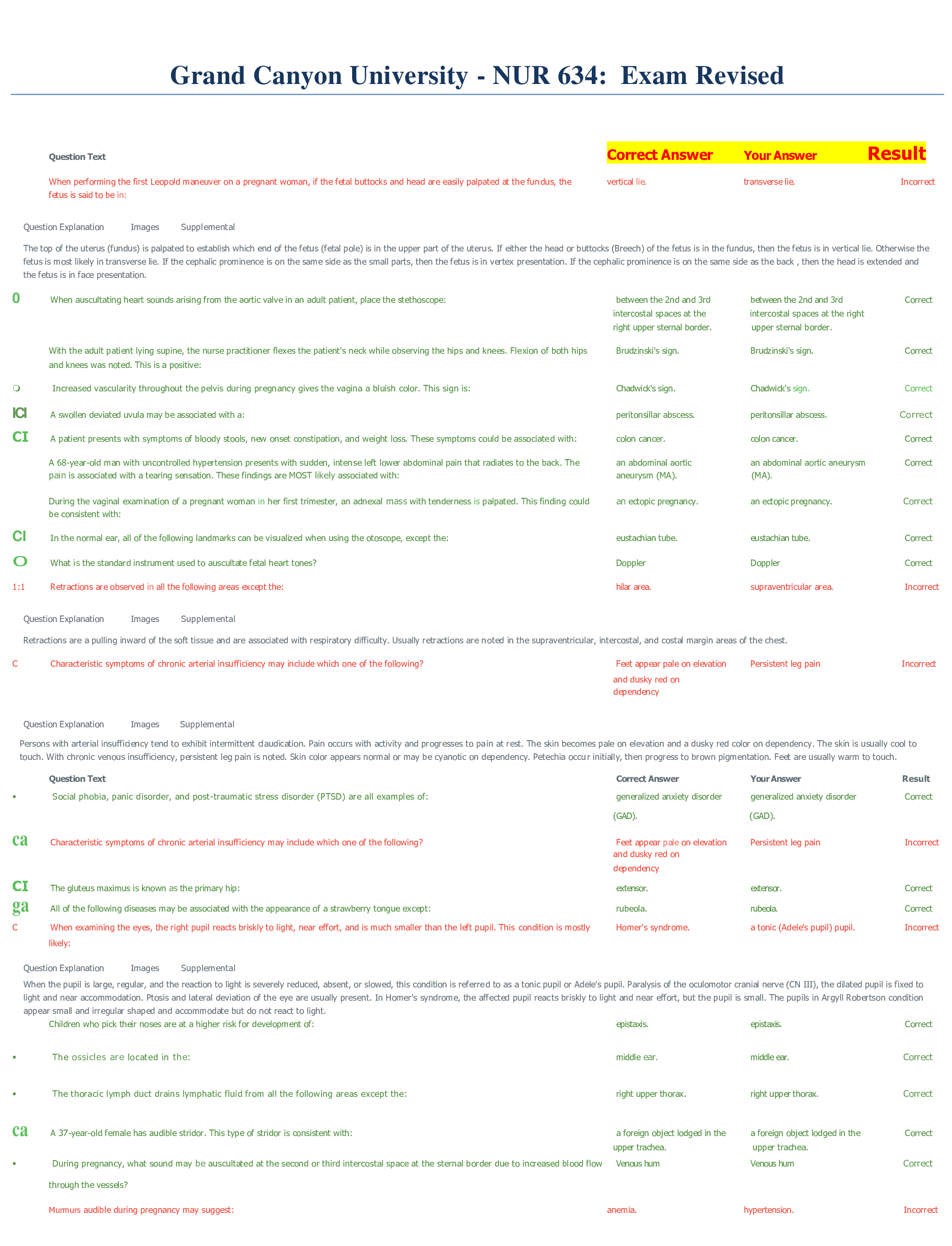
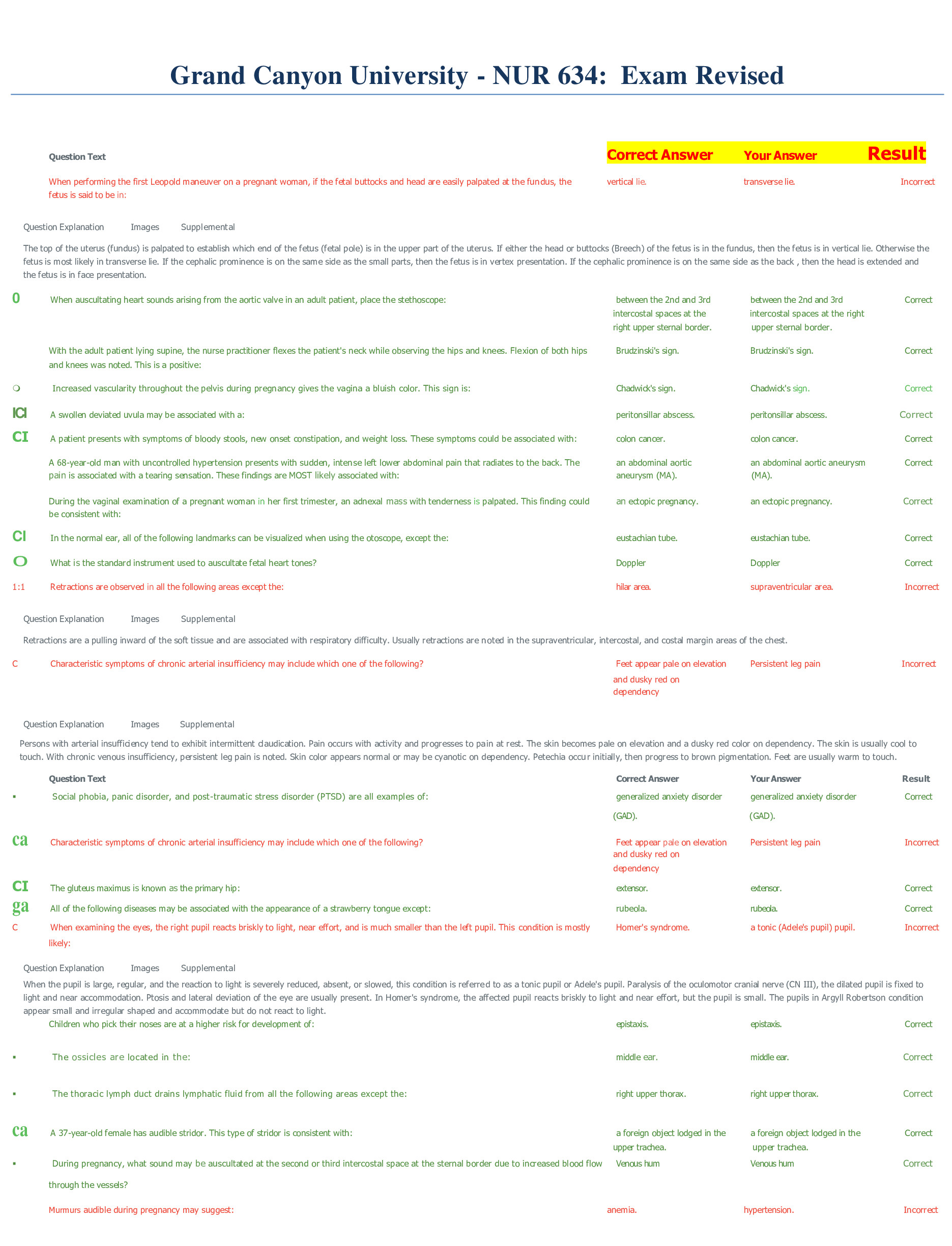
Risk Management and Insurance > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Ammo 67 exam questions and answers 100% pass (All)
Ammo 67 exam questions and answers 100% pass
Document Content and Description Below
Ammo 67 exam questions and answers 100% pass Types of hazmat transportation ✔✔land (highway/rail) sea air Define hazmat ✔✔any material or substance capable of posing an unreasonable risk ... to health, safety, and property when transported. What training does the HAZMAT Familiarization and Safety in Transportation course provide? ✔✔applicability and responsibility emergency response general awareness/familiarization security awareness What if the function of a DD Form 626? ✔✔*Used by the Quality Assurance SpecialistAmmunition Surveillance (QASAS) or vehicle inspector to verify driver documentation and to inspect vehicles before and immediately after they are loaded with HAZMAT *Driver keeps a copy of the form with the shipping papers *Form is used by the receiving ASP or depot for inspection before unloading What do you think the inspector looks for during the vehicle inspection? ✔✔driver's license vehicle's operating condition (brakes, tires, windshield wiper, tires, mirrors, etc.) Who inspects the vehicle? ✔✔Specifically trained personnel will inspect the vehicle What are the vehicle requirements to pass inspection? ✔✔DD Form 626 lists the requirements for a vehicle to pass inspection How many times is the vehicle inspected? ✔✔Before it's loaded After it's loaded Before it's unloaded What happens if the vehicle does not pass inspection? ✔✔The vehicle is not loaded until it is repaired or another vehicle (that can pass inspection) is provided Which section of DD Form 626 may be used as a guide to pre-inspect the vehicle before leaving the motor pool? ✔✔Section II What are the different hazard classes? ✔✔Hazard class: is a grouping of hazardous materials based on their similar characteristics (gas, liquid, solid) 9 classes: Class 1 Explosives Class 2 Gases (Acetylene and oxygen) Class 3 Flammable liquids (Acetone) Class 4 Flammable Solids, Spontaneously Combustible, or Water Reactive (MRE heater on fire) Class 5 Oxidizers or Organic Peroxides (ammonium nitrate) Class 6 Toxic or Infectious Materials (arsenic trioxide) Class 7 Radioactive Material (different forms of uranium) Class 8 Corrosive Material (hydrochloric acid) Class 9 Miscellaneous Hazardous Material (dry ice) Acronym: Every Good Fire Fighter Ought To Recognize Corrosive Materials What is a compatibility group? ✔✔materials can be safely transported and stored together without creating a greater hazard HC 1 materials show compatibility through letters (Compatibility groups identify ammo items that can be shipped together.) Identify hazards class(es), check the shipping papers, package labels, and placards ✔✔Shipping papers: The basic description identifies the material's hazard class Package labels: enables you to identify the hazard class(es) contained in a package Placards: identifies the hazard class of the material a vehicle transports Hazard class knowledge ✔✔As a HAZMAT employee, knowing the hazard class and what they are capable of doing allows you to safety transport or store hazardous materials. First responders must know the hazard class to correctly respond to the type of emergency (gas, liquid, explosive, etc.) With this information, they can safely control and contain a HAZMAT accident and protect the public. What could happen when hazardous materials that react dangerously when in contact with each other are transported together? ✔✔Possible Hazards Because of the nature of hazardous materials, if they come in contact with each other, they are capable of producing other hazards i.e. when bleach and ammonia come in contact with each other, they produce a toxic vapor (which is an inhalation hazard). Hazard Class Division ✔✔Some hazard classes are separated into divisions. These divisions identify the different types of hazard within a hazard class. For example, HC 1 (explosives) can have hazards such as fragmentation or fire in the addition to exploding Learn more HC Division ✔✔HC 1 1.1 Mass explosion hazard (bombs, 155 projectile) 1.2 Fragmentation hazard (some grenades and 105mm cartridges) 1.3 Fire hazard (propellant, artillery charges) 1.4 Minor explosion hazard (small arms ammunition, smoke grenades) 1.5 Very intensive explosives (blasting agents) 1.6 Extremely intensive explosives (no mass explosive hazard) HC2 2.1 Flammable gases (acetylene, butane, hydrogen) 2.2 Non-flammable, non-poisonous compressed gases (helium, nitrogen, and neon) 2.3 Gases poisonous by inhalation (chlorine, ammonia anhydrous, carbon monoxide) HC 3 Materials that ignite easily. This is due to flash point. A flash point is the temperature at which a material gives off enough vapor to ignite. (fuel aviation turbine engine (JP-8), gasoline, and some alcohol beverages) HC 4 4.1 Flammable solids that catch fire easily (safety or strike anywhere matches) 4.2 Spontaneously combustible materials that can catch fire without a separate heat source (charcoal briquettes, linseed oil) 4.3 Dangerous when wet materials (materials that can explode or emit flammable gas when in contact with water) i.e. potassium, sodium, MRE heaters HC 5 5.1 Oxidizer: materials that does not burn on its own, but gives off oxygen, which could cause other materials to burn i.e. ammonium nitrate fertilizer, hydrogen peroxide 5.2 Organic peroxide (liquid or solid) that contain oxygen i.e. polyester resin kits used to patch vehicle tires or repair boats HC 6 6.1 Poisonous materials (liquid or solid) so toxic to humans that it is a hazard to health i.e. potassium cyanide, arsenic 6.2 Infectious substances: an organism that causes virus or infection in humans or animals i.e. medical waste, virus cultures HC 7 A radioactive material is any material containing unstable isotopes I.e. uranium, plutonium, thorium Note: any time you receive or ship radioactive materials, you must work with your Radiation Safety Officer HC 8 Materials (liquid or solid) that causes destruction to the human body upon contact (also includes liquids that corrode metals, like steel or aluminum) i.e. sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide HC 9 Material that presents a hazard during transportation and does not fail under any of the other eight hazard classes I.e. asbestos,, airbag inflators, dry ice when transported by air or vessel, cotton, when transported by land or vessel What type of information is found on a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS)/Safety Data Sheet (SDS)? ✔✔First source of information used to create shipping papers, mark and label packages, and placard vehicles. It provides crucial information for Hazard Class 2 thru 9 materials. Describes who made the material, the ingredients that make up the material, and possible hazards of the material (birth certificate) Why is correct Hazmat information important? ✔✔Correct Hazmat information provides safe and handling procedures, which can prevent accidents MSDS/SDS and Hazmat Communication ✔✔Guides you to the information in the 49 CFR. The 49 CFR gives the information to correctly prepare Hazmat communication (i.e. shipping papers, package markings and labels, and placards) MSDS/SDS Uses ✔✔Describes Class 2 thru Class 9 hazard materials. It is not used to describe Class 1 explosives MSDS/SDS and Hazmat Employees ✔✔*As a Hazmat employee you use a MSDS/SDS as a guide for proper and safe handling of a hazardous material *Emergency personnel *Every installation must have an MSDS/SDS for every hazardous material, other than Class 1, that is shipped or stored on the installation. MSDS/SDS Section ✔✔MSDS/SDS Safety Information Contractor Summary (identifies who to contact if you have questions about the material or the MSDS) Item Description Information: provides the material's common name (The item name is one of the markings on the exterior of a package. It identifies the package contents.) Ingredients Health Hazard Data Fire and Explosion Hazard Information Physical/Chemical Properties Reactivity Data Detail DOT Information: The Detail DOT Information FOR LAND TRANSPORTATION section provides the material's basic description. Detail IMO Information Global Harmonization System ✔✔a SDS serves the same function as a MSDS. All SDS use the same style and format Basic Description ✔✔Identification number Proper shipping name (PSN) Hazard class(es) and division (if applicable) Packing group (if applicable) JHCS Data Sheet and Hazmat Documentation ✔✔Used for Hazard Class 1 materials JHCS Data Sheet 49 CFR Shipping Papers Markings and Labels Placards Hazmat Table ✔✔Middle point between the Joint Hazard Classification System (JHCS) Data Sheet or MSDS/SDS and the Hazmat communication. MSDS/SDS or JHCS Data Sheet 49 CFR Hazmat Communication 49 Code of Federal Regulations ✔✔Federal law governing transportation. It identifies proper HAZMAT communication for: Marking Labeling Placarding Hazmat Table ✔✔Hazmat Certifiers use this table when preparing a hazardous material for transportation. With this table, a Certifier can: Prepare shipping papers Identify placard requirements Identify required package markings and labels ERG Information ✔✔The ERG points first responders to the most appropriate course of action for handling a Hazmat accident to protect people and property. Emergency Response Guidebook ✔✔Is a Department of Transportation (DOT) publication that advises first responders (e.g. firefighters, police officers, etc.) on appropriate emergency response procedures. Driver Responsibilities and the ERG ✔✔*Copy of the ERG is kept with the shipping papers *Copy of the ERG page related to the specific material(s) being transported *Drivers must keep the shipping papers within reach at all times (even when driving) *Ensures the driver can get to the shipping papers and exit the vehicle if an accident occurs ERG Sections ✔✔White pages: contains direction for using the ERG and basic info pertaining to hazardous materials and emergency response Yellow-bordered: lists each material by its 4-digit identification number along with a numbered guide that provides response actions specific to the type of material Orange-bordered: contains the numbered guides listed in the yellow and blue sections. These guides provide the specific emergency response actions according to the material present. Blue-bordered: lists the names of the materials in alphabetical order Green-bordered: is used by first responders. It lists minimum distances for spills (i.e. how far back you need to keep people from the spill). These same materials are highlighted for easy identification in both numeric (Yellow section) and alphabetic (Blue section) lists of the guidebook. Guide Information ✔✔Divided into three sections: Potential Hazards, Public Safety, and Emergency Response Guide 116: provides procedures for flammable gases. Other hazardous materials, like ethylene Potential Hazards: describes possible fire or explosion hazards and potential health effects Public Safety: lists suggested safety precautions used to protect the public Emergency Response: describes special precautions in case of fire, spills, or chemical exposure. It also gives first aid procedures in case of exposure. how often do you need refresher training on Hazmat processes and procedures? ✔✔Because regulations and requirements change, the DTR 4500.9 R, paragraph D(2)(a) mandates you take refresher training every two years. This also includes local requirements, which may require retraining more often. Driving and Parking Rules ✔✔49 CFR, Parts 397.3 thru 397.19 Laws ✔✔397.2 Hazmat-loaded vehicles must follow state and local laws Attendance ✔✔397.5 a and c: Vehicle attendance (keeping the vehicle within the view of the driver) depends on the type of HAZMAT you transport. There are rules in place for all hazardous materials. For example, you cannot leave a vehicle unattended to eat in a restaurant. Parking ✔✔397.7 Parking requirements for a HAZMAT-loaded vehicle depend on the type of HAZMAT (e.g., explosives, corrosives, gases, etc.). Vehicles containing certain types of explosives must follow more strict rules than vehicles carrying other types of HAZMAT. Fires ✔✔397.11 Do not drive a vehicle containing HAZMAT near an open fire, such as a grass fire along a highway, if there is any danger to the vehicle and the contents. Do not park a vehicle containing HAZMAT within 300 ft of an open fire. Smoking ✔✔397.13 Never smoke or carry a lighted cigarette, cigar, or pipe on or within 25 ft of a vehicle containing HAZMAT. Fueling ✔✔397.15 When fueling a vehicle containing HAZMAT: Turn the engine off. Never lock the fuel lever and walk away; keep the pump in your hand. Tires ✔✔397.17 The driver must inspect each tire on a vehicle: Before each trip. Each time the vehicle is parked. You must replace damaged or overheated tires in accordance with the driving and parking rules. Instruction ✔✔Drivers transporting HAZMAT must have: A copy of the driving and parking rules. (49 CFR, Part 397) Shipping papers. (49 CFR, Part 177.817) A written route plan. (49 CFR, Part 397.67) A copy of the material's Emergency Response Guide (ERG) information. (49 CFR, Part 172.602) Shipping Papers ✔✔Carry shipping papers when transporting Hazmat It describes the types of hazardous materials in a shipment. DD Form 2890 is used for shipping Hazmat DD Form 2890 ✔✔Authorized for transport of Hazmat by military or commercial vehicles (e.g. truck or rail) Additional Documents for shipping ✔✔Shipping papers, like the DD Form 2890, are not the only documents required for a hazardous materials shipment. The required documents also include DD Form 626, the MSDS/SDS or JHCS Data Sheet, a copy of the ERG guide page, and a copy of the 49 CFR, §397.3 Driving and Parking Rules. Select each image for details. Marking Guidance ✔✔All markings for hazardous materials will adhere to the standards outlined in both MIL-STD-129 and 49 CFR as applicable. MIL-STD-129 ✔✔The Department of Defense (DoD) requirements for package markings are provided in MIL-STD-129. This document describes marking requirements for: HAZMAT (Section 5.1). Ammunition (Section 5.13) Placards ✔✔A placard is a special sign on a transport vehicle or railcar. Its purpose is to communicate the hazards contained in the vehicle to first responders in the event of an accident. *Placards are required on all four sides of the railcar or motor vehicle containing the hazardous material. *More than one placard can be displayed, depending on the load. Hazmat security awareness ✔✔General awareness/familiarization: 49 CFR, 172.704(a)(1) Emergency response: 49 CFR, 172.704(a)(3) and 172.602(a)(1-7) Security awareness: 49 CFR, 172.704(a)(4). Applicability and responsibility: 49 CFR, 172.702 [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 17 pages
Instant download
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Also available in bundle (1)
.png)
Ammunition Bundled Exams Already Passed!!!
Ammunition Bundled Exams Already Passed!!!
By Nutmegs 1 year ago
$20
15
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 01, 2023
Number of pages
17
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 01, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
75

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)