Chemistry > Lab Experiment > CHEM 214 General Chemistry II Lab - Experiment 008: Dissociation Constants of Acids and Bases. (All)
CHEM 214 General Chemistry II Lab - Experiment 008: Dissociation Constants of Acids and Bases.
Document Content and Description Below
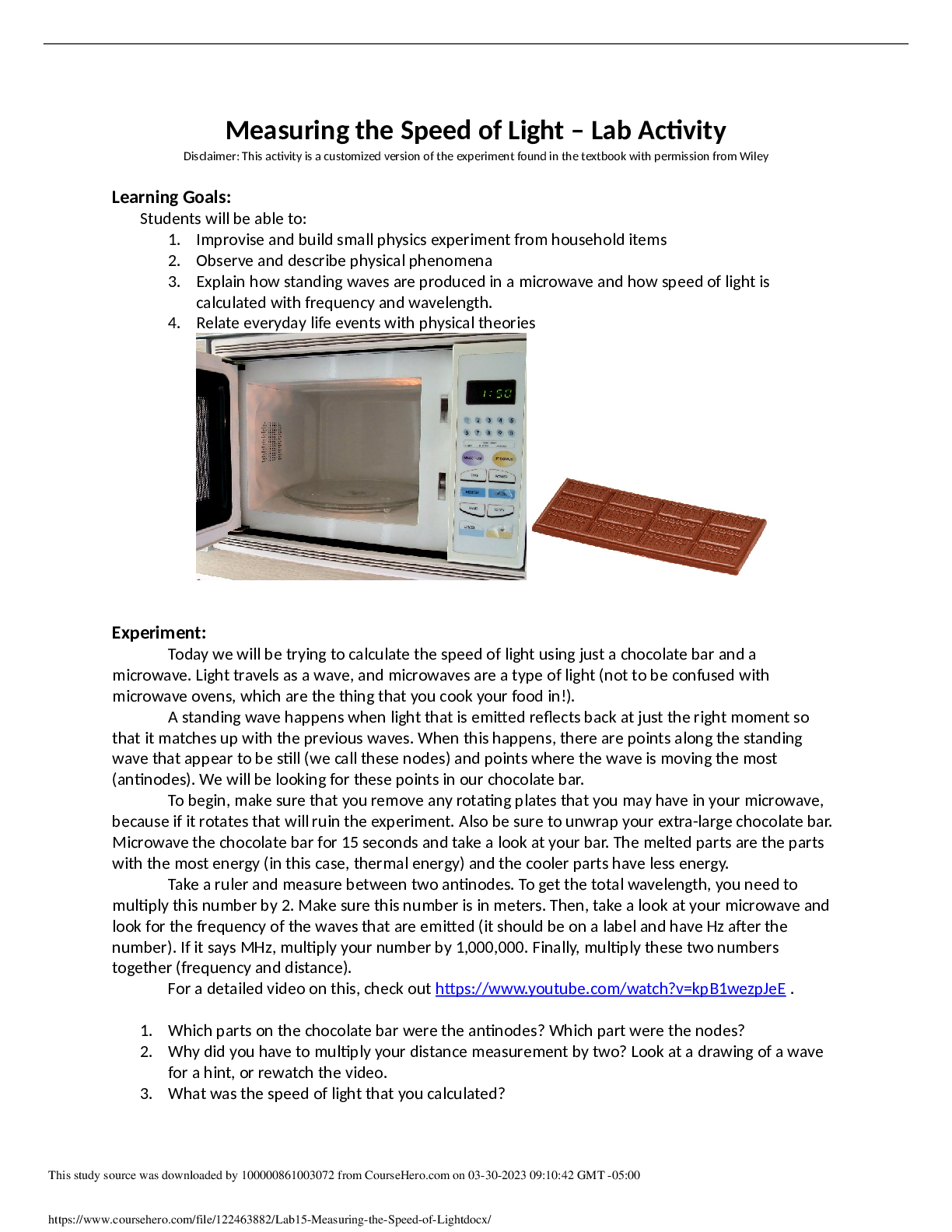
CHEM 214 General Chemistry II Lab - Experiment 008: Dissociation Constants of Acids and Bases References: Suzanne Slayden, 2018, Chemistry 213, 214, 272 Laboratory Experiments, 7th Edition, pages 2... 13-221. George Mason University, Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry. Dissociation Constants; 2020. Dissociation Constants, Distance Learning Summer 2020, accessed via Blackboard. Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to determine the dissociation constant Ka of acetic acid (CH3COOH) and the pH of various phosphate salts (NaH2PO4, Na2HPO4, Na3PO4). This will be done in two different parts, Part A and Part B. Part A will take two different pH recordings of acetic acid, one using pure acetic acid solution and another that has been neutralized by NaOH solution. Part B will take theoretical pH calculations for all three phosphate salt solutions with known concentrations as well as experimental pH calculations using a pH meter. The anticipated outcome is that the experimental dissociation constant of acetic acid and the experimental pH values of the phosphate salts will match their theoretical values. The balanced equations for this experiment are: CH3COOH → CH3COO- + H+ CH3COOH + NaOH → NaCH3CHOO + H2O H3PO4 + H2O → H2PO4- + H3O+ Ka1 = 7.5 x 10-3 H2PO4- + H2O → H2PO42- + H3O+ Ka2 = 6.2 x 10-8 H2PO4- + H2O → H3PO4 + OH- Kb = 1.3 x 10-12 H2PO42- + H2O → PO43- + H3O+ Ka3 = 4.8 x 10-13 H2PO42- + H2O → H2PO4- + OH- Kb = 1.6 x 10-7Materials • 0.1020-M Acetic Acid • 0.0920-M NaOH Solution • NaH2PO4 • Na2HPO4•7H2O • Na3PO4•12H2O • pH Meter • 20-mL Graduated Cylinder • 125 mL Erlenmeyer Flask • 2 Beakers • Distilled Water • Scoopula • Electronic Balance Procedure A. Part A 1. Measure about 20 mL of acetic acid into the 125-mL Erlenmeyer flask using the graduated cylinder. Measure the pH twice. Calculate the Ka. 2. Measure about 8 mL of NaOH into the flask. Swirl. Measure the pH twice. Calculate the concentrations of acetic acid and acetate ion after it has been partially neutralized with NaOH. Calculate the Ka. B. Part B 1. Determine the dominant behaviors (acidic or basic) of the salts by comparing the magnitude of their dissociation constants for H2PO4- and HPO42-. Calculate the expected pH for a 0.10-M solution of NaH2PO4 and Na2HPO4. 2. Dissolve 0.6 grams of NaH2PO4 and Na2HPO4•7H2O in two small beakers each with 30 mL of distilled water. Calibrate the pH meter. Record pH of each solution. Compare the pH values with the theoretical values calculated in Step 1. 3. Record the pH of a Na3PO4•12H2O solution using 0.2 grams in 10 mL of distilled water. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 14 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 20, 2023
Number of pages
14
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 20, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
59

.png)
-2.png)
-2.png)







.png)












.png)

