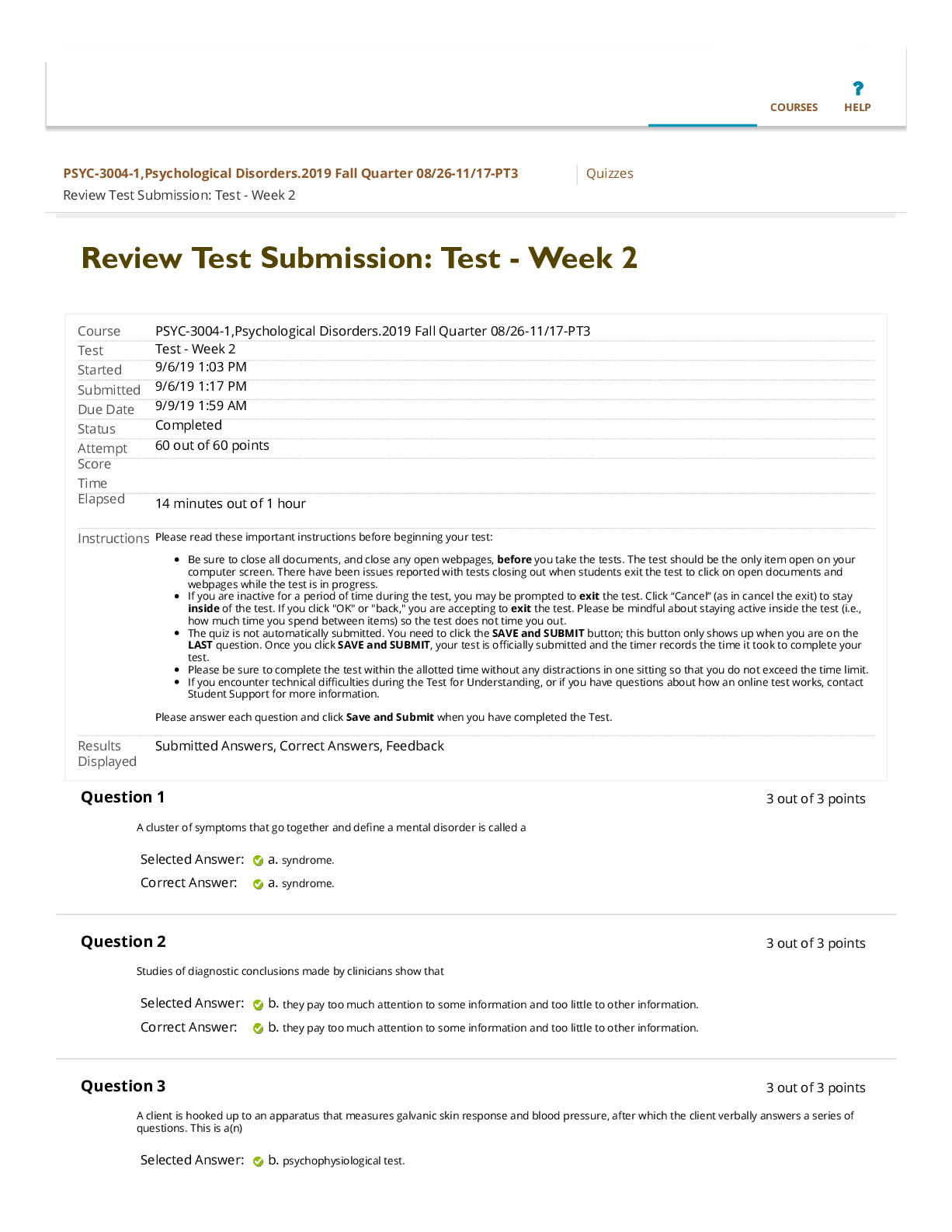
Social Sciences > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Wastewater grade 1 exam questions and answers graded A+ (All)
Wastewater grade 1 exam questions and answers graded A+
Document Content and Description Below
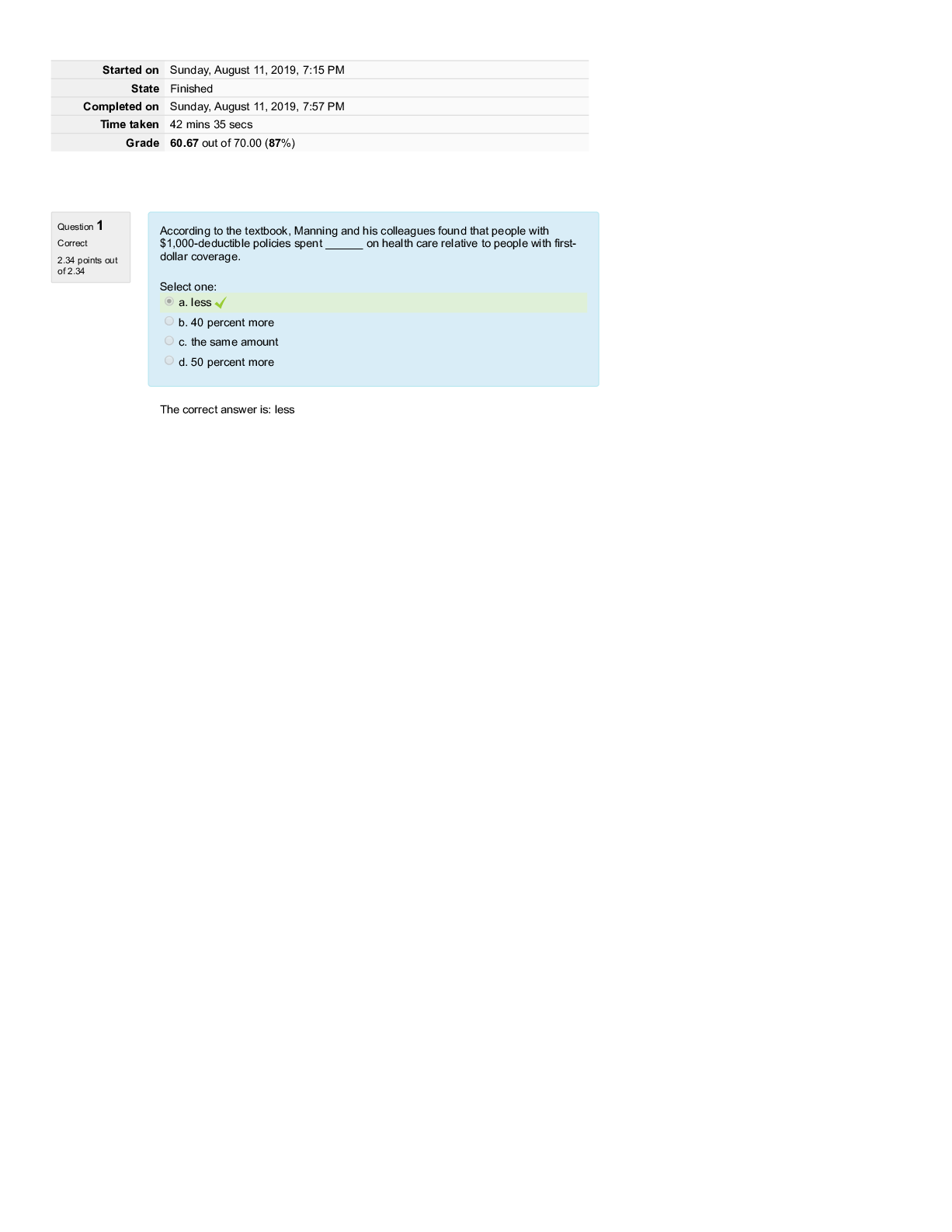
Wastewater grade 1 exam questions and answers graded A+ domestic wastewater ✔✔Comes from schools, homes, hospitals, businesses, light industrial facilities. population equivalents ✔✔100 lb... s wastewater per day, .2 lbs TSS/day, .17 BOD/day industrial wastewater ✔✔Comes from industries. Compatible wastes can be processed by the plant. Incompatible wastes are toxic to the plant. sanitary wastewater ✔✔The combined domestic and industrial waste waters from community. storm water ✔✔Water that runs off roads, parking lots, and other impervious surfaces during rain and snow storms sanitary sewers ✔✔Convey domestic and industrial waste waters, typically from where they are generated to the plant. storm sewers ✔✔Convey storm water, typically from storm drains directly to a point of discharge (stream, river, ocean). combined sewers ✔✔Convey sanitary waste water combined with storm water. Reasons to collect samples ✔✔federal and state regulatory compliance, process control, trouble shooting, special studies including future designs. grab sample ✔✔One time sample. Chlorine residual, coliform tests, settable solids, dissolved oxygen, pH, grease and oil, sulfide tests. Time based composite sample ✔✔Fixed volume of sample is collected after passage of a set amount of time over a certain time period. Flow based composite sample ✔✔Fixed volume of sample is collected after a prescribed amount of flow has passed through the sampling point, or a volume of sample proportional to the flow is collected after passage of a prescribed amount of time over a certain time period. This sample can also be called a flow proportional composite sample. diurnal flow ✔✔Low at night between 2 and 5 am, steady steep increase in flow starting after 5 am, reaching first peak in the late morning or early afternoon, slight decrease through the afternoon, second peak between 6 and 9 pm, and a tapering off of to the low flows of 2 am. BOD ✔✔Depletion of dissovled oxygen in a sample over 5 days at 20c is measured. Direct measure of the amount of dissolved oxygen consumed by aerobic bacteria over five days, indirect measure of the organic strength of waste water, used to asses the performance of WTP and the unit operations and unit processes used in WTP. COD ✔✔This test involves the chemical oxidation of all organics in a sample. Measure of organic strength of waste water, COD is always greater than BOD, In raw municipal sewage COD is typically 2 to 4 times greater than BOD, takes 2 hrs to run COD compared to 5 days for BOD therefore more appropriate for process control. pH ✔✔The log of the reciprocal of the the hydrogen ion concentration. PH 6 is 10 times the hydrogen ion concentration of 7. 5 is 100 times the conc of ph 7. Total solids ✔✔TSS + TDS Settleable solids ✔✔All settleable solids are TSS but not all TSS are settleable. Hydrogen sulfide h2s ✔✔Toxic, flammable and explosive, rotten egg odor, dulls sense of smell, paralyzes ability to breath, corrosive, heavier than air collects in low lying areas. Methane ch4 ✔✔Anaerobic digester have 62-70% methane vol basis. Lel is 5% and uel is 15%.flammable/ explosive. Odorless, not toxic but can asphyxiate at high conc, lighter than air. Anaerobic digester gas ✔✔65% methane, 34% carbon dioxide, 1% other inert gases. Contains less than 1% h2s Parshall flume ✔✔Open channel device that constricts the flow in such away that the depth of flow upstream of the flume is directly related to the flow rate passing through the flume. Does not measure velocity. Carbon dioxide ✔✔Aerobic bacteria exhale carbon dioxide. Anaerobic bacteria produce carbon dioxide. Non flammable, odorless, not toxic but can asphyxiate at high conc, heavier than air. Grit ✔✔Sand, coffee grounds, seeds, small pieces of gravel and metals, eggshells. Removed by velocity controlled grit chambers or aerated grit chambers. Flow is slowed to 1 f/s Objectives of primary treatment ✔✔Remove TSSset and the BOD associated with TSSset, remove floatable material(scum) Performance of primary clarifiers ✔✔>95% SS removal, 40-60% TSS removal, 25-40% BOD removal, detention time 1.5 to 2.5 hrs, weir over flow 10000 to 15000 gal/d ft, hydraulic loading 600 to 1200 gal/d ft2 Hydraulic loading ✔✔Gal/d ft2 (Surface loading or surface over flow rate) how many gallons of water per day are passing through each square foot of clarifier surface area. Performance is directly related to hydraulic loading . Weir overflow rate ✔✔Gal/d ft. Divide flow in gal/ day by weir length in units of feet. Detention time ✔✔Generally 1 hr minimum. If too long(2.5 -3hrs) then odors may be a problem in a primary clarifier and BOD removal may be compromised due to solubilization of BOD in the sludge blanket. Divide vol by influential flow rate. Primary clarifier performance ✔✔The BOD and TSS tests should be run on 24hr, flow weighted primary influent and primary effluent composite samples. SS test should always be a grab sample. Anaerobic digestion ✔✔Stabilization of raw sludge solids is the key. VS, pathogen, and volume reduction and gas production are the process objectives. Acid formers ✔✔Converts part of the complex organic mixture in the influent sludge stream into volatile acids( organic acids) including acetic, propionic, and butyric acids Acetogenesis ✔✔Formation of volatile acids Methane formers ✔✔Convert volatile acids into ch4 and co2. Also called methanogenesis Buffer ✔✔Prevents rapid changes in ph. Most buffer in healthy anaerobic digester is in the form of bicarbonate ion HCO3 Two types of grit removal ✔✔Velocity controlled grit chambers, aerated grit chambers. Velocity in grit chamber is controlled by ✔✔Multiple channels, proportional weir Bod and TSS ✔✔24 hr, flow weighted primary influent and primary effluent composite samples. In mg/l Vs in anaerobic digester is reduced by ✔✔Acid formers and methane formers Mass of vs in digester is reduced by how much ✔✔About 50 to 60% Humus ✔✔Offensive organic matter that is stabilized in the digester Bicarbonate ion HCO3 ✔✔Healthy digesters have this buffer Secondary digesters ✔✔Unheated and unmixed sludge. Allows liquid solids separation and storage upstream of the dewatering facilities. Produce little digester gas. Mixing digesters ✔✔Gas lift or mechanical mixing using pumps or propeller type mixers are common methods to mix. Centrifugal pumps are becoming more common. Heating digester ✔✔Most common method of heating is external heat exchanger. Boilers might be used to provide heated water to the exchanger. Co gen can also be used. Anaerobic digester safety ✔✔Pressure/vacuum relief valves, flame arrester, drip and sedimentation traps, pressure regulators, thermal valve, waste gas burner. Pressure valves ✔✔Occupy common housing with flame arrester, on top of digester. Measured in inches of water column. Typical pressure is 6 to 8 inches of water column. Valve my open to relieve pressure under some of floating cover digester . Vacuum relief valve ✔✔Relieves negative pressure to prevent possible collapse of the digester cover. Typical pressure is 2 inches of water column. Flame arrester ✔✔Box containing 50 to 100 corrugated stamped aluminum sheets called baffles. Any flame that develops in a gas line will be cooled below ignition temp. Drip trap ✔✔Digester gas is quite moist and this water will condense and collect at low spots in the gas piping and may impede gas flow. Potentially damaging digester gas equipment because of pressure. Holds 1 to 2 quarts of water located at low points in gas line. Should be drained once per day. Sediment trap ✔✔Remove sediment and condensate from digester gas by a combination of centrifugal force and a sharp drop in the velocity of the gas as it enters the trap. Pressure regulators ✔✔Installed next to and before waste gas burner. Pressure regulators control the gas pressure in the entire digester gas system and are normally set at 8 inches of water column. A thermal valve is placed between the pressure regulator and the waste gas burner. Thermal valve ✔✔A fusible element which melts at 260 f when exposed to a flame, causes a thermal valve to close shutting off the flow of gas. These valves may be attached to a flame arrester. These valves should be serviced at least once a year. Waste gas burner ✔✔Excess digester gas is burned in a waste gas burner, also known as a flare. Anaerobic digester auxiliary equipment ✔✔Access hole, manometer, sludge sampling manifold, overflow pipe, sight glass, recirculation pump, sludge pumps, sludge density meter. Facultative/ stabilization ponds ✔✔Aerobic top layer and anaerobic bottom layer Pond biology ✔✔Aerobic bacteria use bod to form co2. Algae use co2 and sun light to make o2 which is used by aerobic bacteria. More sun more ph and do. Less sun less ph and do. Algae ✔✔Without light algae use o2 and produce co2. Light only reaches about three feet depth. Detention time of pond ✔✔30 to 60 days or longer. DT= A x depth/Q Organic loading of pond ✔✔20 to 50 lb BOD/d AC or higher. OL= in lb BOD/d / A Hydraulic loading of pond ✔✔HL= Q/A Activate sludge treatment plant important aspects of operation ✔✔Air flow rate( ab do conc), waste activated sludge WAS flow rate, return activated sludge RAS flow rate. DO conc in aeration basin ✔✔1 to 3 mg/l 2 mg/l is often the target. 1 lb BOD in aeration basin needs .... ✔✔1000ft3 of air. More is needed if oxidation of ammonia is desired. How to control growth rate of microorganism in a aeration basin ✔✔Wasting WAS. Mass of microorganism that will grow in activated sludge system is controlled by..... ✔✔Mass of bod influent , growth rate being maintained, temperature of waste water. WAS flow rate controls .... ✔✔Nitrification, mlss conc, sludge quality, effluent quality, secondary clarifier capacity, secondary clarifier sludge blanket depth, oxygen requirements , occurrence of some foam causing organisms. How to fix WAS flow rate to achieve optimal sludge quality... ✔✔Maintain constant mlss or moves conc or mass, maintain a constant mcrt, maintain constant food to microorganism ratio. Mlss and mlvss are what type of variables ✔✔Response variables not control variables. MCRT ✔✔Average time a single bacterium spends in the activated sludge system before it is intentionally removed in the WAS or unintentionally removed in effluent. Range 5 to 15 days. MCRT= (lbs of mlss ab+sec)/ (lbs/d of TSS leaving the system in effluent and WAS) S ✔✔Lbs of mlss in system ab + secondary. E ✔✔Lbs per day of TSS unintentionally lost in effulgent W ✔✔Lbs per day of TSS intentionally removed in the WAS. Food to microorganism ratio ✔✔F:m may be used to determine the conc of mlvss and mlss to be maintained in the aeration basin. Typical ratios are .2 to .5 lb BOD/d lb mlvss. Extended aeration and oxidation ditches operate at f:m ratios of .03 to .1 BOD/ d lb mlvss. F/m= ( lbs bod per day to AB)/(lbs of mlvss in AB) How are mcrt and f/m related ✔✔Inversely related. RAS ✔✔Control of RAS flow is necessary to ensure an adequate supply of microorganisms must be returned to the aeration basin to treat influent waste. The sole purpose of the RAS is to keep the biomass in the aeration basins and out of the secondary clarifiers. Typical RAS rate is 25-50 %, but depends on mlss conc and the settleablity of the mixed liquor. Extended aeration rates are 75-150%. Optimum RAS flow rate is the lowest possible that does not result in a significant secondary sludge blanket. Sludge volume index ✔✔How well activated sludge and mixed liquor solids compact. Not a settleablity test. Units ml/g of activated sludge after 30 min of settling. Mlss conc must be measured on the same sample used in the settling test. Ranges are 80 to 120 ml/g. Greater than 150ml/g are considered bulking sludge. Standard rate trickling filter ✔✔HL= 25-100gpd/ft2, OL= 5-25 lb bod/ d 1000 ft3 of media, media is 6-8 ft rock, recirculation during low flows. High rate trickling filter ✔✔HL= 100-1000 gpd/ft2, OL= 25-300 lb bod/d 1000ft3 of media, media 3-5 ft natural or synthetic, yes recirculation. Roughing filter ✔✔OL= greater than 300 lb of BOD/ d 1000ft3. Generally used to reduce organic loading to downstream biological treatment processes. Disinfection ✔✔Kills pathogenic organisms. Does not sterilize. Chlorine ✔✔Powerful oxidizing agent. Greenish yellow color, pungent similar to bleach detectable at .2 to .4 ppm, 2.5 times heavier than air will sink to low points, boiling point is - 29.15 f, escaping liquid chlorine will turn into gas immediately, one volume of liquid cl2 converts to 460 volumes of gas. Vaporizes from skin to cause frostbite, not explosive or flammable but can react violently with many substances. Severe irritant, when mixed with water it forms acid, primary route of exposure is eyes and respiratory system. OSHA max level chlorine exposure ✔✔1 ppm Niosh limit for chlorine ✔✔10 ppm Chlorine should be separated from... ✔✔Ammonia and ammonia compounds, sulfur dioxide, hydrocarbons( oils, greases, solvents, even in small amounts) can can explosions when mixed. Factors affecting chlorination ✔✔Effluent quality, ammonia, nitrite. Effectiveness is measured by Coliform eff numbers. Tests used to measure total and fecal Coliform conc. ✔✔Multiple tube fermentation technique and the membrane filtration technique. Multiple tube fermentation Reported as mpn of bacteria per 100ml of effluent. Membrane filtration technique are reported as colonies per 100 ml of effluent. Chlorine storage ✔✔1 ton tanks, 150 lb tanks. Have metal plugs that melt between 158-165f. Oxidation pond ✔✔Treat primary effulent Polishing pond ✔✔Secondary effluent Thief hole ✔✔Access point for anaerobic digester sampling. Prevents gas from escaping from digester. ppm ✔✔Mg/l [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 15 pages
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
.png)
Wastewater Treatment Operator Certification Bundled Exams with Certified Solutions (2022/2023)
Wastewater Treatment Operator Certification Bundled Exams with Certified Solutions (2022/2023)
By Nutmegs 1 year ago
$25
21
Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 17, 2023
Number of pages
15
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 17, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
70

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)







.png)


.png)

