Health Care > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Adult Health HESI Review Questions with Complete Solutions (All)
Adult Health HESI Review Questions with Complete Solutions
Document Content and Description Below
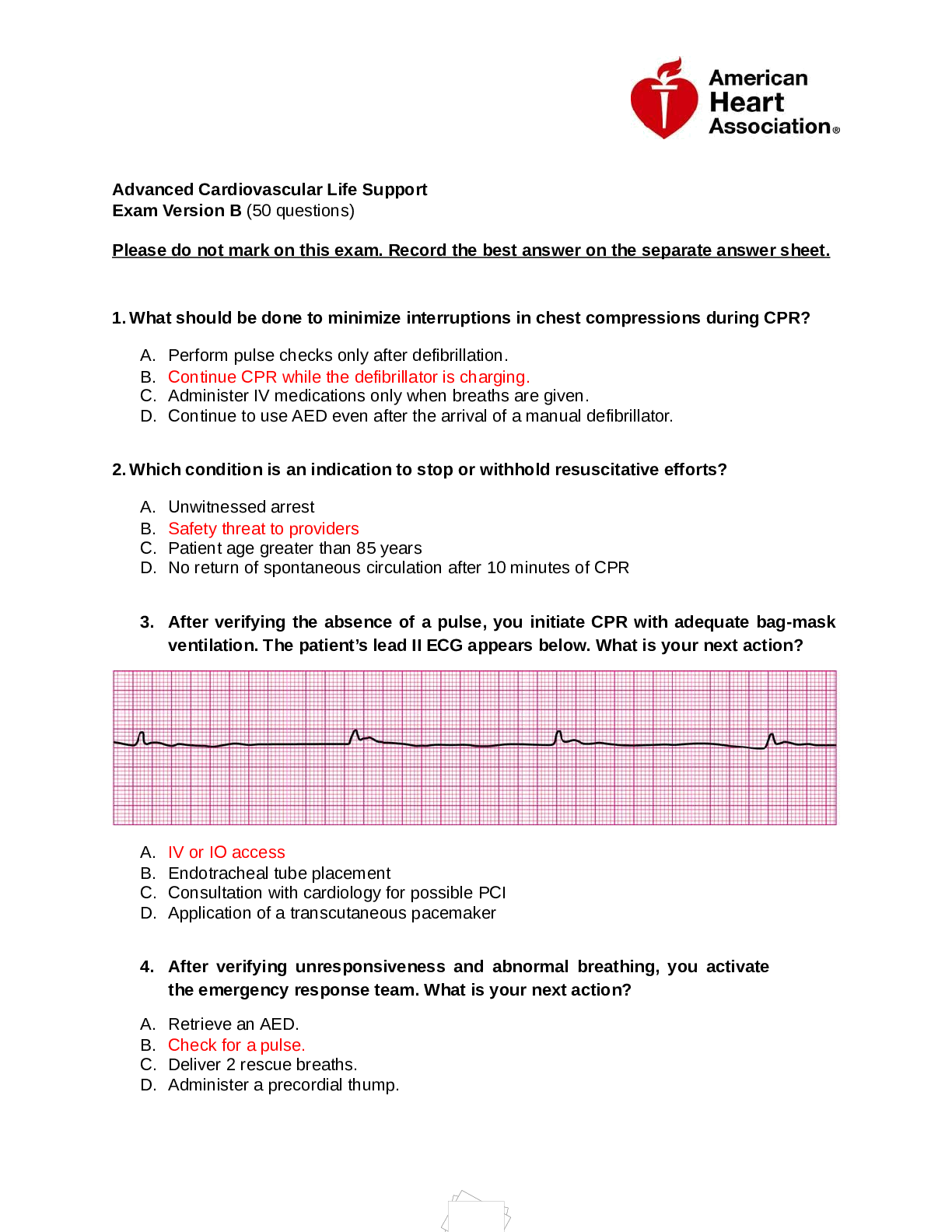
Adult Health HESI Review Questions with Complete Solutions A central venous catheter has been inserted via a jugular vein, and a radiograph has confirmed placement of the catheter. A prescription h... as been received for a medication STAT, but IV fluids have not yet been started. Which action should the nurse take prior to administering the prescribed medication? A. Assess for signs of jugular venous distention. B. Obtain the needed intravenous solution. C. Flush the line with heparinized solution. D. Flush the line with normal saline. ✔✔Answer, D Rationale- Medication can be administered via a central line without additional IV fluids. The line should first be flushed with a normal saline solution to ensure patency. Insufficient evidence exists on the effectiveness of flushing catheters with heparin. Option A will not affect the decision to administer the medication and is not a priority. Administration of the medication STAT is of greater priority than option B. A client is ready for discharge following the creation of an ileostomy. Which instruction should the nurse include in discharge teaching? A. Replace the stoma appliance every day. B. Use warm tap water to irrigate the ileostomy. C. Change the bag when the seal is broken. D. Measure and record the ileostomy output. ✔✔Answer- C Rationale- A seal must be maintained to prevent leakage of irritating liquid stool onto the skin. Option A is excessive and can cause skin irritation and breakdown. Ileostomies produce liquid fecal drainage, so option B is not necessary. Option D is not needed. An older male client comes to the outpatient clinic complaining of pain in his left calf. The nurse notices a reddened area on the calf of his right leg that is warm to the touch, and the nurse suspects that the client may have thrombophlebitis. Which additional assessment is most important for the nurse to perform? A. Measure the client's calf circumference. B. Auscultate the client's breath sounds. C. Observe for ecchymosis and petechiae. D. Obtain the client's blood pressure. ✔✔Answer- B Rationale- All these techniques provide useful assessment data. The most important is to auscultate the client's breath sounds because the client may have a pulmonary embolus secondary to the thrombophlebitis. Option A may provide data that support the nurse's suspicion of thrombophlebitis. Option C is the least helpful assessment because bruising is not a typical finding associated with thrombophlebitis. Option D is always useful in evaluating the client's response to a problem but is of less immediate priority than breath sound auscultation. The nurse is caring for a critically ill client with cirrhosis of the liver who has a nasogastric tube draining bright red blood. The nurse notes that the client's serum hemoglobin and hematocrit levels are decreased. Which additional change in laboratory data should the nurse expect? A. Increased serum albumin level B. Decreased serum creatinine C. Decreased serum ammonia level D. Increased liver function test results ✔✔Answer- C Rationale- The breakdown of glutamine in the intestine and the increased activity of colonic bacteria from the digestion of proteins increase ammonia levels in clients with advanced liver disease, so removal of blood, a protein source, from the intestine results in a reduced level of ammonia. Options A, B, and D will not be significantly affected by the removal of blood. What is digoxin ✔✔Blood pressure medication with high toxicity Signs of hyperkalemia ✔✔Tall/spiked T waves, prolonged QT interval, widening QRS wave The breakdown of glutamine in the intestine and the increased activity of colonic bacteria from the digestion of proteins increase ammonia levels in clients with advanced liver disease, so removal of blood, a protein source, from the intestine results in a reduced level of ammonia. Options A, B, and D will not be significantly affected by the removal of blood. A. Reduce the daily intake of animal fat to 10% of the diet within 6 weeks. B. Exhibit regular, soft-formed stool within 1 month. C. Demonstrate the irrigation procedure correctly within 1 week. D. Attend an ostomy support group within 2 weeks. ✔✔Answer- D, attend an ostomy support group within 2 weeks Rationale- Attending a support group will be beneficial to the client and should be encouraged because adaptation to the ostomy can be difficult. This goal is attainable and is measurable. Option A is not specifically related to ileostomy care. The client with an ileostomy will not be able to accomplish option B. Option C is not necessary. The nurse is administering a nystatin suspension for stomatitis. Which instruction will the nurse provide to the client when administering this medication? A. "Hold the medication in your mouth for a few minutes before swallowing it." B. "Do not drink or eat milk products for 1 hour prior to taking this medication." C. "Dilute the medication with juice to reduce the unpleasant taste and odor." D. "Take the medication before meals to promote increased absorption." ✔✔Answer- A Rationale- Nystatin suspension is prescribed for fungal infections of the mouth. The client should swish the medication in the mouth for 2 minutes and then swallow. Option B does not affect administration of this medication. The medication should not be diluted because this will reduce its effectiveness. Option D is not necessary. Which data would the nurse expect to find when reviewing laboratory values of an 80-year-old man who is in good health overall? A. Complete blood count reveals increased white blood cell (WBC) and decreased red blood cell (RBC) counts. B. Chemistries reveal an increased serum bilirubin level with slightly increased liver enzyme levels. C. Urinalysis reveals slight protein in the urine and bacteriuria, with pyuria. D. Serum electrolytes reveal a decreased sodium level and increased potassium level. ✔✔Answer- C Rationale- In older adults, the protein found in urine slightly rises, probably as a result of kidney changes or subclinical urinary tract infections, and clients frequently experience asymptomatic bacteriuria and pyuria as a result of incomplete bladder emptying. Laboratory findings in options A, B, and D are not considered to be normal findings in an older adult. An older client is admitted with a diagnosis of bacterial pneumonia. Which symptom should the nurse report to the health care provider after assessing the client? A. Leukocytosis and febrile B. Polycythemia and crackles C. Pharyngitis and sputum production D. Confusion and tachycardia ✔✔Answer- D Rationale- The onset of pneumonia in the older client may be signaled by general deterioration, confusion, increased heart rate, and/or increased respiratory rate. Options A, B, and C are often absent in the older client with bacterial pneumonia. The nurse is assessing a male client with acute pancreatitis. Which finding requires the most immediate intervention by the nurse? A. The client's amylase level is three times higher than the normal level. B. While the nurse is taking the client's blood pressure, he has a carpal spasm. C. On a 1 to 10 scale, the client tells the nurse that his epigastric pain is at 7. D. The client states that he will continue to drink alcohol after going home. ✔✔Answer- B Rationale- A positive Trousseau sign indicates hypocalcemia and always requires further assessment and intervention, regardless of the cause (40% to 75% of those with acute pancreatitis experience hypocalcemia, which can have serious, systemic effects). A key diagnostic finding of pancreatitis is serum amylase and lipase levels that are two to five times higher than the normal value. Severe boring pain is an expected symptom for this diagnosis, but dealing with the hypocalcemia is a priority over administering an analgesic. Long-term planning and teaching do not have the same immediate importance as a positive Trousseau sign. A male client has just undergone a laryngectomy and has a cuffed tracheostomy tube in place. When initiating bolus tube feedings postoperatively, when should the nurse inflate the cuff? A. Immediately after feeding B. Just prior to tube feeding C. Continuous inflation is required D. Inflation is not required ✔✔Answer- B Rationale- The cuff should be inflated before the feeding to block the trachea and prevent food from entering if oral feedings are started while a cuffed tracheostomy tube is in place. It should remain inflated throughout the feeding to prevent aspiration of food into the respiratory system. Options A and D place the client at risk for aspiration. Option C places the client at risk for tracheal wall necrosis. The nurse initiates neurologic checks for a client who is at risk for neurologic compromise. Which manifestation typically provides the first indication of altered neurologic function? A. Change in level of consciousness B. Increasing muscular weakness C. Changes in pupil size bilaterally D. Progressive nuchal rigidity ✔✔Answer- A Rationale- A decrease or change in the level of consciousness is usually the first indication of neurologic deterioration. Options B and C may also occur but are much less likely to be the first sign of neurologic compromise. Option D is often a sign of meningitis. Based on the clinical manifestations of Cushing syndrome, which nursing intervention would be appropriate for a client who is newly diagnosed with Cushing syndrome? A. Monitor blood glucose levels daily. B. Increase intake of fluids high in potassium. C. Encourage adequate rest between activities. D. Offer the client a sodium-enriched menu. ✔✔Answer- A Rationale- ushing syndrome results from a hypersecretion of glucocorticoids in the adrenal cortex. Clients with Cushing syndrome often develop diabetes mellitus. Monitoring of serum glucose levels assesses for increased blood glucose levels so that treatment can begin early. A common finding in Cushing syndrome is generalized edema. Although potassium is needed, it is generally obtained from food intake, not by offering potassium-enhanced fluids. Fatigue is usually not an overwhelming factor in Cushing syndrome, so an emphasis on the need for rest is not indicated A low-calorie, low-carbohydrate, low-sodium diet is not recommended. What can insulin do? ✔✔Increase serum potassium level (and blood glucose of course) The nurse is observing an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) performing morning care for a bedridden client with Huntington disease. Which care measure is most important for the nurse to supervise? A. Oral Care B. Bathing C. Foot Care D. catheter care ✔✔Answer- A Rationale- The client with Huntington disease experiences problems with motor skills such as swallowing and is at high risk for aspiration, so the highest priority for the nurse to observe is the UAP's ability to perform oral care safely. Options B, C, and D do not necessarily require registered nurse (RN) supervision because they do not ordinarily pose life-threatening consequences. The nurse assesses a postoperative client whose skin is cool, pale, and moist. The client is very restless and has scant urine output. Oxygen is being administered at 2 L/min, and a saline lock is in place. Which intervention should the nurse implement first? A. Measure the urine specific gravity. B. Obtain IV fluids for infusion per protocol. C. Prepare for insertion of a central venous catheter. D. Auscultate the client's breath sounds. ✔✔Answer- B Rationale- The client is at risk for hypovolemic shock because of the postoperative status and is exhibiting early signs of shock. A priority intervention is the initiation of IV fluids to restore tissue perfusion. Options A, C, and D are all important interventions but are of lower priority than option B. In assessing a client diagnosed with primary aldosteronism, the nurse expects the laboratory test results to indicate a decreased serum level of which substance? A. Sodium B. Phosphate C. Potassium D. Glucose ✔✔Answer- C Rationale- Clients with primary aldosteronism exhibit a profound decline in serum levels of potassium; hypokalemia; hypertension is the most prominent and universal sign. The serum sodium level is normal or elevated, depending on the amount of water resorbed with the sodium. Option B is influenced by parathyroid hormone (PTH). Option D is not affected by primary aldosteronism. What is the result of end-stage renal disease ✔✔Elevated serum lipid levels What is the result of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) ✔✔ketonuria What is associated with end-stage renal disease ✔✔Hyperkalemia? During the change of shift report, the charge nurse reviews the infusions being received by clients on the oncology unit. The client receiving which infusion should be assessed first? A. Continuous IV infusion of magnesium B. One-time infusion of albumin C. Continuous epidural infusion of morphine D. Intermittent infusion of IV vancomycin ✔✔Answer- C Rationale- All four of these clients have the potential to have significant complications. The client with the morphine epidural infusion is at highest risk for respiratory depression and should be assessed first. Option A can cause hypotension. The client receiving option B is at lowest risk for serious complications. Although option D can cause nephrotoxicity and phlebitis, these problems are not as immediately life threatening as option C. A 55-year-old male client has been admitted to the hospital with a medical diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Which risk factor is the most significant in the development of this client's COPD? A. The client's father was diagnosed with COPD in his 50s. B. A close family member contracted tuberculosis last year. C. The client smokes one to two packs of cigarettes per day. D. The client has been 40 pounds overweight for 15 years. ✔✔Answer- C Rationale- Smoking, considered to be a modifiable risk factor, is the most significant risk factor for the development of COPD. The exact mechanism of genetic and hereditary implications for the development of COPD is still under investigation, although exposure to similar predisposing factors (e.g., smoking or inhaling secondhand smoke) may increase the likelihood of COPD incidence among family members. Options B and D do not exceed the risks associated with cigarette smoking in the development of COPD. Which description of symptoms is characteristic of a client diagnosed with trigeminal neuralgia (tic douloureux)? A. Tinnitus, vertigo, and hearing difficulties B. Sudden, stabbing, severe pain over the lip and chin C. Unilateral facial weakness and paralysis D. Difficulty in chewing, talking, and swallowing ✔✔Answer- B Rationale- Trigeminal neuralgia is characterized by paroxysms of pain, similar to an electric shock, in the area innervated by one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve (cranial V). Option A would be characteristic of Ménière syndrome (cranial nerve VIII). Option C would be characteristic of Bell palsy (cranial nerve VII). Option D would be characteristic of disorders of the hypoglossal (cranial nerve XII). A client with chronic asthma is admitted to the PACU complaining of pain at a level of 8 on a 1 to 10 scale, with a blood pressure of 124/78 mm Hg, pulse of 88 beats/min, and respirations of 20 breaths/min. The PACU recovery prescription is "Morphine, 2 to 4 mg IV push, while in recovery for pain level over 5." Which intervention should the nurse implement? A. Give the medication as prescribed to decrease the client's pain. B. Call the anesthesia provider for a different medication for pain. C. Use nonpharmacologic techniques before giving the medication. D. Reassess the pain level in 30 minutes and medicate if it remains elevated. ✔✔Answer- B Rationale- The nurse should call the provider for a different medication because morphine is a histamine-releasing opioid and should be avoided when the client has asthma. Option A is unsafe because it puts the client at risk for an asthma exacerbation. Even if the drug were safe for the client, options C and D both disregard the prescription and the client's need for pain relief in the immediate postoperative period. The nurse is caring for a client with a chest tube to water seal drainage that was inserted 10 days ago because of a ruptured bullae and pneumothorax. Which finding should the nurse report to the health care provider before the chest tube is removed? A. Tidaling of water in water seal chamber B. Bilateral muffled breath sounds at bases C. Temperature of 101° F D. Absence of chest tube drainage for 2 days ✔✔Answer- A Rationale- Tidaling (rising and falling of water with respirations) in the water seal chamber should be reported to the health care provider before the chest tube is removed to rule out an unresolved pneumothorax or persistent air leak, which is characteristic of a ruptured bullae caused by abnormally wide changes in negative intrathoracic pressure. Option B may indicate hypoventilation from chest tube discomfort and usually improves when the chest tube is removed. Option C usually indicates an infection, which may not be related to the chest tube. Option D is an expected finding. A hospitalized client is receiving nasogastric tube feedings via a small-bore tube and a continuous pump infusion. He begins to cough and produces a moderate amount of white sputum. Which action should the nurse take first? A. Auscultate the client's breath sounds. B. Turn off the continuous feeding pump. C. Check placement of the nasogastric tube. D. Measure the amount of residual feeding. ✔✔Answer- B Rationale- A productive cough may indicate that the feeding has been aspirated. The nurse should first stop the feeding to prevent further aspiration. Options A, C, and D should all be performed before restarting the tube feeding if no evidence of aspiration is present and the tube is in place. learn hepatitis b, a , c etc ✔✔ The nurse is caring for a client with a fractured right elbow. Which assessment finding has the highest priority and requires immediate intervention? A. Ecchymosis over the right elbow area B. Deep unrelenting pain in the right arm C. An edematous right elbow D. The presence of crepitus in the right elbow ✔✔Answer- B Rationale- Compartment syndrome is a condition involving increased pressure and constriction of the nerves and vessels within an anatomic compartment, causing pain uncontrolled by opioids and neurovascular compromise. Option A is an expected finding. Option C related to compartment syndrome cannot be seen, and any visible edema is an expected finding related to the injury. Option D is an expected finding. A 43-year-old homeless, malnourished female client with a history of alcoholism is transferred to the ICU. She is placed on telemetry, and the rhythm strip shown is obtained. The nurse palpates a heart rate of 160 beats/min, and the client's blood pressure is 90/54 mm Hg. Based on these findings, which IV medication should the nurse administer? A. Amiodarone (Cordarone) B. Magnesium sulfate C. Lidocaine (Xylocaine) D. Procainamide (Pronestyl) ✔✔Answer- B Rationale- Because the client has chronic alcoholism, she is likely to have hypomagnesemia. Option B is the recommended drug for torsades de pointes, which is a form of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (VT) usually associated with a prolonged QT interval that occurs with hypomagnesemia. Options A and D increase the QT interval, which can cause the torsades to worsen. Option C is the antiarrhythmic of choice in most cases of drug-induced monomorphic VT, not torsades. What is the correct location for placement of the hands for manual chest compressions during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) on the adult client? A. Just above the xiphoid process, on the upper third of the sternum B. Below the xiphoid process, midway between the sternum and the umbilicus C. Just above the xiphoid process, on the lower third of the sternum D. Below the xiphoid process, midway between the sternum and the first rib ✔✔Answer- C A client in the emergency department is bleeding profusely from a gunshot wound to the abdomen. What action should the nurse immediately take to promote maintenance of the client's blood pressure above a systolic pressure of 90 mm Hg? A. Place the client in a 45-degree Trendelenburg position to promote cerebral blood flow. B. Turn the client prone to place pressure on the abdominal wound to help staunch the bleeding. C. Maintain the client in a supine position to reduce diaphragmatic pressure and visualize the wound. D. Put the client on the right side to apply pressure to the liver and spleen to stop hemorrhaging. ✔✔Answer- C Rationale- Placing the client in a supine position reduces diaphragmatic pressure, thereby enhancing oxygenation, and allows for visualization of the abdominal wound. Option A compromises diaphragmatic expansion and inhibits pressoreceptor activity. Option B places the client at risk of evisceration of the abdominal wound and increased bleeding. Option D will not stop internal bleeding in the liver and spleen caused by the gunshot wound. A client is diagnosed with an acute small bowel obstruction. Which assessment finding requires the most immediate intervention by the nurse? A. Fever of 102° F B. Blood pressure of 150/90 mm Hg C. Abdominal cramping D. Dry mucous membranes ✔✔Answer- A Rationale- A sudden increase in temperature is an indicator of peritonitis. The nurse should notify the health care provider immediately. Options B, C, and D are also findings that require intervention by the nurse but are of less priority than option A. Option B may indicate a hypertensive condition but is not as acute a condition as peritonitis. Option C is an expected finding in clients with small bowel obstruction and may require medication. Option D indicates probable fluid volume deficit, which requires fluid volume replacement. The nurse is assessing a 75-year-old client for symptoms of hyperglycemia. Which symptom of hyperglycemia is an older adult most likely to exhibit? A. Polyuria B. Polydipsia C. Weight loss D. Infection ✔✔Answer- D Rationale- Signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia in older adults may include fatigue, infection, and evidence of neuropathy (e.g., sensory changes). The nurse needs to remember that classic signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia, such as options A, B, and C and polyphagia, may be absent in older adults. A client diagnosed with chronic kidney disease (CKD) 2 years ago is regularly treated at a community hemodialysis facility. Before his scheduled dialysis treatment, which electrolyte imbalance should the nurse anticipate? A. Hypophosphatemia B. Hypocalcemia C. Hyponatremia D. Hypokalemia ✔✔Answer- B Rationale- Hypocalcemia develops in CKD because of chronic hyperphosphatemia, not option A. Increased phosphate levels cause the peripheral deposition of calcium and resistance to vitamin D absorption needed for calcium absorption. Prior to dialysis, the nurse would expect to find the client hypernatremic and hyperkalemic, not with option C or D. A 58-year-old client who has no health problems asks the nurse about receiving the pneumococcal vaccine. Which statement given by the nurse would offer the client accurate information about this vaccine? A. The vaccine is given annually before the flu season to those older than 50 years. B. The immunization is administered once to older adults or those at risk for illness. C. The vaccine is for all ages and is given primarily to those persons traveling overseas to areas of infection. D. The vaccine will prevent the occurrence of pneumococcal pneumonia for up to 5 years. ✔✔Answer- B Rationale- It is usually recommended that persons older than 65 years and those with a history of chronic illness should receive the vaccine once in their lifetime. Some recommend receiving the vaccine at 50 years of age. The influenza vaccine is given once a year. Although the vaccine might be given to a person traveling overseas, that is not the main rationale for administering the vaccine. The vaccine is usually given once in a lifetime, but with immunosuppressed clients or clients with a history of pneumonia, revaccination is sometimes required. A client is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of severe acute diverticulitis. Which nursing intervention has the highest priority? A. Place the client on NPO status. B. Assess the client's temperature. C. Obtain a stool specimen. D. Administer IV fluids. ✔✔Answer- A Rationale- A client with acute severe diverticulitis is at risk for peritonitis and intestinal obstruction and should be made NPO to reduce risk of intestinal rupture. Options B, C, and D are important but are less of a priority than option A, which is implemented to prevent a severe complication. A client who is receiving an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor for hypertension calls the clinic and reports the recent onset of a cough to the nurse. Which action should the nurse implement? A. Advise the client to come to the clinic immediately for further assessment. B. Instruct the client to discontinue use of the drug and to make an appointment at the clinic. C. Suggest that the client learn to accept the cough as a side effect to a necessary prescription. D. Encourage the client to keep taking the drug until seen by the health care provider. ✔✔Answer- D Rationale- Coughing is a common side effect of ACE inhibitors and is not an indication to discontinue the medication. Immediate evaluation is not needed. Antihypertensive medications should not be stopped abruptly because rebound hypertension may occur. Option C is demeaning because the cough may be very disruptive to the client, and other antihypertensive medications may produce the desired effect without the adverse effect. The nurse on a medical-surgical unit is receiving a client from the postanesthesia care unit (PACU) with a Penrose drain. Before choosing a room for this client, which information is most important for the nurse to obtain? A. If suctioning will be needed for drainage of the wound B. If the family would prefer a private or semiprivate room C. If the client also has a Hemovac in place D. If the client's wound is infected ✔✔Answer- D Rationale- The fact that the client has a Penrose drain should alert the nurse to the possibility that the surgical wound is infected. Penrose drains provide a sinus tract or opening and are often used to provide drainage of an abscess. To avoid contamination of another postoperative client, it is most important to place any client with an infected wound in a private room. A Penrose drain does not require option A. Although option B is helpful information, it does not have the priority of option D. A Hemovac is used to drain fluid from a dead space and is not a determinant for the room assignment. Which consideration is most important when the nurse is assigning a room for a client being admitted with progressive systemic sclerosis (scleroderma)? A. Provide a room that can be kept warm. B. Make sure that the room can be kept dark. C. Keep the client close to the nursing unit. D. Select a room that is visible from the nurses' desk. ✔✔Answer- A Rationale- Abnormal blood flow in response to cold (Raynaud phenomenon) is precipitated in clients with scleroderma. Option B is not a significant factor. Stress can also precipitate the severe pain of Raynaud phenomenon, so a quiet environment is preferred to option C, which is often very noisy. Option D is not necessary. what is the normal urine specific gravity ✔✔ ventricular fibrilation ✔✔is a life-threatening emergency When assigning clients on a medical-surgical floor to an RN and a PN, it is best for the charge nurse to assign which client to the PN? A. A young adult with bacterial meningitis with recent seizures B. An older adult client with pneumonia and viral meningitis C. A female client in isolation with meningococcal meningitis D. A male client 1 day postoperative after drainage of a brain abscess ✔✔Answer- B Rationale- The most stable client is option B. Options A, C, and D are all at high risk for increased intracranial pressure and require the expertise of the RN for assessment and management of care. The nurse receives the client's next scheduled bag of TPN labeled with the additive NPH insulin. Which action should the nurse implement? A. Hang the solution at the current rate. B. Refrigerate the solution until needed. C. Prepare the solution with new tubing. D. Return the solution to the pharmacy. ✔✔Answer- D Rationale- Only regular insulin is administered by the IV route, so the TPN solution containing NPH insulin should be returned to the pharmacy. Options A, B, and C are not indicated because the solution should not be administered. The nurse is reviewing routine medications taken by a client with chronic angle-closure glaucoma. Which medication prescription should the nurse question? A. Antianginal with a therapeutic effect of vasodilation B. Anticholinergic with a side effect of pupillary dilation C. Antihistamine with a side effect of sedation D. Corticosteroid with a side effect of hyperglycemia ✔✔Answer- B Rationale- Clients with angle-closure glaucoma should not take medications that dilate the pupil because this can precipitate acute and severely increased intraocular pressure. Options A, C, and D do not cause increased intracranial pressure, which is the primary concern with angle-closure glaucoma. When developing a discharge teaching plan for a client after the insertion of a permanent pacemaker, the nurse writes a goal of "The client will verbalize symptoms of pacemaker failure." Which behavior indicates that the goal has been met? A. The client demonstrates the procedures to change the rate of the pacemaker using a magnet. B. The client carries a card in his wallet stating the type and serial number of the pacemaker. C. The client tells the nurse that it is important to report redness and tenderness at the insertion site. D. The client states that changes in the pulse and feelings of dizziness are significant changes. ✔✔Answer- D Rationale- Changes in pulse rate and/or rhythm may indicate pacer failure. Feelings of dizziness may be caused by a decreased heart rate, leading to decreased cardiac output. The rate of a pacemaker is not changed by a client, although the client may be familiar with this procedure as explained by his health care provider. Option B is an important step in preparing the client for discharge but does not demonstrate knowledge of the symptoms of pacer failure. Option C indicates symptoms of possible incisional infection or irritation but does not indicate pacer failure. The nurse is planning care for a client with diabetes mellitus who has gangrene of the toes to the midfoot. Which goal should be included in this client's plan of care? A. Restore skin integrity. B. Prevent infection. C. Promote healing. D. Improve nutrition ✔✔Answer- B Rationale- The prevention of infection is a priority goal for this client. Gangrene is the result of necrosis (tissue death). If infection develops, there is insufficient circulation to fight the infection and the infection can result in osteomyelitis or sepsis. Because tissue death has already occurred, options A and C are unattainable goals. Option D is important but of less priority than option B. Which serum laboratory value should the nurse monitor carefully for a client who has a nasogastric (NG) tube to suction for the past week? A. White blood cell count B. Albumin C. Calcium D. Sodium ✔✔Answer- Sodium Rationale- Monitoring serum sodium levels for hyponatremia is indicated during prolonged NG suctioning because of loss of fluids. Changes in levels of option A, B, or C are not typically associated with prolonged NG suctioning. Urinary catheterization is prescribed for a postoperative female client who has been unable to void for 8 hours. The nurse inserts the catheter, but no urine is seen in the tubing. Which action will the nurse take next? A. Clamp the catheter and recheck it in 60 minutes. B. Pull the catheter back 3 inches and redirect upward. C. Leave the catheter in place and reattempt with another catheter. D. Notify the health care provider of a possible obstruction. ✔✔Answer- C Rationale- It is likely that the first catheter is in the vagina, rather than the bladder. Leaving the first catheter in place will help locate the meatus when attempting the second catheterization. The client should have at least 240 mL of urine after 8 hours. Option A does not resolve the problem. Option B will not change the location of the catheter unless it is completely removed, in which case a new catheter must be used. There is no evidence of a urinary tract obstruction if the catheter could be easily inserted. The nurse prepares to insert a nasogastric tube in a client with hyperemesis who is awake and alert. Which intervention(s) is(are) correct? (Select all that apply.) A. Place the client in a high Fowler position. B. Help the client assume a left side-lying position. C. Measure the tube from the tip of the nose to the umbilicus. D. Instruct the client to swallow after the tube has passed the pharynx. E. Assist the client in extending the neck back so the tube may enter the larynx. ✔✔Answer- A, D [Show More]
Last updated: 10 months ago
Preview 1 out of 45 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 07, 2023
Number of pages
45
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 07, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
138

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)










.png)


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)




