Psychology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > AQA GCSE Psychology Memory Questions and Answers 100% Pass (All)
AQA GCSE Psychology Memory Questions and Answers 100% Pass
Document Content and Description Below
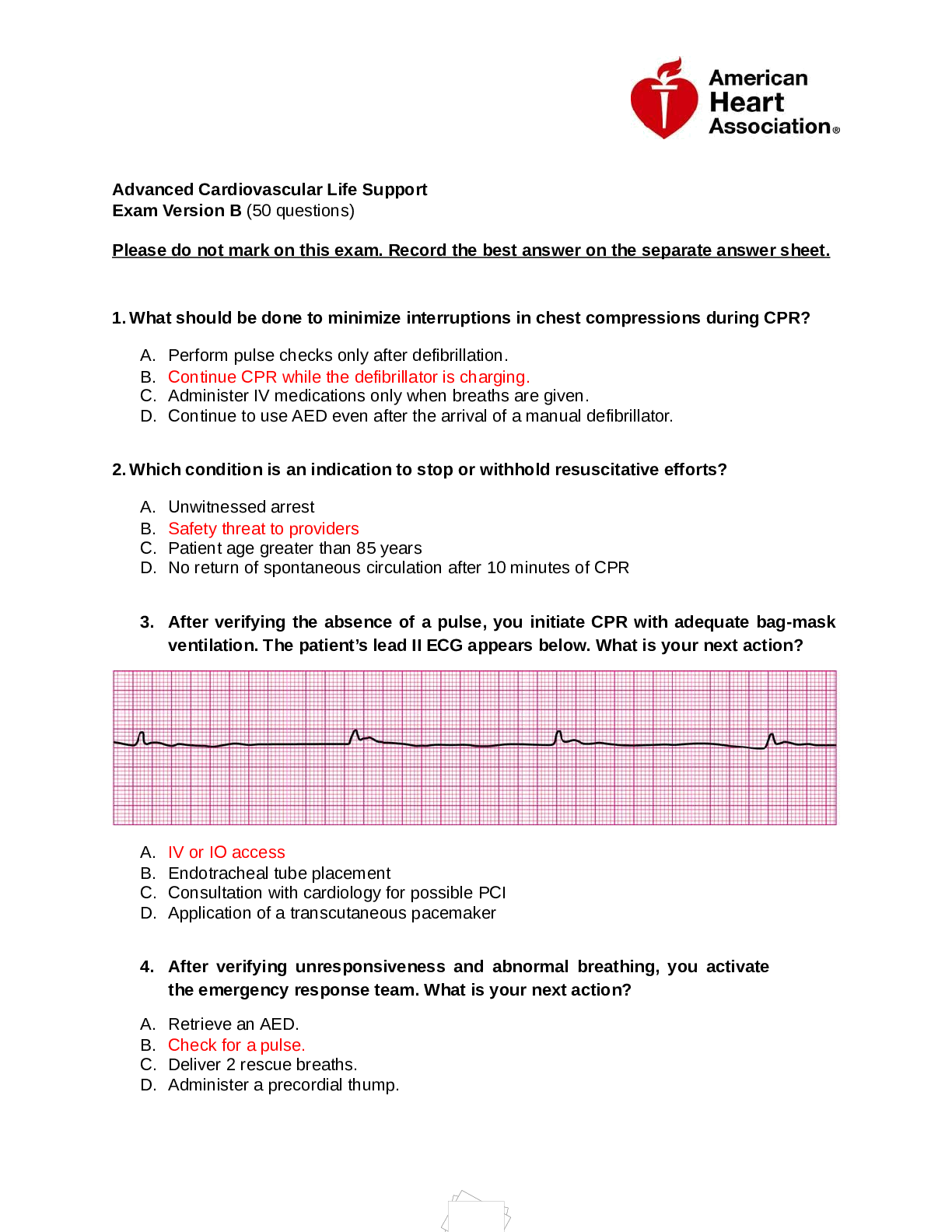
AQA GCSE Psychology Memory Questions and Answers 100% Pass Free recall ✔✔Learning procedure in which material that has been learned may be repeated in any order. Recognition recall ✔✔Recal... l from a list presented, individuals pick out which they can remember. Cued recall ✔✔Reproducing information from memory by making use of some kind of aid or hint to assist retrieval ( paired associate learning) Definition of memory ✔✔The retention of learning or experience. Storage of information over time. Encoding ✔✔Putting information into storage Storage ✔✔Keeping information stored Retrieval ✔✔Getting information back out of storage when required. Three Forms of Storage ✔✔1.Sensory memory, 2.Short term memory (STM) 3.Long term memory (LTM) Atkinson & Shiffrin (1971) ✔✔Atkinson and Shiffrin (1971) developed the Multi Store Model. Multi Store Model (MSM) ✔✔One explanation of memory: Most widely used and accepted. Atkinson and Shiffrin proposed that memory is made up of 3 memory stores - sensory memory (SM), short-term memory (STM), and long-term memory (LTM). For information to be transferred to LTM it must be rehearsed while in STM otherwise it is forgotten. Peterson and Peterson (1959) ✔✔They showed participants trigrams and then told them to count back in 3's so as to block the rehearsal loop to find out how long the duration of STM is. After 3 seconds around 90% recalled them correctly but after 18 seconds this reduced to less than 10% Supports the Multi store Model explanation of memory Peterson and Peterson Evaluation ✔✔1. State your criticism: Peterson and Peterson's 1959 study was artificial. 2. Justify your criticism: Artificial because they used nonsense trigrams to test memory, which are not to real-life memory tasks so the experiment lacks ecological validity! 3. Explain why (strength/Limitation) You cant generalise the findings to real life Murdock (1962) ✔✔Aim: to provide evidence to support the multi store explanation of memory. Murdock presented participants with a list of words at a rate of about one second. He found that participants recall words from the beginning(known as the primacy effect) and the end of the list (positions 1,2,3 and 18,19,20) Murdock claimed that the recency effect is evidence to show that the last few words are still in the term store and the primacy effect is evidence to show that the first few words were still in the long-term store. Recency Effect ✔✔When people tend to remember the last few words, because they were recently heard. Primacy Effect ✔✔Remembering items presented first. Barbara Milner (1966) ✔✔Milner's patient, H.M, following brain surgery to cure him eof pilepsy, the patient suffered damage to his memory. Given some information, he could remember it as long as he attended to it. His STM was normal. However, he seemed unable to store new information in LTM. The inability to store new information in LTM after brain damage is called anterograde amnesia. This suggests that brain damage affected LTM but not STM, in which the 2 stores must be separate and distinct. This evidence supports the Multi-store model. F.C. Bartlett (1930's) ✔✔Bartlett suggests that we only store some elements of new experiences in memory, and, when we remember the events we reconstruct them, filling in missing info with our own schemas. Schema: Our own stored opinions, prejudices, expectations, stereotypes that help us reconstruct memories. Serial Reproduction ✔✔The passing of information from persons to persons. Repeated Reproduction ✔✔The way information is passed to persons over time lengths. Craik and Lockhart (1975) ✔✔Aim: To find out whether or not how the word was processed affected how well it was recalled. Method: Participants questions about specific words and were asked to answer Yes/No. some questions required semantic processing; others required phonetic processing and visual processing. participant's had to then recognise which words they had already seen. Results: words that require semantic processing were more likely to be remembered, the least remembered words were those that required visual processing. Conclusion: Processing material in a deep way, recall is better. Levels of Processing: ✔✔VISUAL/STRUCTURAL: (Shallow) words remembered least. 15% of people remembered these words. E.G is the word CLEAR in lowercase? PHONETIC: (Deep) VISUAL/STRUCTURAL [Show More]
Last updated: 11 months ago
Preview 1 out of 5 pages

Also available in bundle (2)

GCSE Psychology Bundled Exams Questions and Answers with Verified Solutions
GCSE Psychology Bundled Exams Questions and Answers with Verified Solutions
By Nutmegs 11 months ago
$22
15

AQA A Level Psychology Memory Bundled Exams Questions and Answers 100% Pass
AQA A Level Psychology Memory Bundled Exams Questions and Answers 100% Pass
By Nutmegs 11 months ago
$19
7
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 10, 2023
Number of pages
5
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 10, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
82

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)










.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)


.png)
.png)


.png)
.png)

