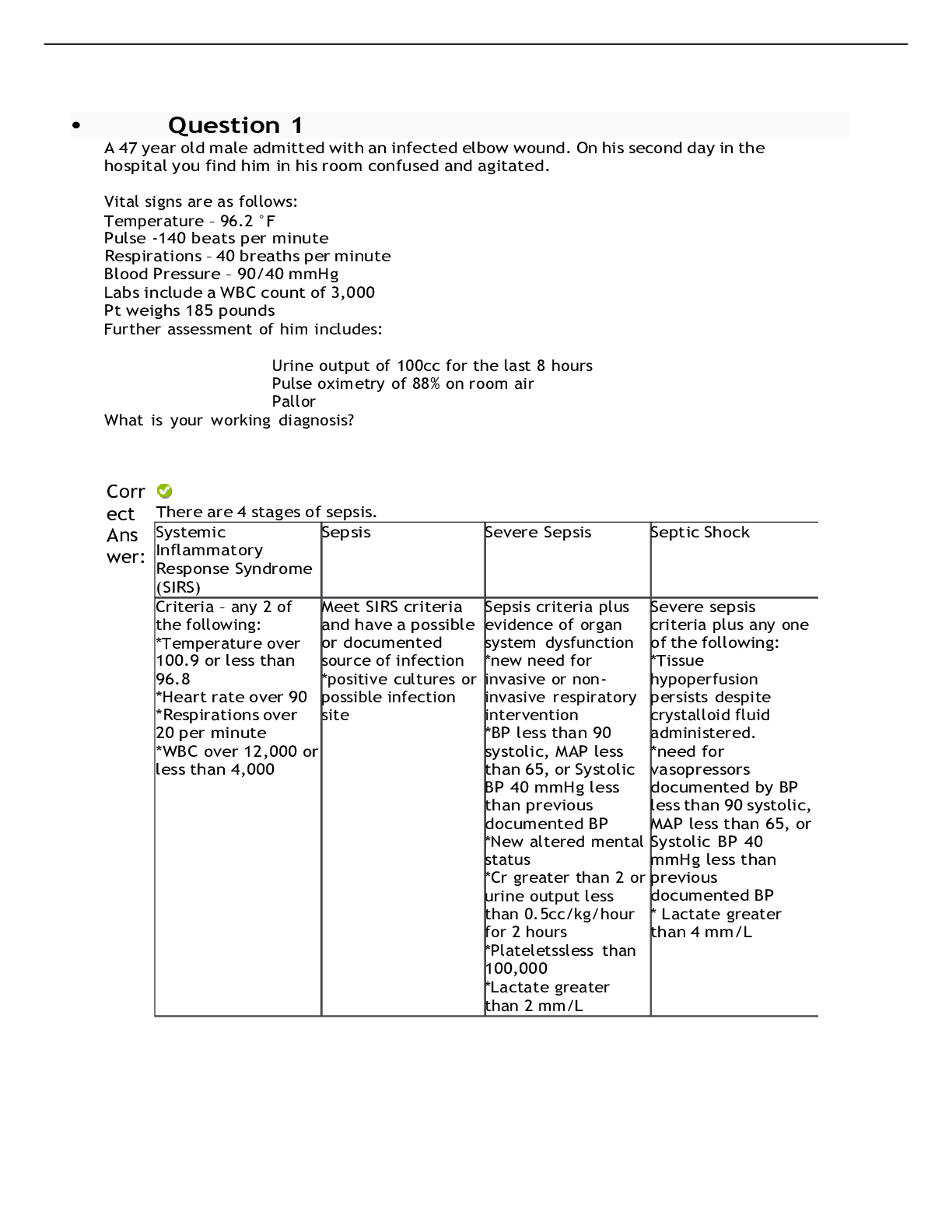
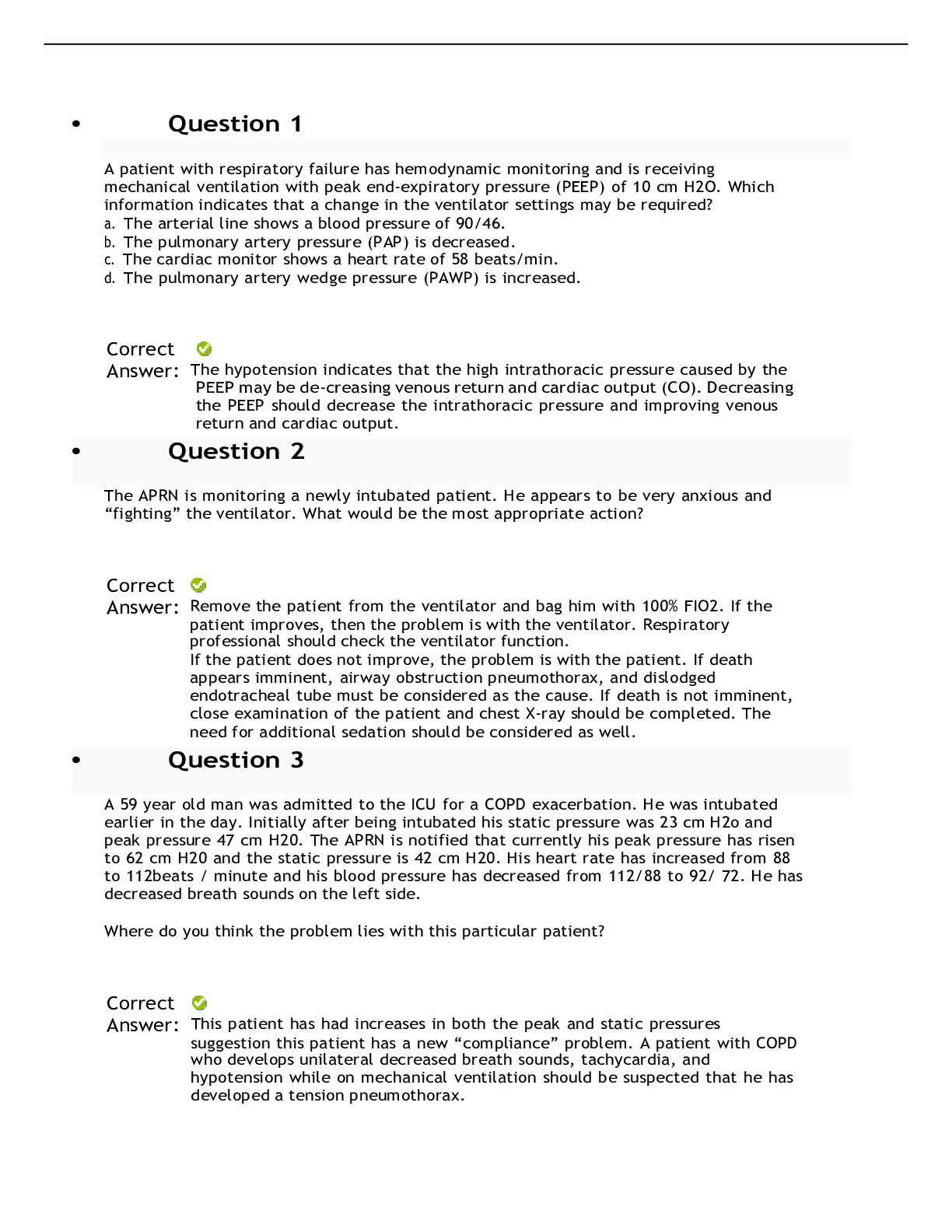
A patient with respiratory failure has hemodynamic monitoring and is receiving mechanical ventilation with peak end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of 10 cm H2O. Which information indicates that a change i... n the ventilator settings may be required? a. The arterial line shows a blood pressure of 90/46. b. The pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) is decreased. c. The cardiac monitor shows a heart rate of 58 beats/min. d. The pulmonary artery wedge pressure (PAWP) is increased. Correct Answer: The hypotension indicates that the high intrathoracic pressure caused by the PEEP may be de-creasing venous return and cardiac output (CO). Decreasing the PEEP should decrease the intrathoracic pressure and improving venous return and cardiac output. The APRN is monitoring a newly intubated patient. He appears to be very anxious and “fighting” the ventilator. What would be the most appropriate action? Correct Answer: Remove the patient from the ventilator and bag him with 100% FIO2. If the patient improves, then the problem is with the ventilator. Respiratory professional should check the ventilator function. If the patient does not improve, the problem is with the patient. If death appears imminent, airway obstruction pneumothorax, and dislodged endotracheal tube must be considered as the cause. If death is not imminent, close examination of the patient and chest X-ray should be completed. The need for additional sedation should be considered as well. A 59 year old man was admitted to the ICU for a COPD exacerbation. He was intubated earlier in the day. Initially after being intubated his static pressure was 23 cm H2o and peak pressure 47 cm H20. The APRN is notified that currently his peak pressure has risen to 62 cm H20 and the static pressure is 42 cm H20. His heart rate has increased from 88 to 112beats / minute and his blood pressure has decreased from 112/88 to 92/ 72. He has decreased breath sounds on the left side. Where do you think the problem lies with this particular patient? Correct Answer: This patient has had increases in both the peak and static pressures suggestion this patient has a new “compliance” problem. A patient with COPD who develops unilateral decreased breath sounds, tachycardia, and hypotension while on mechanical ventilation should be suspected that he has developed a tension pneumothorax. A 34 year ole email who weights 96 kg (211 lbs.) and is 165 cm (5 ft. 6 inches) tall has chest trauma due to a motorcycle accident. The patient has just been intubated, sedated and paralyzed with morphine sulfate and pancuronium bromide. What initial ventilator settings are appropriate for this patient? Correct Answer: Assist control mode (A/C) is utilized after intubation. Tidal volume is based on the patients ideal body weight (not actual body weight). Ideal body weight for this patient is 63 kg. Tidal volume is set at 8-10 ml/kg or 500-600 ml in this patient. FIO2 should initially be 100% with an initial PEEP of 5 and respiratory rate of 12 - 14. ABG should be obtained after intubation and appropriate adjustments made. A 40 year-old. 6-foot tall man has been inpatient on the step down unit for the past 2 days. He was admitted for fever and cough with production of yellow sputum. His admission blood pressure was 128/72 and initial chest x-ray showed a left lower lobe infiltrate. His ABG on room air showed: pH 7.31, PCO2 30, PO2 78, HCO3 17. He was started on antibiotics and progress notes from he past two days indicate improvement in his condition. The APRN is called by the nurse because of worsening of the patients condition. On your arrival to the room, vitals signs are. BP. 86/60 P 118 RR 38 oxygen saturation on a non-rebreather mask is 78% (this am it was 97% on 2L per NC). The patient is laboring to breath with accessory muscle use. He is less responsive, diaphoretic, and is speaking in short sentences. Repeat chest x-ray shows bilateral diffuse lung opacities. ABG on the non-rebreather mask show: pH 7.18, PCO2 47, PO2 56, HCO3 13. The decision to intubate the patient is made. What initial ventilator settings would you order? Correct Answer: Ventilator settings include the mode of mechanical ventilation, tidal volume, respiratory rate, the inspired oxygen concentration (FiO2), and the level of positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP). Assist control mode is usually initiated after intubation however there is varying data on the use of different modes without clear evidenced based guidelines on this. FiO2 is usually started at 100% and weaned down based on patient response. Tidal volumes are calculated based on the patient’s ideal body weight (not their actual weight). Ideal body weight is calculated by utilizing the patients height To calculate the ideal body weight in kilograms, you can use the following formulas: Men: [(height in inches – 60) X 2.2] + 50 Women: [(height in inches – 60) X 2.2] + 45 Once you have calculated the ideal body weight, the tidal volume is calculated at 6-8 cc/ kg The patient in this case is 6-foot tall (72 inches). Using the formula above, his ideal body weight is about 76kg. A tidal volume of 600 cc would be 8 ml/kg The respiratory rate should be determined based on an assessment of the patient’s minute ventilation requirements. For example, a patient with a normal bicarbonate of 24 who was intubated for a procedure may only need 6- 8 liters/minute of ventilation whereas a patient in severe sepsis with a bicarbonate of 10 may require upwards of 20-25 liters/minute of ventilation to maintain an adequate acid-base status. Once you derive an estimate of the minute ventilation (VE ) needs of the patient, you can use your previously determined tidal volume and simple division to calculate an appropriate respiratory rate (RR = VE/tidal volume) The initial PEEP is usually set at 5 cm H2O. The PEEP is typically not decreased below 5 cm H2O but can be increased as necessary (up to 15 to 20 cm H20) to support oxygenation in patients with severe hypoxemia A 59 year old man was admitted to the ICU for a COPD exacerbation. He was intubated earlier in the day. Initially after being intubated his static pressure was 23 cm H2o and peak pressure 47 cm H20. The APRN is notified that currently his peak pressure has risen to 62 cm H20 and the static pressure is 42 cm H20. His heart rate has increased from 88 to 112beats / minute and his blood pressure has decreased from 112/88 to 92/ 72. He has decreased breath sounds on the left side. What management steps should you institute at this point? Correct Answer: A chest X-ray should be obtained to look for evidence of a pneumothorax, new pleural effusion, developing ARDS. Examine the patient for any abdominal distention. If the patient becomes hemodynamically unstable and there is high index of suspicion for a tension pneumothorax, a large bore needle should be placed into the second intercostal space along the mid-clavicular line to decompress the pneumothorax. Chest tube placement would be indicated after initial needle placement for decompression. Four hours after mechanical ventilation is initiated for a patient with chronic obstructive pulmo-nary disease (COPD), the patient's arterial blood gas (ABG) results include a pH of 7.50, PaO2 of 80 mm Hg, PaCO2 of 29 mm Hg, and HCO3- of 23 mEq/. What change in ventilator settings would be indicated? Correct Answer: The patient's PaCO2 and pH indicate respiratory alkalosis. In mechanically ventilated patients who have respiratory alkalosis, the tidal volume and/or respiratory rate may need to be de-creased. Inadequate sedation and pain control may contribute to respiratory alkalosis in patients breathing over the set ventilator rate. The PaO2 is appropriate for a patient with COPD, The APRN is notified that an intubated patients endotracheal tube (ET) was marked at 21 cm and is not at the 24 cm line. The patient appears anxious and restless. What action should the APRN take? Correct Answer: Advancement of the ET could cause the tube to be displaced into the right [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 5 pages
Instant download
Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 18, 2021
Number of pages
5
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 18, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
112


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)

.png)
.png)