Mathematics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > MATH 225N-Chamberlain College of Nursing MATH225N WEEK 8 Statistics FINAL EXAM. Rated 100% (All)
MATH 225N-Chamberlain College of Nursing MATH225N WEEK 8 Statistics FINAL EXAM. Rated 100%
Document Content and Description Below
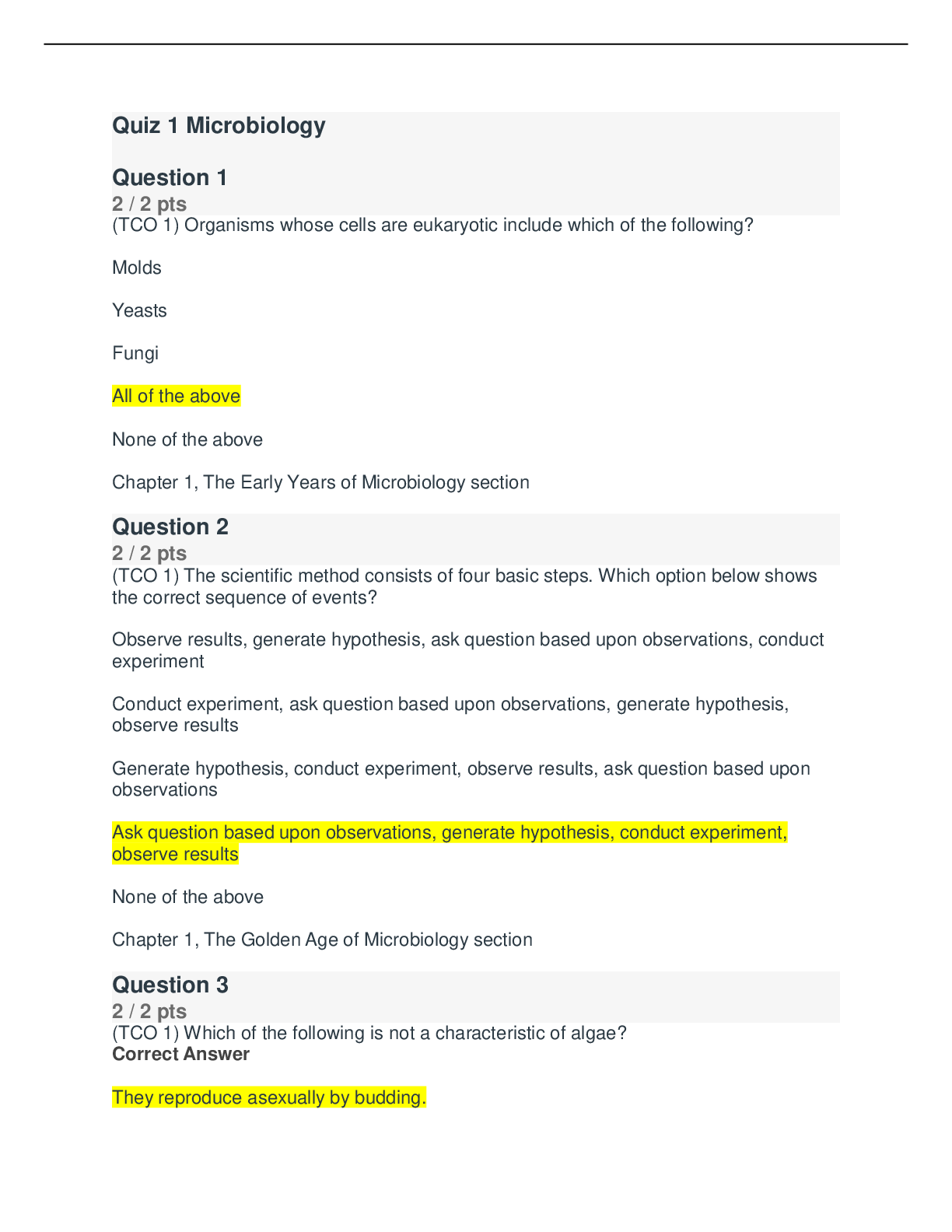
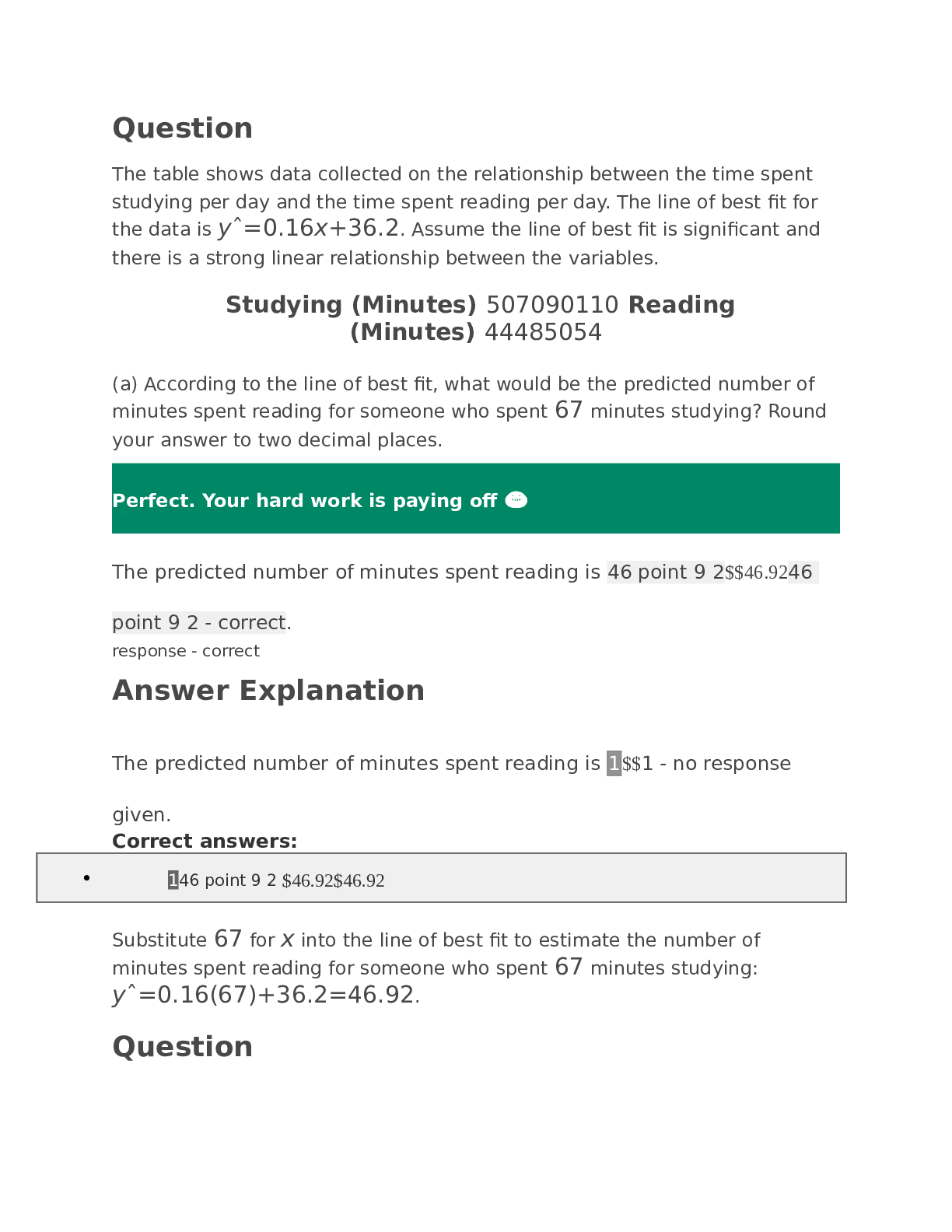
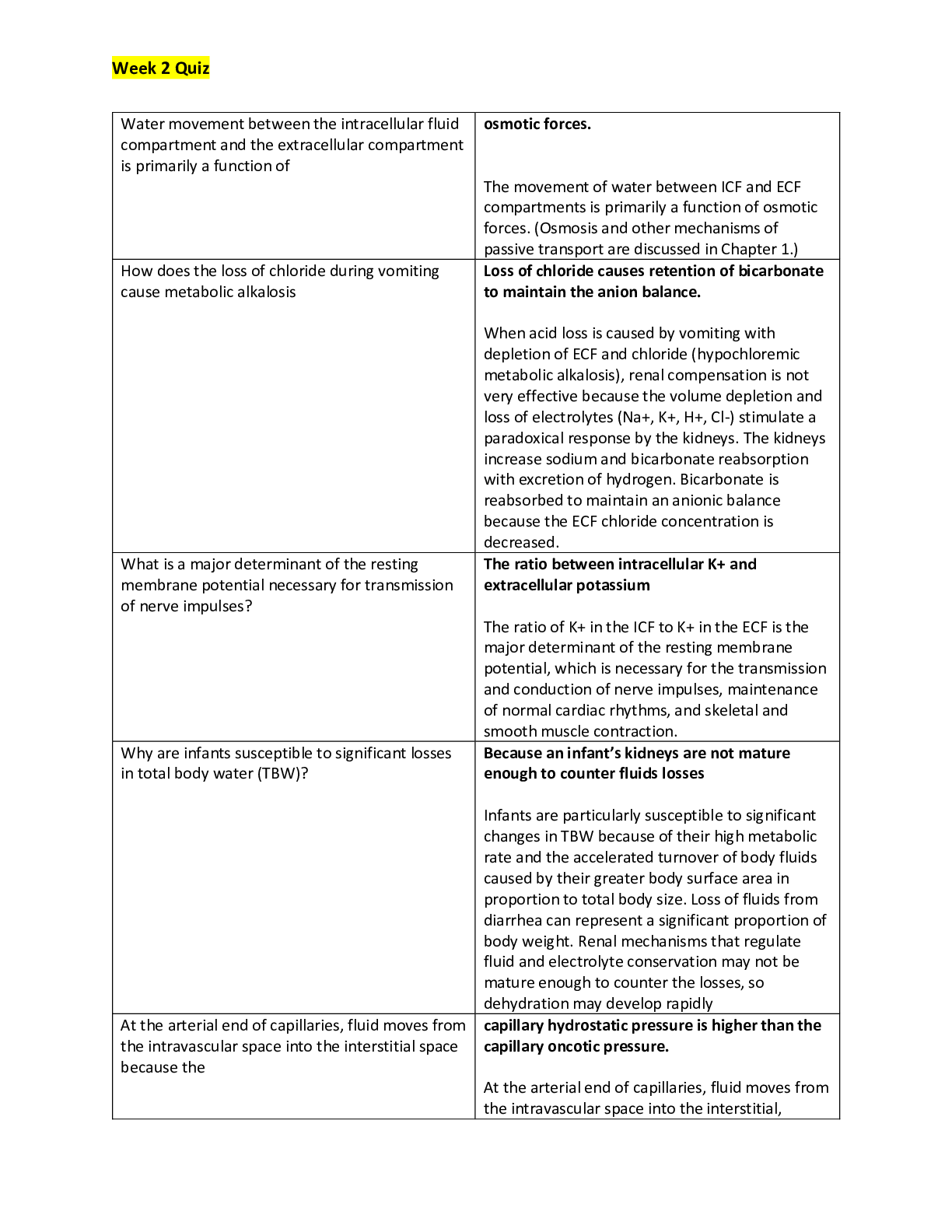
MATH 225N-Chamberlain College of Nursing MATH225N WEEK 8 Statistics FINAL EXAM. 1/1 POINTS A fitness center claims that the mean amount of time that a person spends at the gym per visit is 33 minute... s. Identify the null hypothesis, H0, and the alternative hypothesis, Ha, in terms of the parameter μ. That is correct! H0: μ≠33; Ha: μ=33 H0: μ=33; Ha: μ≠33 H0: μ≥33; Ha: μ<33 H0: μ≤33; Ha: μ>33 Answer Explanation Correct answer: H0: μ=33; Ha: μ≠33 Let the parameter μ be used to represent the mean. The null hypothesis is always stated with some form of equality: equal (=), greater than or equal to (≥), or less than or equal to (≤). Therefore, in this case, the null hypothesis H0 is μ=33. The alternative hypothesis is contradictory to the null hypothesis, so Ha is μ≠33. QUESTION 2 1/1 POINTS The answer choices below represent different hypothesis tests. Which of the choices are right-tailed tests? Select all correct answers. That is correct! H0:X≥17.1, Ha:X<17.1 H0:X=14.4, Ha:X≠14.4 H0:X≤3.8, Ha:X>3.8 H0:X≤7.4, Ha:X>7.4 H0:X=3.3, Ha:X≠3.3 Answer Explanation Correct answer: H0:X≤3.8, Ha:X>3.8 H0:X≤7.4, Ha:X>7.4 Remember the forms of the hypothesis tests. Right-tailed: H0:X≤X0, Ha:X>X0. Left-tailed: H0:X≥X0, Ha:X<X0. Two-tailed: H0:X=X0, Ha:X≠X0. So in this case, the right-tailed tests are: H0:X≤7.4, Ha:X>7.4 H0:X≤3.8, Ha:X>3.8 QUESTION 3 0/1 POINTS Find the Type II error given that the null hypothesis, H0, is: a building inspector claims that no more than 15% of structures in the county were built without permits. That's not right. The building inspector thinks that no more than 15% of the structures in the county were built without permits when, in fact, no more than 15% of the structures really were built without permits. The building inspector thinks that more than 15% of the structures in the county were built without permits when, in fact, more than 15% of the structures really were built without permits. The building inspector thinks that more than 15% of the structures in the county were built without permits when, in fact, at most 15% of the structures were built without permits. The building inspector thinks that no more than 15% of the structures in the county were built without permits when, in fact, more than 15% of the structures were built without permits. Answer Explanation Correct answer: The building inspector thinks that no more than 15% of the structures in the county were built without permits when, in fact, more than 15% of the structures were built without permits. A Type II error is the decision not to reject the null hypothesis when, in fact, it is false. In this case, the Type II error is when the building inspector thinks that no more than 15% of the structures were built without permits when, in fact, more than 15% of the structures were built without permits. Your answer: The building inspector thinks that more than 15% of the structures in the county were built without permits when, in fact, at most 15% of the structures were built without permits. Content attribution- Opens a dialog QUESTION 4 1/1 POINTS Suppose a chef claims that her meatball weight is less than 4 ounces, on average. Several of her customers do not believe her, so the chef decides to do a hypothesis test, at a 10% significance level, to persuade them. She cooks 14 meatballs. The mean weight of the sample meatballs is 3.7 ounces. The chef knows from experience that the standard deviation for her meatball weight is 0.5 ounces. H0: μ≥4; Ha: μ<4 α=0.1 (significance level) What is the test statistic (z-score) of this one-mean hypothesis test, rounded to two decimal places? That is correct! $$Test statistic = −2.24 Answer Explanation Correct answers: $\text{Test statistic = }-2.24$Test statistic = −2.24 The hypotheses were chosen, and the significance level was decided on, so the next step in hypothesis testing is to compute the test statistic. In this scenario, the sample mean weight, x¯=3.7. The sample the chef uses is 14 meatballs, so n=14. She knows the standard deviation of the meatballs, σ=0.5. Lastly, the chef is comparing the population mean weight to 4 ounces. So, this value (found in the null and alternative hypotheses) is μ0. Now we will substitute the values into the formula to compute the test statistic: z0=x¯−μ0σn√=3.7−40.514√≈−0.30.134≈−2.24 So, the test statistic for this hypothesis test is z0=−2.24. QUESTION 5 1/1 POINTS What is the p-value of a right-tailed one-mean hypothesis test, with a test statistic of z0=1.74? (Do not round your answer; compute your answer using a value from the table below.) z1.51.61.71.81.90.000.9330.9450.9550.9640.9710.010.9340. 9460.9560.9650.9720.020.9360.9470.9570.9660.9730.030.9 370.9480.9580.9660.9730.040.9380.9490.9590.9670.9740.0 50.9390.9510.9600.9680.9740.060.9410.9520.9610.9690.97 50.070.9420.9530.9620.9690.9760.080.9430.9540.9620.970 0.9760.090.9440.9540.9630.9710.977 That is correct! $$0.041 Answer Explanation Correct answers: $0.041$0.041 The p-value is the probability of an observed value of z=1.74 or greater if the null hypothesis is true, because this hypothesis test is right-tailed. This probability is equal to the area under the Standard Normal curve to the right of z=1.74. A standard normal curve with two points labeled on the horizontal axis. The mean is labeled at 0.00 and an observed value of 1.74 is labeled. The area under the curve and to the right of the observed value is shaded. Using the Standard Normal Table, we can see that the p-value is equal to 0.959, which is the area to the left of z=1.74. (Standard Normal Tables give areas to the left.) So, the p-value we're looking for is p=1−0.959=0.041. QUESTION 6 1/1 POINTS Kenneth, a competitor in cup stacking, claims that his average stacking time is 8.2 seconds. During a practice session, Kenneth has a sample stacking time mean of 7.8 seconds based on 11 trials. At the 4% significance level, does the data provide sufficient evidence to conclude that Kenneth's mean stacking time is less than 8.2 seconds? Accept or reject the hypothesis given the sample data below. H0:μ=8.2 seconds; Ha:μ<8.2 seconds α=0.04 (significance level) z0=−1.75 p=0.0401 That is correct! Do not reject the null hypothesis because the p-value 0.0401 is greater than the significance level α=0.04. Reject the null hypothesis because the p-value 0.0401 is greater than the significance level α=0.04. Reject the null hypothesis b [Show More]
Last updated: 10 months ago
Preview 1 out of 64 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 26, 2022
Number of pages
64
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 26, 2022
Downloads
4
Views
205

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)

.png)
.png)







.png)