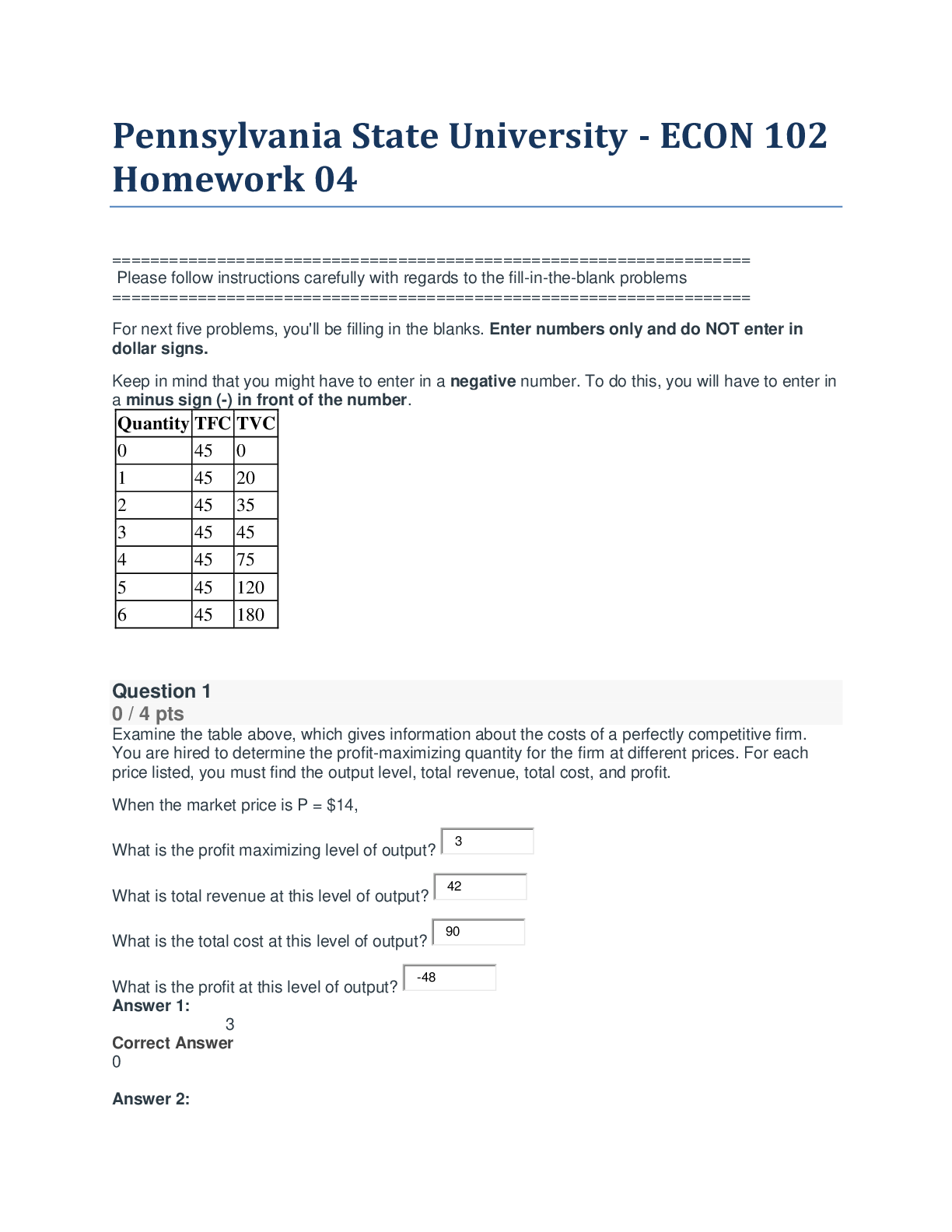
Pharmacology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Maryville NURS 615 Pharm 3 exam with all the correct answers (100% Verified 2020/2021 exam) (All)
Maryville NURS 615 Pharm 3 exam with all the correct answers (100% Verified 2020/2021 exam)
Document Content and Description Below
Maryville NURS 615 Pharm 3 exam with all the correct answers (100% Verified 2020/2021 exam) How do antigout medications work? Correct Answer- by inhibiting the infiltration and phagocytosis of leukocy... tes, thus decreasing the breakdown of uric acid to urate crystals. Deposition of urate crystals causes Correct Answer- pain and inflammation What is Colchicine Correct Answer- anti-gout medication how does Colchicine work? Correct Answer- Works by inhibiting inflammation, reducing pain and swelling common side effects of Colchicine Correct Answer- GI problems (diarrhea) use with caution in elderly Also can cause blood dyscrasias & abdominal pain patient education with Colchicine Correct Answer- Can be given with food & milk to decrease GI issues Avoid beer, ale, & wine: may cause gout attack Increase fluid intake: increases excretion of uric acid Avoid smoked meats & high-protein diets Low dose of Colchicine Correct Answer- Low dose colchicine is 1.2mg followed by 0.6mg one hour later or 1.8 milligrams total High dose of Colchicine Correct Answer- high dose colchicine is 1.2mg followed by 0.6mg every four to six hours; or 4.8mg total. Difference between high dose and low dose Colchicine Correct Answer- The difference between the two is low dose is as effective as high dose with a lower side effect profile. Lab values to monitor with Colchicine Correct Answer- Check renal function test, BUN, Creatine Patient education with Colchicine Correct Answer- Almost always causes some degree of diarrhea, make sure patients are aware of this side effect Patient education with Febuxostat (Uloric) Correct Answer- Gout may worsen with therapy initially Dietary changes to decrease gout attacks and uric acid deposits. Correct Answer- Avoid beer, ale, & wine Increase fluid intake: increases excretion of uric acid Avoid smoked meats & high-protein diets WHO 3 step ladder for pain medication Correct Answer- What is not a first line for pain medication? Correct Answer- Narcotics Recommendations for pain treatment Correct Answer- You want to start with NSAIDs first and then work your way up from there. types of Corticosteroid treatment Correct Answer- Prednisone, Cortisone, Dexamethasone how do Corticosteroids work? Correct Answer- Suppress the inflammatory & immune systems by inhibiting the synthesis of chemical mediators. what are the chemical mediators that Corticosteroids work on? Correct Answer- Prostaglandins, leukotrienes, & histamines Corticosteroids and inflammation Correct Answer- Decreases inflammation which decreases swelling, warmth, redness, & pain. Uses for corticosteroid treatment Correct Answer- Addison's disease, hormone replacement, cancer therapy SLE, arthritis, IBD, & to suppress graft rejection contraindications for corticosteroid treatment Correct Answer- Systemic fungal infections & with live vaccine Use corticosteroids cautiously with: Correct Answer- Pregnancy, kids, HTN, heart failure, renal impairment, & with infections resistant to treatment Patient education with corticosteroids Correct Answer- Don't discontinue abruptly, doses may need increased during stress, symptoms of Cushing's and GI bleeding Problem with taking Corticosteroids for greater than 6 months Correct Answer- The main thing you want to worry about is osteoporosis it can also worsen diabetic control and patients should report any tarry black stools or abdominal pain. Other common side effects with Corticosteroids Correct Answer- Peptic ulcers, GI bleeding, edema, hyperglycemia, delayed wound healing, fluid & electrolyte imbalances Why is it important to tapper the corticosteroid? Correct Answer- Tapering must be done carefully to avoid both recurrent activity of the underlying disease process and possible cortisol deficiency resulting from the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis or HPA suppression during the period of steroid therapy Black box warning Correct Answer- Increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, myocardial-infarction and stroke which can be fatal. What increases risk of black box warning occurring with NSAIDs. Correct Answer- Risk increases with duration of use. Patients with cardiovascular disease or with risk factors for cardiovascular disease may be a greater risk. NSAIDs and GI system Correct Answer- Increased risk of serious gastrointestinal adverse effects including: bleeding, ulceration, and perforation the stomach or intestines can be fatal. Can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients are at greater risk for serious GI events. Ibuprofen and mechanism of action Correct Answer- Exact mechanism of action is unknown. A non-selective cox-2 inhibitor in that it inhibits two isoforms of psychologic oxygenase cox-1 and cox-2. A non-selective inhibitor of cyclooxygenase, believed to be due to inhibition of cox-2 which decreases the synthesis of prostaglandins in mediating the inflammation pain, fever, and swelling. Ibuprofen and antipyretic effects Correct Answer- Antipyretic effects may be due to action on the hypothalamus resulting in an increase of peripheral blood flow, basil dilation, and subsequent heat dissipation. Ibuprofen versus NSAIDs Correct Answer- The analgesic and antipyretic and anti-inflammatory activity of NSAIDs appear to operate mainly through inhibition of cox-2. Resident inhibition of cox-1 would be responsible for the unwanted effects on the GI tract. Inhibition of cox-1 is thought to cause some of the side effects of ibuprofen including GI ulceration like aspirin and indomethacin. Ibuprofen versus NSAIDs Correct Answer- like aspirin and indomethacin. Ibuprofen is also a reversible inhibitor of the cox pathway. On the other hand, aspirin is a non-reversible inhibitor of the cox pathway. cox enzyme pathway - Cyclooxygenase is: Correct Answer- the prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase (PTGS) Cyclooxygenase is the prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase (PTGS)- what does it do? Correct Answer- Inhibits the formation & release of prostaglandin. PTGS converts arachidonic to PGH2 which is converted to other prostaglandins that mediate pain, inflammation, & fever. PGH2 is also converted to thromboxane-A2 which stimulates platelet aggregation leading to formation of blood clots. What happens when one part of the cox pathway is blocked Correct Answer- Understand that blocking one part of the cox pathway can lead to a build up of different products acetaminophen Mechanism of action Correct Answer- The main mechanism is performed a proposed is the inhibition of cox. And recent findings suggest that it's highly selective cox-2. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 22 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 23, 2022
Number of pages
22
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 23, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
62

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)

.png)
.png)